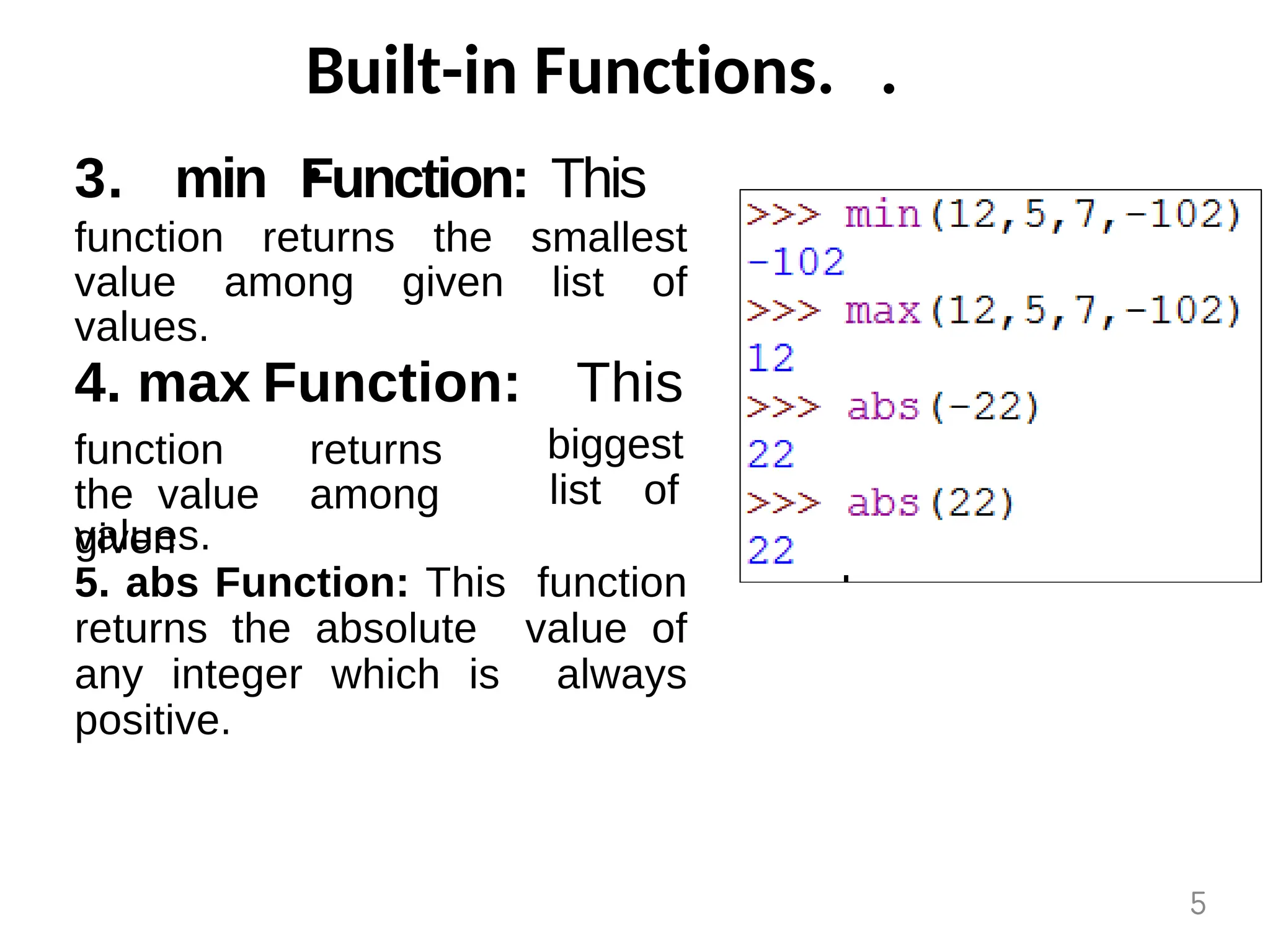
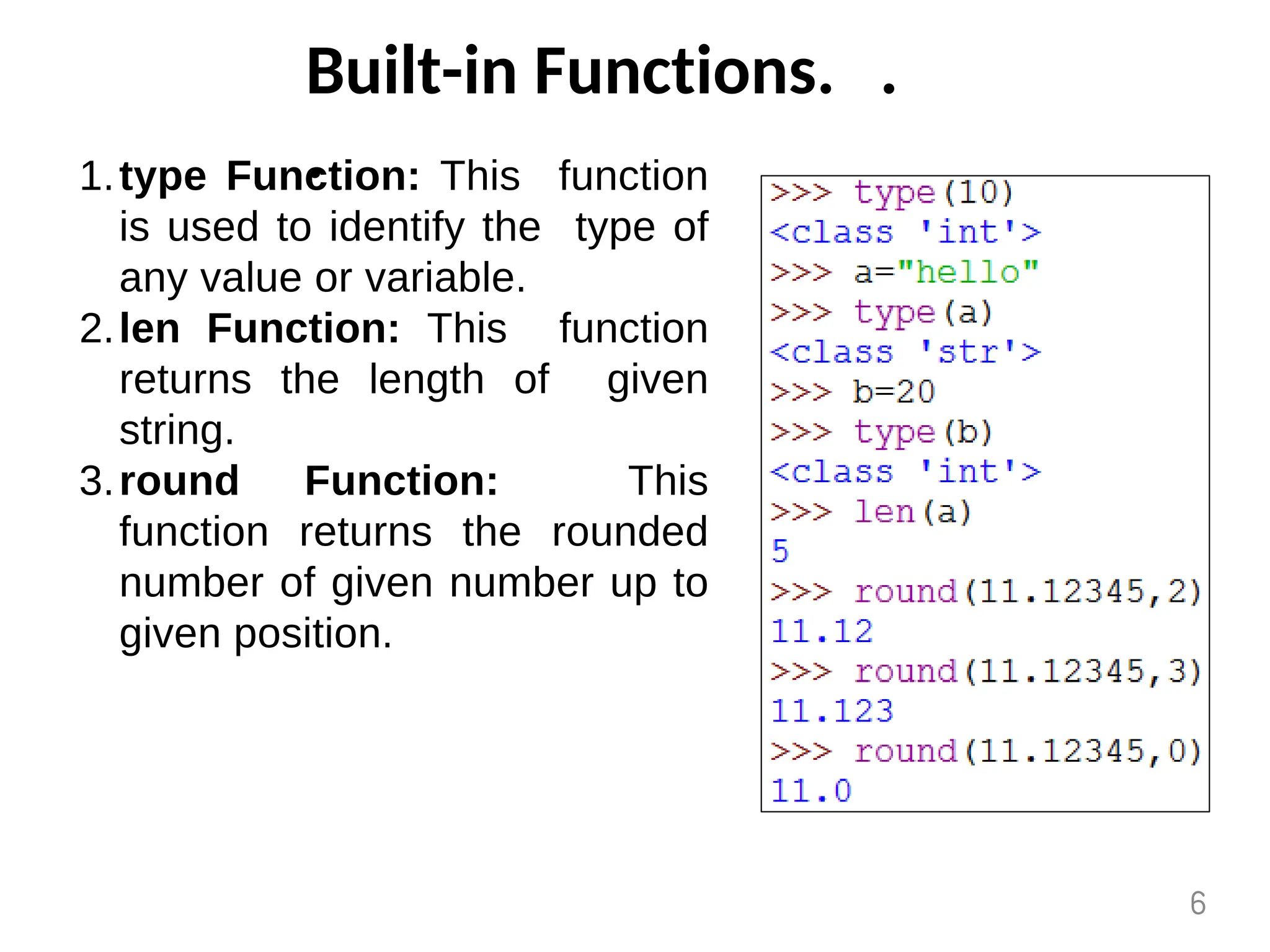
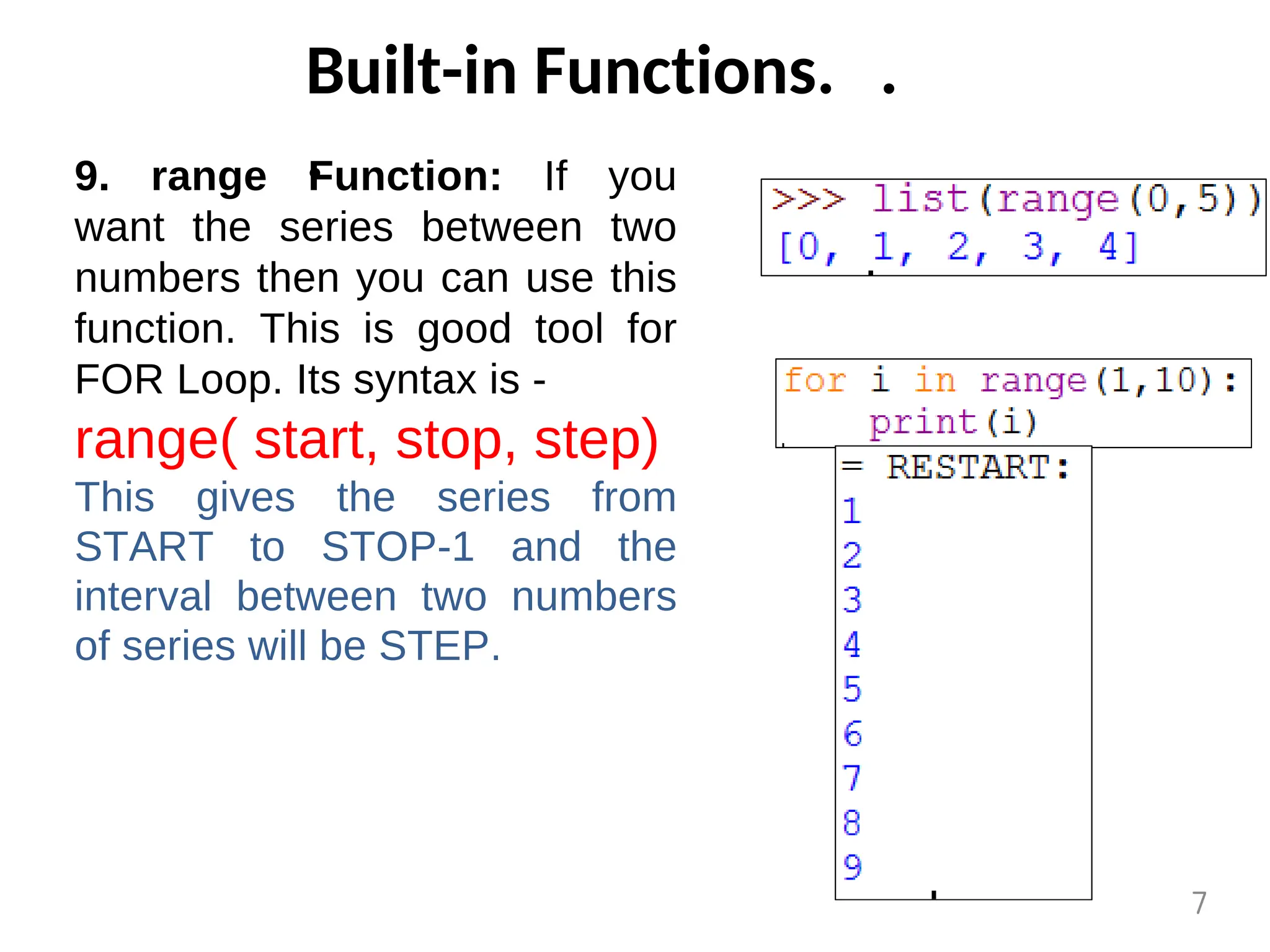
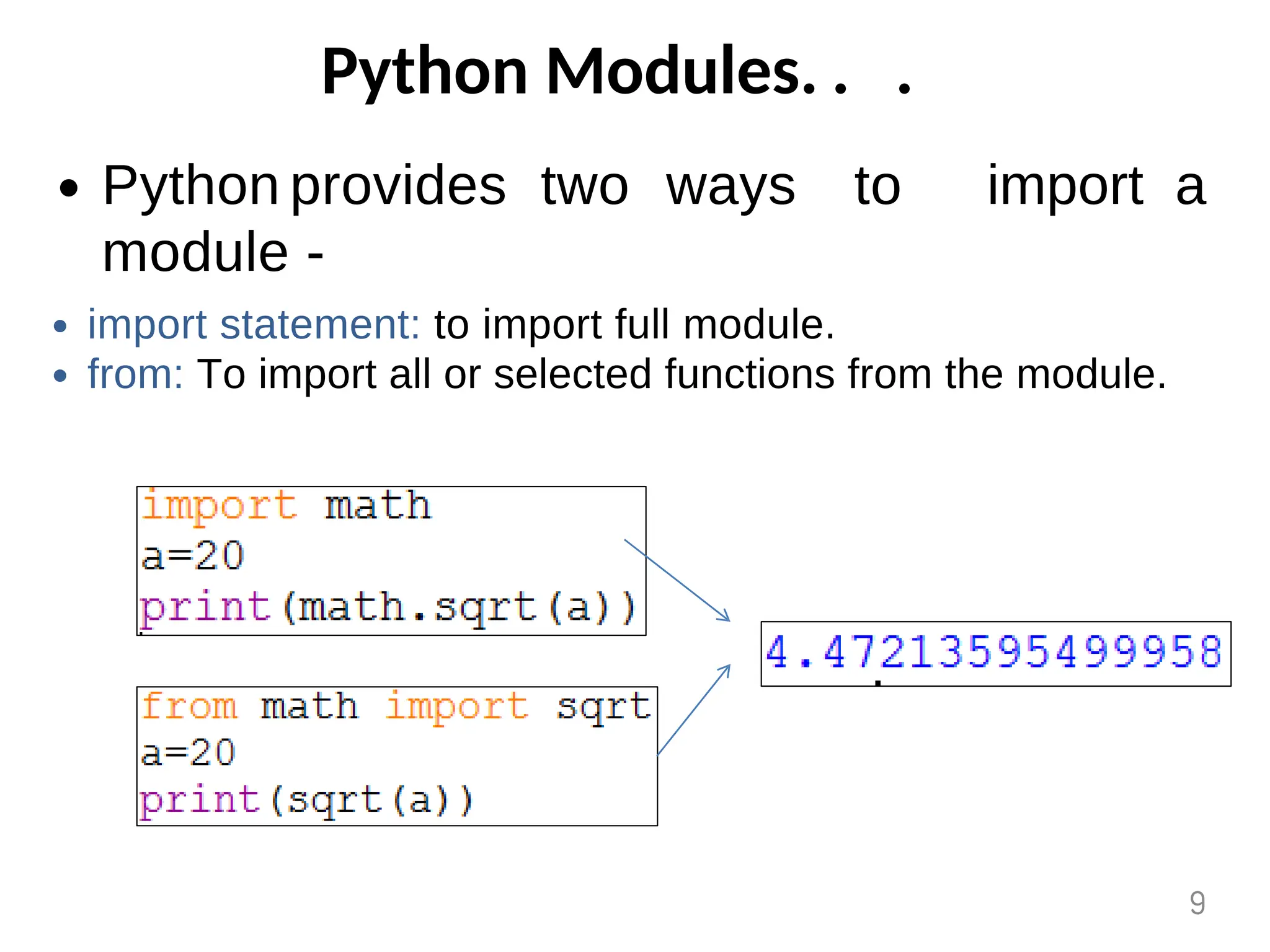
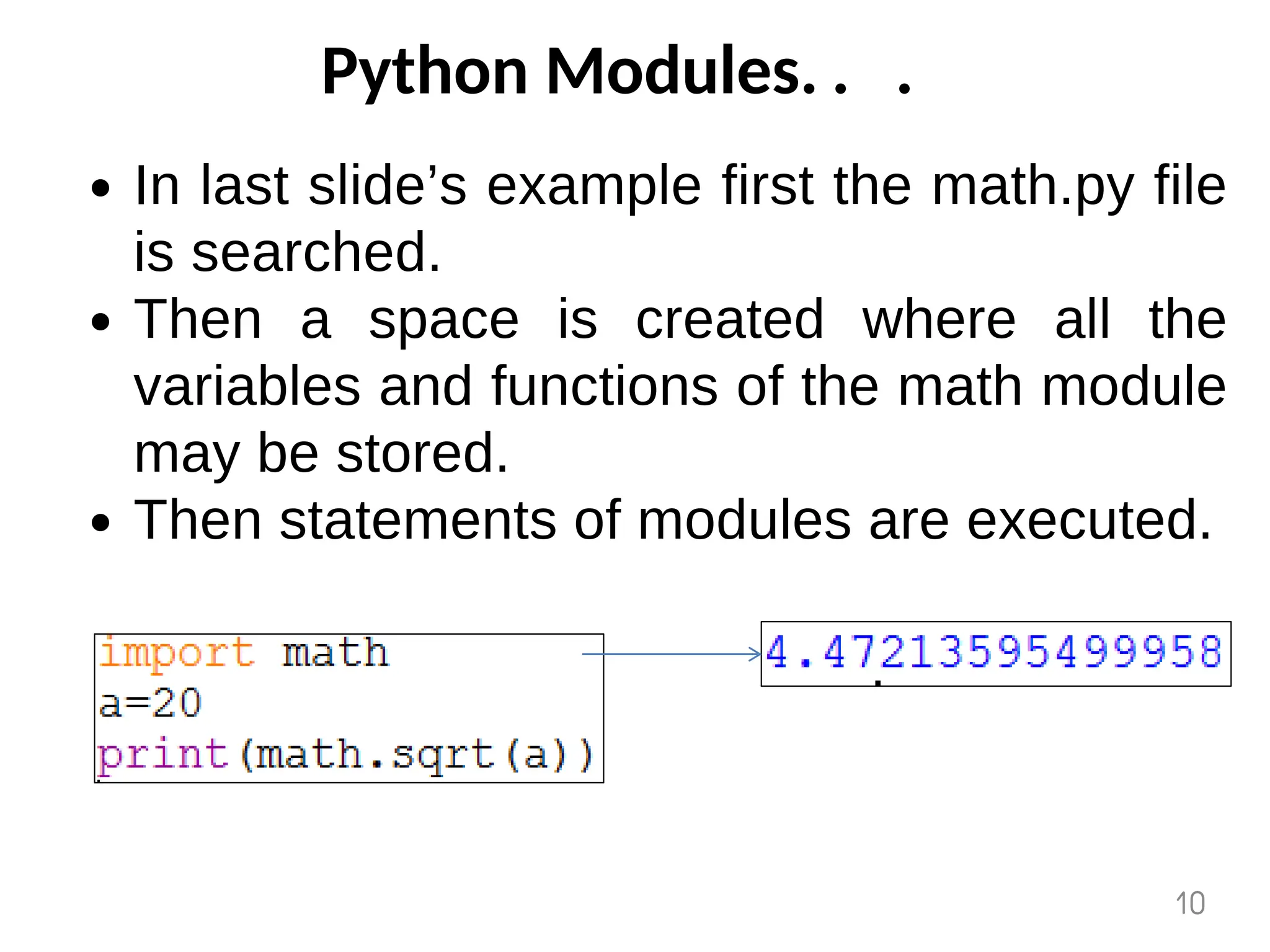
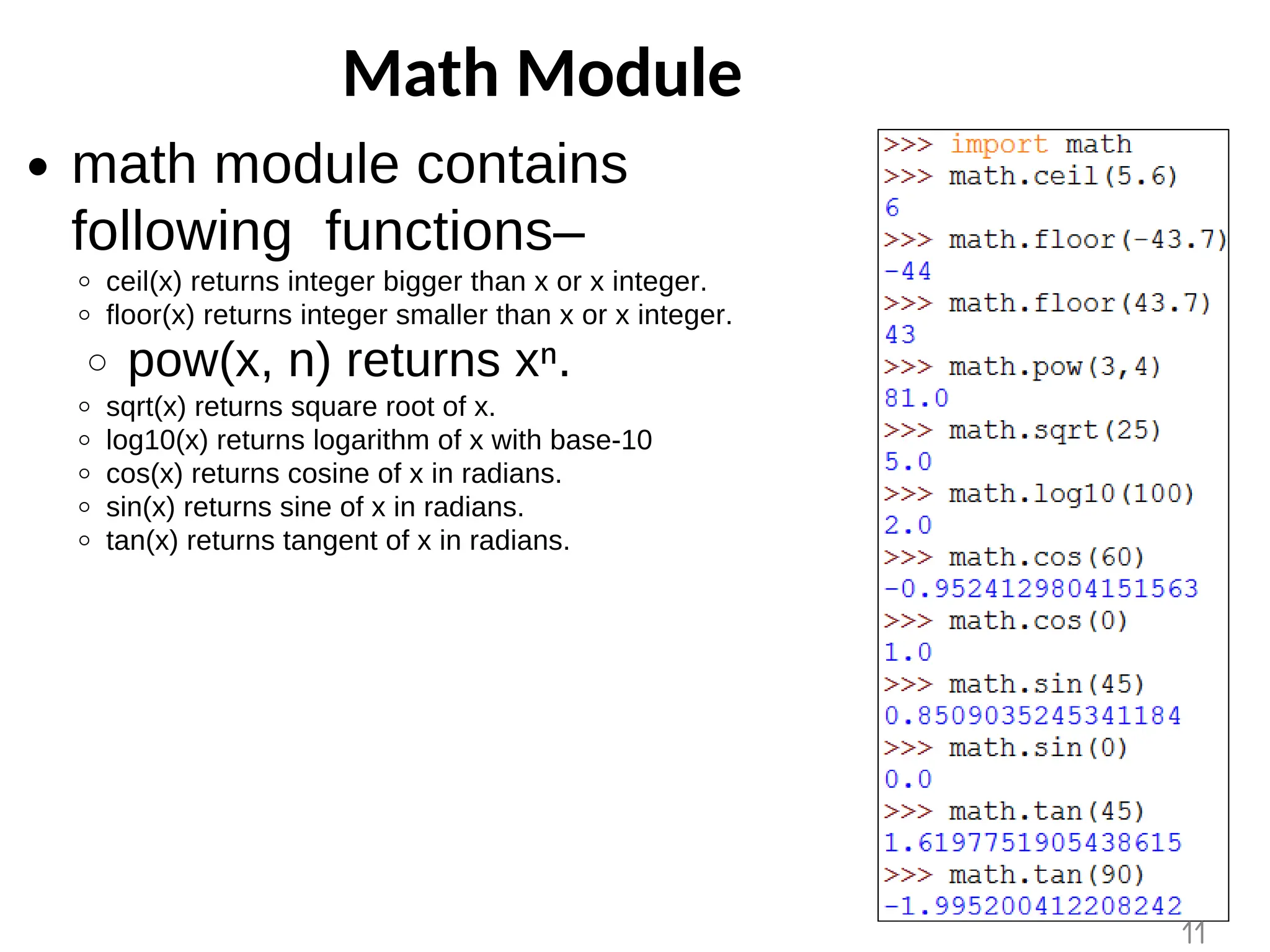
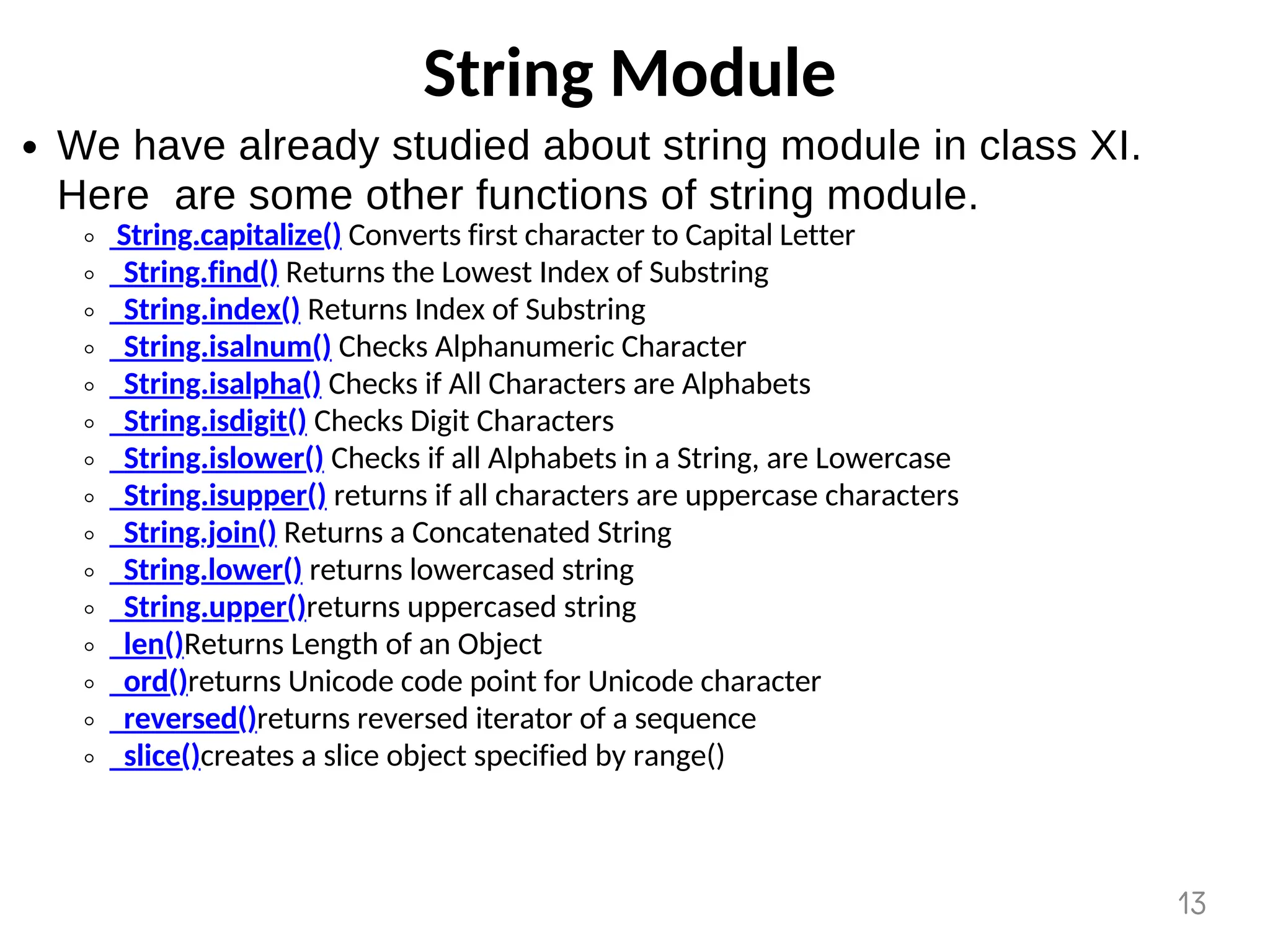
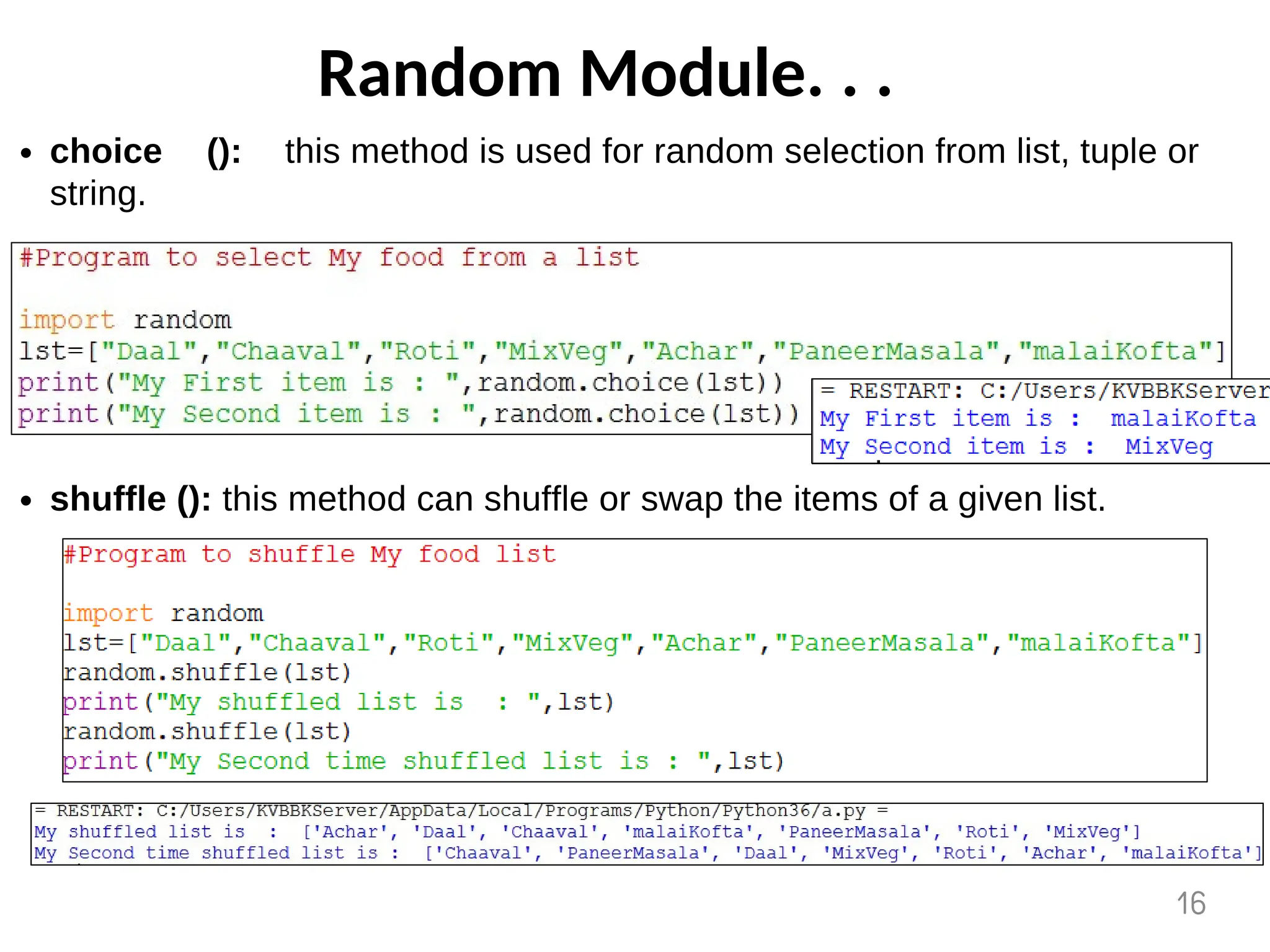
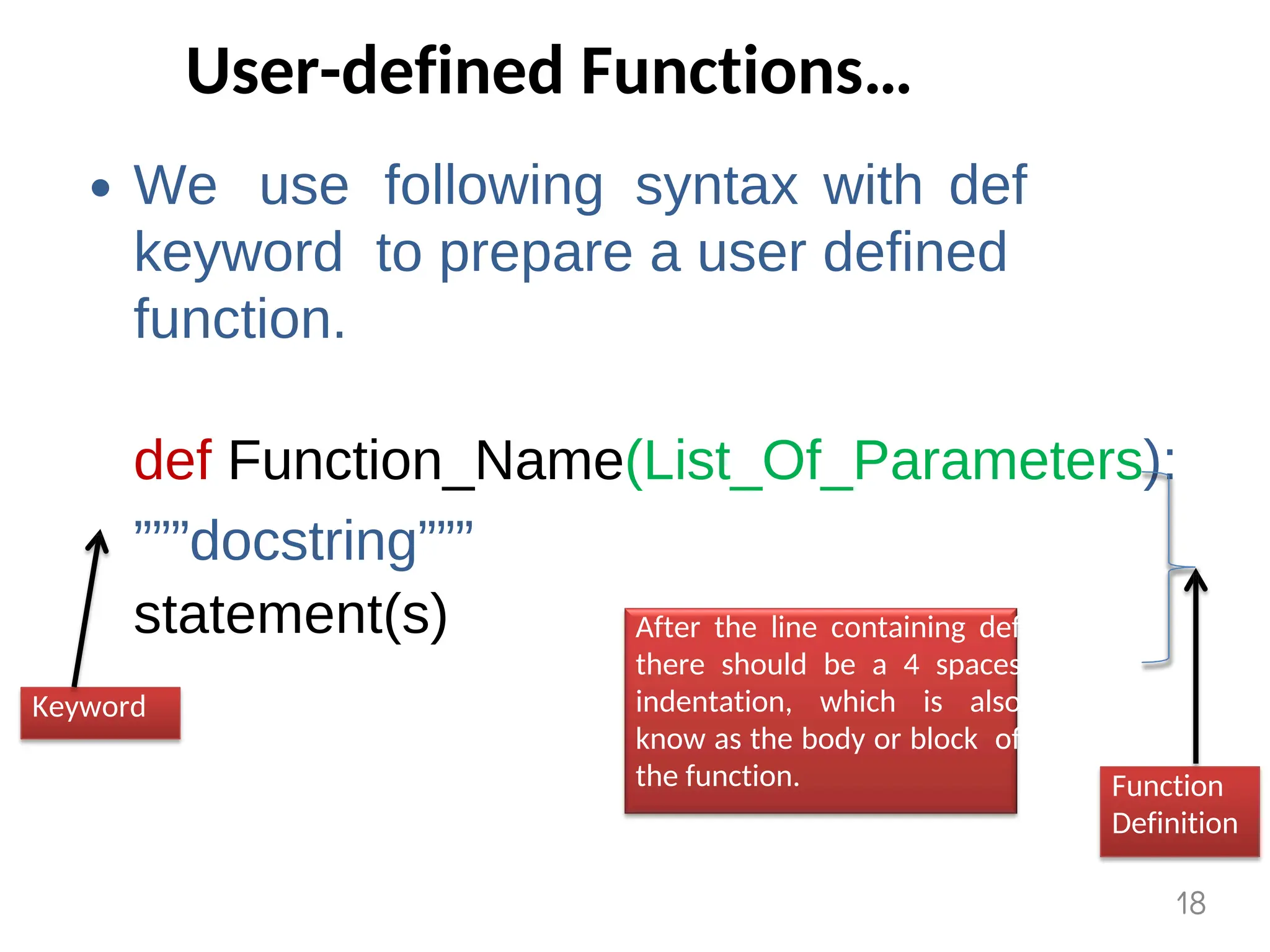
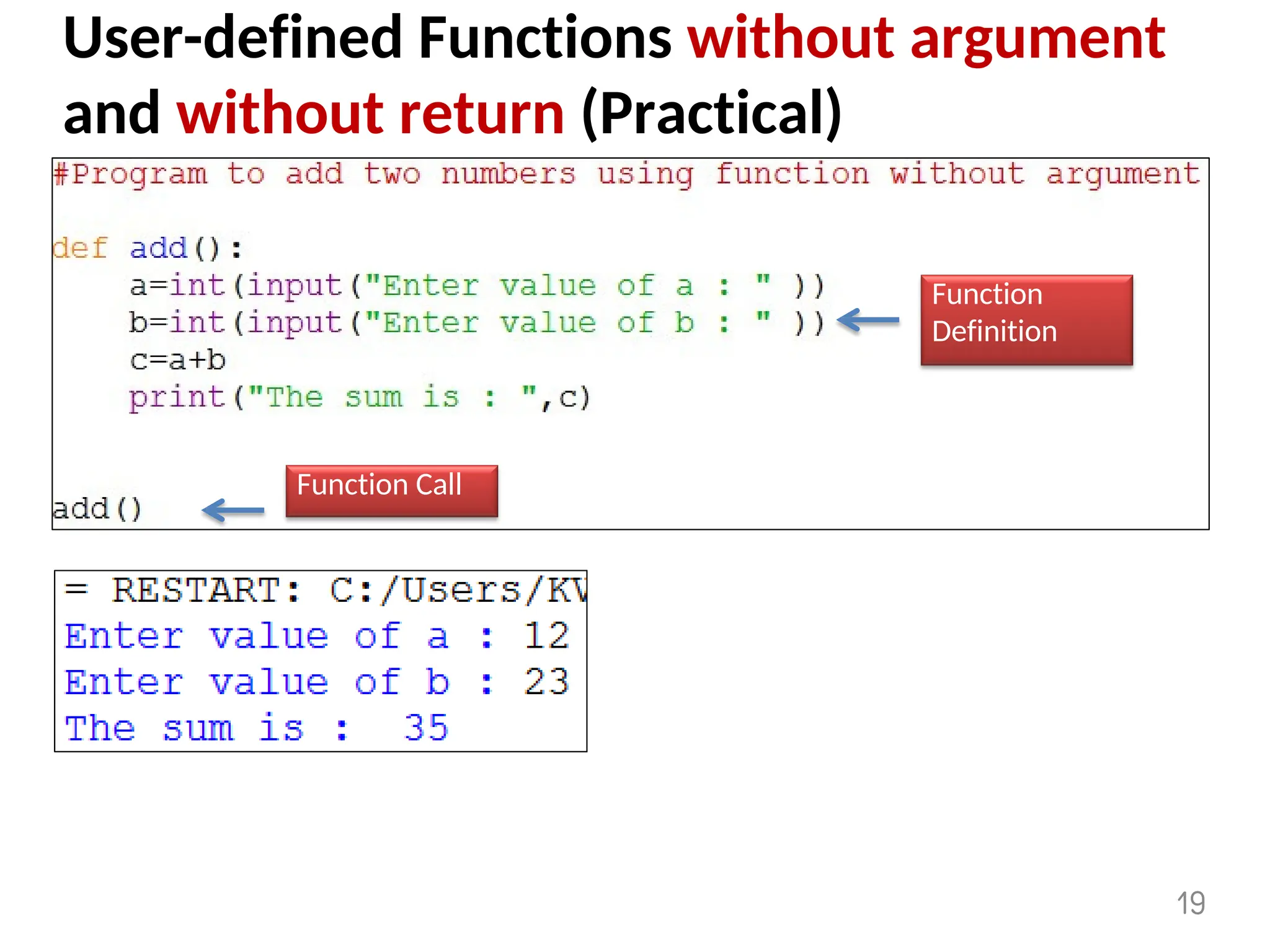
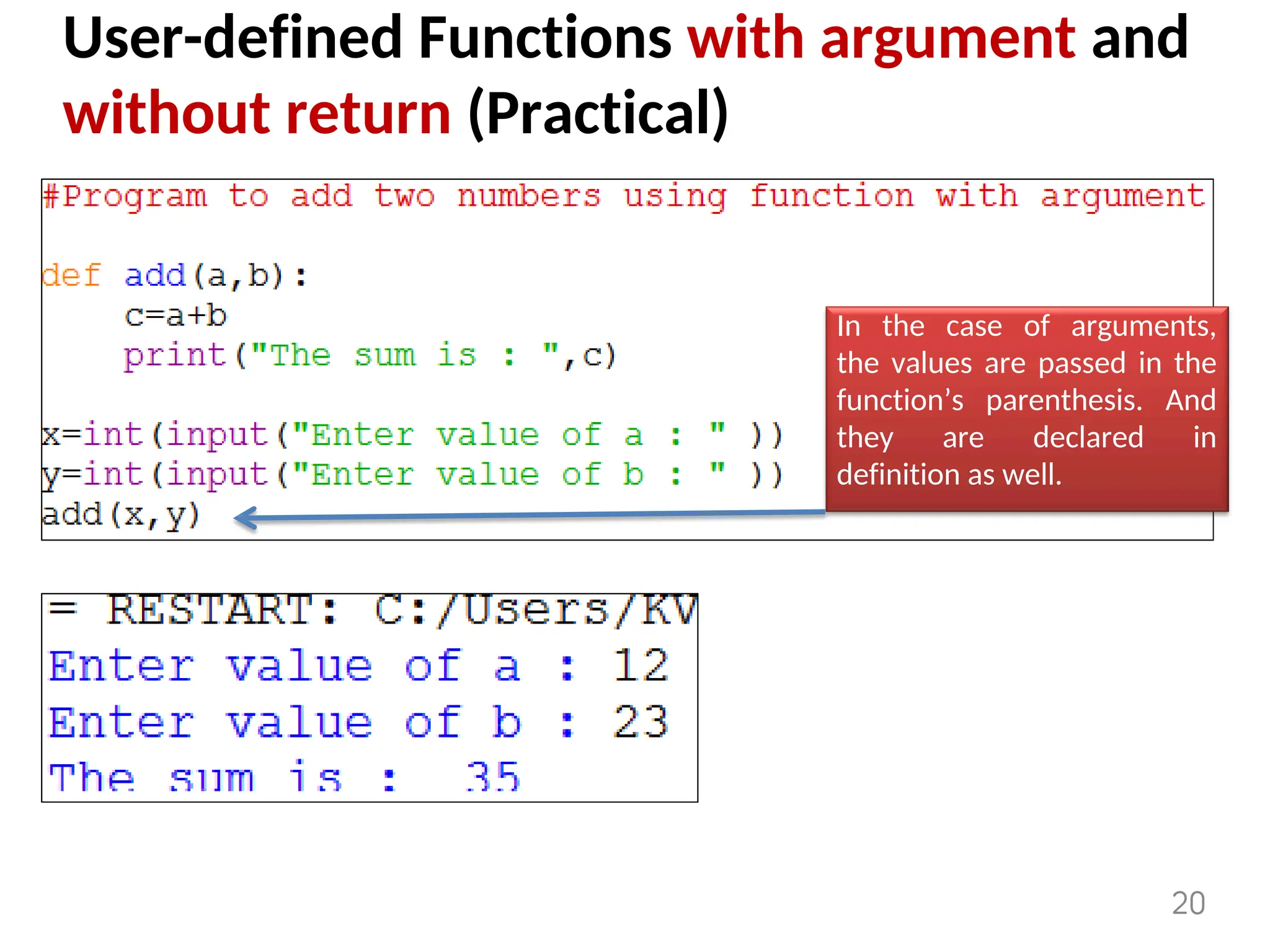
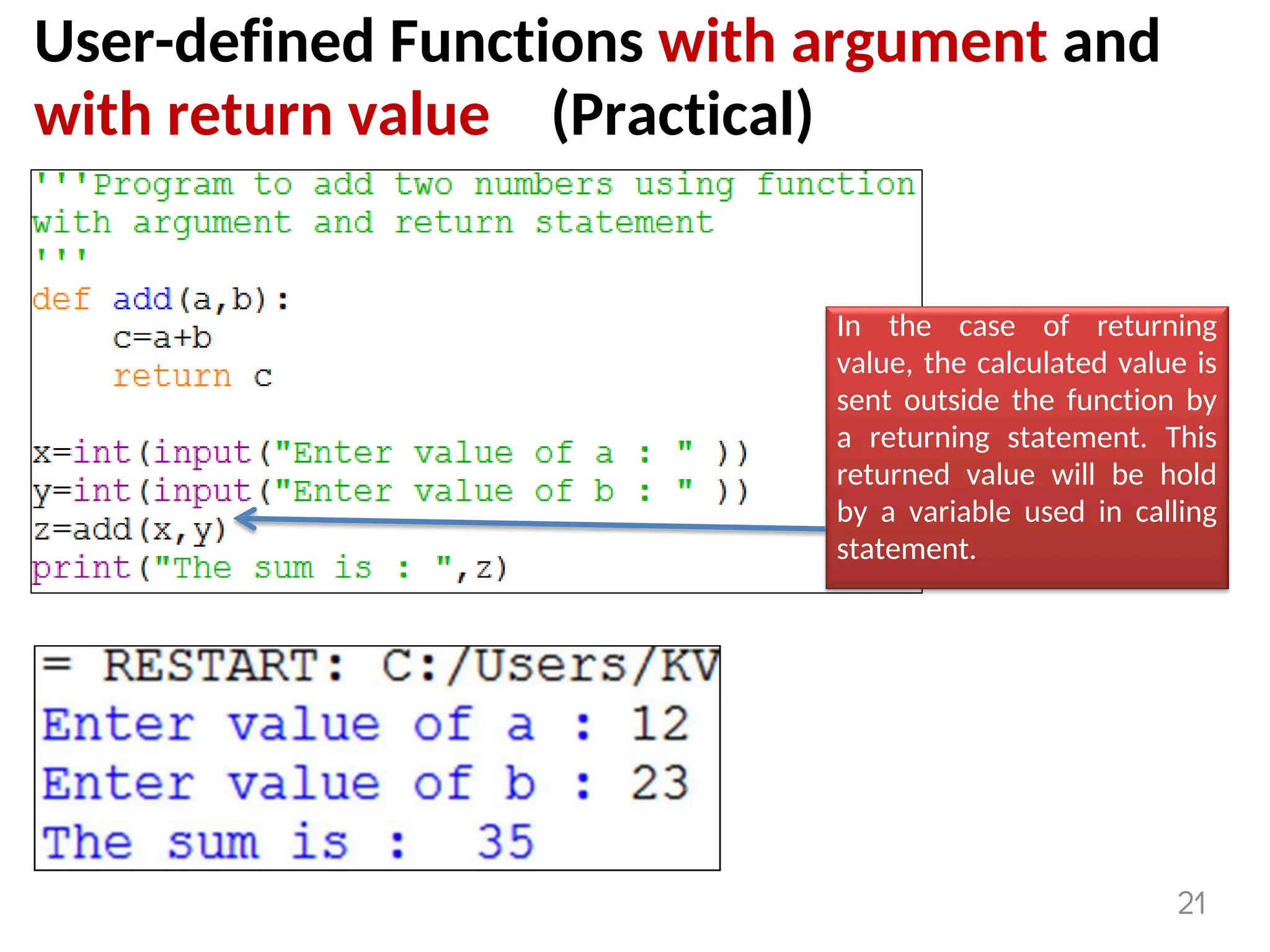
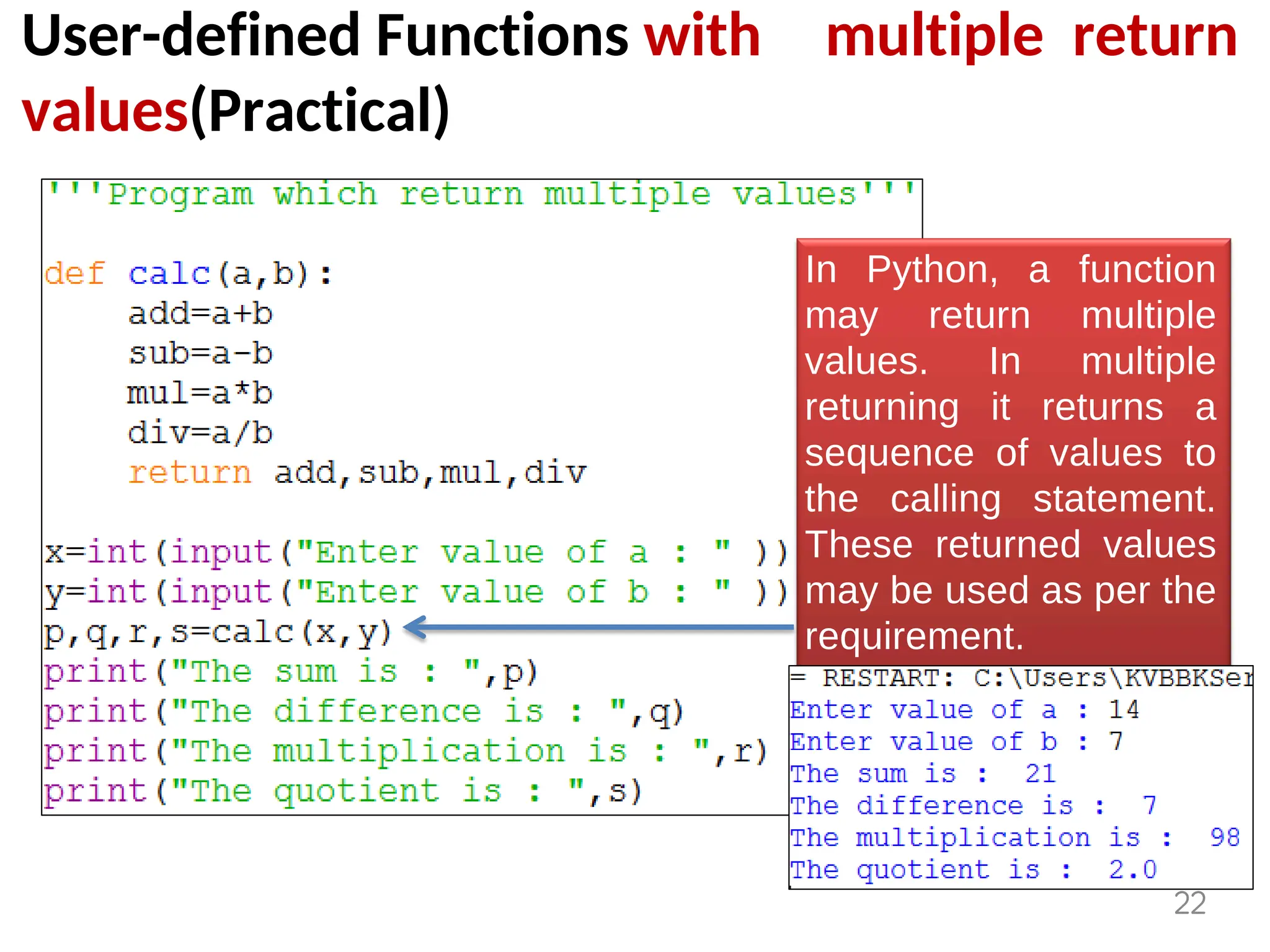
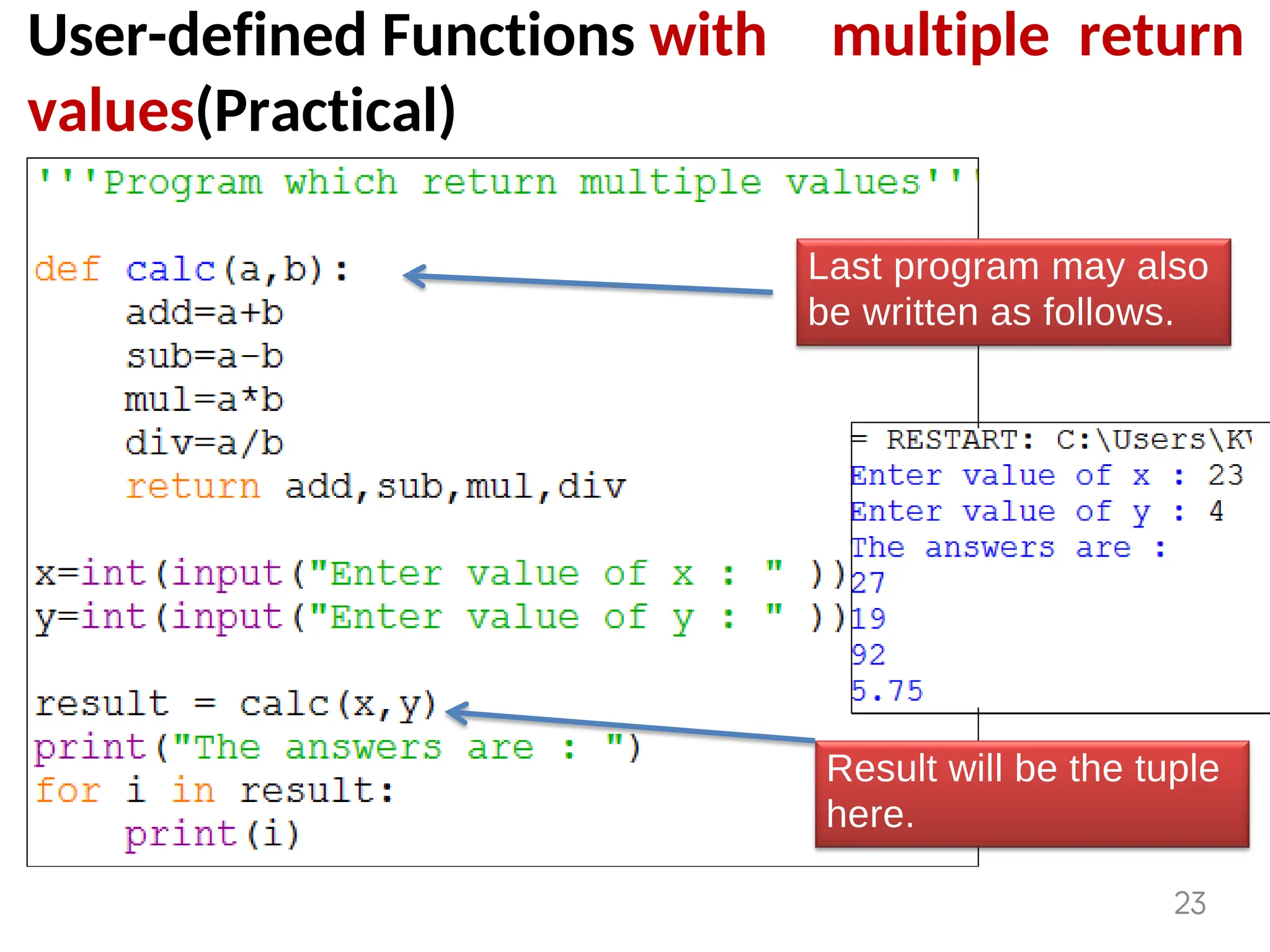
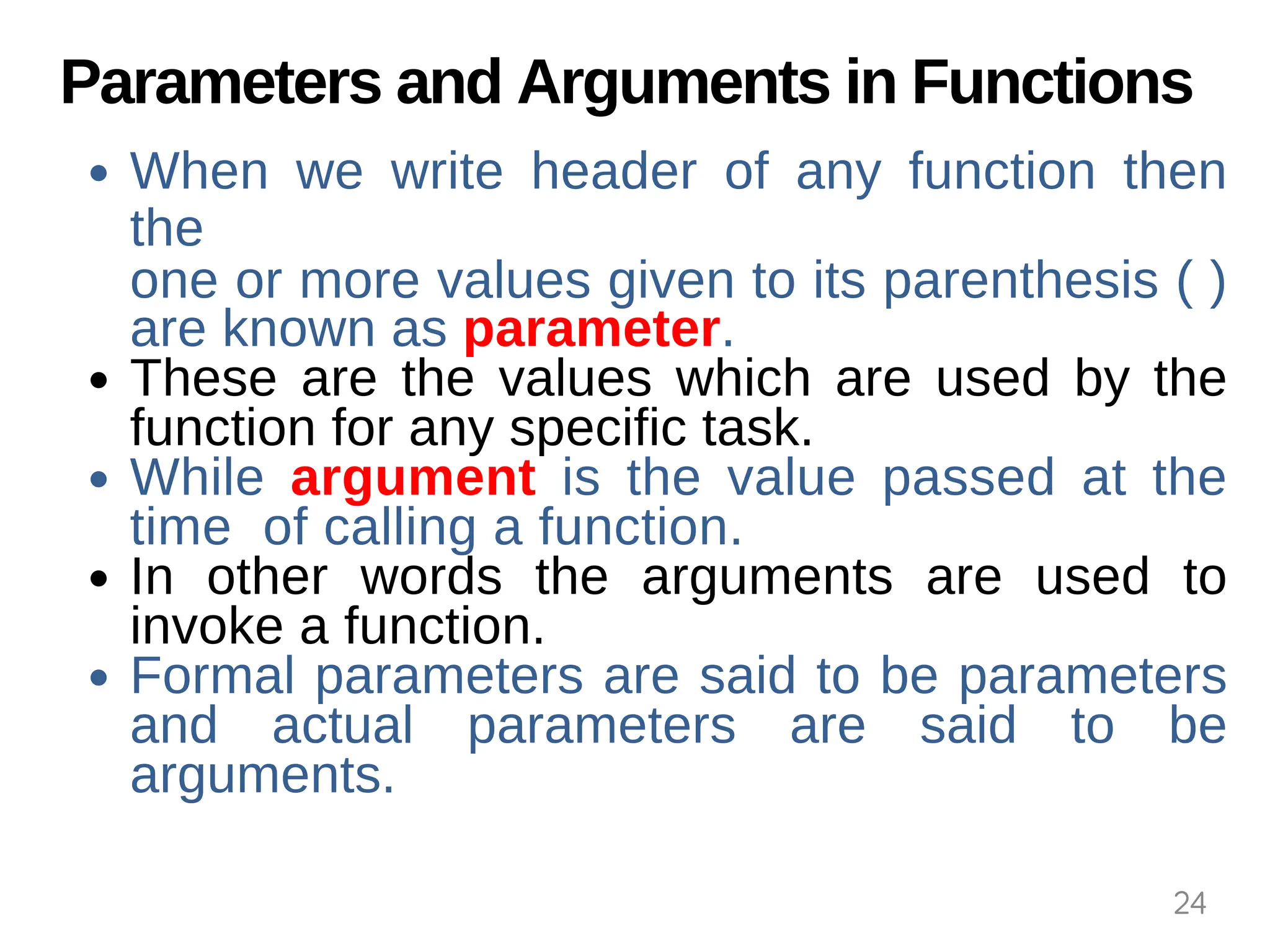
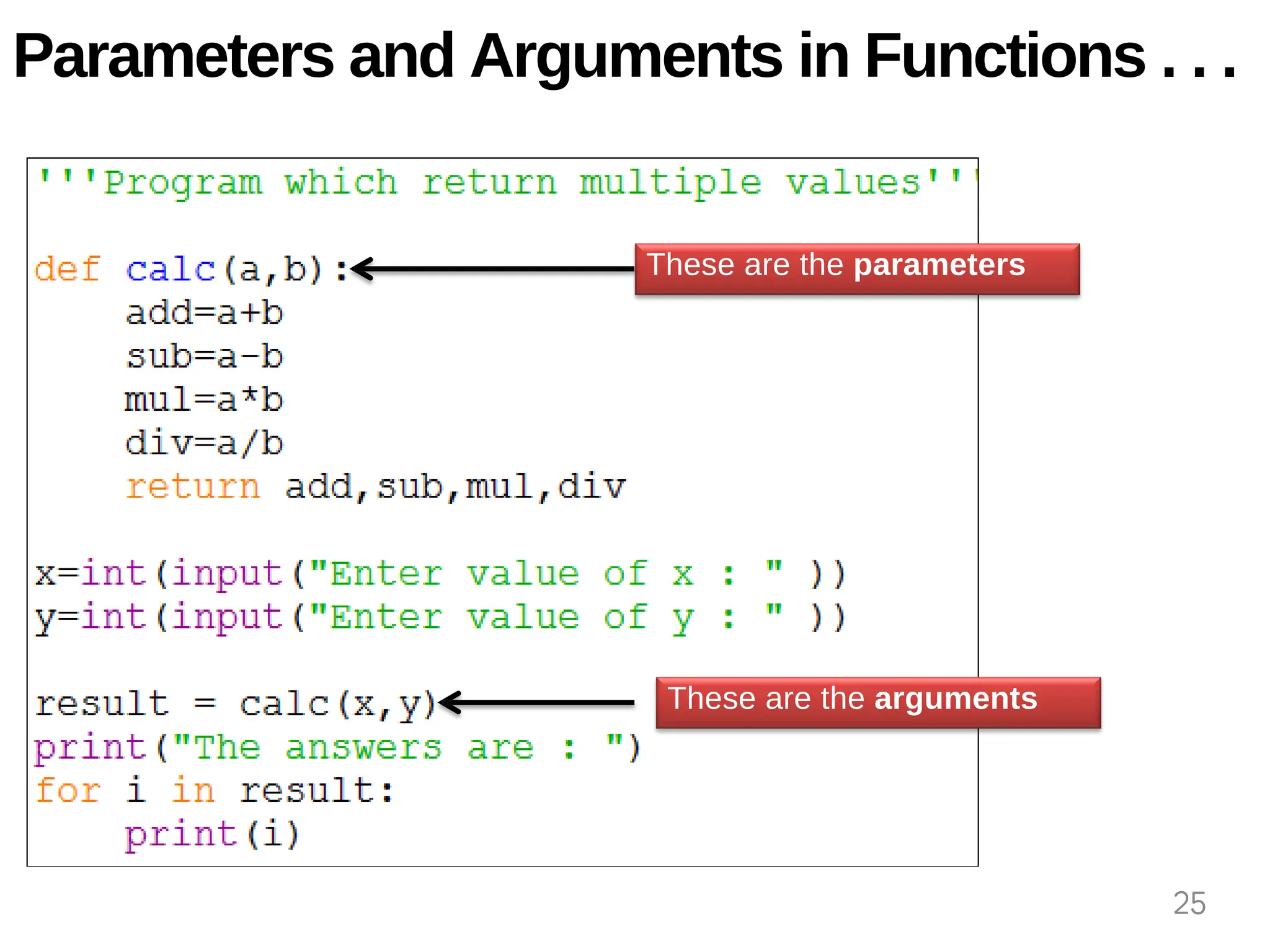
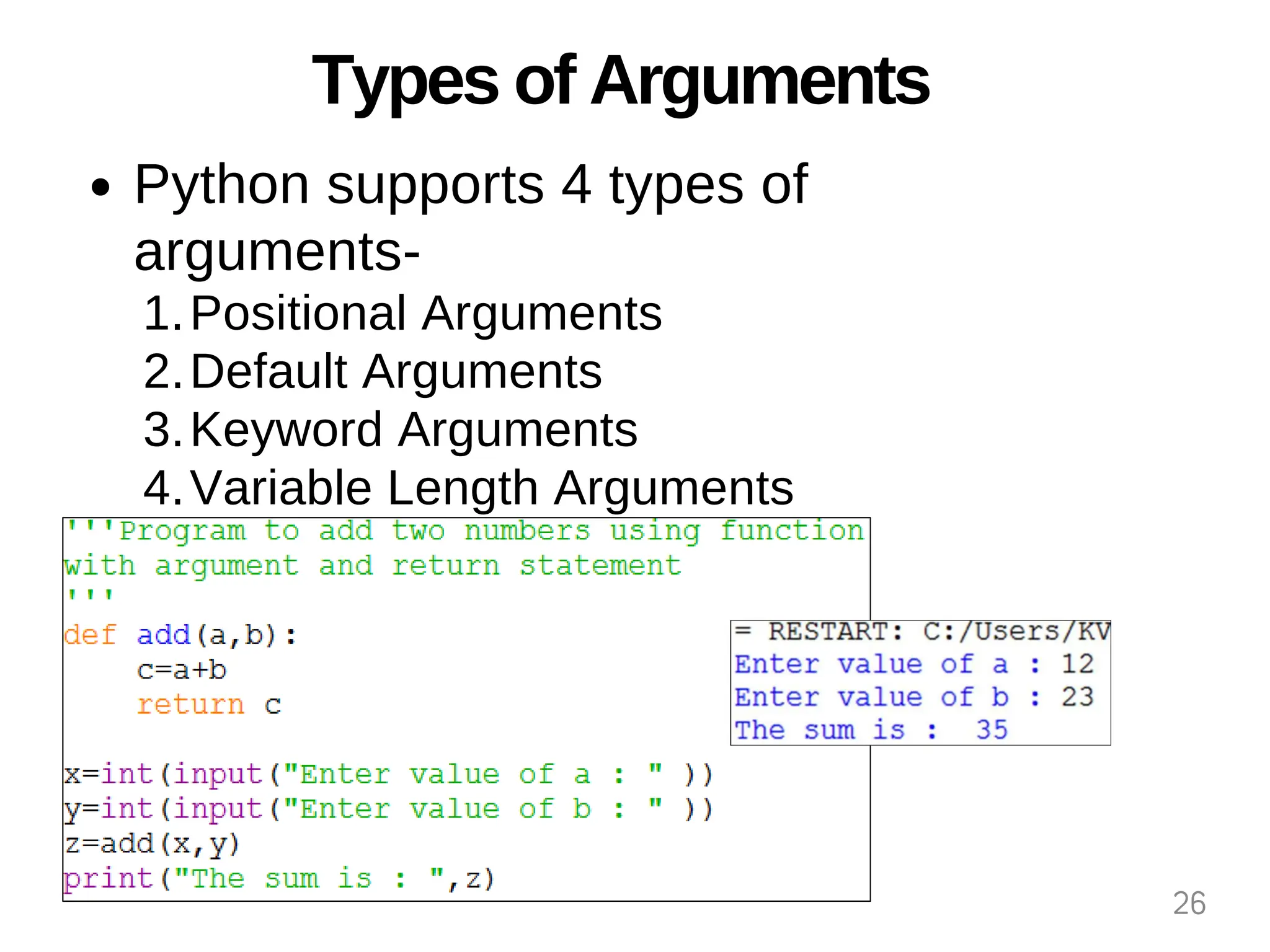
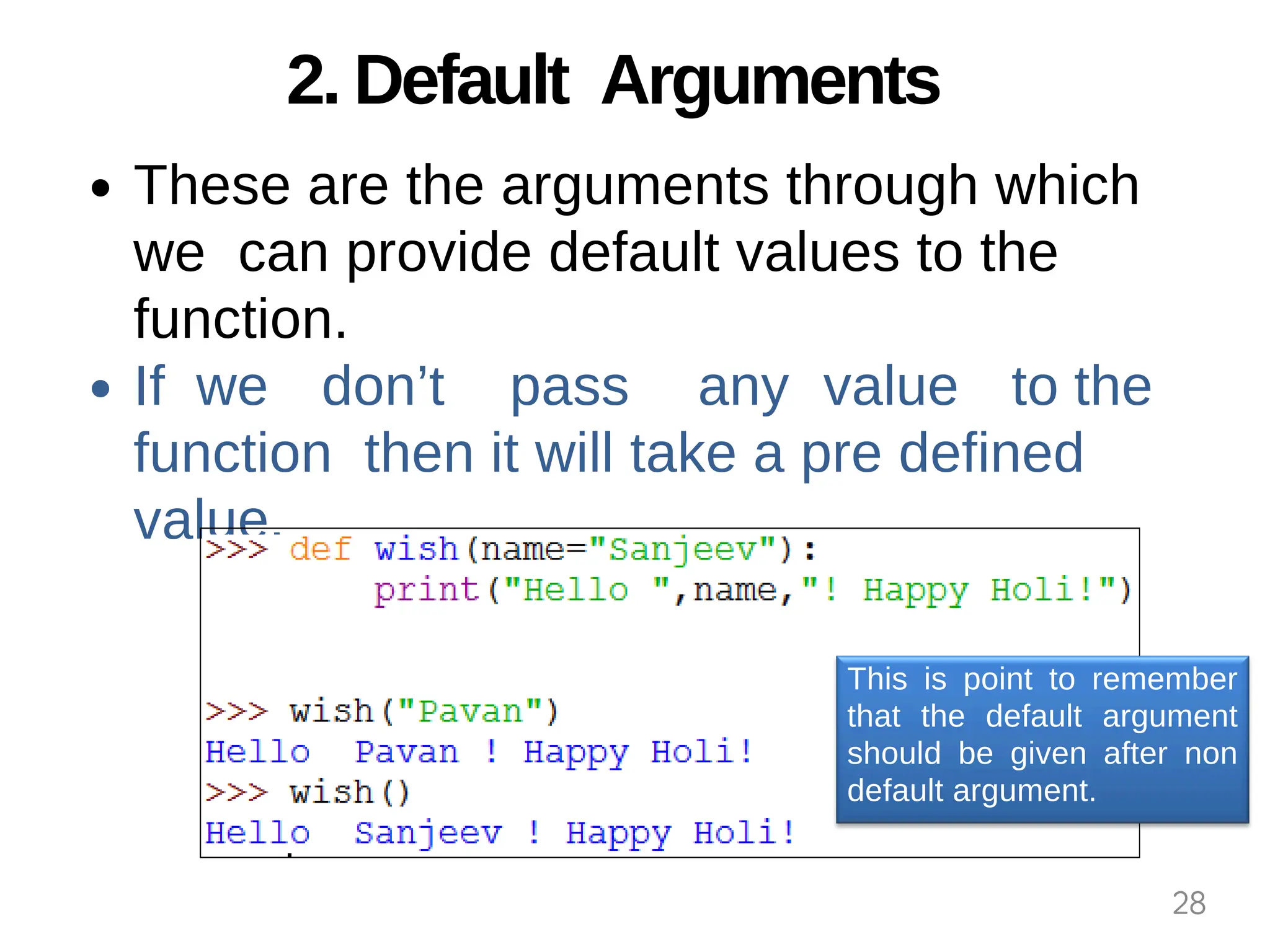
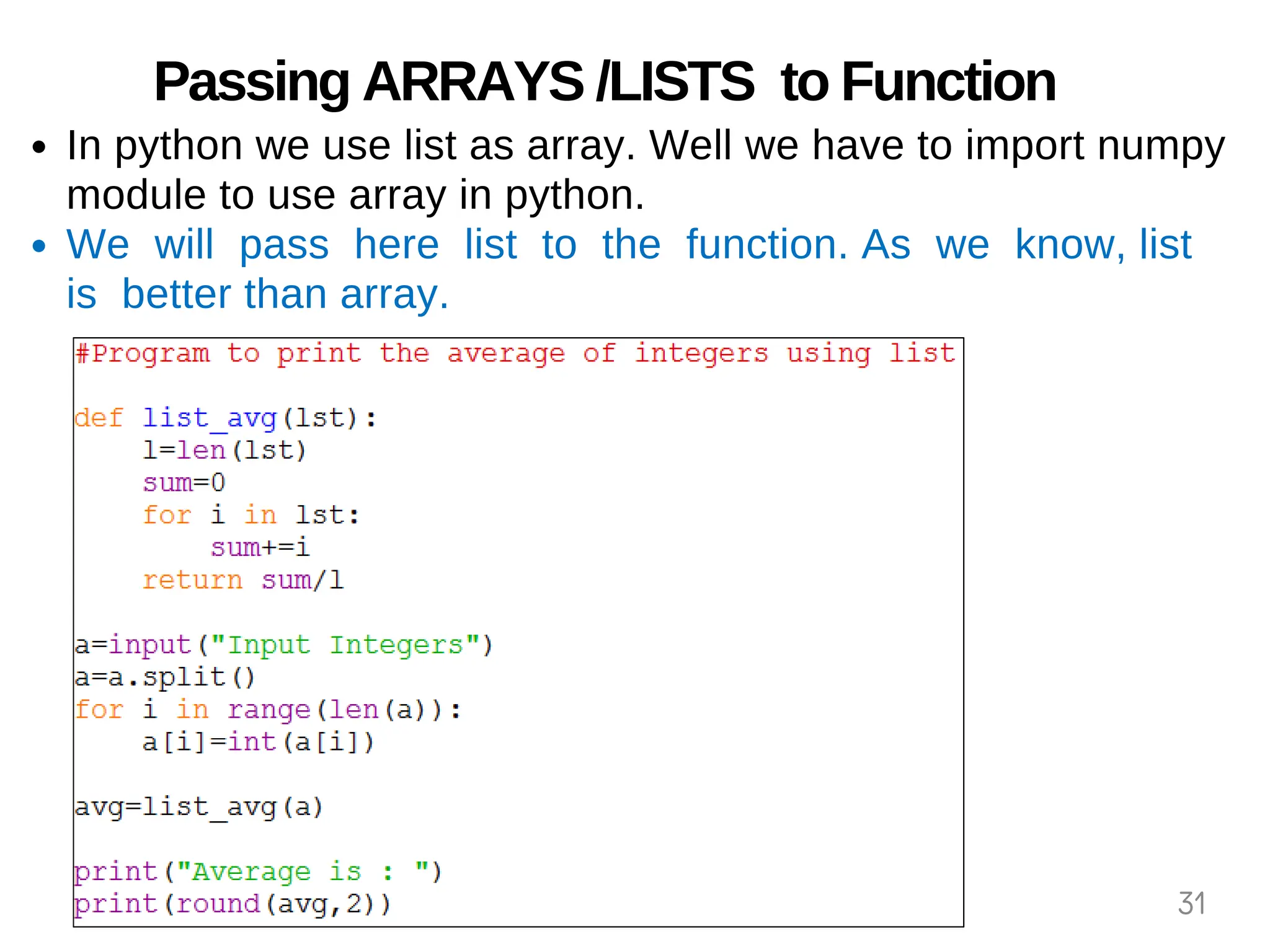
The document provides an overview of functions in Python, explaining their types (built-in, user-defined, and modules) and various built-in functions such as type conversion, input handling, and string manipulation. It also discusses user-defined functions, including syntax, arguments, and the concept of recursion. Additionally, the document touches on modules, their usage in structuring code, and different types of arguments supported by Python functions.