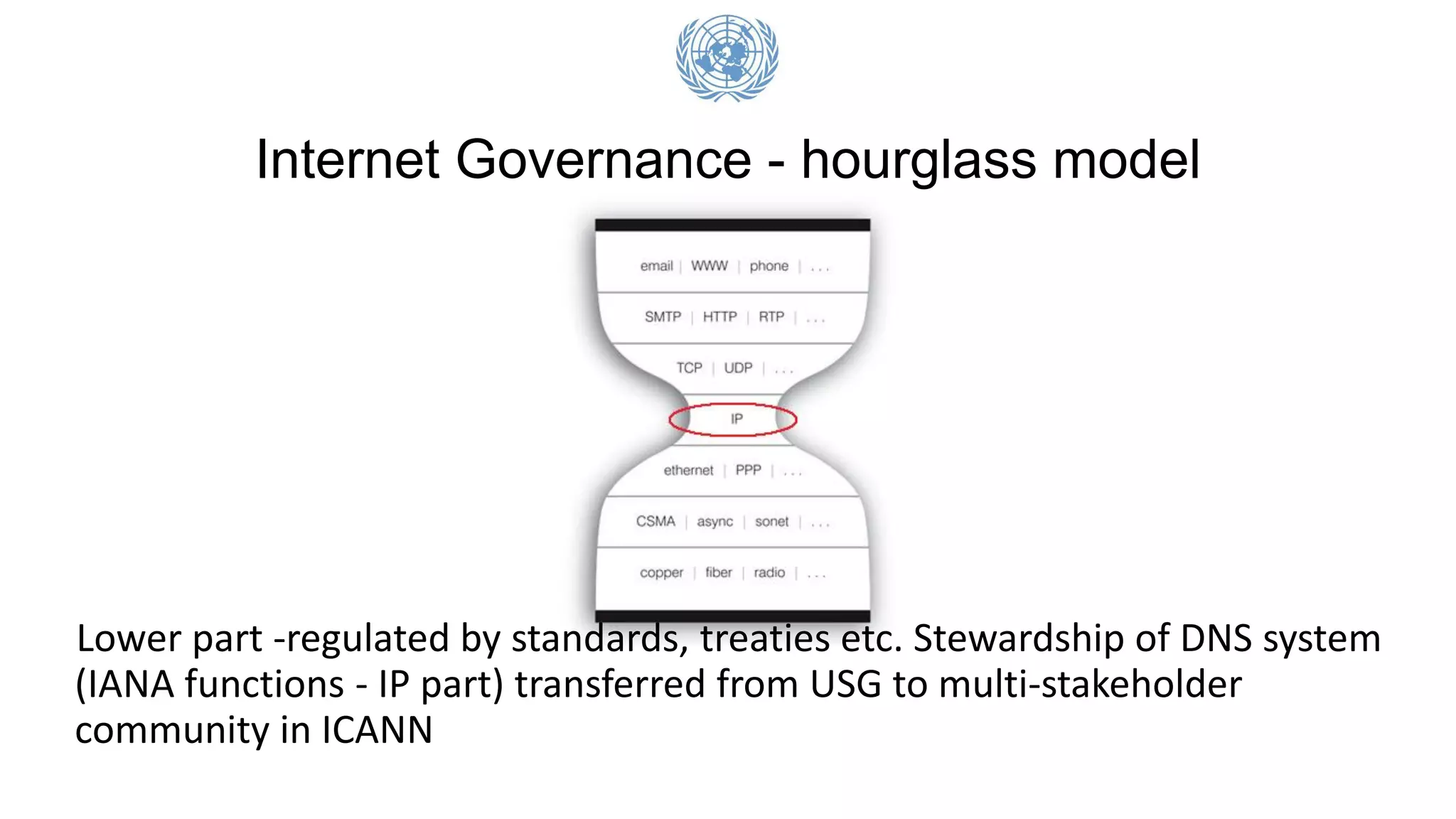
The document outlines the United Nations' perspective on digital public policy, addressing global issues in the digital age and key international programs like the SDGs and Paris Agreement. It discusses the challenges posed by the fourth industrial revolution, emphasizing the need for a multi-stakeholder approach in internet governance and public policy. It also highlights the role of various international organizations in shaping policies around critical issues such as data protection, security, and digital inclusion.