11133546 PY4097 Poster
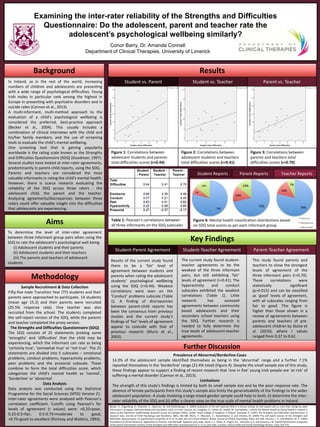
- 1. Examining the inter-rater reliability of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire: Do the adolescent, parent and teacher rate the adolescent’s psychological wellbeing similarly? Conor Barry, Dr. Amanda Connell Department of Clinical Therapies, University of Limerick Background Aims Methodology Results Key Findings In Ireland, as in the rest of the world, increasing numbers of children and adolescents are presenting with a wide range of psychological difficulties. Young Irish males in particular rank among the highest in Europe in presenting with psychiatric disorders and in suicide rates (Cannon et al., 2013). A multi-informant, multi-method approach to the evaluation of a child’s psychological wellbeing is considered the preferred, best-practice approach (Becker et al., 2004). This usually includes a combination of clinical interviews with the child and his/her family members, and the use of screening tools to evaluate the child’s mental wellbeing. One screening tool that is gaining popularity worldwide is the rating scale known as the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) (Goodman, 1997). Several studies have looked at inter-rater agreements, predominantly in parent-child reports, using the SDQ. Parents and teachers are considered the most valuable informants in rating the child’s mental health. However, there is scarce research evaluating the reliability of the SDQ across three raters - the adolescent child, the parent and the teacher. Analysing agreements/discrepancies between three raters could offer valuable insight into the difficulties that adolescents are experiencing. Student vs. Parent Student vs. Teacher Parent vs. Teacher Figure 1: Correlations between adolescent students and parents total difficulties scores (r=0.44) Figure 2: Correlations between adolescent students and teachers total difficulties scores (r=0.41) Figure 3: Correlations between parents and teachers total difficulties scores (r=0.70) Table 1: Pearson’s correlations between all three informants on the SDQ subscales To determine the level of inter-rater agreement between three informant group pairs when using the SDQ to rate the adolescent’s psychological well being: (i) Adolescent students and their parents (ii) Adolescent students and their teachers (iii) The parents and teachers of adolescent students Figure 4: Mental health classification distributions based on SDQ total scores as per each informant group Sample Recruitment & Data Collection Fifty-five male Transition Year (TY) students and their parents were approached to participate. 14 students (mean age 15.3) and their parents were recruited (25.5% response rate). One teacher was also recruited from the school. The students completed the self-report version of the SDQ, while the parents and teacher completed the proxy version. The Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) The SDQ consists of 25 statements probing some ‘strengths’ and ‘difficulties’ that the child may be experiencing, which the informant can rate as being ‘certainly true’, ‘somewhat true’ or ‘not true’. The 25 statements are divided into 5 subscales – emotional problems, conduct problems, hyperactivity problems, peer problems and the prosocial subscale. These combine to form the total difficulties score, which categorises the child’s mental health as ‘normal’, ‘borderline’ or ‘abnormal’. Data Analysis Data analysis was conducted using the Statistical Programme for the Social Sciences (SPSS) Version 21. Inter-rater agreements were analysed with Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Cutoffs using Pearson’s for levels of agreement (r values) were: <0.25=poor, 0.25-0.5=fair, 0.5-0.75=moderate to good, >0.75=good to excellent (Portney and Watkins, 1993). Student-Parent Agreement Results of the current study found there to be a ‘fair’ level of agreement between students and parents when rating the adolescent students’ psychological wellbeing using the SDQ (r=0.44). Weakest correlations were seen on the ‘Conduct’ problems subscale (Table 1). A finding of discrepancies between parent-child reports has been the consensus from previous studies and the current study’s findings of ‘fair’ levels of agreement appear to coincide with that of previous research (Muris et al., 2003). Student-Teacher Agreement The current study found student- teacher agreements to be the weakest of the three informant pairs, but still exhibiting ‘fair’ levels of agreement (r=0.41). The hyperactivity and conduct subscales exhibited the weakest correlations (Table 1). Little research has assessed agreements between community based adolescents and their secondary school teachers using the SDQ. Further research is needed to fully determine the true levels of adolescent-teacher agreements. Parent-Teacher Agreement This study found parents and teachers to show the strongest levels of agreement of the three informant pairs (r=0.70). These correlations were statistically significant (p=0.015) and can be classified as ‘good’ levels of agreement, with all subscales ranging from fair to good. This figure is higher than those shown in a review of agreements between parents and teachers of pre- adolescent children by Stone et al. (2010), where r values ranged from 0.37 to 0.62. Student-Parent Agreement Student-Teacher Agreement Parent-Teacher Agreement Student Reports Parent Reports Teacher Reports Further Discussion Becker, A., Hagenberg, N., Roessner, V., Woerner, W. and Rothenberger, A. (2004) Evaluation of the self-reported SDQ in a clinical setting: Do self-reports tell us more than ratings by adult informants?, European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 13(2), ii17-ii24. Cannon, M., Coughlan, H., Clarke, M., Harley, M. and Kelleher I. (2013) The Mental Health of Young People in Ireland: a report of the Psychiatric Epidemiology Research across the Lifespan (PERL). Dublin: Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland. Goodman, R. (1997) The Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire: a research note, Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 38(5), 581-586. Muris, P., Meesters, C., Eijkelenboom, A. and Vincken, M. (2004) The self‐report version of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire: Its psychometric properties in 8‐ to 13‐year‐old non‐clinical children, British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 43(4), 437-448. Portney, L. G. and Watkins, M. P. (1993) Foundation of Clinical Research: Application to Practice. East Norwalk: Appleton and Lange. Stone, L.L., Otten, R., Engels, R.C., Vermulst, A.A. and Janssens, J.M. (2010) Psychometric properties of the parent and teacher versions of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire for 4- to 12-year-olds: a review, Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 13(3), 254-274. Prevalence of Abnormal/Borderline Cases 14.3% of the adolescent sample identified themselves as being in the ‘abnormal’ range and a further 7.1% reported themselves in the ‘borderline’ range (21.4% total) (Figure 4). Despite the small sample size of this study, these findings appear to support a finding of recent research that ‘one in five’ young Irish people are ‘at risk’ of suffering a mental disorder (Cannon et al., 2013). Limitations The strength of this study’s findings is limited by both its small sample size and by the poor response rate. The absence of female participants from this study’s sample also limits the generalisability of the findings to the wider adolescent population. A study involving a large mixed-gender sample could help to both; (i) determine the inter- rater reliability of the SDQ and (ii) offer a clearer view on the true scale of mental health problems in Ireland.