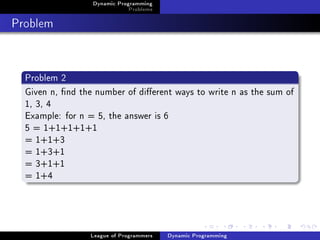
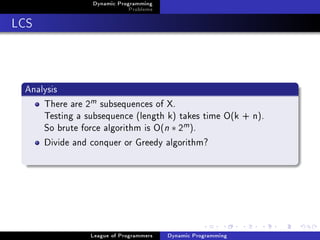
The document discusses dynamic programming problems and solutions. It begins by defining dynamic programming as a technique for problems with optimal substructure, where optimal solutions to subproblems can be used to find the optimal solution to the overall problem. It then provides examples of dynamic programming problems like Fibonacci numbers, counting ways to write a number as a sum, and finding the longest common subsequence (LCS) of two strings. For each problem, it outlines defining relevant subproblems, writing recurrences, solving base cases, and providing implementations.







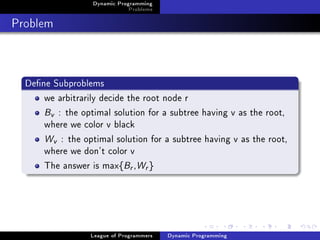
![Dynamic Programming
Problems
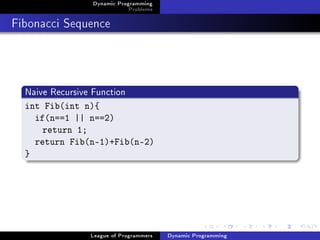
Fibonacci Sequence
DP Solution O(n)
Fib[1] = Fib[2] = 1;
for(i=3;iN;i++)
Fib[i] = Fib[i-1]+Fib[i-2]
League of Programmers Dynamic Programming](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-dp-121216023326-phpapp02/85/03-dp-12-320.jpg)




![Dynamic Programming
Problems
Problem
Implementation
D[0]=D[1]=D[2]=1; D[3]=2;
for(i=4;i=n;i++)
D[i]=D[i-1]+D[i-3]+D[i-4];
League of Programmers Dynamic Programming](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-dp-121216023326-phpapp02/85/03-dp-19-320.jpg)




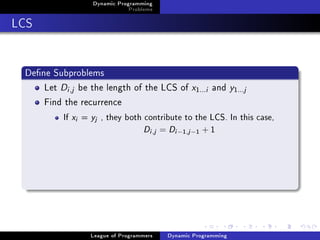
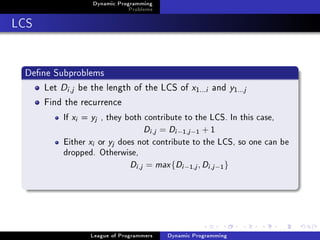

![Dynamic Programming
Problems
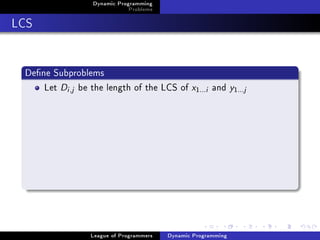
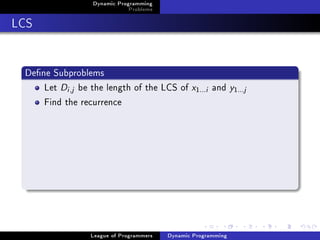
LCS
Implementation
for(i=0;i=n;i++) D[i][0]=0;
for(j=0;j=m;j++) D[0][j]=0;
for(i=1;i=n;i++) {
for(j=1;j=m;j++) {
if(x[i]==y[j])
D[i][j]=D[i-1][j-1]+1;
else
D[i][j]=max(D[i-1][j],D[i][j-1]);
}
}
League of Programmers Dynamic Programming](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-dp-121216023326-phpapp02/85/03-dp-33-320.jpg)
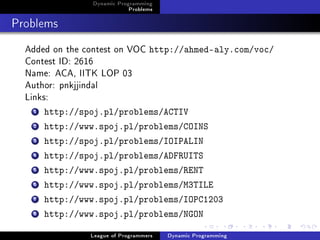
![Dynamic Programming
Problems
LCS
Recovering the LCS
Modify the algorithm to also build a matrix D[1 . . . n; 1 . . . m],
recording how the solutions to subproblems were arrived at.
League of Programmers Dynamic Programming](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-dp-121216023326-phpapp02/85/03-dp-34-320.jpg)
![Dynamic Programming
Problems
Longest Non Decresing Subsequence
Problem 4
Given an array [1 , 2 , 5, 2, 8, 6, 3, 6, 9, 7]. Find a subsequence
which is non decreasing and of maximum length.
1-5-8-9 forms a non decreasing subsequence
So does 1-2-2-6-6-7 but it is longer
League of Programmers Dynamic Programming](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-dp-121216023326-phpapp02/85/03-dp-35-320.jpg)
![Dynamic Programming
Problems
LNDS
Subproblem
Length of LNDS ending at i th location
Implementation
for(i=0;i100;i++) {
max=0;
for(j=0;ji;j++) {
if(A[i]=A[j] L[j]max)
max = L[j];
}
L[i] = max+1;
}
League of Programmers Dynamic Programming](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-dp-121216023326-phpapp02/85/03-dp-37-320.jpg)