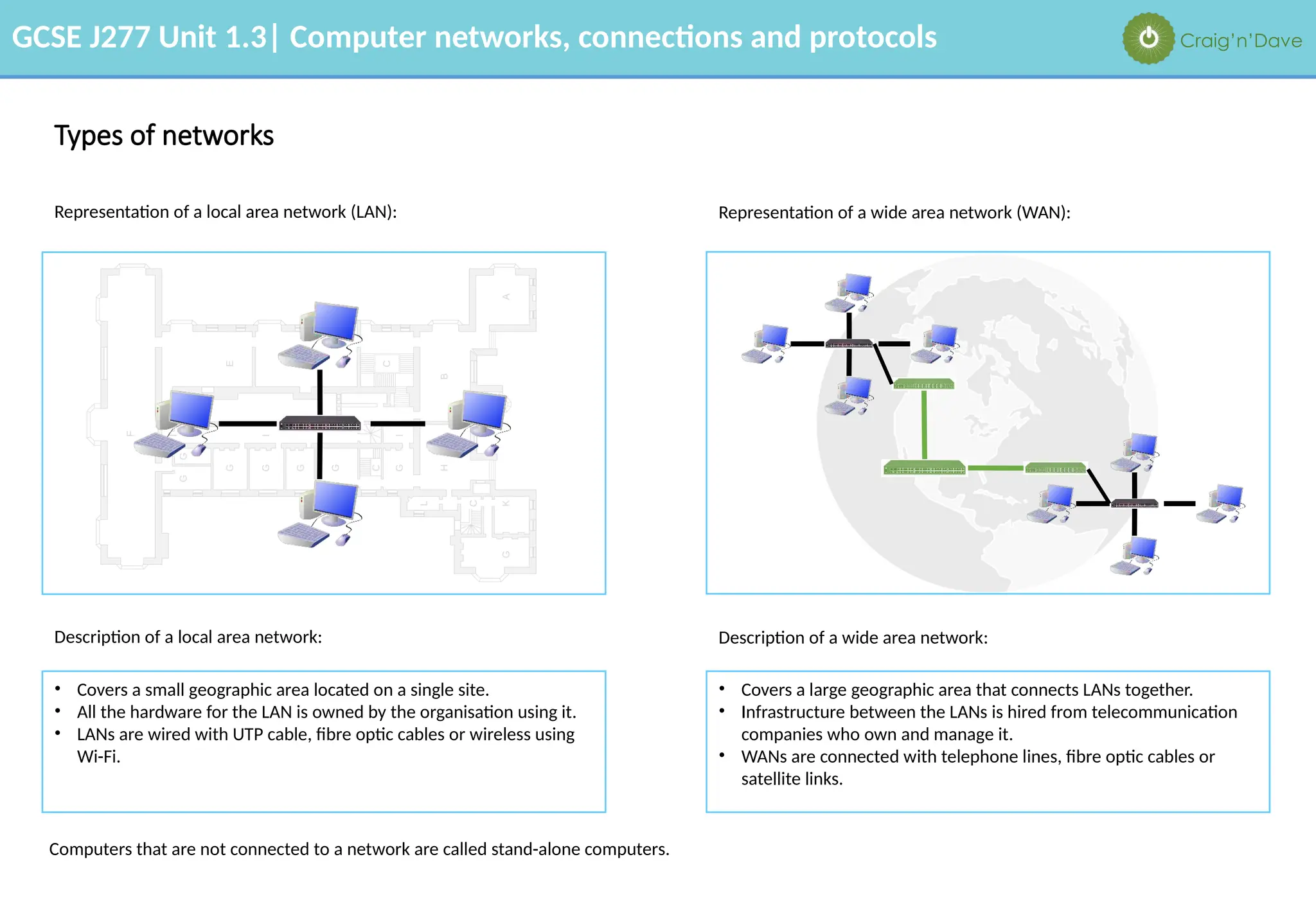
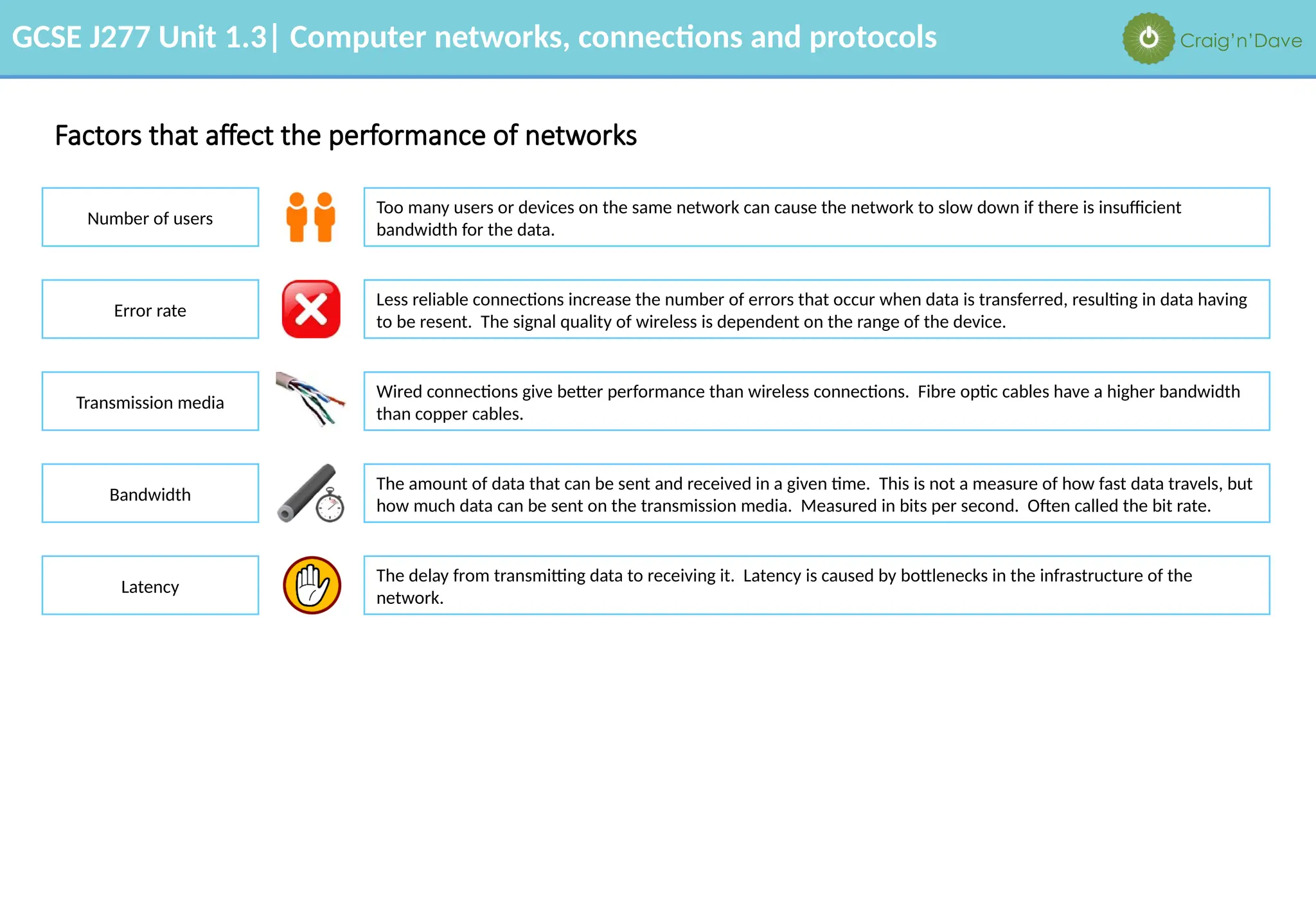
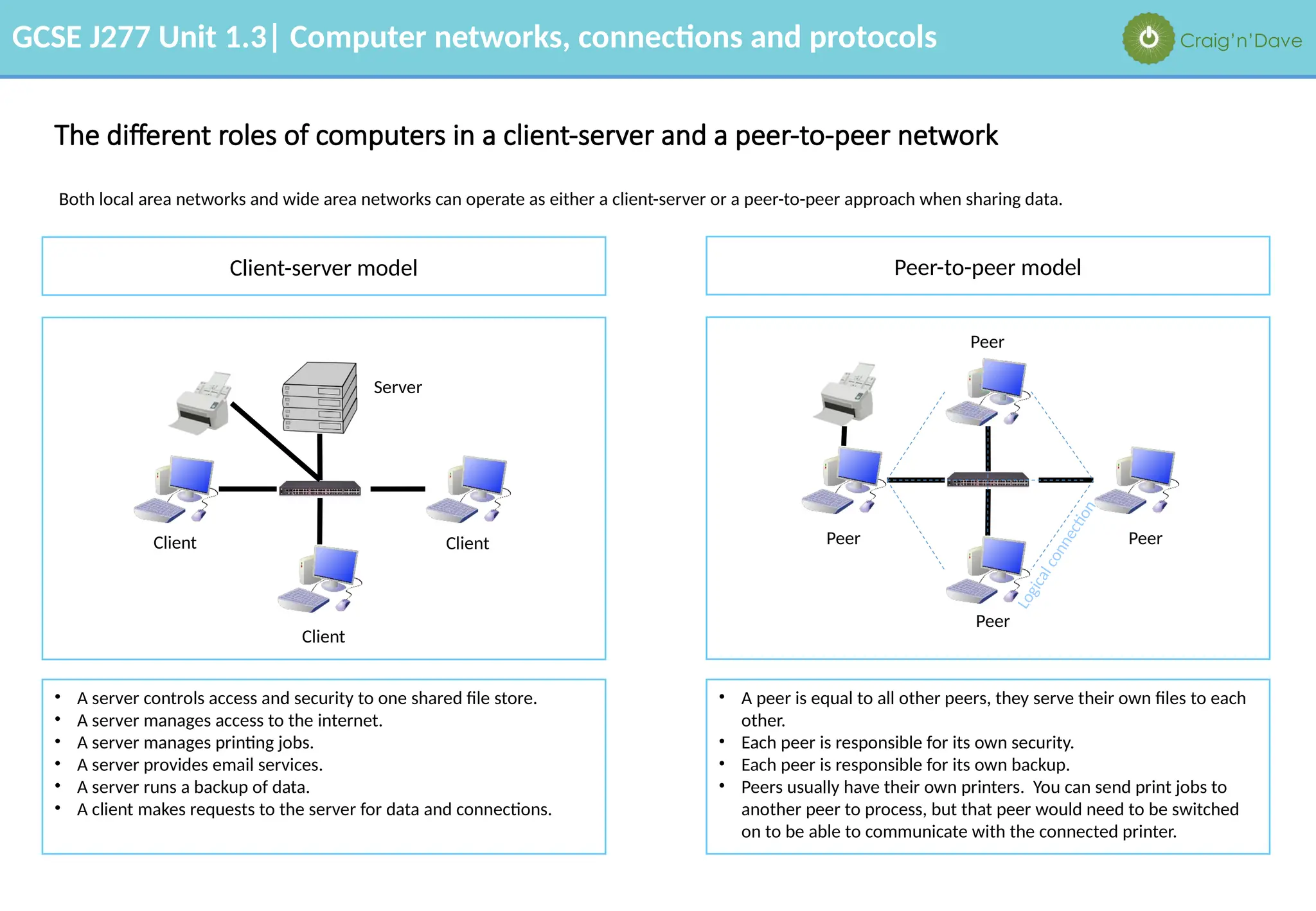
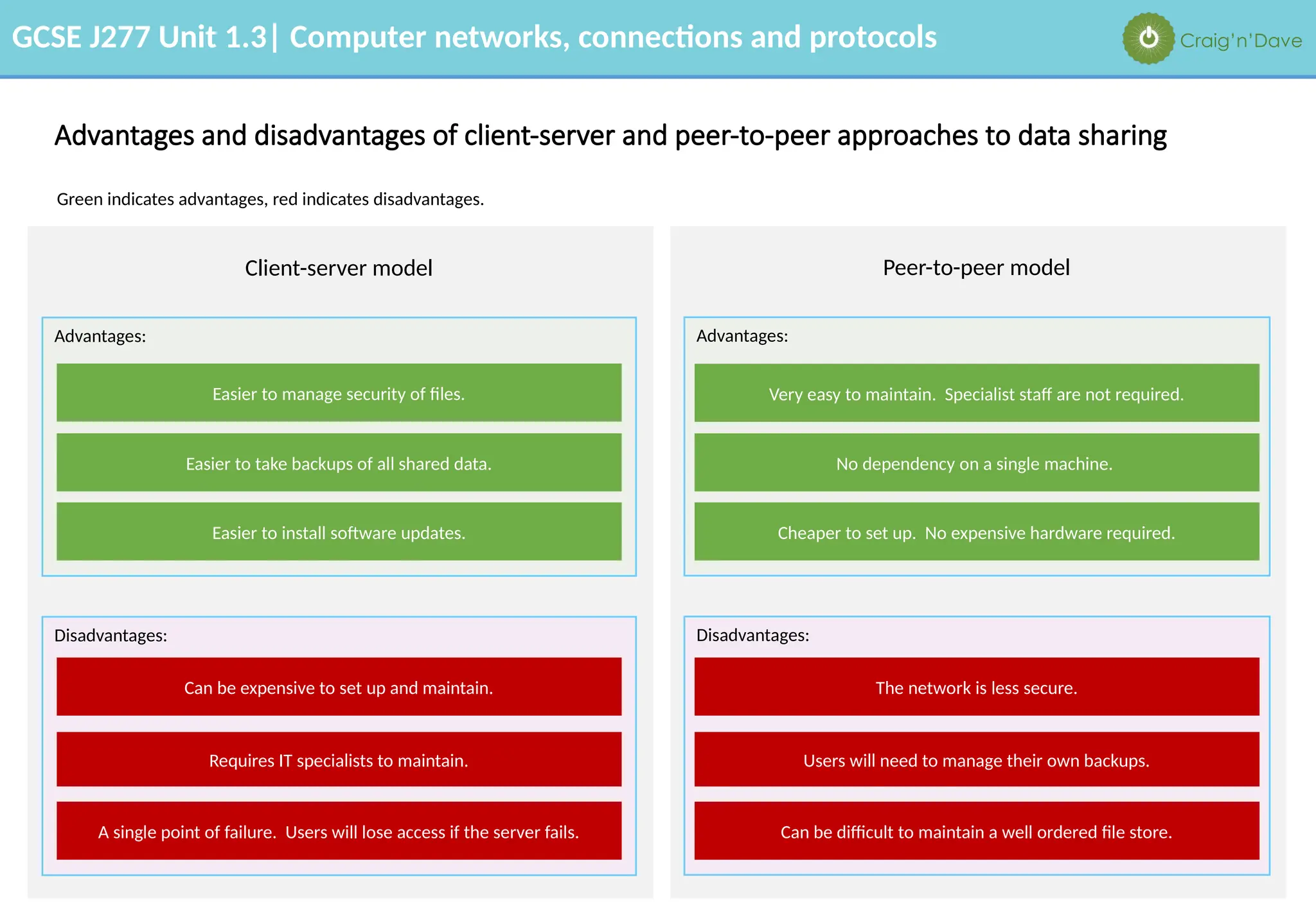
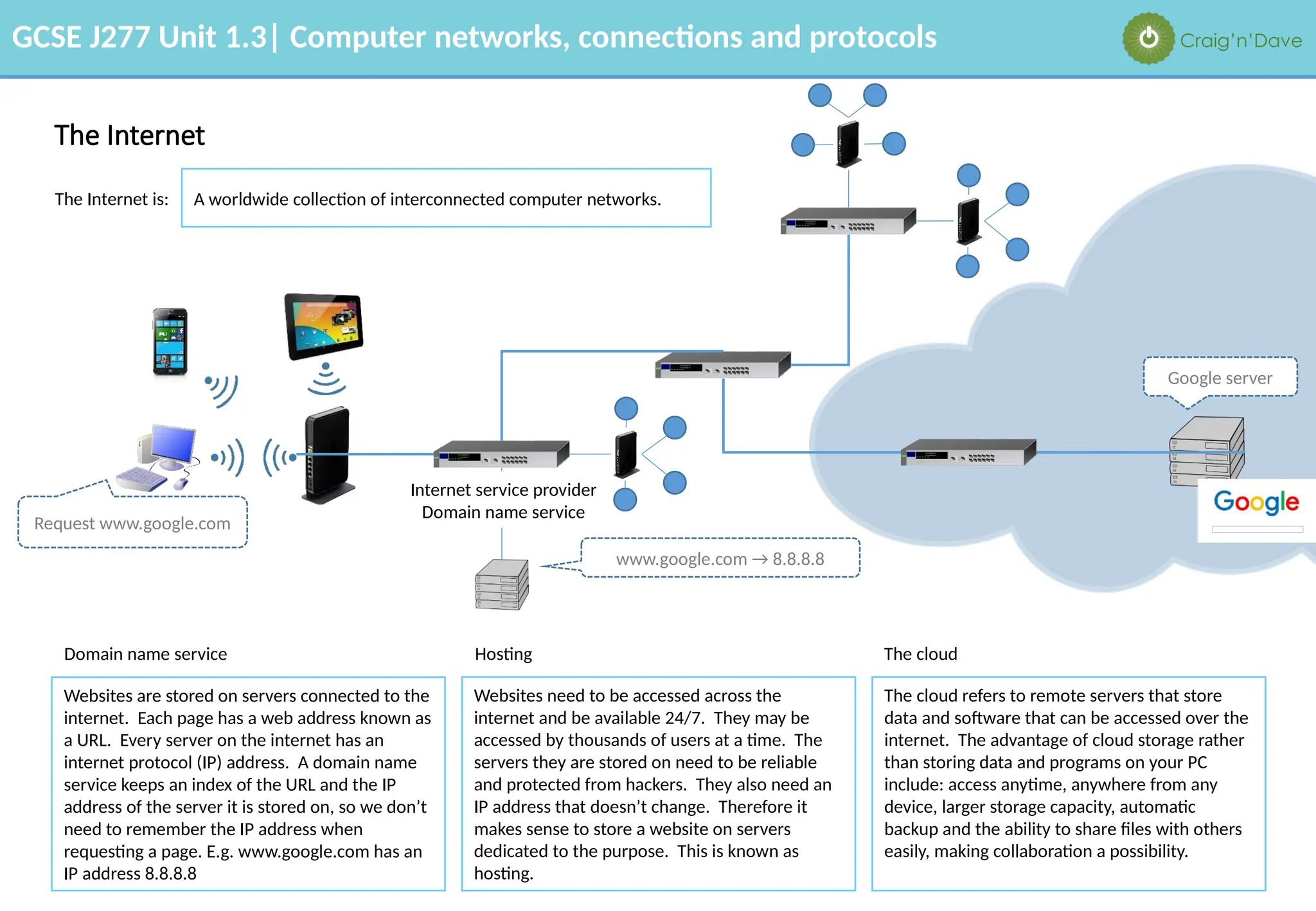
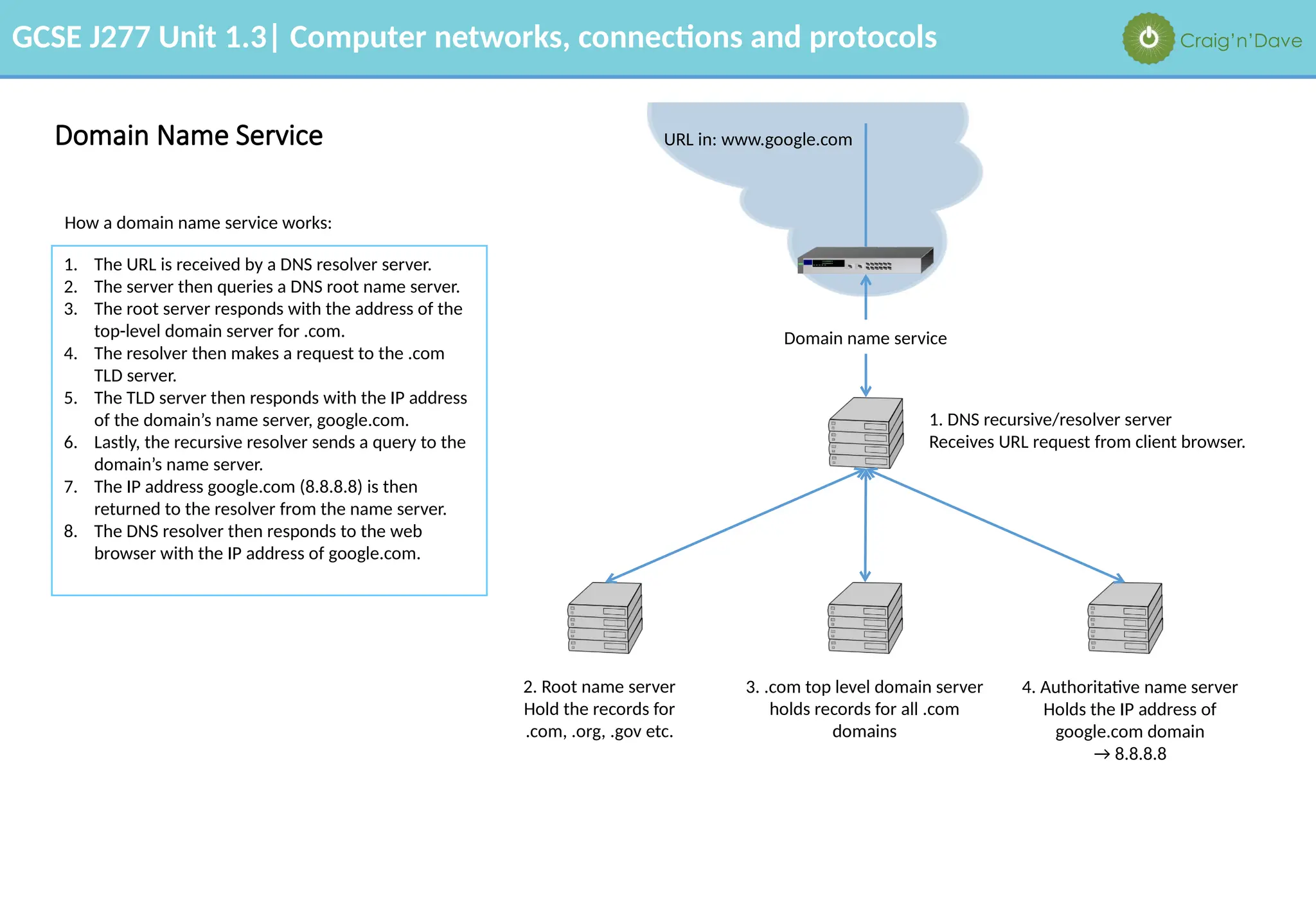
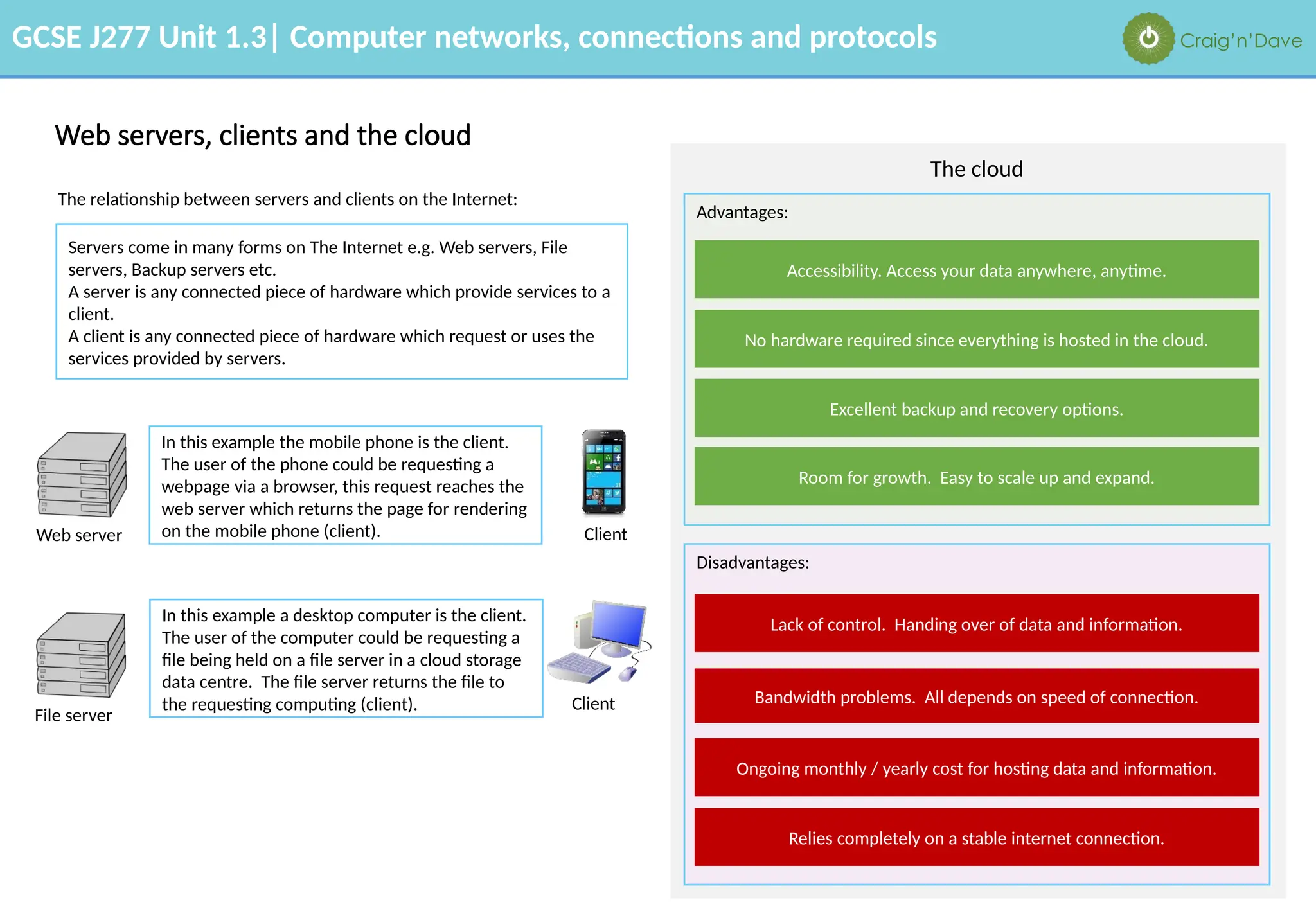
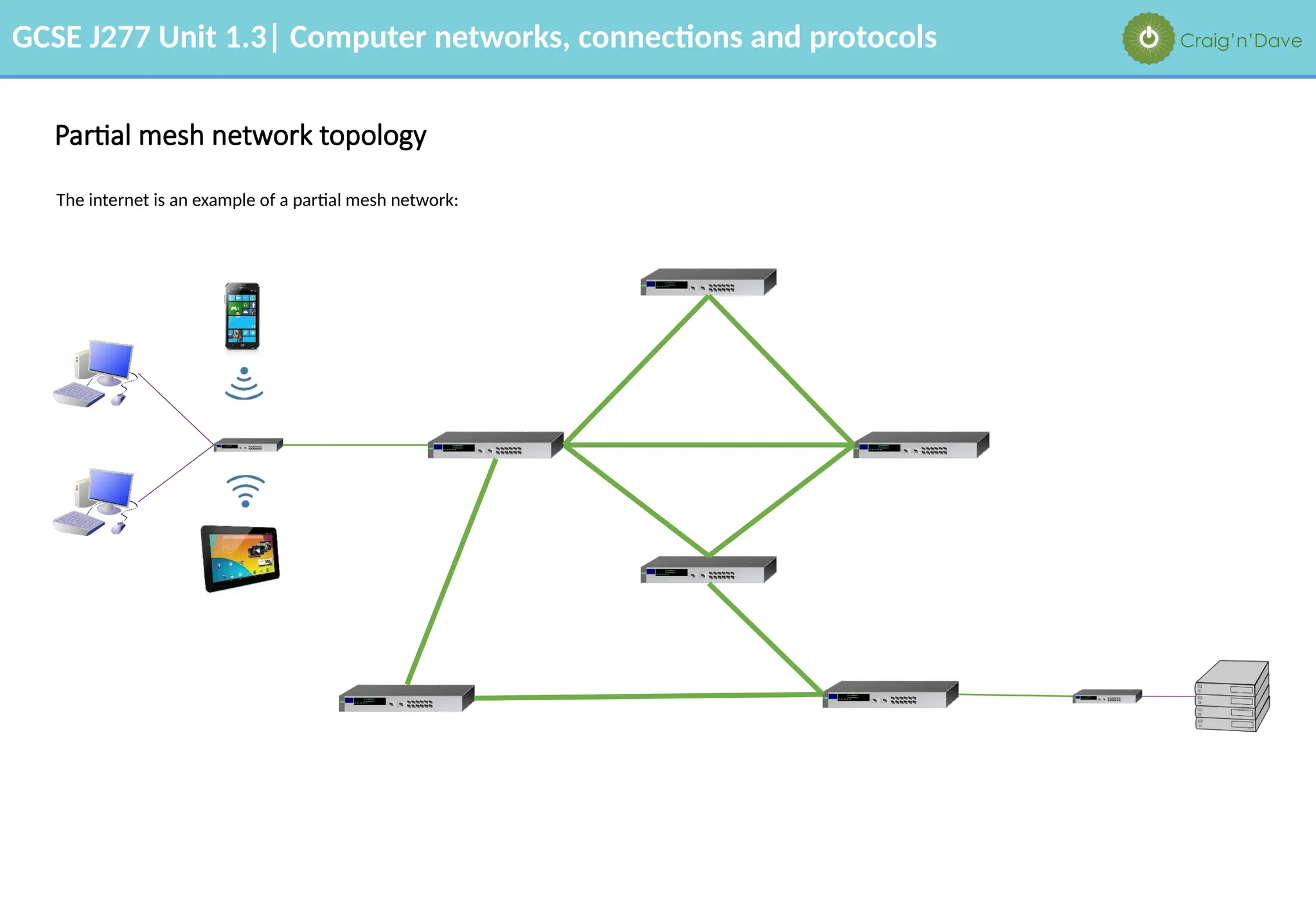
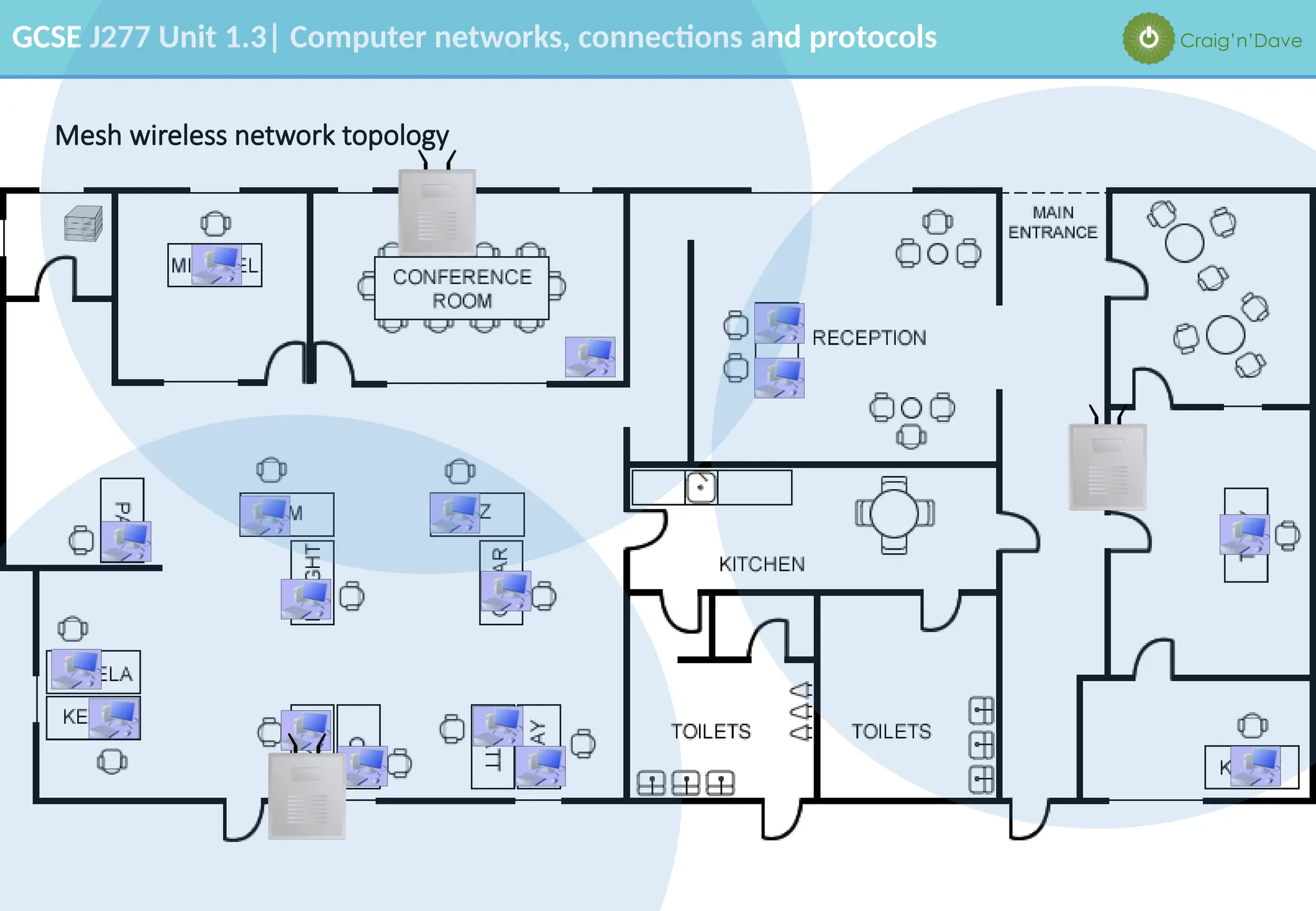
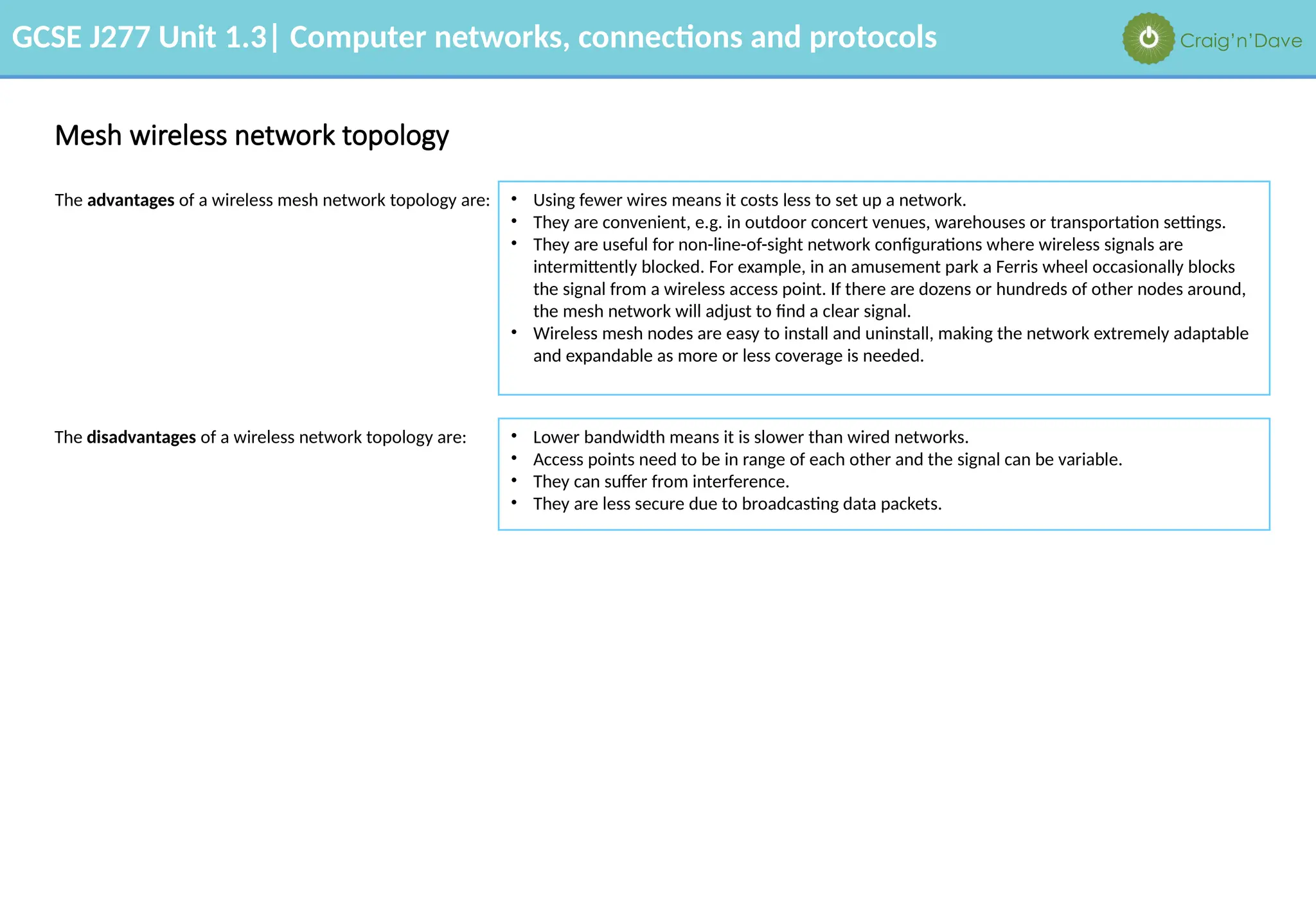
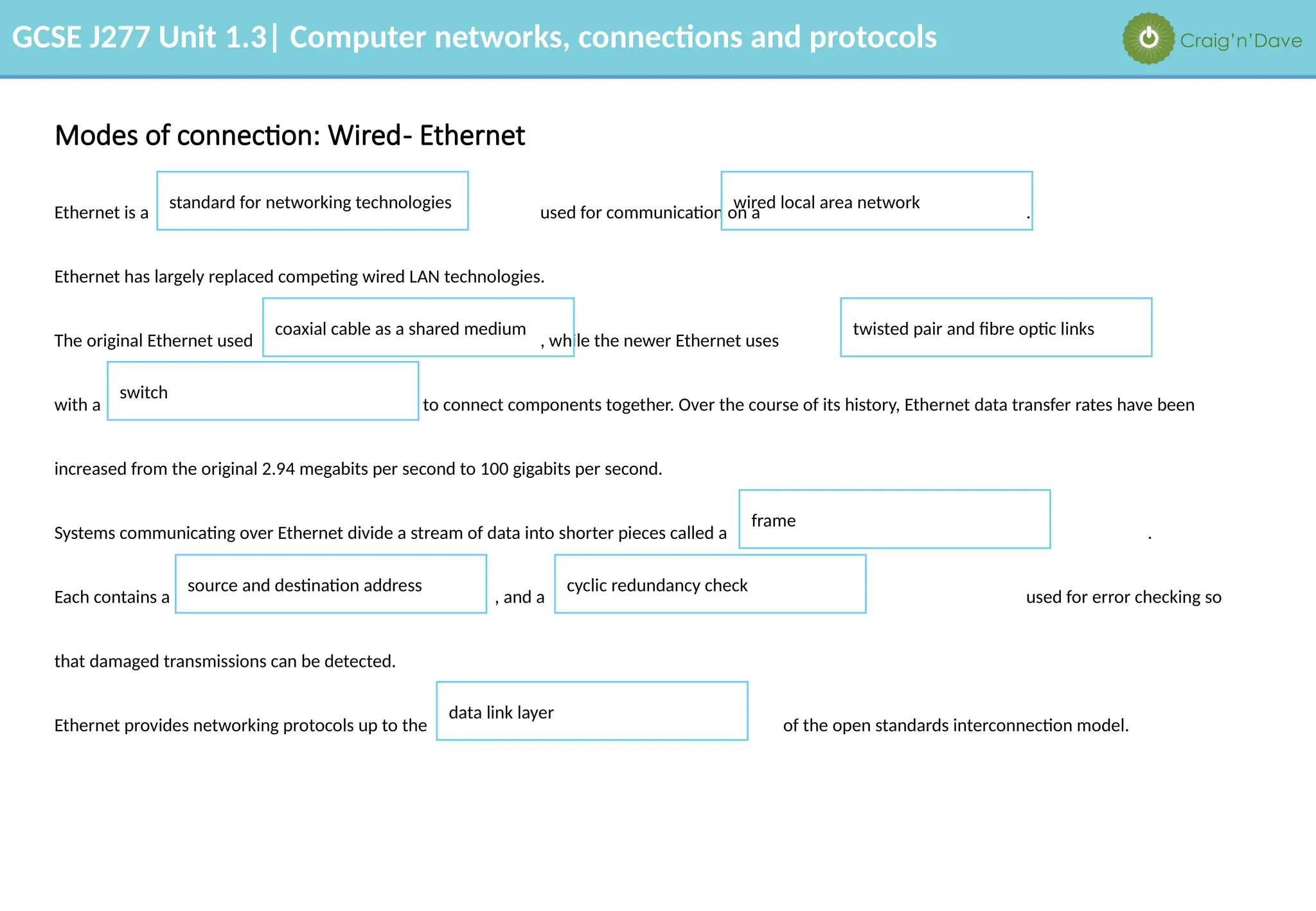
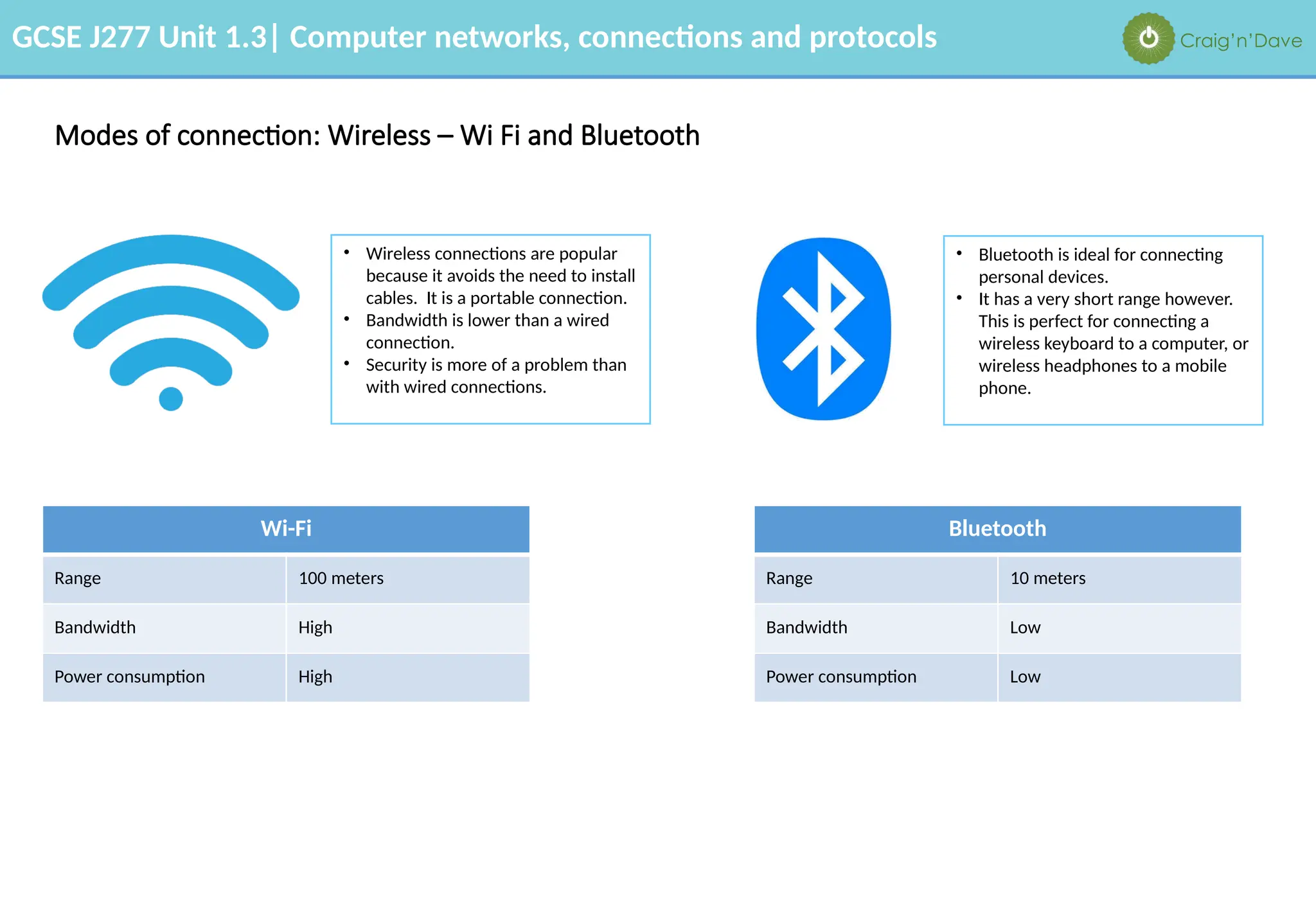
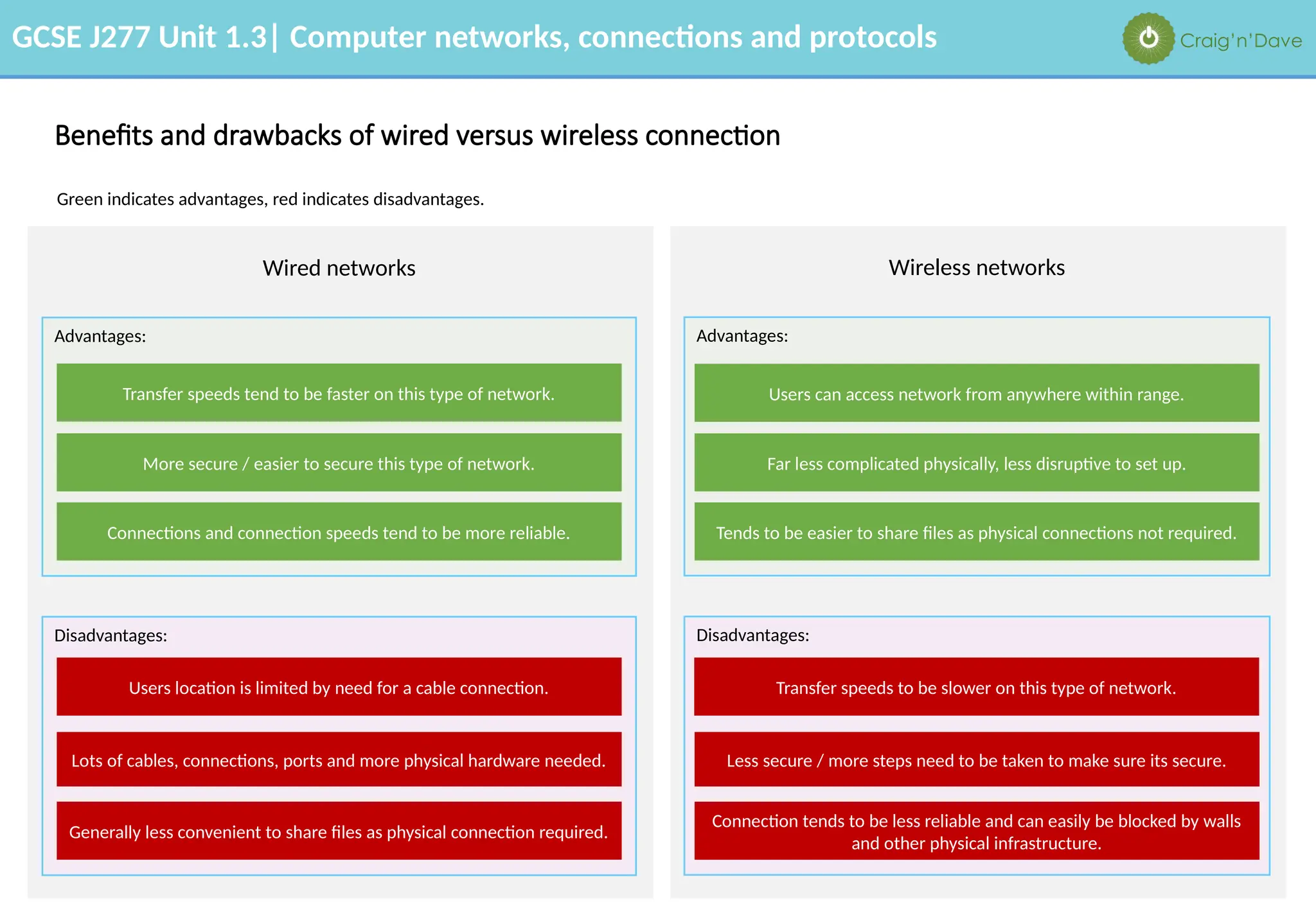
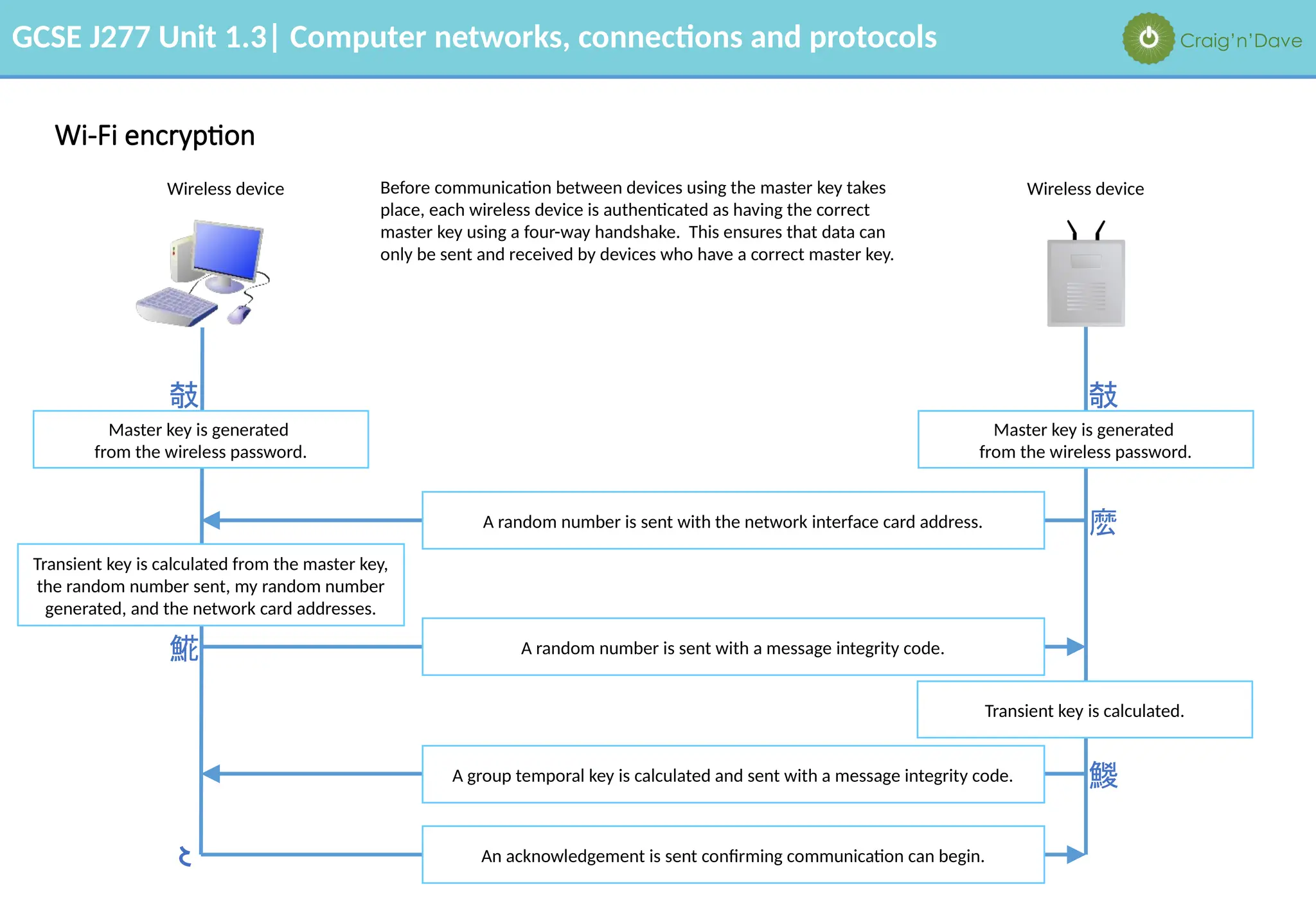
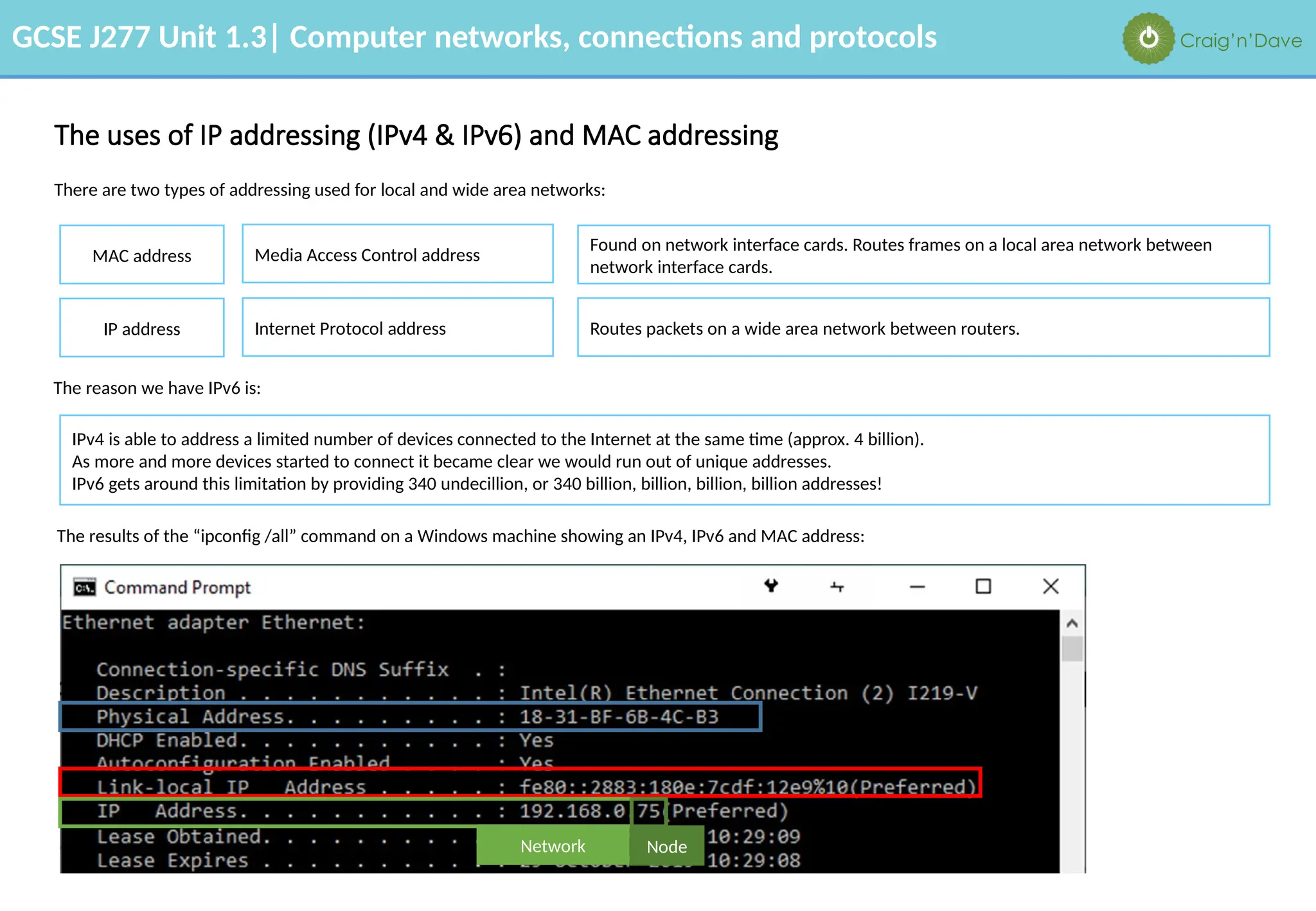
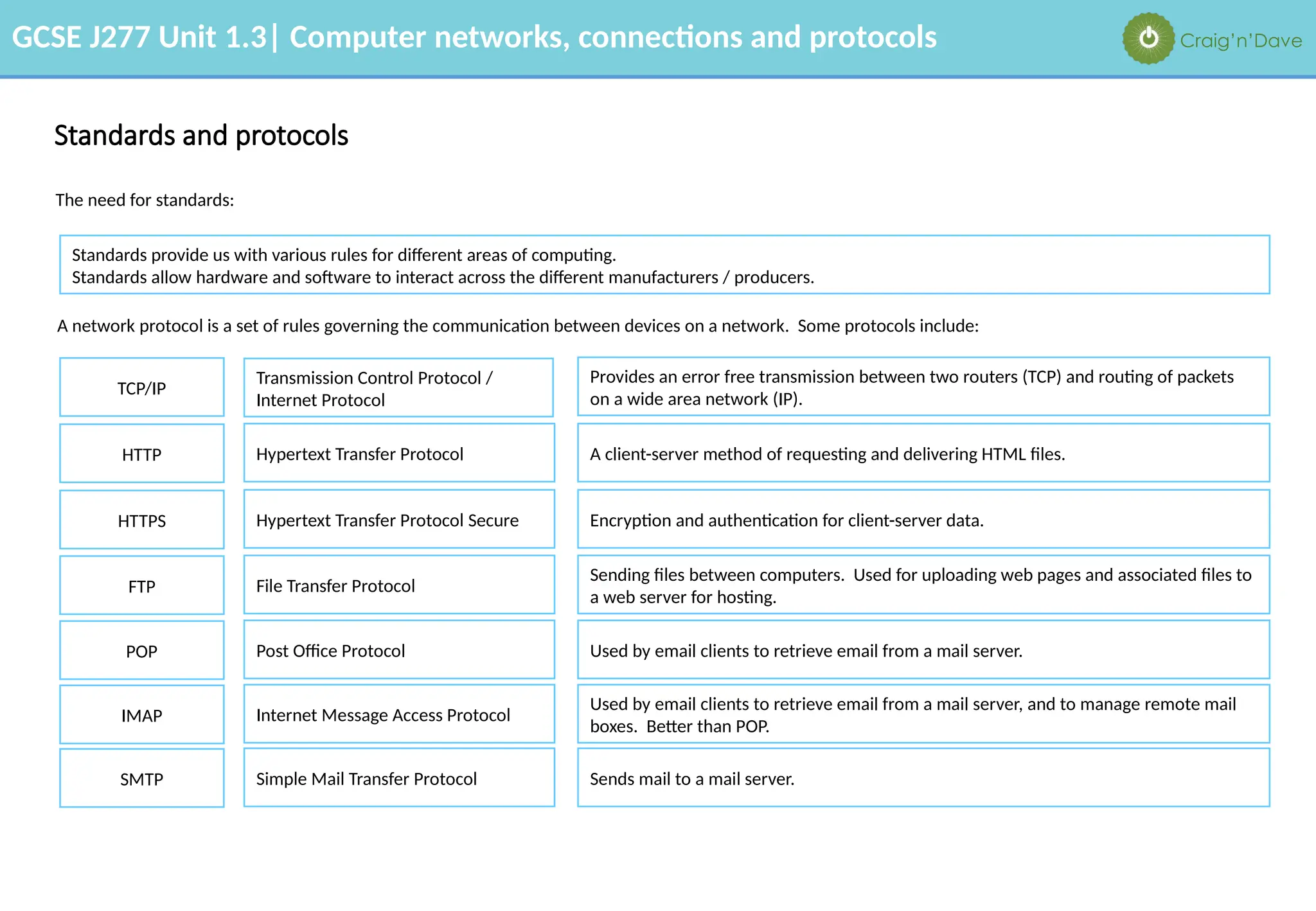
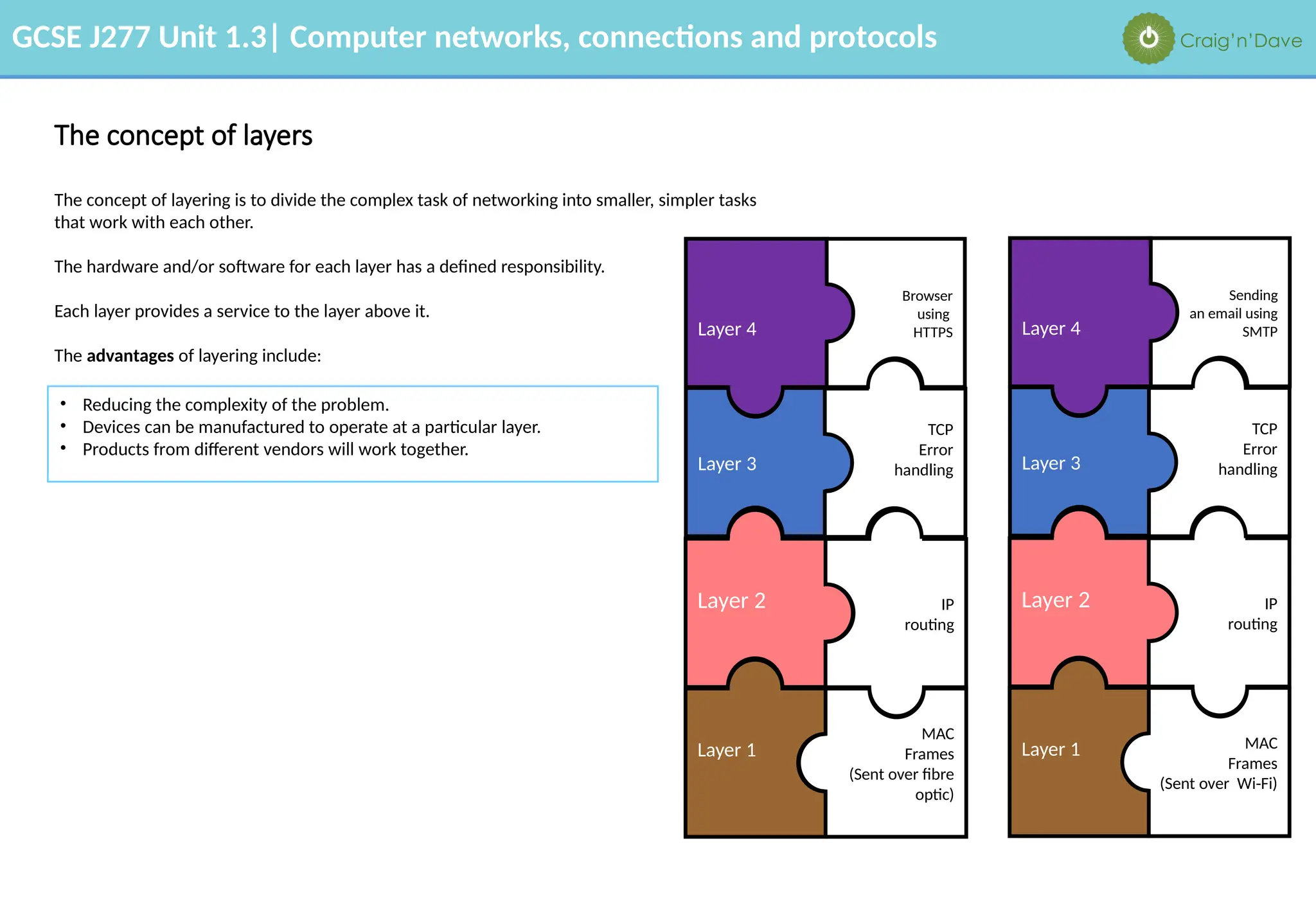
The document outlines various aspects of computer networks, including types of networks (LAN and WAN), hardware components, roles of different computer models (client-server vs. peer-to-peer), and network performance factors. It also covers connection methods (wired and wireless), protocols, Internet structure, and advantages/disadvantages of various networking topologies and security measures. Learning objectives and recommendations for network solutions in different scenarios are included to guide study for the GCSE J277 curriculum.