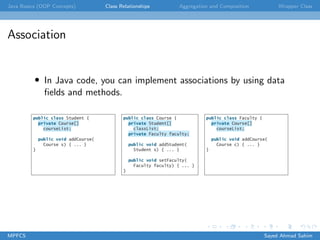
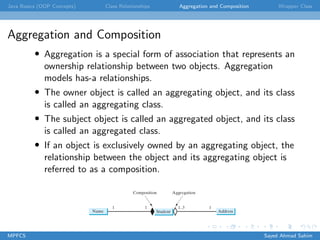
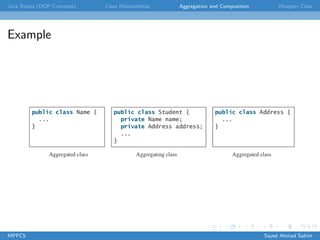
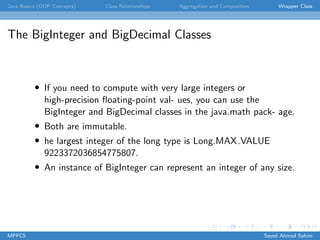
This document discusses several key object-oriented programming concepts in Java including abstraction, encapsulation, association, aggregation, composition, wrapper classes, autoboxing, unboxing, and the BigInteger and BigDecimal classes. It provides examples and explanations of each concept. Class abstraction separates implementation from use while encapsulation hides implementation details. Association describes a relationship between classes. Aggregation models "has-a" relationships while composition represents exclusive ownership. Wrapper classes allow primitive types to be used as objects. Autoboxing and unboxing automatically convert between primitives and wrapper classes. BigInteger and BigDecimal support very large integers and high-precision decimals.