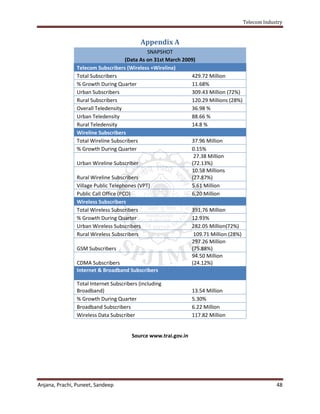
The telecom industry in India has experienced rapid growth, contributing significantly to GDP. It began with a phased privatization approach, first allowing private investment in value-added services, then cellular and basic services. TRAI regulates competition between providers. Key highlights of the report include the history and structure of the industry, major players, competitive advantages like a large talent pool and low labor costs, emerging technologies like 3G and rural expansion opportunities. The future includes acquiring more rural customers, selling more services to existing users, and government initiatives to further growth.



































![Telecom Industry
10 References
[1] IBEF report 2007-08 : Telecommunication - MARKET & OPPORTUNITIES.
[2] Cellular Statistics – Cellular Operator Association of India
[3] IAMAI & eTechnology Group@IMRB: MOBILE VALUE ADDED SERVICES IN INDIA- A Report.
[4] Telenor Entering India: Investment Update
[5] Voice and Data(May 2009): Mobile Number Portability - Poaching with Portability.
[6] Business India : Telecom Takeover, Bharti-MTN deal
[7] Moneycontrol.com: Idea Spice deal
[8] Business Standard: Vodafone Hutch deal
[9] IntoMobile: India’s 3G License Plans Updated.
[10]World Bank Report: Spectrum auctions in India: lessons from experience
Anjana, Prachi, Puneet, Sandeep 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18590980-telecom-sector-in-india-121031051538-phpapp01/85/18590980-telecom-sector-in-india-47-320.jpg)