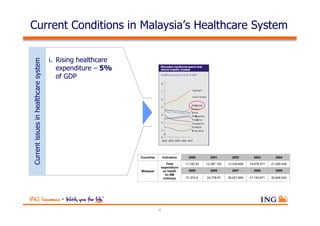
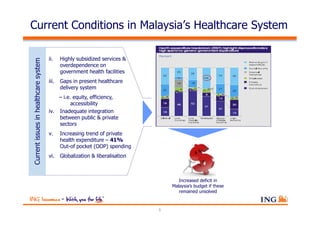
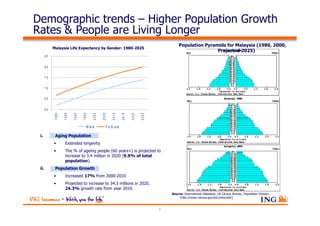
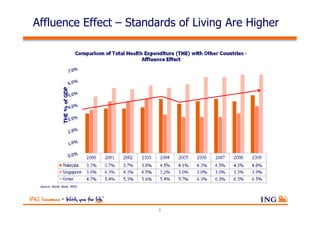
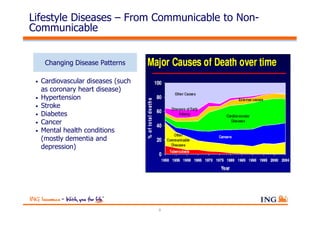
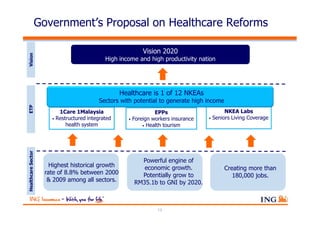
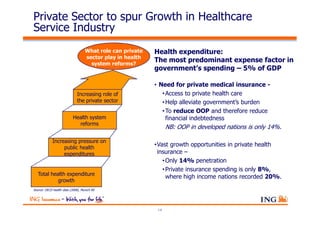
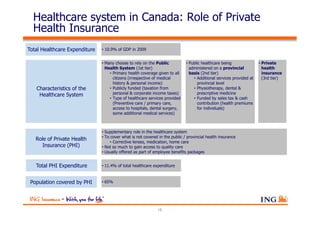
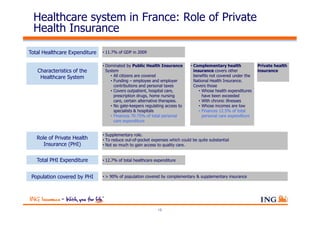
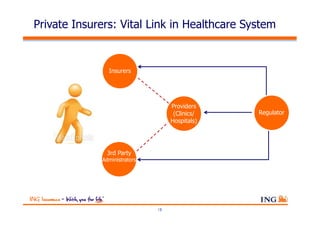
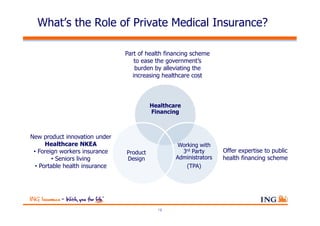
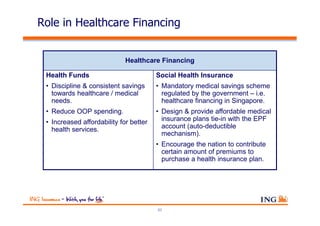
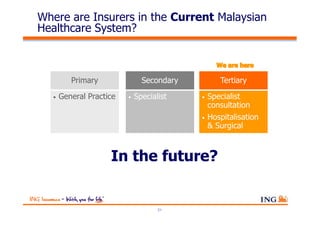
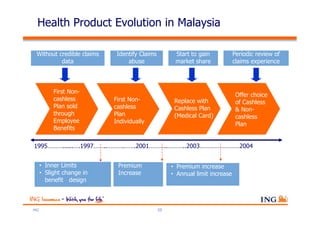
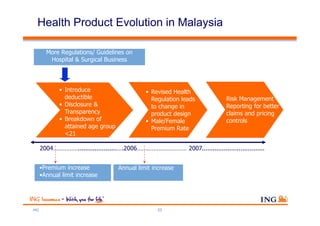
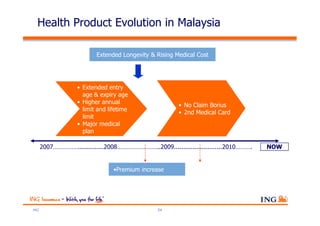
The document outlines the evolving landscape of Malaysia's healthcare system, highlighting the increasing role of private medical insurance amid rising healthcare expenditures and demographic changes. It emphasizes the need for private health insurance to alleviate government burdens and ensure access to quality healthcare, while also noting the significant growth opportunities within the private sector. Additionally, it discusses the anticipated contributions from private medical insurance to improve healthcare financing and to address the challenges faced by the country's healthcare delivery system.