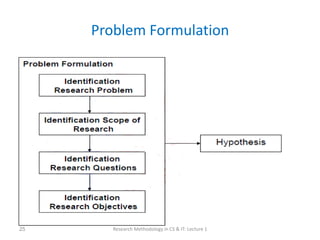
This document provides an overview of a course on research methodology in computer science and information technology. The course aims to develop students' research skills, enable exploration of degree specialization areas, and prepare students for independent learning during the research process. Topics covered in the course include research types, data collection methods, data analysis, research ethics, and idea generation. Students will be assessed through assignments, a research proposal, scientific paper, and thesis presentation.