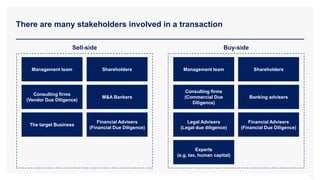
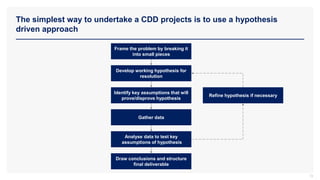
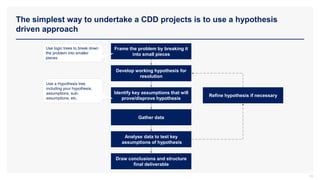
The document provides an overview of commercial due diligence (CDD) and outlines a hypothesis-driven approach for conducting CDD projects. It details the three key types of due diligence—financial, commercial, and legal—and emphasizes the importance of analyzing future performance of target companies. Additionally, it highlights stakeholders involved in transactions and the methods for validating hypotheses about company performance.