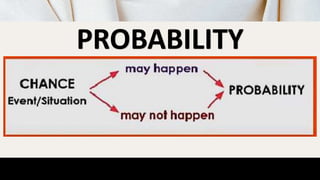
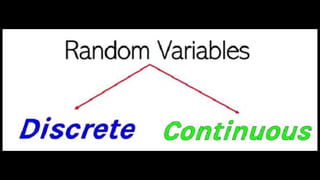
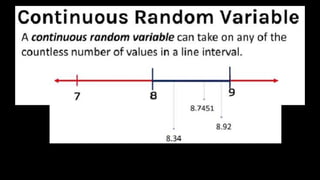
This document defines key probability terms and provides examples of experiments and outcomes. It begins by defining an experiment, sample space, event, and outcome. An experiment is any activity that can be repeated under similar conditions, a sample space is the set of all possible outcomes, an event is a subset of the sample space, and an outcome is an element in the sample space. Examples are provided of rolling dice and calculating probabilities. The document then provides examples of discrete and continuous random variables and asks students to classify variables as discrete or continuous.