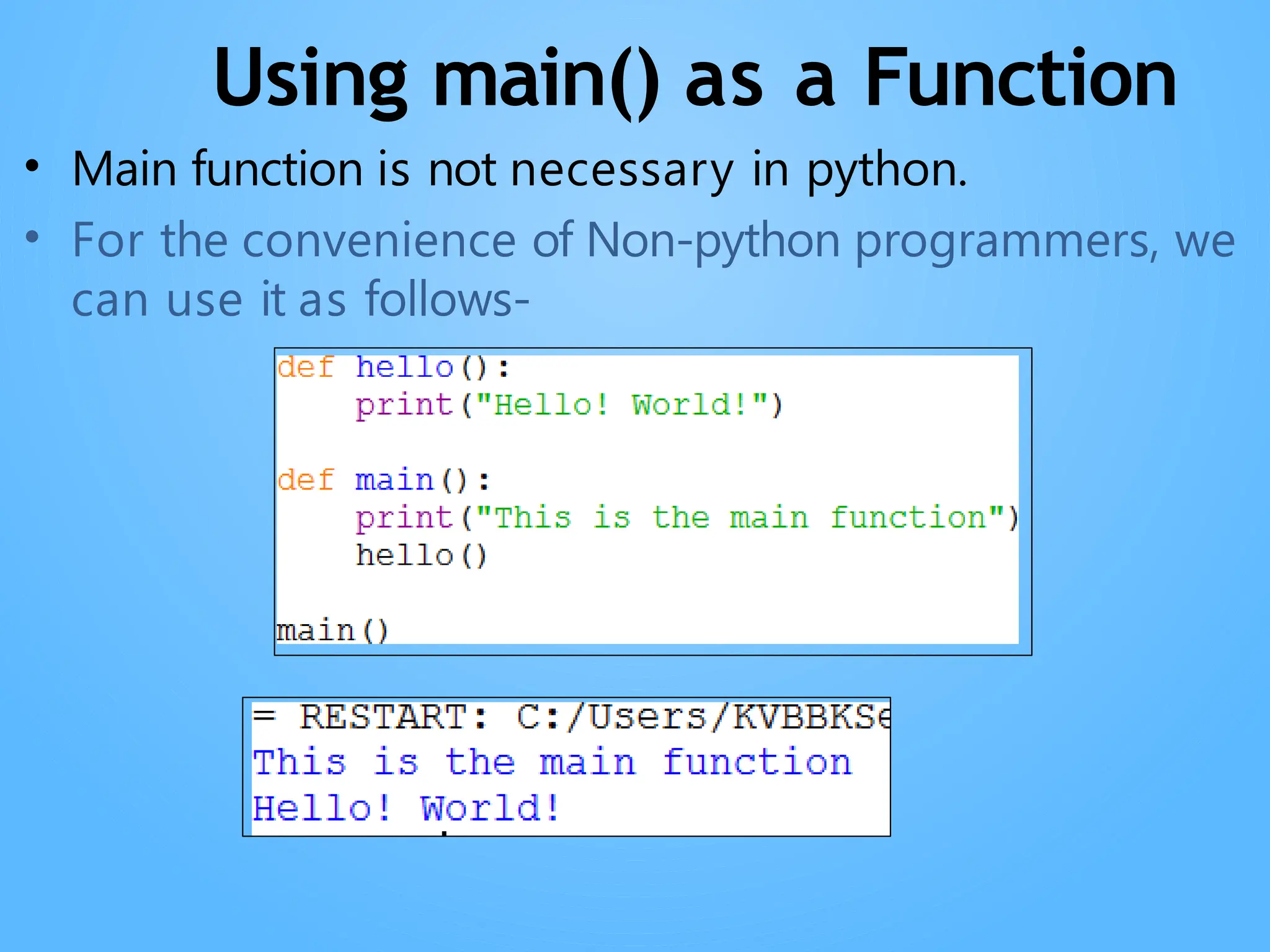
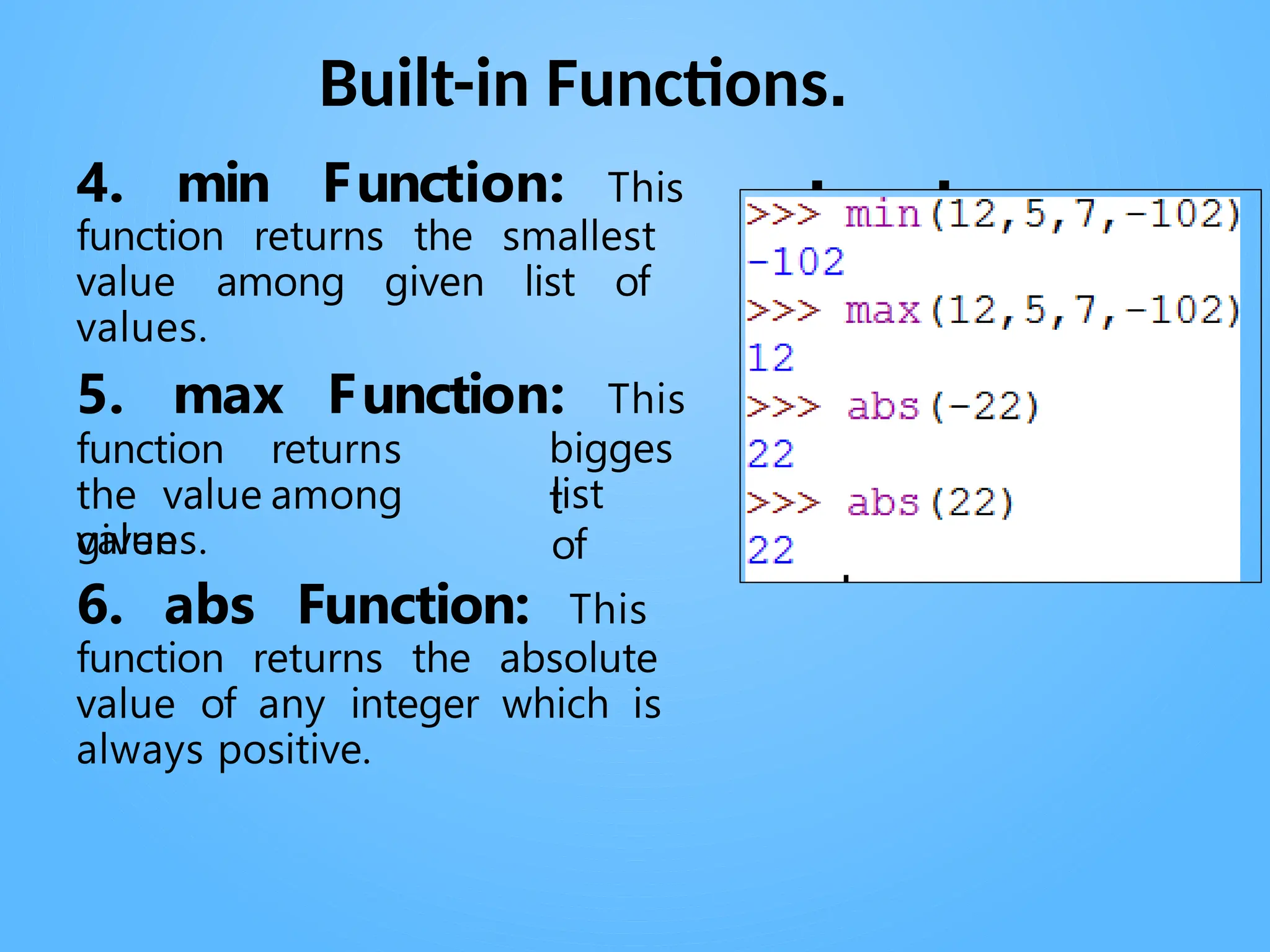
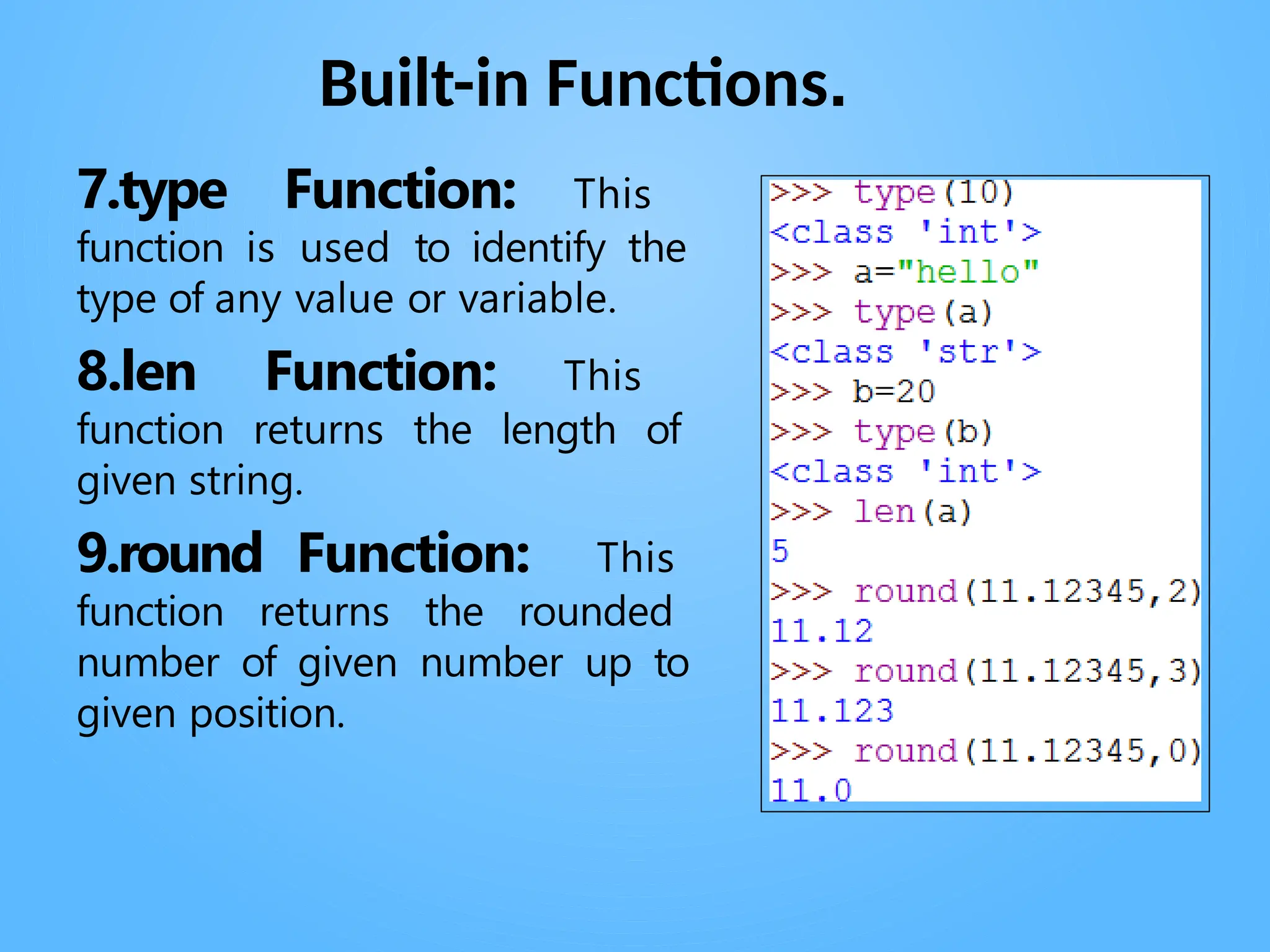
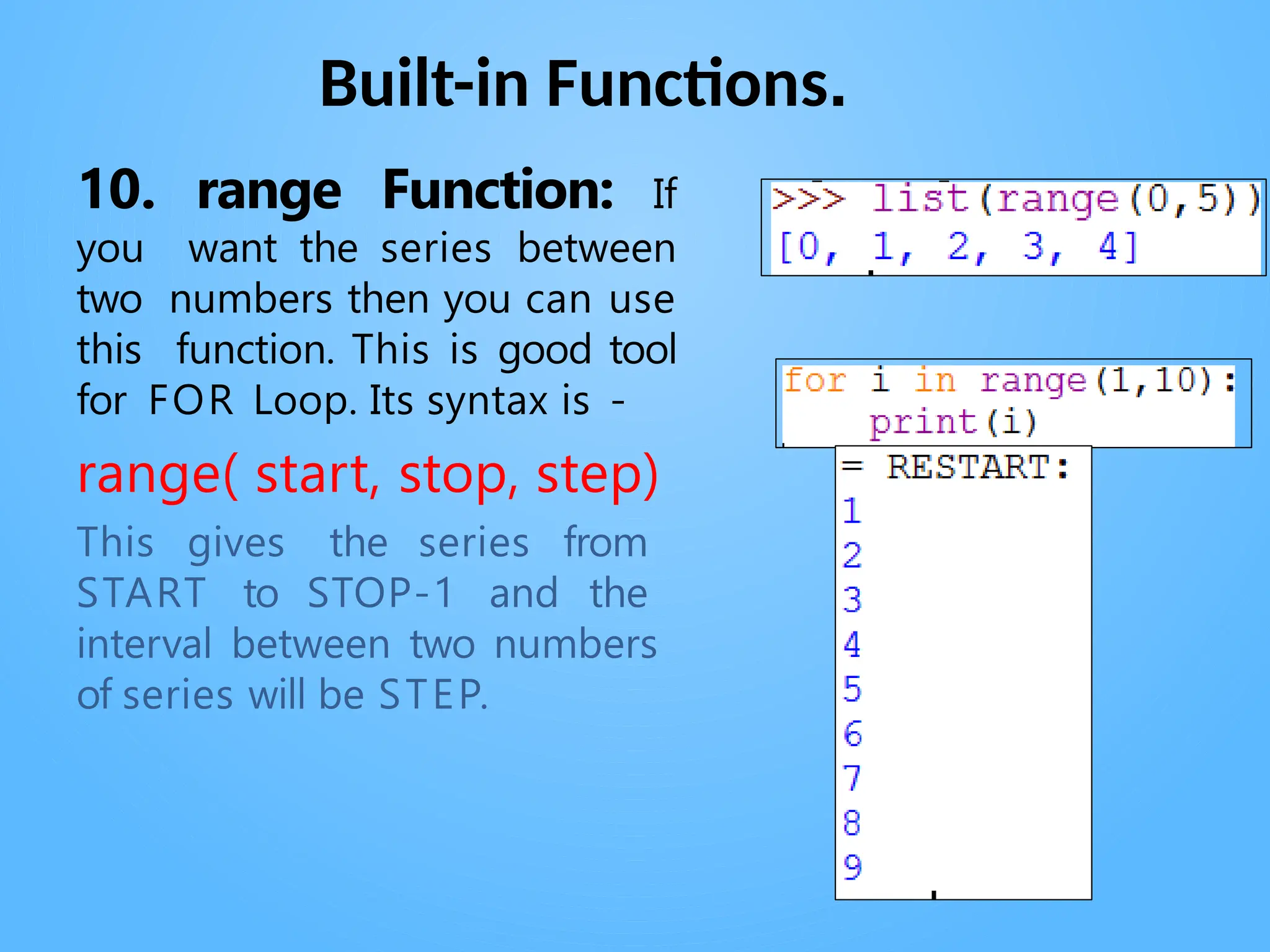
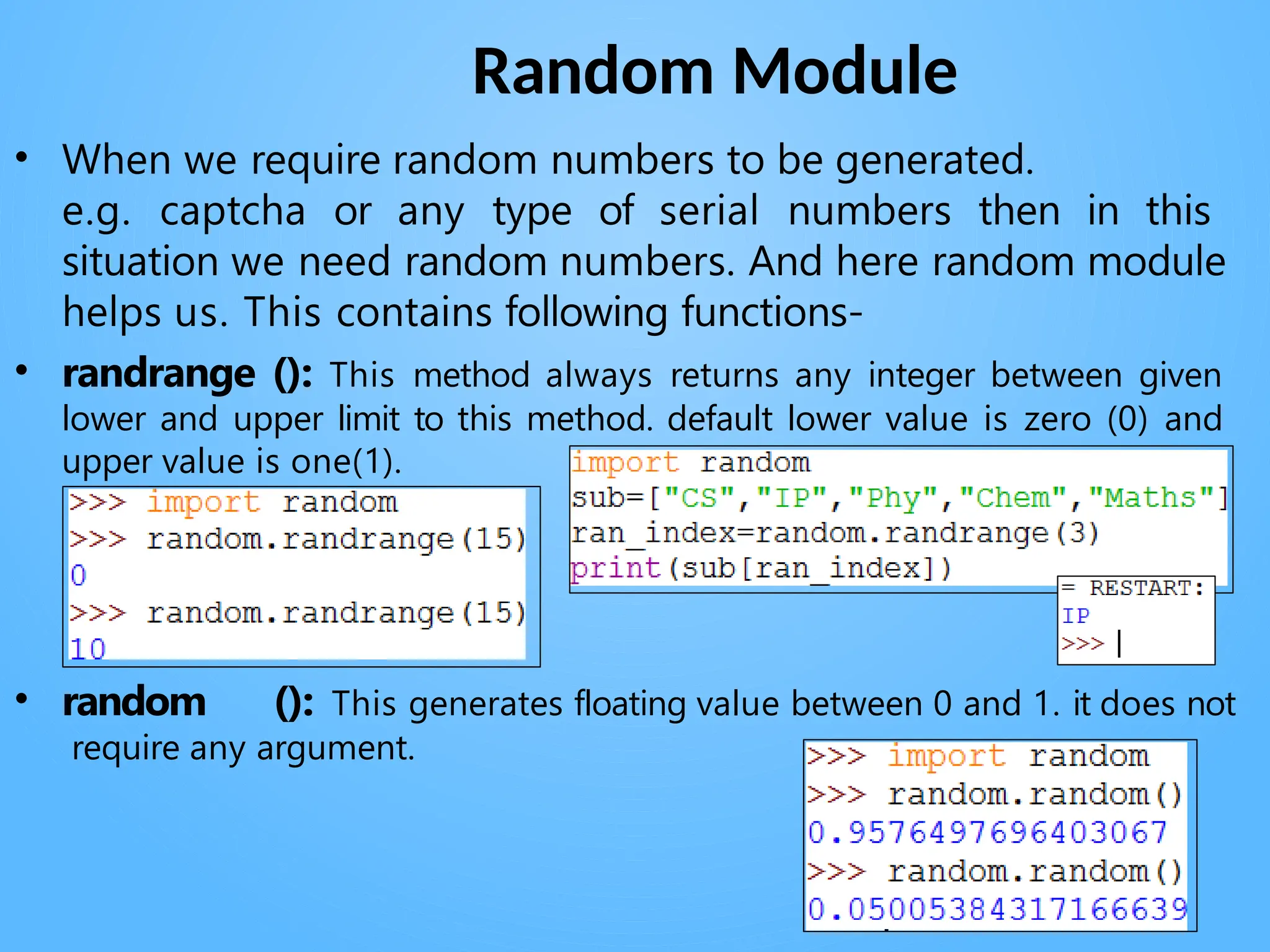
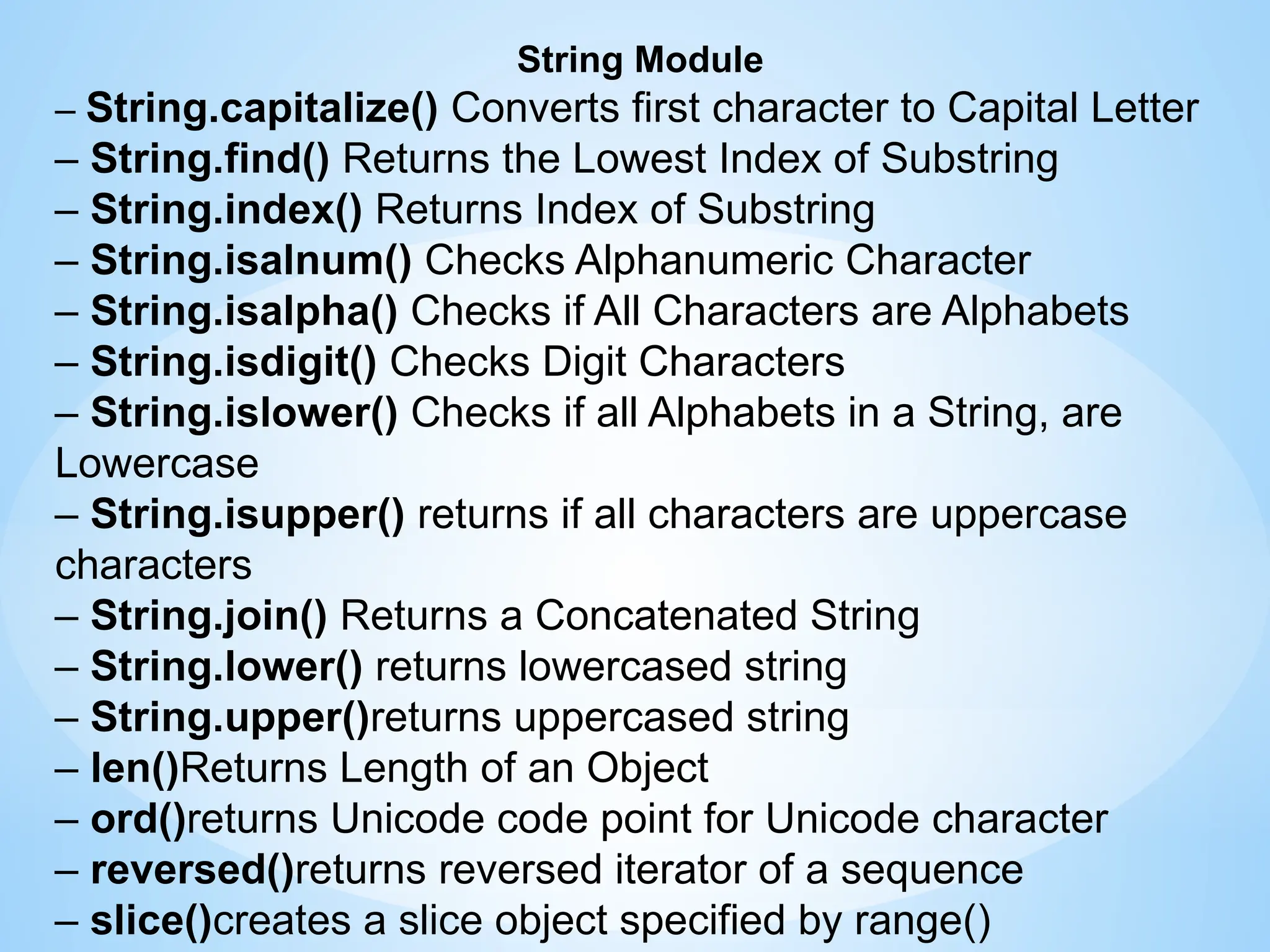
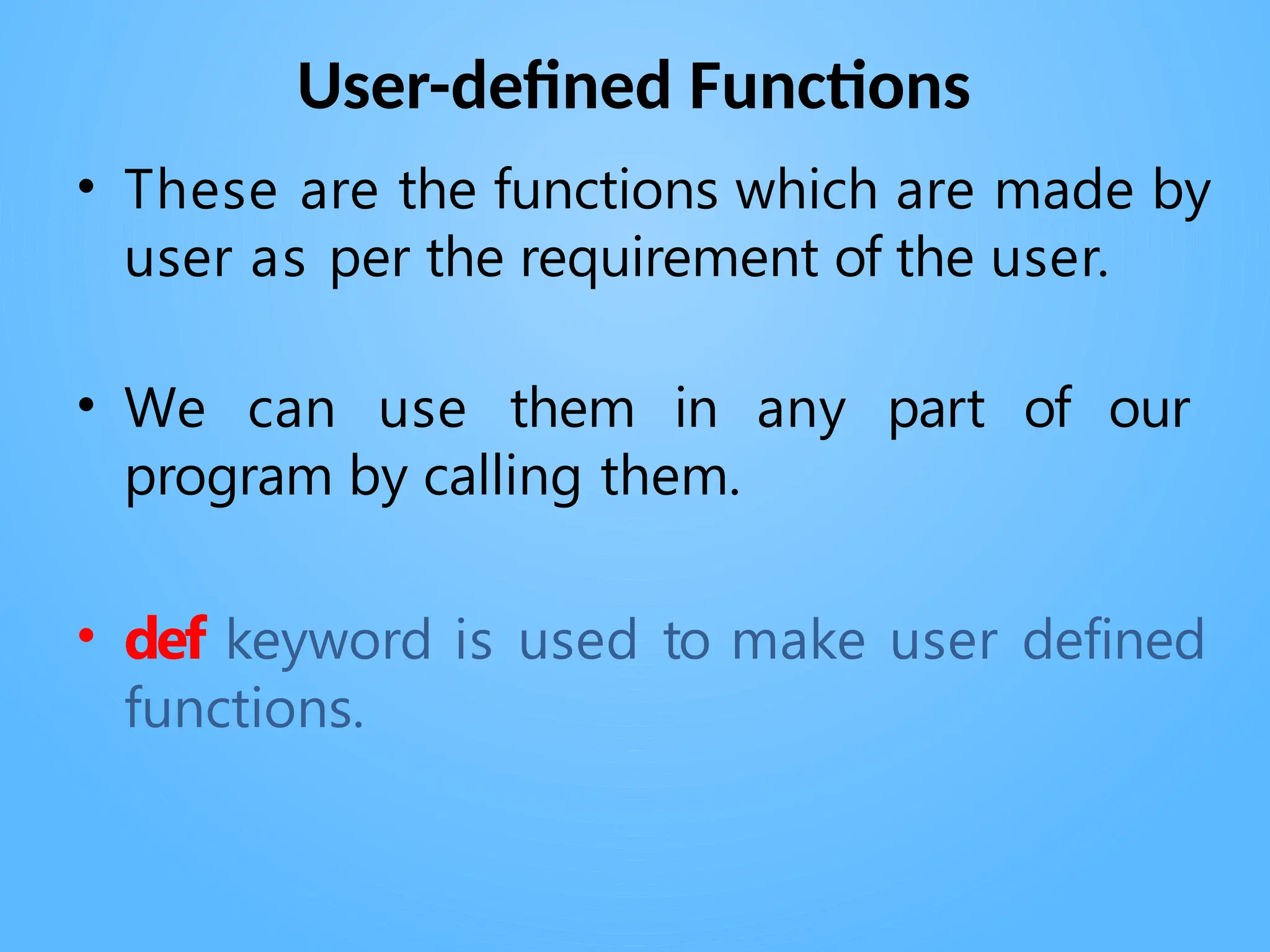
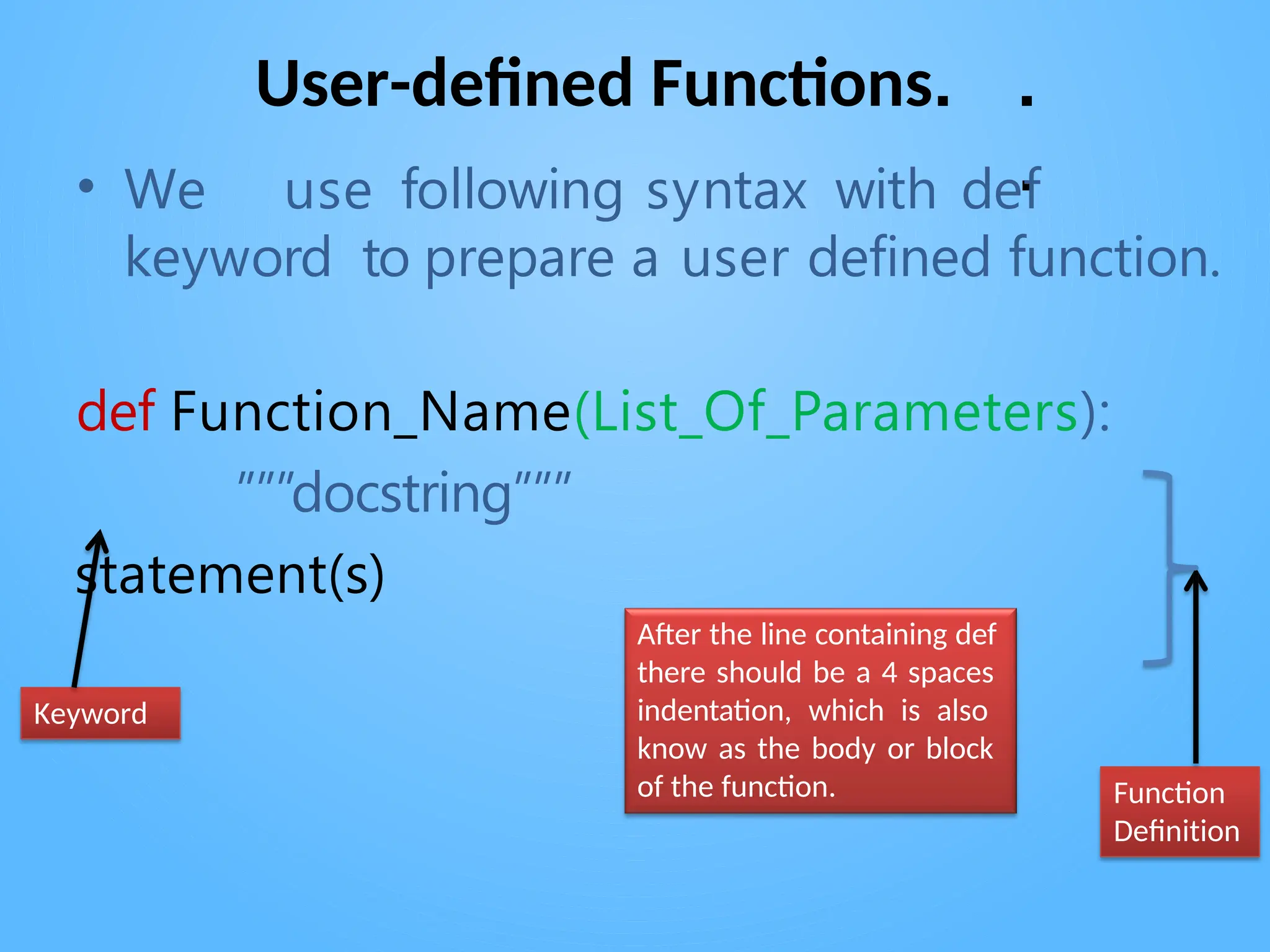
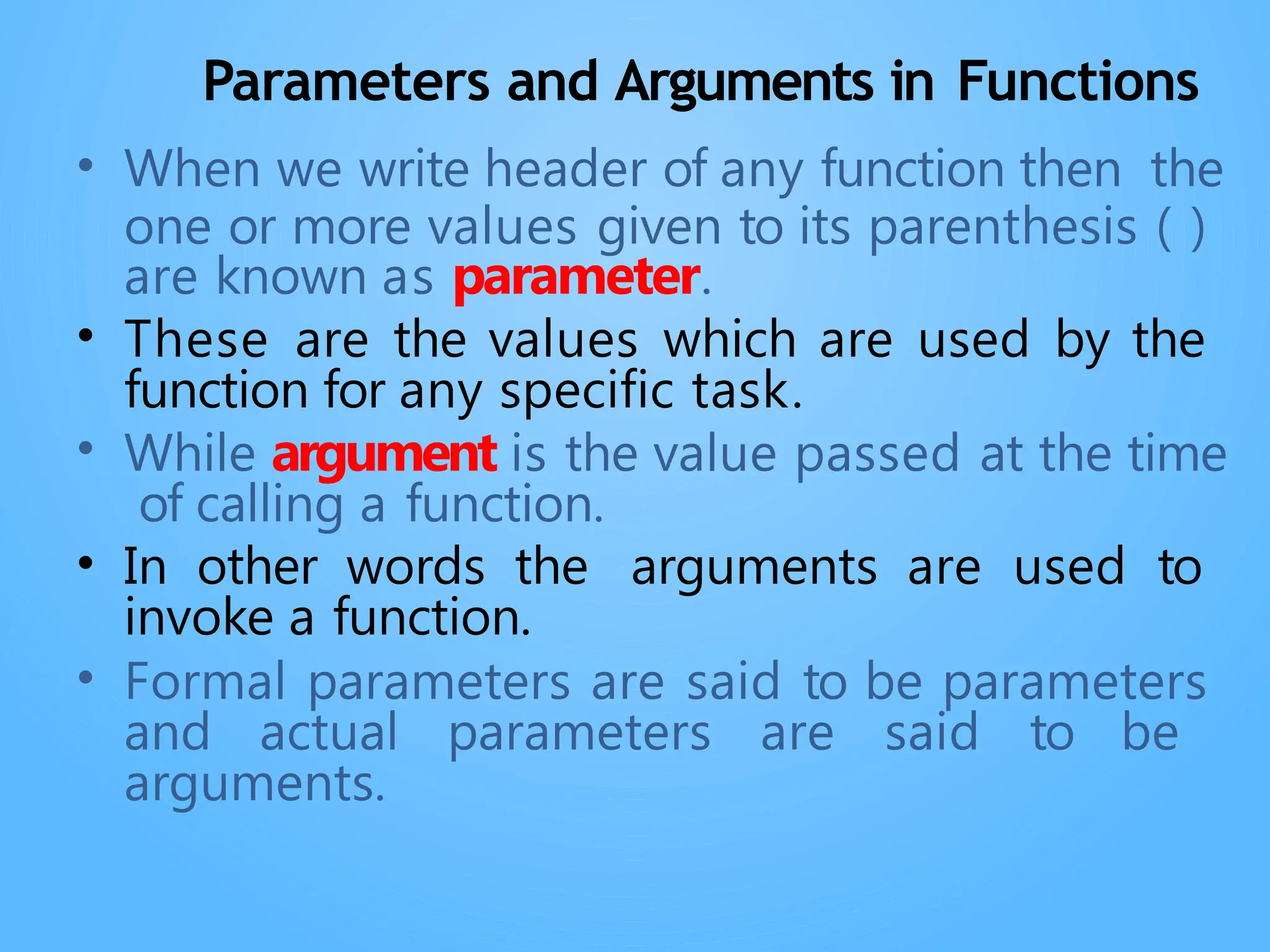
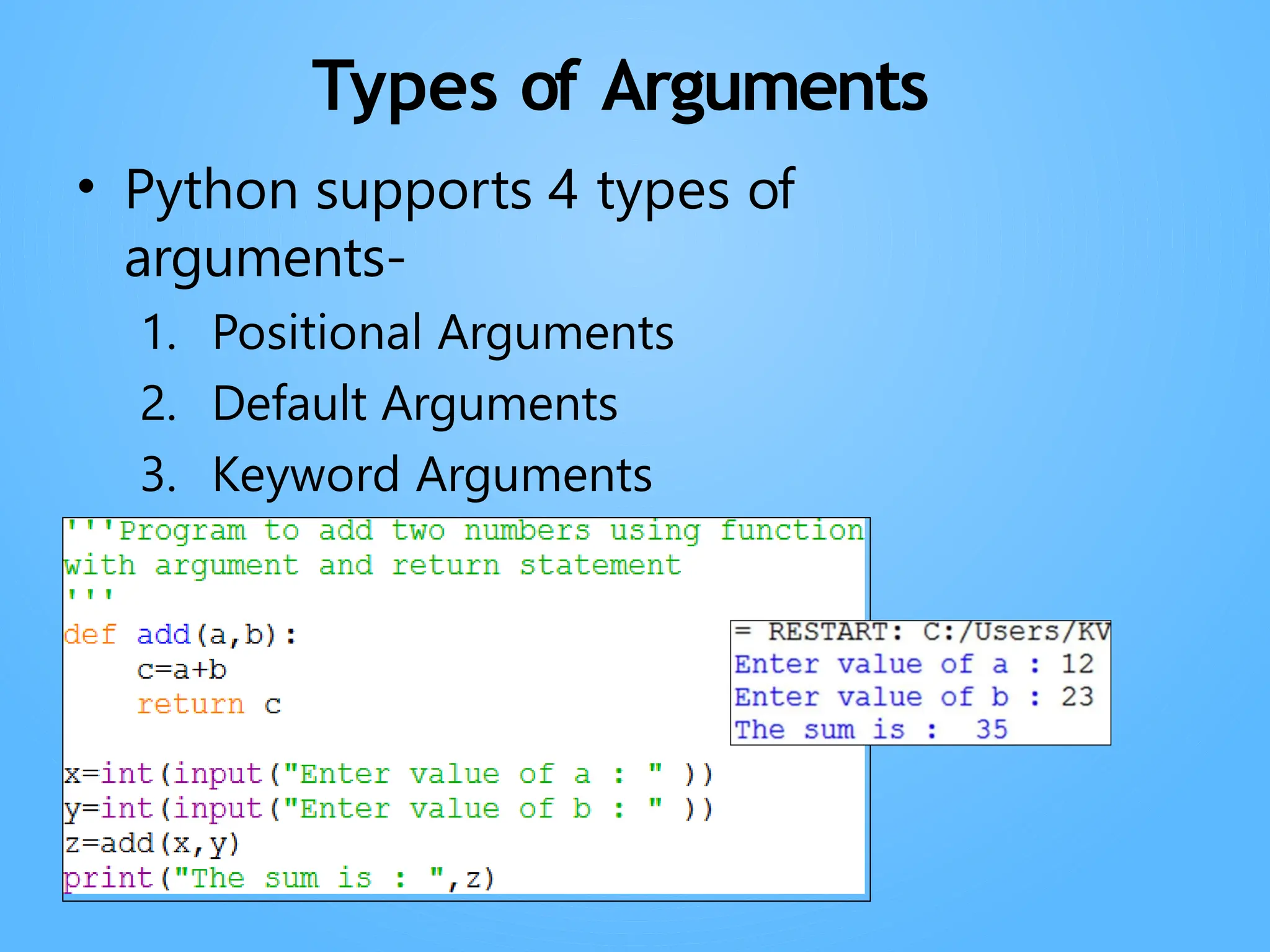
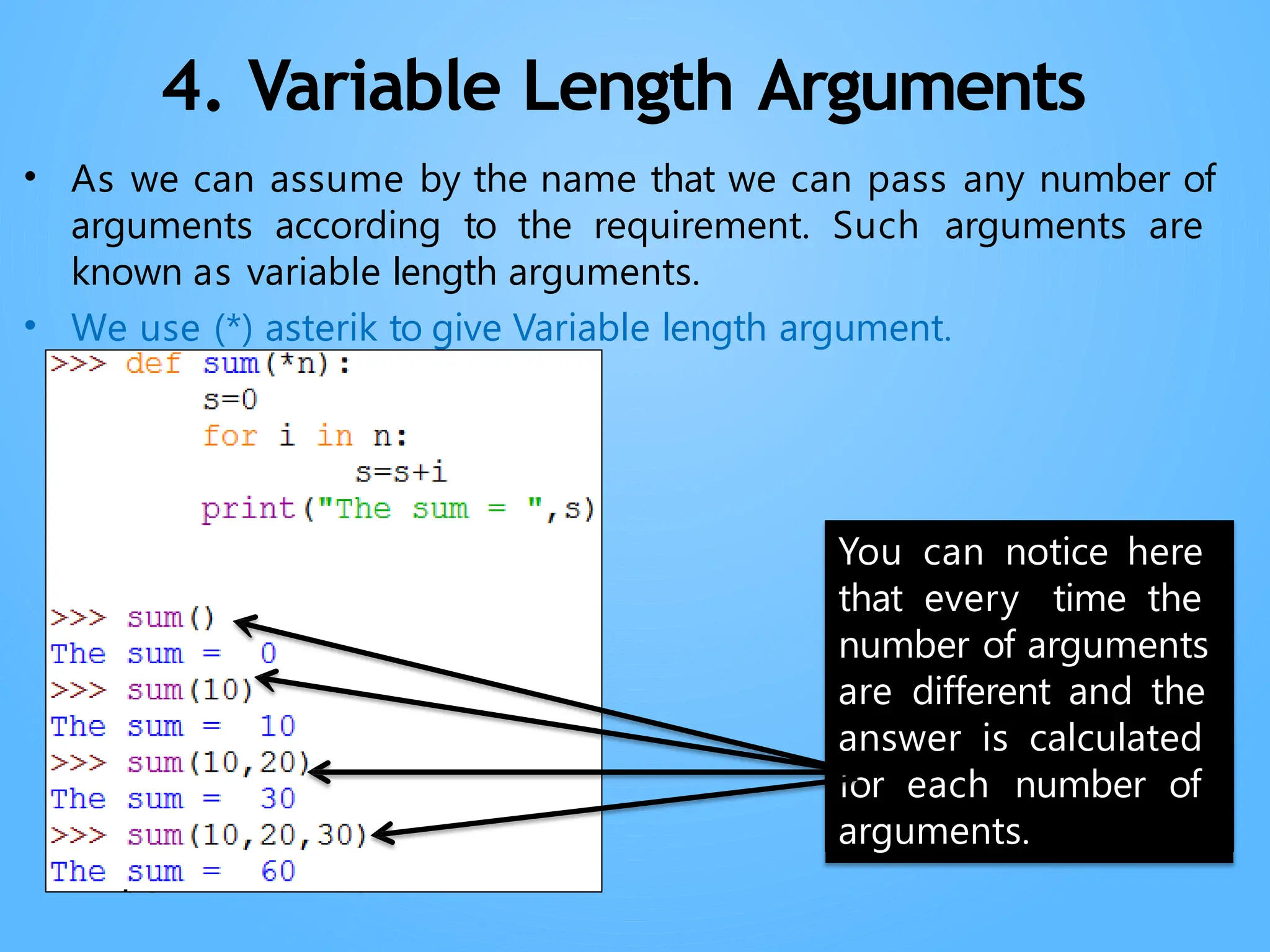
Chapter 3 discusses functions in Python, covering their definition, advantages, and categorization into built-in, module, and user-defined functions. It highlights various built-in functions for type conversion, input, and mathematical operations, as well as the benefits of modularity and reusability. Additionally, it explains how to create user-defined functions and the concept of parameter passing, including positional, default, and keyword arguments.







![*Module name : statistics
This module provides functions for calculating statistics of
numeric (Real-valued) data. It can be included in the program
by using the following statements:
*import statistics
Function syntax Argument Return Example
Output
statistics.mean(x) x is a numeric
sequence
arithmetic
mean
>>> statistics.
mean([11,24,32,45,51])
32.6
statistics.median(x) x is a numeric
sequence
median
(middle
value) of x
>>>statistics.
median([11,24,32,45,51])
32
statistics.mode(x) x is a sequence mode
(the most
repeated
value)
>>> statistics.
mode([11,24,11,45,11])
11
>>> statistics.
mode(("red","blue","red"))
'red'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionxii1-241101165839-b2bfeb21/75/function_xii-BY-APARNA-DENDRE-1-pdf-pptx-17-2048.jpg)






![Write python code to print average of list elements
def list_avg(li):
sum=0
for i in li:
sum=sum+i
return sum/n
li=[]
n=int(input('Enter size of elements to be enter in list:'))
c=0
while c<n:
a=int(input('Enter numbers in list:'))
li.append(a)
c=c+1
print(li)
avg1=list_avg(li)
print('Average of list is;',round(avg1,2))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionxii1-241101165839-b2bfeb21/75/function_xii-BY-APARNA-DENDRE-1-pdf-pptx-33-2048.jpg)
![*Output is
Enter size of elements to be enter in
list:4
Enter numbers in list:34
Enter numbers in list:5
Enter numbers in list:23
Enter numbers in list:56
[34, 5, 23, 56]
Average of list is; 29.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionxii1-241101165839-b2bfeb21/75/function_xii-BY-APARNA-DENDRE-1-pdf-pptx-34-2048.jpg)