The document discusses the production of ammonia via the Haber process. Key points:
- Ammonia is produced by reacting nitrogen and hydrogen gases over an iron catalyst at high temperature (450°C) and pressure (200 atm).
- The balanced equation for the reaction is: N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3
- Unreacted gases are recycled in the process. Ammonia is then cooled to be liquified.

![a) Explain what you understand by the term “electrolysis”. ______________________________ ___________________________ [2] b) Name the ore from which aluminium is extracted. ___________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-3-320.jpg)
![a) Explain what you understand by the term “electrolysis”. Electrolysis is the breaking down / decomposing / splitting of a substance by passing electricity through it. [2] b) Name the ore from which aluminium is extracted. Bauxite – accept alumina [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-4-320.jpg)

![(i) Explain what is meant by each of the terms below: Anode _____________________ [1] Cathode ___________________ [1] Electrolyte _________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-6-320.jpg)
![(i) Explain what is meant by each of the terms below: Anode is the positive electrode [1] Cathode is the negative electrode [1] Electrolyte is the substance through which the electricity passes [1] and is broken down [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-7-320.jpg)
![(ii) Give two reasons why graphite is a suitable material from which to make the anode and cathode. _____________________________ __________________________ [2] (iii) Why is the aluminium oxide dissolved in molten cryolite? __________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-8-320.jpg)
![(ii) Give two reasons why graphite is a suitable material from which to make the anode and cathode. Graphite is a good conductor [1] and is cheaper (than platinum)/inert [1] (iii) Why is the aluminium oxide dissolved in molten cryolite? The molten cryolite lowers the melting point of the aluminium oxide / so reducing costs / saving energy [1] increase conductivity [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-9-320.jpg)
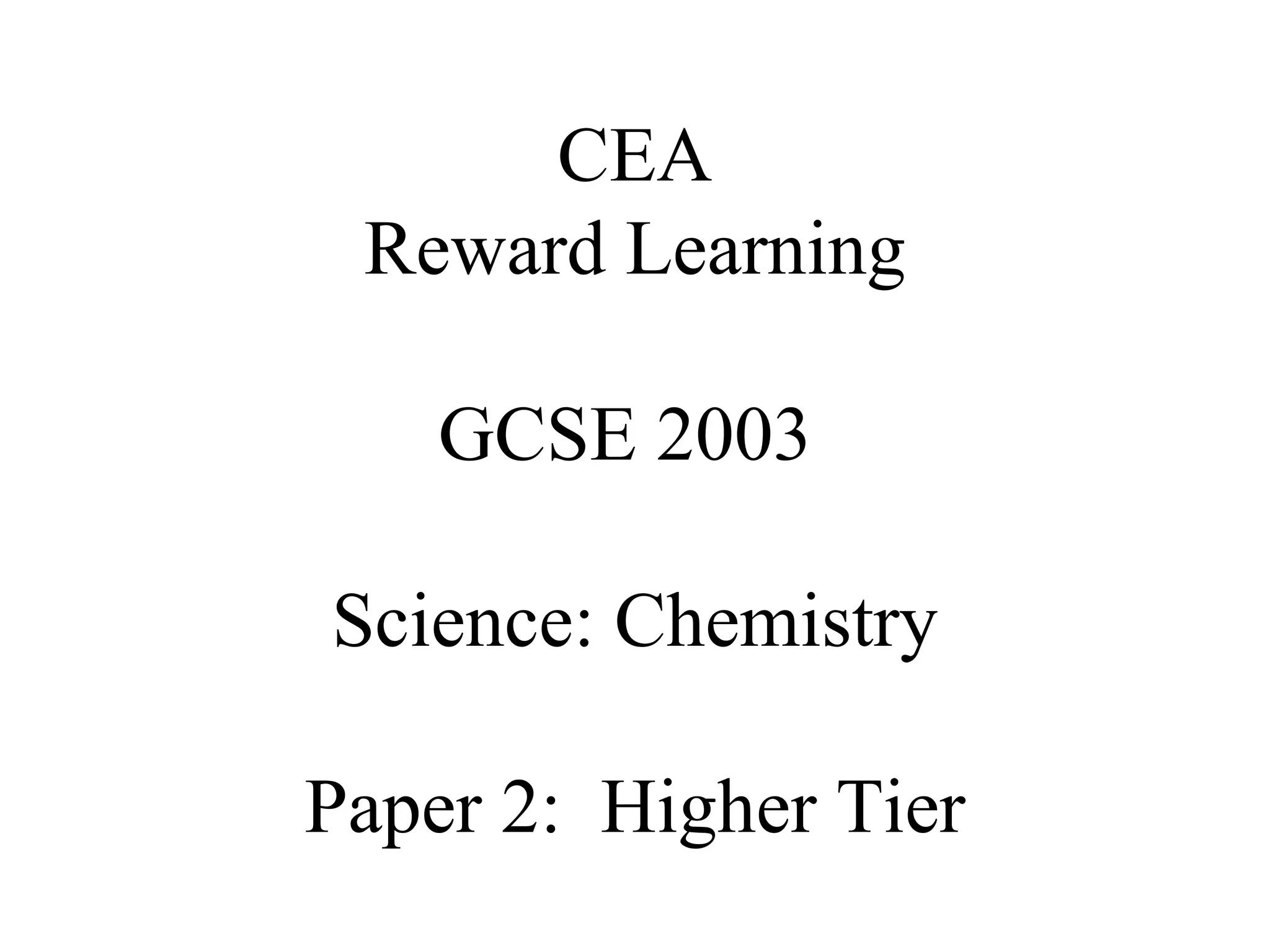
![d)(i) Name the products formed a the electrodes during electrolysis and give balanced, ionic equations for the reactions taking place. Anode Cathode Name of Product Oxygen [1] Aluminium [1] Balanced ionic equation 2O 2- -> O 2 + 4e - [1] 6O 2- -> 3O 2 + 12e - [2] Al3+ 3e- -> Al [2] Or 4Al 3+ + 12e - -> 4Al [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-11-320.jpg)
![(ii) At which electrode is reduction taking place? Explain your answer. _____________________________ _____________________________ __________________________ [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-12-320.jpg)
![(ii) At which electrode is reduction taking place? Explain your answer. Reduction is taking place at the cathode [1]. Reduction is the gain of the electrons [1] the aluminium ions are gaining electrons [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-13-320.jpg)
![e) Aluminium is an extremely important metal with widespread uses. Give two uses of aluminium and the property on which each use depends. Use ______________________ [1] Property __________________ [2] Use ______________________ [1] Property __________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-14-320.jpg)
![e) Aluminium is an extremely important metal with widespread uses. Give two uses of aluminium and the property on which each use depends. Use overhead power cables [1] Property low density / good conductor [1] Use Alloy [1] Property low density (but high strength) [1] Use saucepans [1] Property good thermal conductor [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-15-320.jpg)
![f) Aluminium is widely recycled. Suggest two reasons why aluminium metal is recycled. _____________________________ __________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-16-320.jpg)
![f) Aluminium is widely recycled. Suggest two reasons why aluminium metal is recycled. Aluminium is expensive to extract from its ore/cheaper to recycle [1] Bauxite reserves are running out/reduces landfill [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-17-320.jpg)
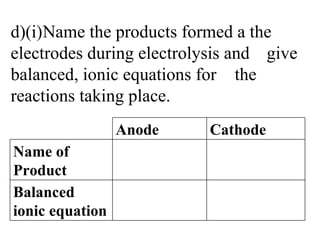
![2a) A solution of zinc sulphate may be prepared by the addition of an excess of one of the following substances A, B, C or D to dilute sulphuric acid. As well as zinc sulphate solution, each reaction produces at least one other product. Hydrogen [1] Water [1] Water [1] Carbon Dioxide [1] Water [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-19-320.jpg)
![(i) Complete boxes 1 to 5 in the diagram to show the names of the other products in the reactions. [5] (ii) write balanced, symbol equations for the reaction of dilute sulphuric acid with substances: B _______________________ [2] D _______________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-20-320.jpg)
![(i) Complete boxes 1 to 5 in the diagram to show the names of the other products in the reactions. [5] (ii) Write balanced, symbol equations for the reaction of dilute sulphuric acid with substances: B ZnO + H 2 SO 4 -> ZnSO 4 + H 2 O [2] D ZnCO 3 + H 2 SO 4 -> ZnSO 4 + H 2 O + CO 2 [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-21-320.jpg)
![(iii) Give two observations that you would make when the reaction in method D was complete. _____________________________ __________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-22-320.jpg)
![(iii) Give two observations that you would make when the reaction in method D was complete. Gas production stops/fizzing stops [1] No more solid reacts/solid remaining [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-23-320.jpg)
![b) Sulphuric Acid is a strong acid. (i) What is the pH of a sample dilute sulphuric acid? __________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-24-320.jpg)
![b) Sulphuric Acid is a strong acid. (i) What is the pH of a sample dilute sulphuric acid? 0 – 2 [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-25-320.jpg)

![(ii) Give the name and the formulae of the ions present in all acids and alkalis. Name Formula Ion present in all acids Hydrogen [1] H 3 O + /H + (aq) Ion present in all alkalis Hydroxide [1] OH - (aq)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-27-320.jpg)
![(iii) Write an ionic equation for neutralisation. __________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-28-320.jpg)
![(iii) Write an ionic equation for neutralisation. H + + OH - -> H 2 O [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-29-320.jpg)
![c) It was decided to use substance D to make zinc sulphate by adding an excess of zinc carbonate to sulphuric acid. (i) Explain giving experimental detail, how a pure, dry sample of zinc sulphate, ZnSO 4 .7H 2 O, could be prepared from this completed reaction. __________________________________ _______________________________ [6] Quality of written communication [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-30-320.jpg)
![c) It was decided to use substance D to make zinc sulphate by adding an excess of zinc carbonate to sulphuric acid. (i) Explain giving experimental detail, how a pure, dry sample of zinc sulphate, ZnSO 4 .7H 2 O, could be prepared from this completed reaction. Filter [1] heat [1] to evaporate some water/to concentrate the solution [1] allow to cool [1] and recrystallise [1] filter [1] dry between two sheets of filter paper / dessicator / low temp oven [1] Quality of written communication [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-31-320.jpg)
![(ii) A sample of zinc sulphate crystals is dissolved in water. Describe how you would test for the presence of the sulphate ion in this solution. Reagent: ______________________ Result: ______________________ ___________________________ [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-32-320.jpg)
![(ii) A sample of zinc sulphate crystals is dissolved in water. Describe how you would test for the presence of the sulphate ion in this solution. Reagent: barium chloride (sodium) [1] Result: white [1] precipitate [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-33-320.jpg)
![d) Substance C, zinc hydroxide, was used to prepare zinc sulphate solution. (i) Zinc hydroxide reacts with both acids and alkalis. What term is used to describe this property of zinc hydroxide? ___________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-34-320.jpg)
![d) Substance C, zinc hydroxide, was used to prepare zinc sulphate solution. (i) Zinc hydroxide reacts with both acids and alkalis. What term is used to describe this property of zinc hydroxide? Amphoteric [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-35-320.jpg)
![(ii) Write a balanced, symbol equation for the reaction of zinc hydroxide with sodium hydroxide solution. ___________________________ [3] (iii) what other metal hydroxide reacts in a similar way with acids and alkalis? ___________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-36-320.jpg)
![(ii) Write a balanced, symbol equation for the reaction of zinc hydroxide with sodium hydroxide solution. [3] Zn(OH) 2 + 2NaOH -> Na 2 ZNO 2 + 2H 2 O Allow: Zn(OH) 2 + 2NaOH -> Na 2 ZN(OH) 4 And: Zn(OH) 2 + 2OH - -> Zn(OH) 2- 4 (iii) what other metal hydroxide reacts in a similar way with acids and alkalis? Aluminium (hydroxide) [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-37-320.jpg)
![3 Many scientists contributed to the development of the Periodic Table of the elements. a) Define what is meant by the term “element”. _____________________________ ___________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-38-320.jpg)
![3 Many scientists contributed to the development of the Periodic Table of the elements. a) Define what is meant by the term “element”. A (pure) substance which cannot be broken down [1] by chemical means [1] or contains only one type [1] of atom [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-39-320.jpg)

![b) From the elements list choose: (i) two elements in the same Group of the Periodic Table. __________ and __________ [2] (ii) three metallic elements __________, __________ and __________ [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-41-320.jpg)
![b) From the elements list choose: (i) two elements in the same Group of the Periodic Table. Oxygen [1] and Sulphur [1] (ii) three metallic elements Magnesium [1], Sodium [1] and Aluminium [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-42-320.jpg)
![(iii) an element with seven electrons in the outer shell __________________________ [1] (iv) a semi-metal and give a reason why it can be classified in this way. Element ______________________ Reason _______________________ __________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-43-320.jpg)
![(iii) an element with seven electrons in the outer shell Chlorine [1] (iv) a semi-metal and give a reason why it can be classified in this way. Element Silicon [1] Reason It has properties of both metals and non-metals, e.g. it conducts electricity [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-44-320.jpg)
![c) Element X reacts vigorously with cold water to produce a compound with formula XOH and hydrogen gas. In which Group of the Periodic Table is element X found? __________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-45-320.jpg)
![c) Element X reacts vigorously with cold water to produce a compound with formula XOH and hydrogen gas. In which Group of the Periodic Table is element X found? Group I / Group l / alkali metals [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-46-320.jpg)
![d) Atoms are extremely small. The radius of a hydrogen atom is approximately 0.000 000 000 1 m. Atoms of different elements are of different sizes. (i) how does the atomic size change on going down Group II? ___________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-47-320.jpg)
![d) Atoms are extremely small. The radius of a hydrogen atom is approximately 0.000 000 000 1 m. Atoms of different elements are of different sizes. (i) how does the atomic size change on going down Group II? It increases [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-48-320.jpg)
![(ii) How does the atomic size change on moving across Period 3 from sodium to chlorine? ___________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-49-320.jpg)
![(ii) How does the atomic size change on moving across Period 3 from sodium to chlorine? It decreases [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-50-320.jpg)
![e)(i) Barium is a typical Group II element. Complete the table below to show the formulae of the compounds named. [3] Name of Compound Formula of Compound Barium oxide Barium chloride Barium sulphate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-51-320.jpg)
![e)(i) Barium is a typical Group II element. Complete the table below to show the formulae of the compounds named. [3] Name of Compound Formula of Compound Barium oxide BaO Barium chloride BaCl 2 Barium sulphate BaSO 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-52-320.jpg)
![(ii) Using your knowledge of the Periodic Table, predict whether barium will react more vigorously or less vigorously than calcium. Explain your answer. _____________________________ _____________________________ __________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-53-320.jpg)
![(ii) Using your knowledge of the Periodic Table, predict whether barium will react more vigorously or less vigorously than calcium. Explain your answer. Barium will react more vigorously [1] (than calcium). Barium is below Ca in Group II/the reactivity increases as the group is descended [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-54-320.jpg)
![(iii) Write a balanced, symbol equation to show how barium reacts with cold water. __________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-55-320.jpg)
![(iii) Write a balanced, symbol equation to show how barium reacts with cold water. Ba + 2H 2 O -> Ba(OH) 2 + H 2 [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-56-320.jpg)
![4a) Ammonia is used in many household cleaning products. It has a very strong penetrating smell. State two other physical properties of ammonia. __________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-57-320.jpg)
![4a) Ammonia is used in many household cleaning products. It has a very strong penetrating smell. State two other physical properties of ammonia . Gas / low melting point / low boiling point [1] Higher than air [1] (very) soluble in water [1] colourless [1] Max [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-58-320.jpg)
![(i) Describe a chemical test for ammonia, giving the result of the test. _____________________________ ___________________________ [3] (ii) Name the compound A. ___________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-60-320.jpg)
![(i) Describe a chemical test for ammonia, giving the result of the test . Hydrogen chloride / concentrated hydrochloric acid [1] white [1] smoke/fumes/solid [1] (ii) Name the compound A. Ammonium Chloride [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-61-320.jpg)
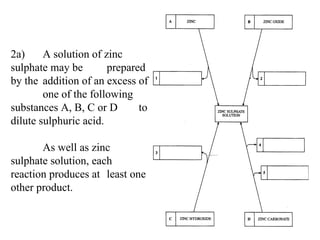
![(iii) Describe the production of ammonia in the Haber-Bosch process. Your answer should include the name of the catalyst used, the approximate temperature and pressure and a balanced, symbol equation. __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ ______________________________ [7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-62-320.jpg)
![(iii) Describe the production of ammonia in the Haber-Bosch process. Your answer should include the name of the catalyst used, the approximate temperature and pressure and a balanced, symbol equation. The key points of this answer are: nitrogen [1] hydrogen [1] catalyst – iron [1]*, temperature – 450 o C ± [1]*, pressure – 200 atm ± [1]*, N 2 + 3H 2 ≈ 2NH 3 [2]* reversible arrow not essential to cool to liquify ammonia [1] unreacted gases recycled [1] Max [7] from [9]. * Are essential parts.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-63-320.jpg)
![c) Garden lawn fertiliser often contains ammonium nitrate in addition to iron(II) sulphate, which is used to kill moss. (i) write a balanced, symbol equation for the reaction of ammonia and nitric acid to produce ammonium nitrate. ___________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-64-320.jpg)
![c) Garden lawn fertiliser often contains ammonium nitrate in addition to iron(II) sulphate, which is used to kill moss. (i) write a balanced, symbol equation for the reaction of ammonia and nitric acid to produce ammonium nitrate. NH 3 + HNO 3 -> NH 4 NO 3 [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-65-320.jpg)
![(ii) Describe, giving practical details, how you would prove that lawn fertiliser pellets contain iron(II) sulphate and not iron(III) sulphate. Give the expected result. _____________________________ _____________________________ __________________________ [5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-66-320.jpg)
![(ii) Describe, giving practical details, how you would prove that lawn fertiliser pellets contain iron(II) sulphate and not iron(III) sulphate. Give the expected result. Add water [1], add ammonia solution/NaOH solution [1], green [1], ppt [1], red brown (ppt) indicates Fe 3+ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-67-320.jpg)
![(iii) State two environmental problems which occur when excess fertiliser is leached out of the soil and into lakes and rivers. _____________________________ __________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-68-320.jpg)
![(iii) State two environmental problems which occur when excess fertiliser is leached out of the soil and into lakes and rivers. Eutrophication [1] Contamination of water supply [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-69-320.jpg)
![d) Ammonia is used to manufacture nitric acid. This process involves the catalytic oxidation of ammonia and occurs in three stages. Stage 1 _____________________ Stage 2 _____________________ Stage 3 _____________________[6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-70-320.jpg)

![(ii) Name the material used as a catalyst in this process. ___________________________ [1] (iii) Which stage, 1, 2 or 3 involves use of the catalyst? ___________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-72-320.jpg)
![(ii) Name the material used as a catalyst in this process. Platinum / platinum-rhodium [1] (iii) Which stage, 1, 2 or 3 involves use of the catalyst? Stage 1 [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-73-320.jpg)

![(i) Which one of these ions is present in the greatest concentration? ___________________________ [1] (ii) Which of these ions is needed to makes strong teeth and healthy bones? ___________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-75-320.jpg)
![(i) Which one of these ions is present in the greatest concentration? Hydrogen carbonate [1] (ii) Which of these ions is needed to makes strong teeth and healthy bones? Calcium [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-76-320.jpg)
![(iii) This water is “sparkling”. What gas is used to make it fizzy? _______________________________ [1] (iv) Use the information from the label to give the name and formula of two compounds which could be present in this mineral water. [4] Name ___________ Formula __________ Name ___________ Formula __________](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-77-320.jpg)
![(iii) This water is “sparkling”. What gas is used to make it fizzy? Carbon dioxide [1] (iv) Use the information from the label to give the name and formula of two compounds which could be present in this mineral water. [4] Name Calcium sulphate [1] Formula CaSO 4 [1] Name Calcium chloride [1] Formula CaCl 2 [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-78-320.jpg)
![(v) An open bottle of sparkling mineral water was placed in the fridge for a day, and another placed in sunlight. Which bottle of water will be less fizzy at the end of the day? Explain your answer. __________________________________ __________________________________ _______________________________ [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-79-320.jpg)
![(v) An open bottle of sparkling mineral water was placed in the fridge for a day, and another placed in sunlight. Which bottle of water will be less fizzy at the end of the day? Explain your answer. Bottle in sunlight [1] increase in temperature [1] decrease solubility of gases [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-80-320.jpg)
![(vi) Describe how you would find the approximate pH of the sparkling mineral water. _____________________________ ___________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-81-320.jpg)
![(vi) Describe how you would find the approximate pH of the sparkling mineral water. Universal solution /pH paper [1] compare colour to pH chart [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-82-320.jpg)
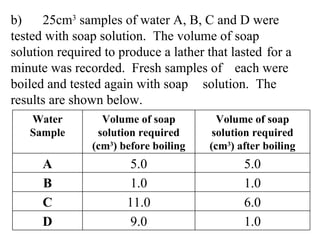
![i) What is meant by the term “hard water”? _________________________ [2] (ii) Which of the four samples contains temporary hardness only? _________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-84-320.jpg)
![i) What is meant by the term “hard water”? Does not later [1] easily with soap [1] (ii) Which of the four samples contains temporary hardness only? Sample D [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-85-320.jpg)
![(iii) Which of the four samples contains both permanent and temporary hardness? Explain your answer. _____________________________ _____________________________ __________________________ [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-86-320.jpg)
![(iii) Which of the four samples contains both permanent and temporary hardness? Explain your answer. Sample C [1] some [1] hardness remained / removed on boiling [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-87-320.jpg)
![(iv) Give a balanced, symbol equation for the reaction taking place when sample D is boiled. ___________________________ [2] (v) Ion exchange can be used to soften hard water. Explain, in terms of ions, how this method works. ______________________________ ___________________________ [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-88-320.jpg)
![(iv) Give a balanced, symbol equation for the reaction taking place when sample D is boiled. Ca(HCO 3 ) 2 -> CaCO 3 + H 2 O + CO 2 [2] (v) Ion exchange can be used to soften hard water. Explain, in terms of ions, how this method works. Calcium ions in hard water [1] exchanged [1] with Na + ions [1] on resin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-89-320.jpg)

![(i) What is meant by the term “hydrocarbon”? ___________________________ [2] (ii) To which homologous series does butane belong? ___________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-91-320.jpg)
![(i) What is meant by the term “hydrocarbon”? Contains carbon and hydrogen atoms [1] only [1] (ii) To which homologous series does butane belong? Alkanes [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-92-320.jpg)
![(iii) Draw the structural formula of butane showing all the bonds in the compound. [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-93-320.jpg)
![(iii) Draw the structural formula of butane showing all the bonds in the compound. [2] H H H H I I I I H – C – C – C – C – H I I I I H H H H](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-94-320.jpg)
![b) Petrol is a hydrocarbon fuel burnt in car engines. It is obtained from crude oil and consists mainly of octane. (i) Name the two products formed when octane burns completely in a plentiful supply of air. ___________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-95-320.jpg)
![b) Petrol is a hydrocarbon fuel burnt in car engines. It is obtained from crude oil and consists mainly of octane. (i) Name the two products formed when octane burns completely in a plentiful supply of air. Carbon dioxide [1] water/steam [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-96-320.jpg)
![(ii) If a car engine is not serviced correctly the octane does not burn completely. Name the poisonous product formed in this reaction. ___________________________ [1] (iii) Name the industrial method used to obtain petrol from crude oil. ___________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-97-320.jpg)
![(ii) If a car engine is not serviced correctly the octane does not burn completely. Name the poisonous product formed in this reaction. Carbon monoxide [1] (iii) Name the industrial method used to obtain petrol from crude oil. Fractional [1] distillation [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-98-320.jpg)
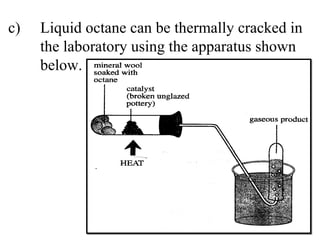
![(i) Why is it possible to collect the products over water? _______________________________ [1] (ii) What is meant by the term “cracking”? _______________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-100-320.jpg)
![(i) Why is it possible to collect the products over water? Not very soluble in water/insoluble [1] (ii) What is meant by the term “cracking”? Breaking down large molecules [1] into smaller molecules [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-101-320.jpg)
![(iii) When octane, C 8 H 18 , is cracked, ethene and one other hydrocarbon is produced. Write a balanced, symbol equation for the cracking of octane. ______________________________ ___________________________ [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-102-320.jpg)
![(iii) When octane, C 8 H 18 , is cracked, ethene and one other hydrocarbon is produced. Write a balanced, symbol equation for the cracking of octane. C 8 H 18 -> C 2 H 4 + C 6 H 14 [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-103-320.jpg)
![(iv) Ethene is an alkene. Describe a chemical test which could be used to prove than an alkene was produced. State the result of the test. _________________________________ _________________________________ _______________________________ [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-104-320.jpg)
![(iv) Ethene is an alkene. Describe a chemical test which could be used to prove than an alkene was produced. State the result of the test. (bubble into) bromine water [1] red brown to [1] colourless / decolourised [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-105-320.jpg)
![d) “Gasochol” is an alternative fuel which contains up to 20% ethanol. The ethanol is produced by the fermentation of sugar cane. (i) Draw the structural formula of ethanol showing all the bonds in the compound. [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-106-320.jpg)
![d) “Gasochol” is an alternative fuel which contains up to 20% ethanol. The ethanol is produced by the fermentation of sugar cane. (i) Draw the structural formula of ethanol showing all the bonds in the compound. [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-107-320.jpg)
![(ii) Write a balanced, symbol equation for the combustion of ethanol in a plentiful supply of air. _______________________________ [2] (iii) Describe how ethanol is produced by fermentation. __________________________________ __________________________________ _______________________________ [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-108-320.jpg)
![(ii) Write a balanced, symbol equation for the combustion of ethanol in a plentiful supply of air. C 2 H 5 OH + 3O 2 -> 2CO 2 + 3H 2 O[2] (iii) Describe how ethanol is produced by fermentation. The key points of this answer are: sugar/grapes, yeast, exclude air, control temperature, CO 2 produced (Max [4] from [5])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-109-320.jpg)
![(iv) Give one other use of ethanol, apart from as a fuel. ___________________________ [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-110-320.jpg)
![(iv) Give one other use of ethanol, apart from as a fuel. Alcoholic beverage / solvent [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20032-090322115404-phpapp01/85/2003-2-111-320.jpg)