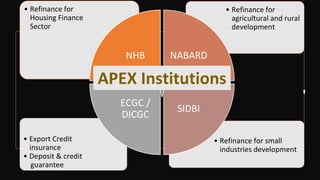
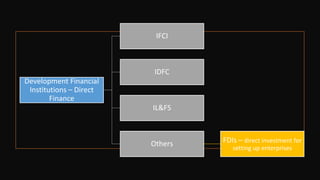
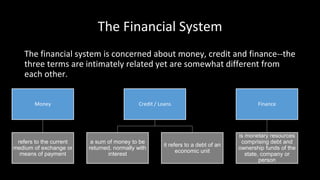
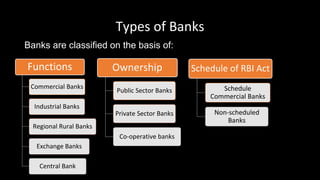
The document provides an overview of the Indian financial system and banking system. It discusses the key components of the financial system including financial institutions, financial markets, financial instruments, and financial services. It then describes the major players in the Indian financial sector including various regulators like RBI, SEBI, and IRDA. It also discusses the different types of banks operating in India based on their functions, ownership, and schedule under the RBI Act. Finally, it summarizes the roles and functions of commercial banks and the RBI.