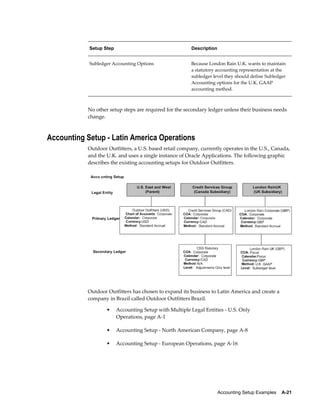
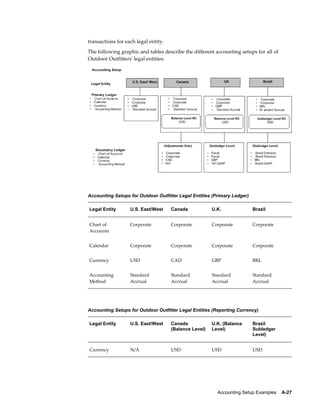
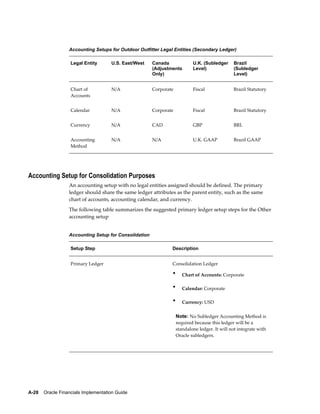
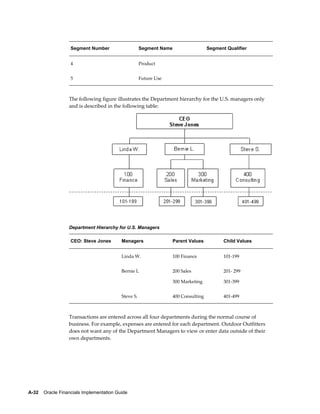
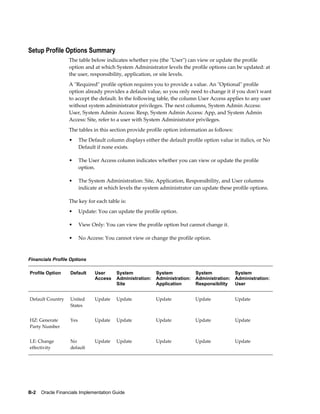
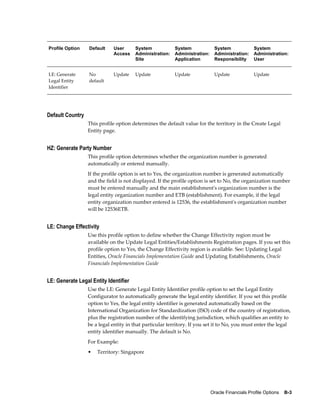
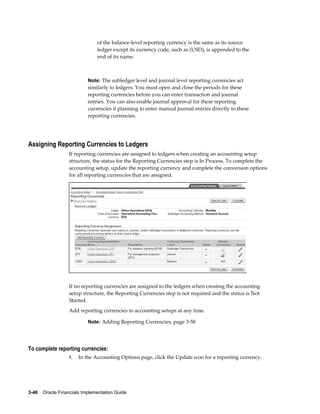
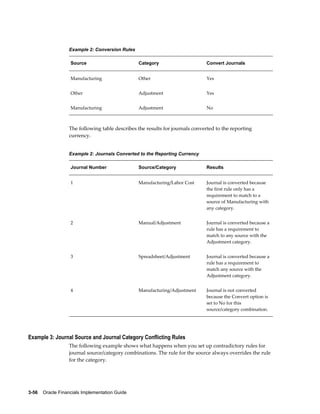
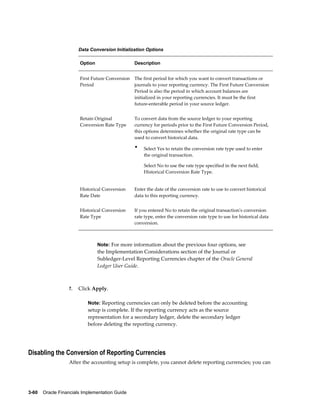
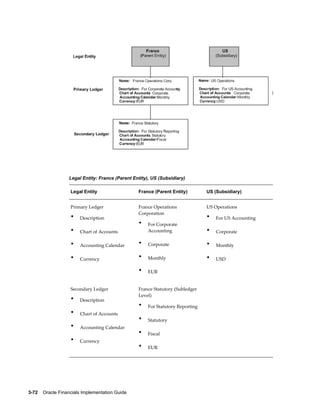
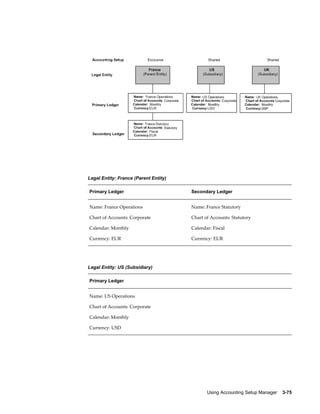
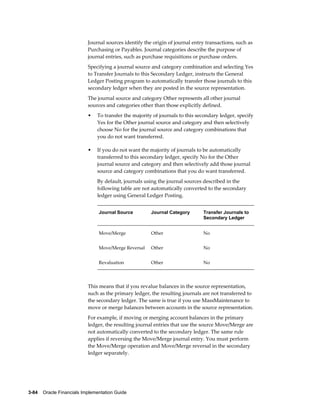
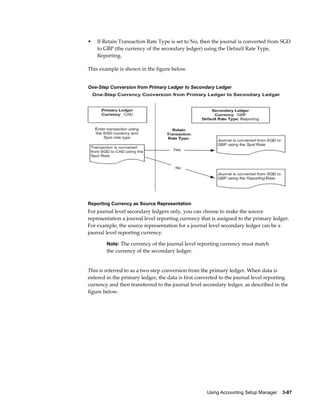
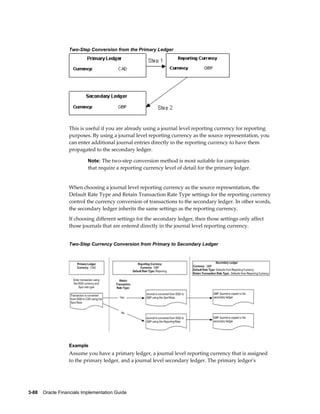
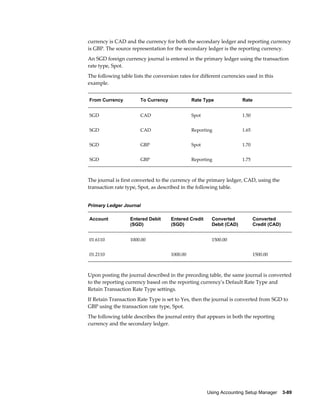
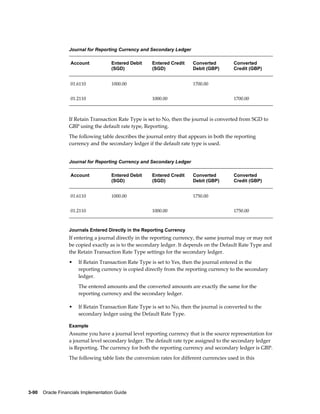
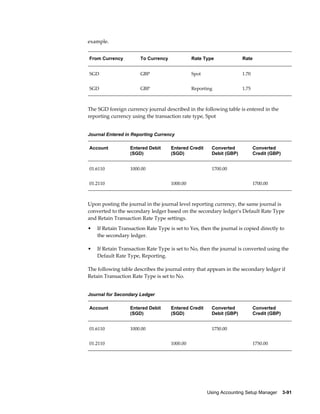
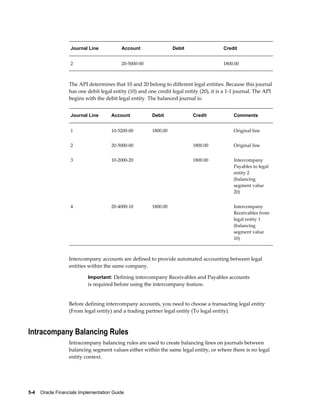
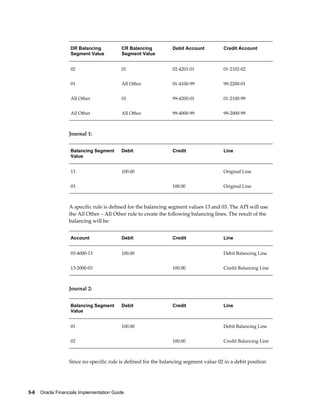
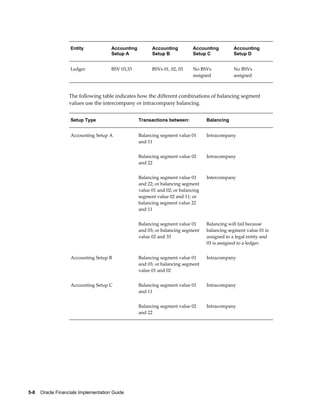
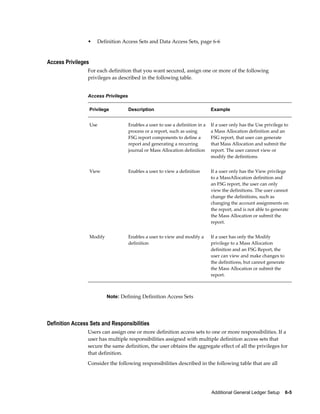
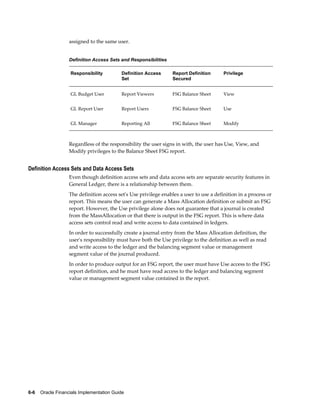
This document provides an implementation guide for Oracle Financials Release 12. It outlines considerations for designing accounting setups, including whether to use one or multiple legal entities. It describes how to create accounting setups using the Accounting Setup Manager, including defining legal entities, ledgers, reporting currencies, and journal conversion rules. It also provides examples of different accounting setup structures and comparisons of feature support across different setup options.




















































































































































![7-6 Oracle Financials Implementation Guide
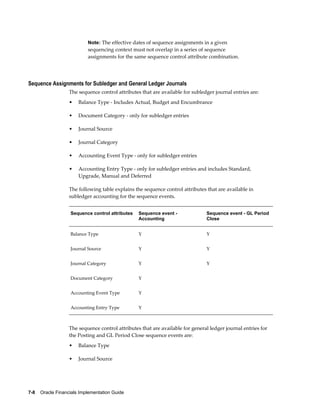
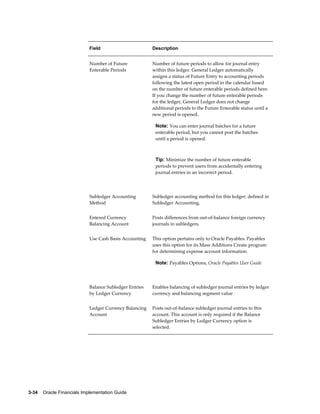
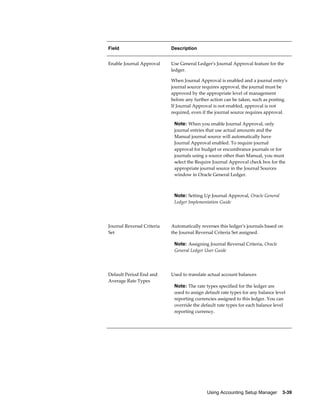
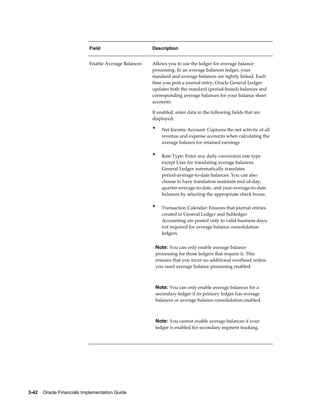
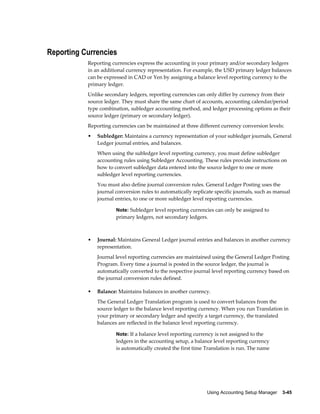
• Sequence Events – GL Period Close and Posting
• Validate Sequence By – Journal Effective Date and Reference Date for the
Accounting sequence event. Posting Date and Journal Effective Date for GL Period
Close sequence event
• Assign Sequence By – Posting Date, Journal Effective Date and Reference Date.
• Balancing Segment Values – Specify the balancing segment values that are fiscal in
nature. This is used only by GL Period Close sequence event. When the GL period
is closed, only fiscal journal entries are sequenced.
Note: To use this option, balancing segment values must be
assigned to the legal entity in your accounting setup.
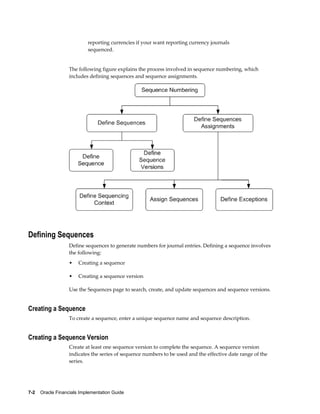
Assigning a Sequence
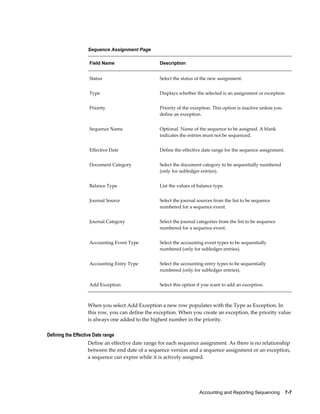
After you define the Sequencing Context, use the Assign Sequences page to assign the
sequences to journal entries. A sequence assignment uses a combination of the
sequencing context, sequence entity, and sequence event to sequentially number the
journal entries.
Before assigning the sequences, you must determine the following sequence control
attributes:
• Effective date range
• Balance Type
• Journal Source
• Journal Category
• Accounting Event Type (only for subledger journal entries)
• Accounting Entry Type (only for subledger journal entries)
• Document Category (only for subledger journal entries)
Sequence Assignments Page
Use the Create Assignments [Sequence Context] page to create and update assignments
and exceptions for a sequence context.
The following table explains selected fields in the Create Assignments page.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/120finig-150805230033-lva1-app6892/85/120finig-176-320.jpg)