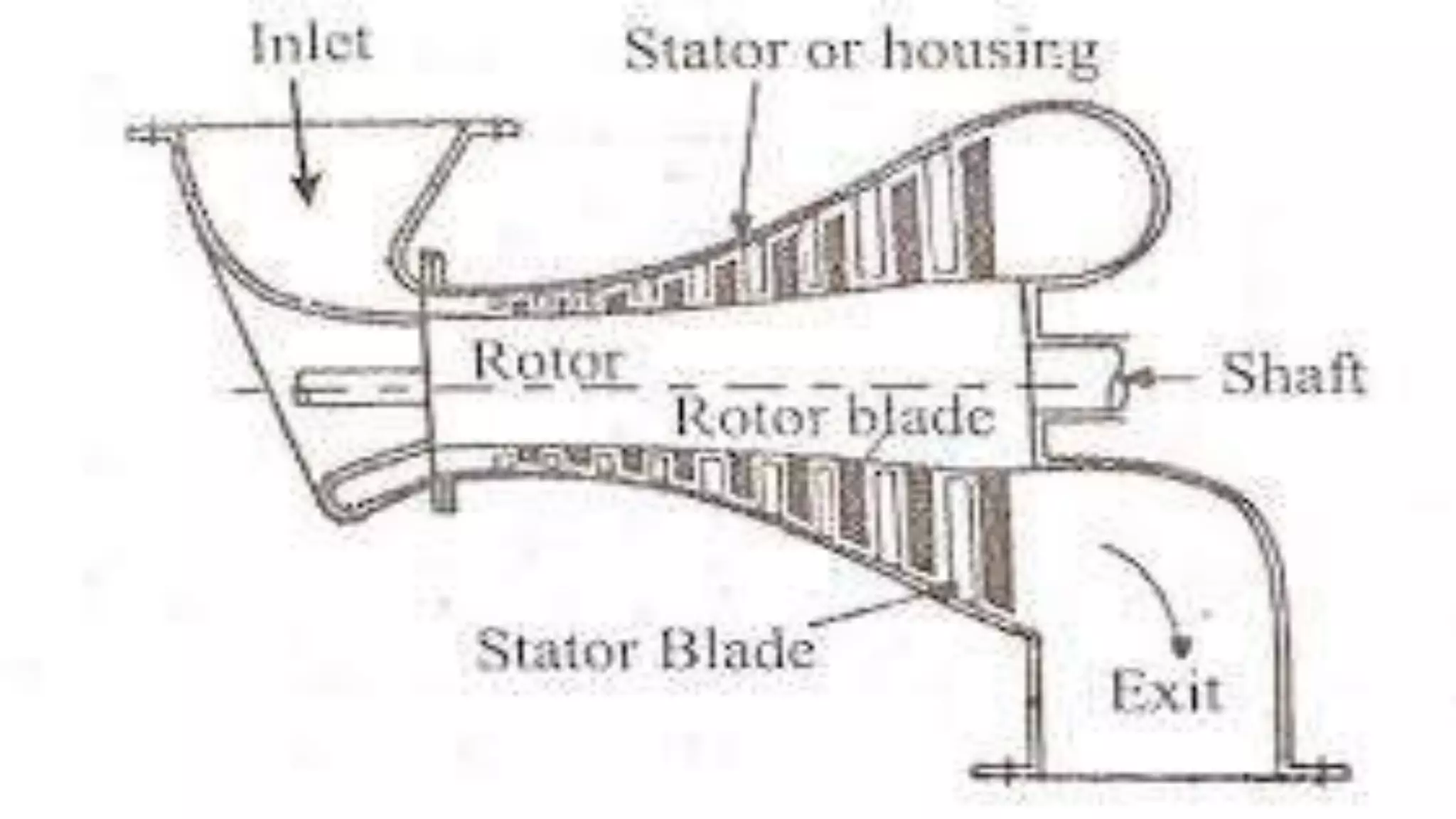
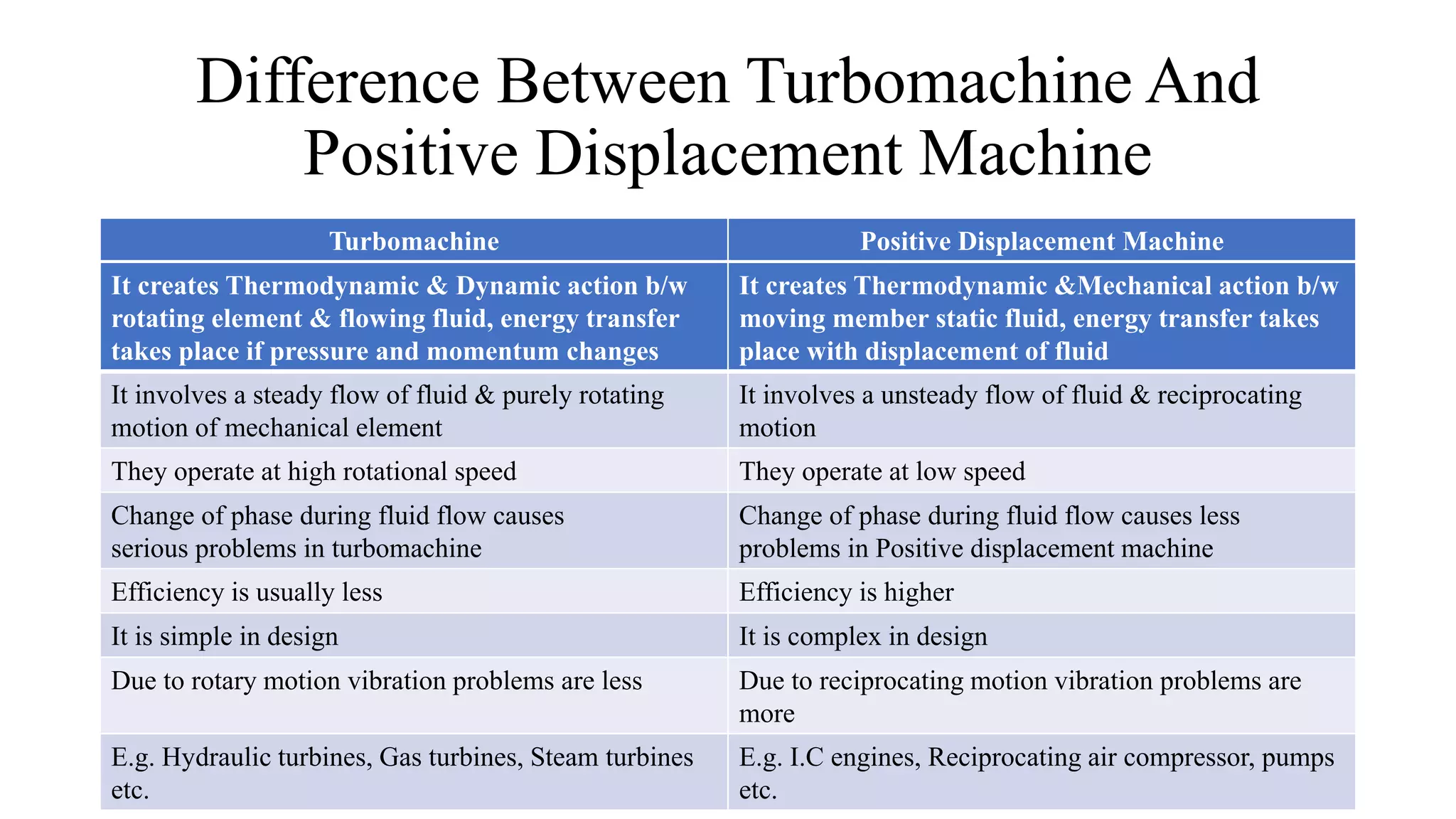
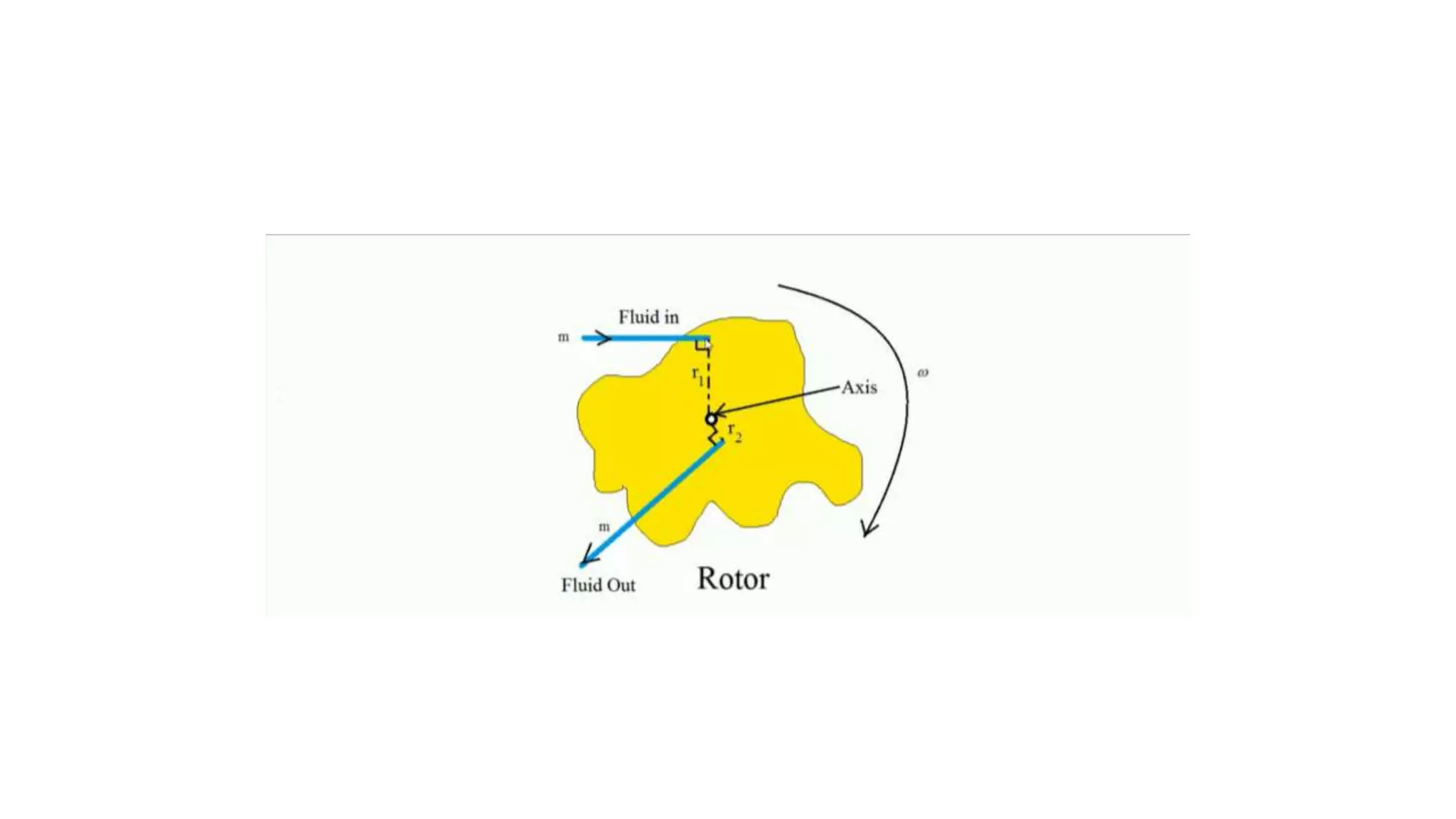
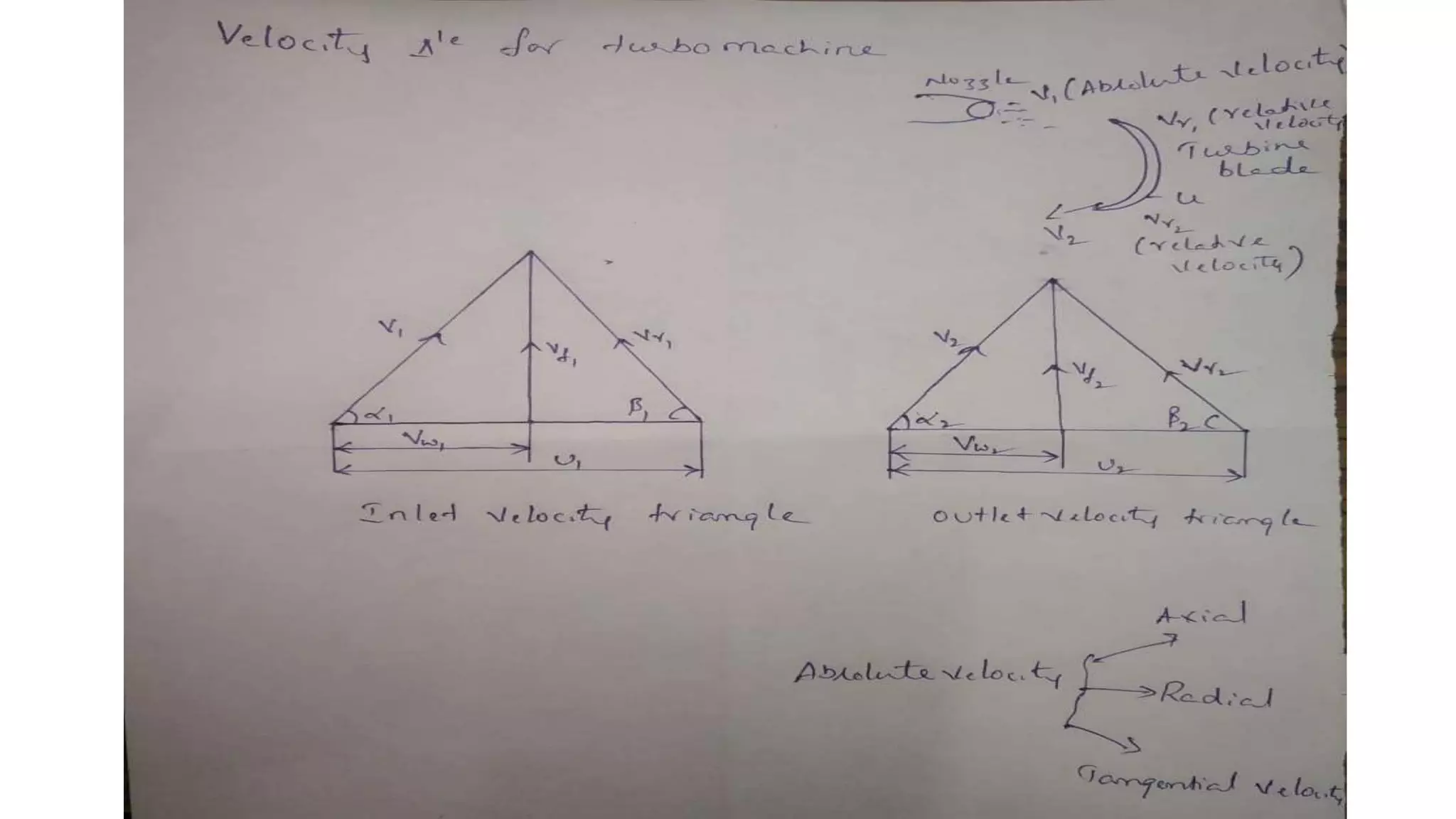
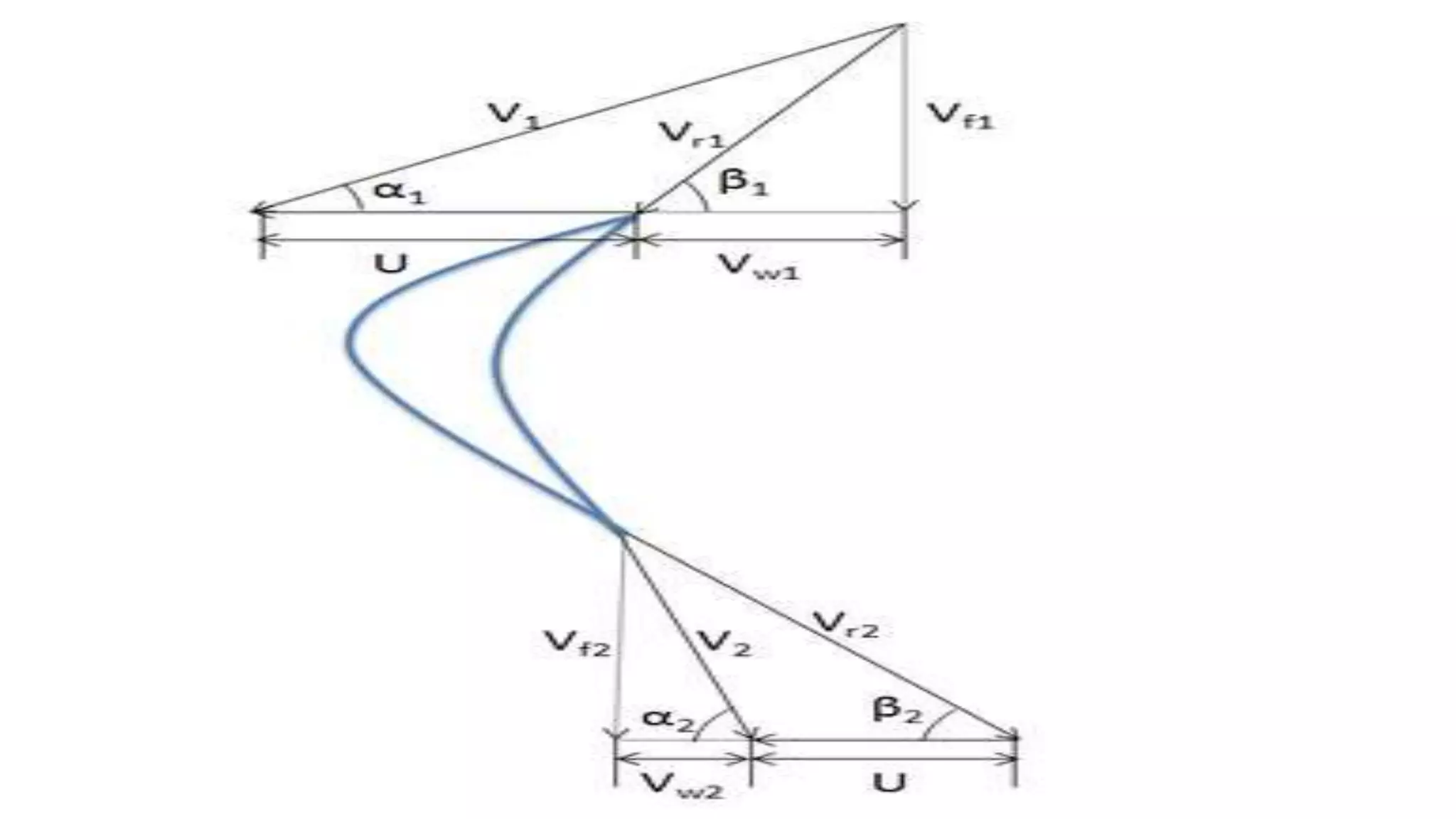
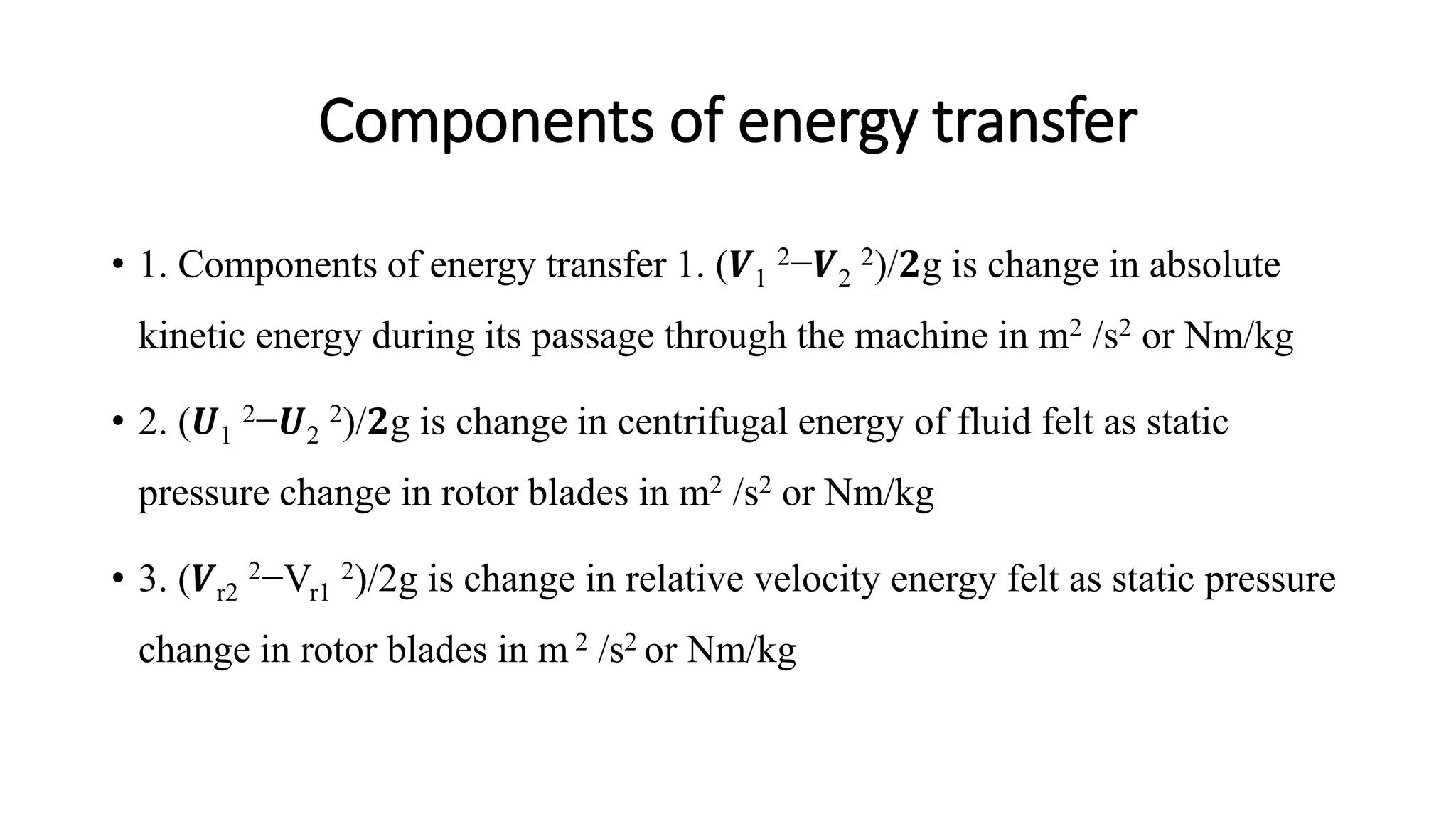
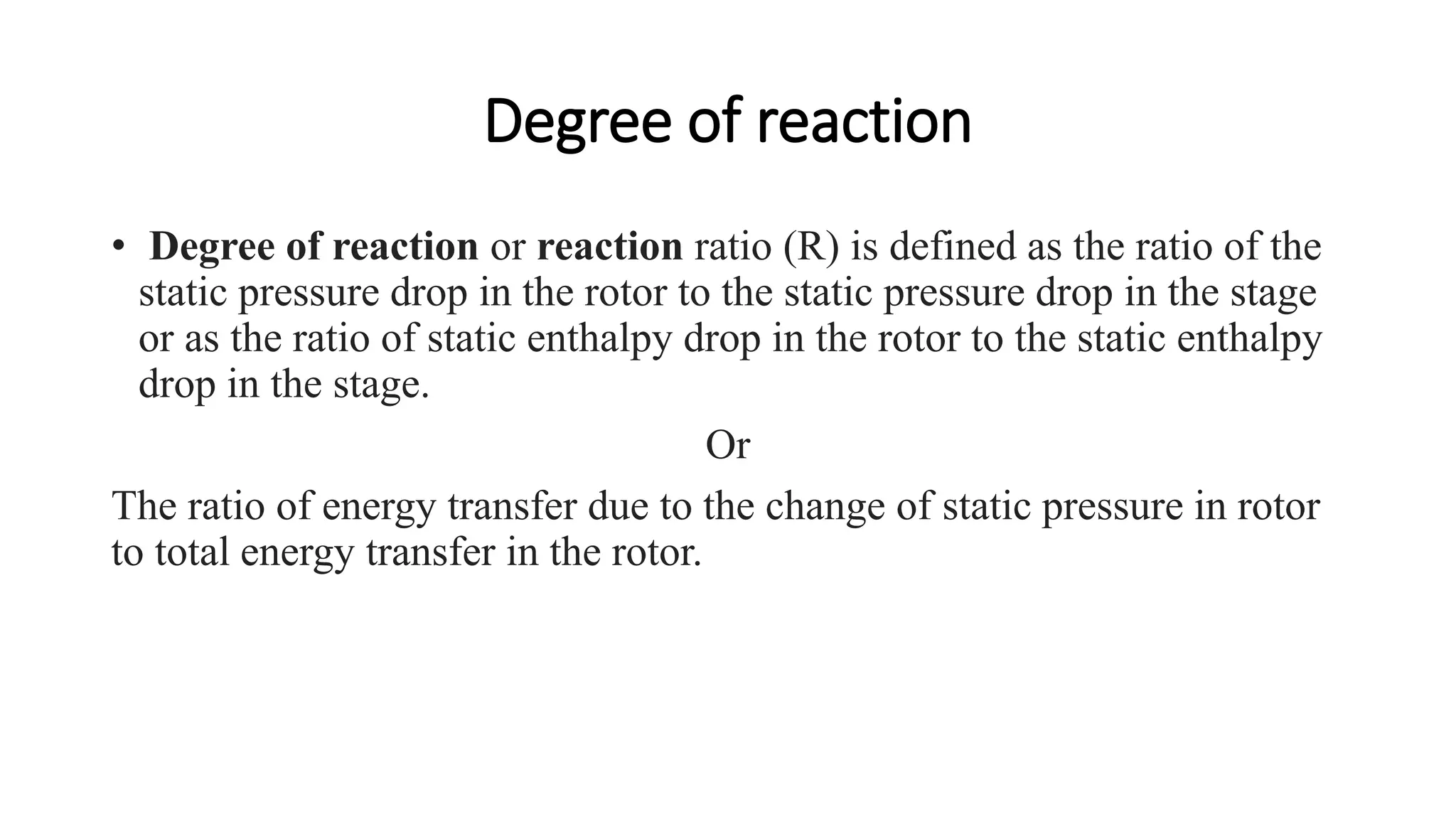
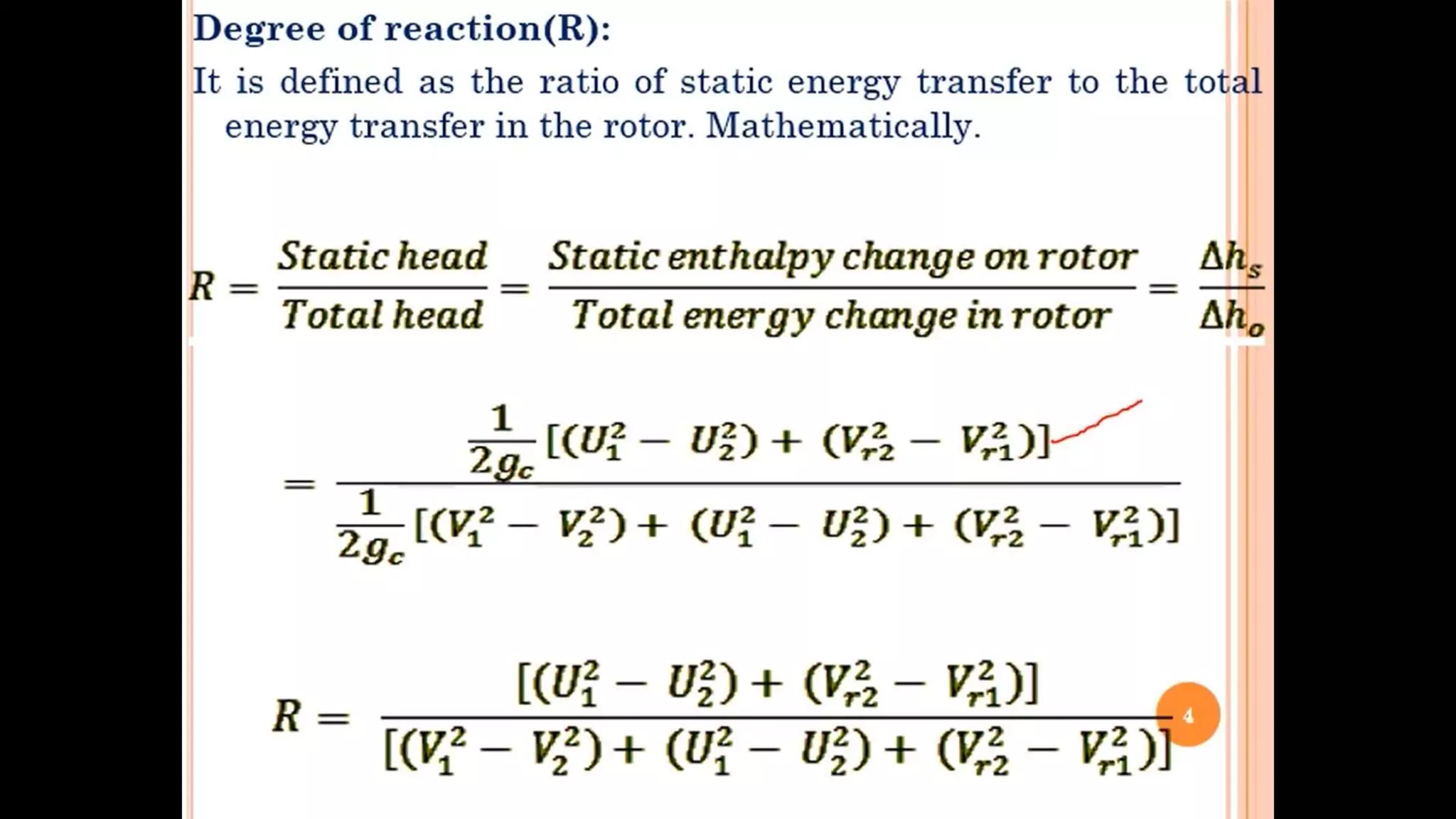
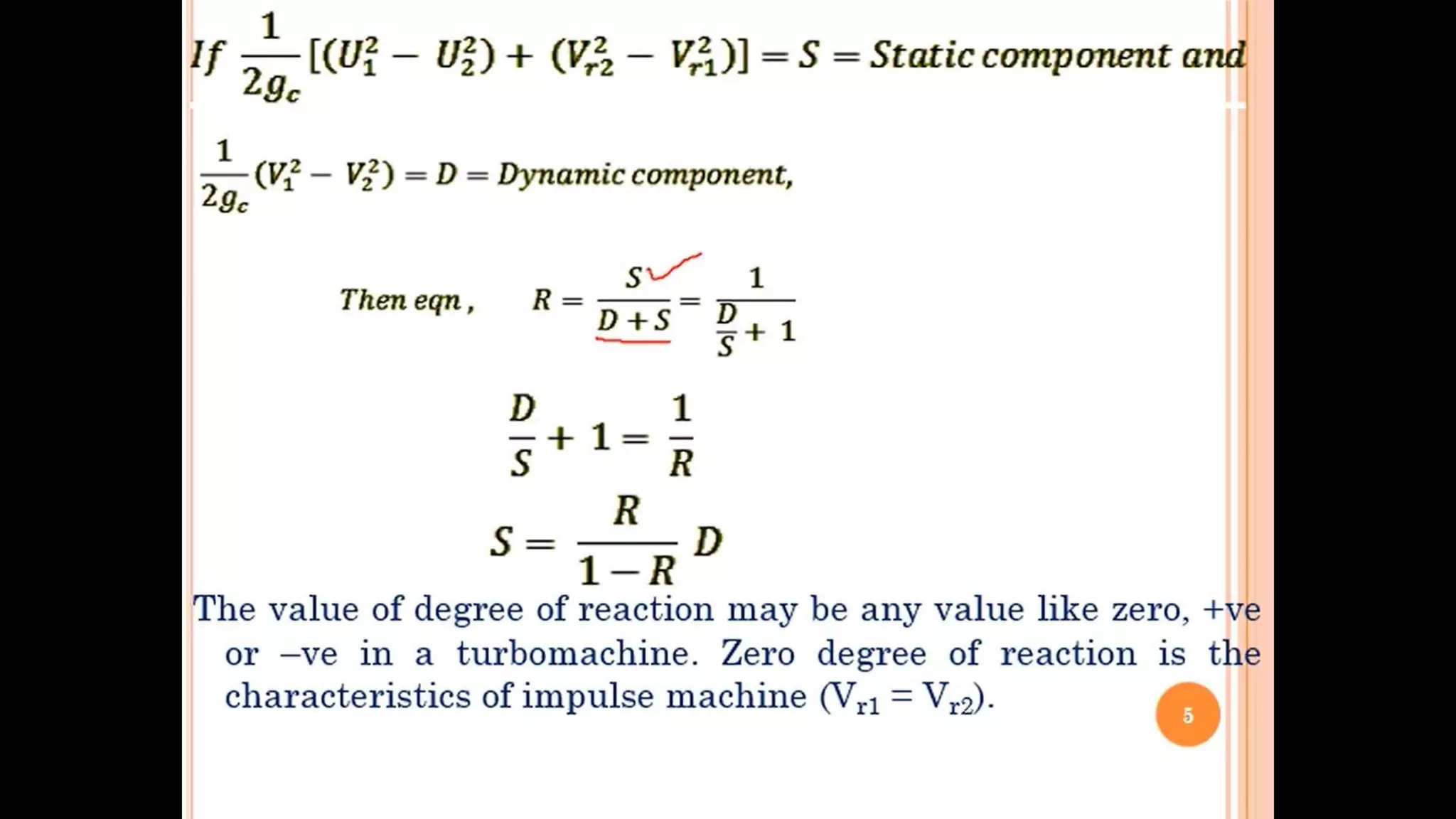
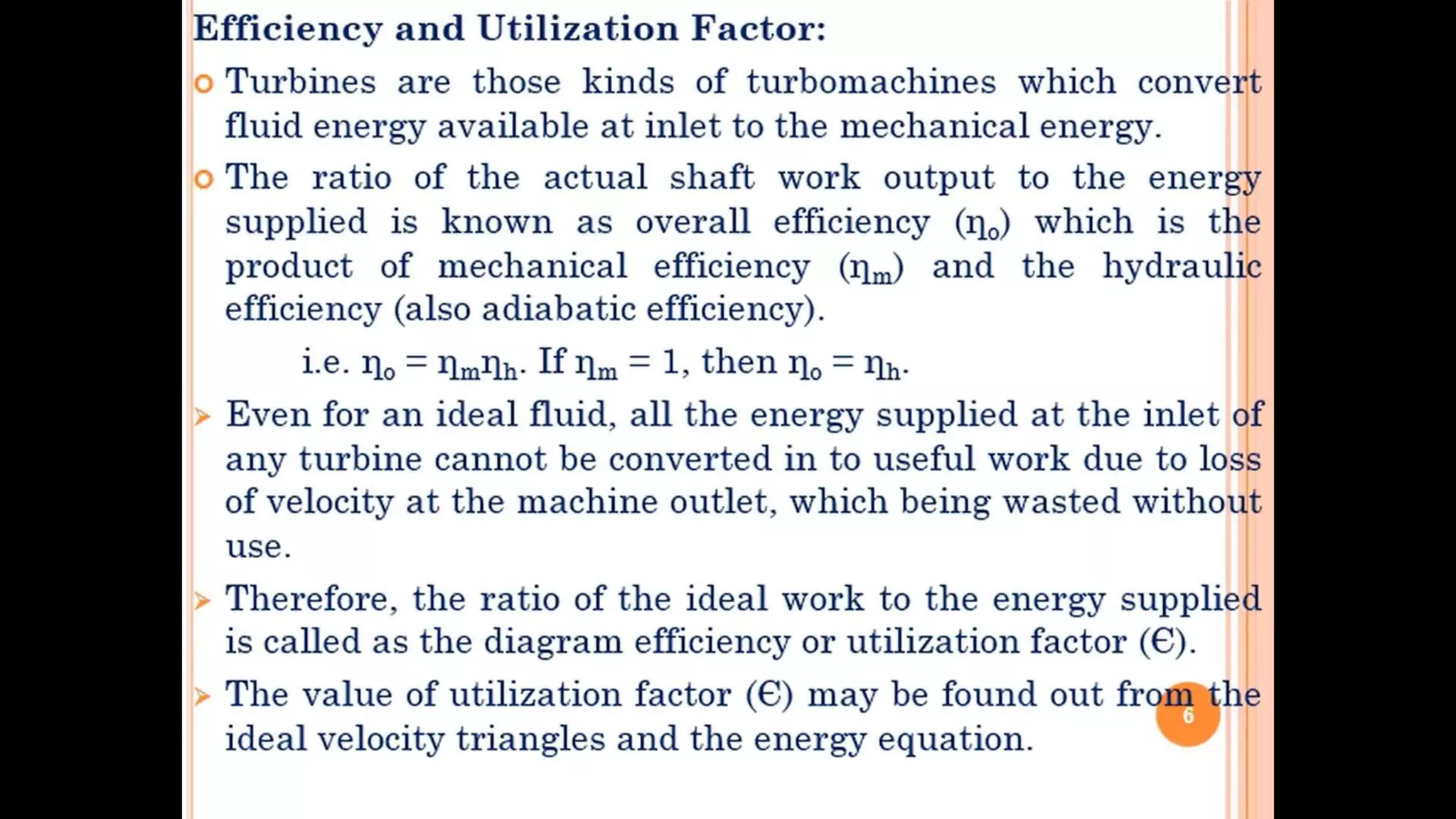
The document discusses turbo machines and their components and functioning. It defines a turbo machine as any device that extracts or imparts energy from a continuously moving fluid stream. Turbo machines contain a rotor and stator and operate via dynamic interaction between a rotating element and flowing fluid, resulting in pressure and momentum changes. Examples provided are turbines, compressors, and pumps. Key components are identified as the rotor, stator, shaft, and housing. The document also compares turbo machines to positive displacement machines and discusses energy exchange concepts like Euler's turbine equation and the degree of reaction.