More Related Content
Similar to 5th Grade Correlation Chart
Similar to 5th Grade Correlation Chart (20)
5th Grade Correlation Chart
- 1. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
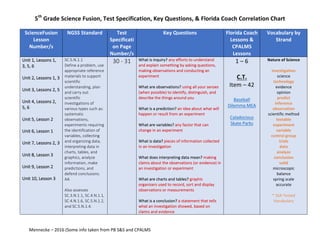
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Unit 1, Lessons 1,
3, 5, 6
Unit 2, Lessons 1, 3
Unit 3, Lessons 2, 5
Unit 4, Lessons 2,
5, 6
Unit 5, Lesson 2
Unit 6, Lesson 1
Unit 7, Lessons 2, 3
Unit 8, Lesson 3
Unit 9, Lesson 2
Unit 10, Lesson 3
SC.5.N.1.1
Define a problem, use
appropriate reference
materials to support
scientific
understanding, plan
and carry out
scientific
investigations of
various types such as:
systematic
observations,
experiments requiring
the identification of
variables, collecting
and organizing data,
interpreting data in
charts, tables, and
graphics, analyze
information, make
predictions, and
defend conclusions.
AA
Also assesses
SC.3.N.1.1, SC.4.N.1.1,
SC.4.N.1.6, SC.5.N.1.2,
and SC.5.N.1.4.
30 - 31 What is inquiry? any efforts to understand
and explain something by asking questions,
making observations and conducting an
experiment
What are observations? using all your senses
(when possible) to identify, distinguish, and
describe the things around you
What is a prediction? an idea about what will
happen or result from an experiment
What are variables? any factor that can
change in an experiment
What is data? pieces of information collected
in an investigation
What does interpreting data mean? making
claims about the observations (or evidence) in
an investigation or experiment
What are charts and tables? graphic
organizers used to record, sort and display
observations or measurements
What is a conclusion? a statement that tells
what an investigation showed, based on
claims and evidence
1 – 6
C.T.
Item – 42
Baseball
Dilemma MEA
Caladocious
Skate Parks
Nature of Science
investigation
science
technology
evidence
opinion
predict
inference
observation
scientific method
testable
experiment
variable
control group
trials
data
analyze
conclusion
valid
microscopic
balance
spring scale
accurate
* SSA Tested
Vocabulary
- 2. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Unit 1, Lessons 3,
4, 6
Unit 2, Lesson 2
Unit 5, Lesson 4
SC.5.N.1.2
Explain the difference
between an
experiment and other
types of scientific
investigation.
Assessed as SC.5.N.1.1
30 - 31 What is an investigation? an examination
or “inquiry” into something
What is an experiment? the part (step) in
a science investigation that tests the
prediction (hypothesis)
What is a model? a picture, idea, or
object that represents an object or
process
How do models help us learn science?
making models helps us understand an
object, event or process by answering
questions like, "What does it look like?”
and “How does it work?”
4
C.T.
Item – 42
Experiment
or
Investigatio
n?
Unit 1, Lesson 3
Unit 4, Lesson 3
Unit 7, Lesson 2
SC.5.N.1.3
Recognize and explain
the need for repeated
experimental trials.
Assessed as
SC.5.N.2.2.
34 - 35 What is an experimental trial? a repeat of
a test or observation
How does collecting data help answer a
question? the data (and observations) are
evidence that helps answer the the
question
Why is it important to do more than one
trail for the same experiment? the more
6
C.T.
Item – 41
3 Methods for
Measuring
Volume
- 4. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Unit 1, Lesson 3
Unit 3, Lesson 1
Unit 4, Lesson 5
Unit 8, Lesson 2
Unit 9, Lesson 2
Unit 10, Lessons
1,4
SC.5.N.1.4
Identify a control
group and explain its
importance in an
experiment.
Assessed as
SC.5.N.1.1.
30 - 31 What is a control? any variable in an
experiment that is purposely kept the
same or is unchanged
Why is it important to control all the
variables in an experiment except for one
variable? to justify that the results of the
experiments are only caused by that one
variable (or factor)
6
C.T.
Item – 29
Investigating
Variables
Solve the
Dissolving
Problem
Transformation
of Energy:
Constructing an
Electromagnet
Unit 1, Lessons 3. 4
Unit 3, Lesson 6
Unit 3, Lesson 2
Unit 4, Lesson 1
SC.5.N.1.5
Recognize and explain
that authentic
scientific investigation
frequently does not
parallel the steps of
"scientific method."
32 - 33 What is a scientific method? the
traditional steps of a scientific
investigation are: 1. Asking a question and
researching what is already known about
it (purpose/research) 2. Making a new
prediction (hypothesis) 3. Planning and
investigation (materials/procedures) 4.
Collecting and recording data
6
C.T.
Item – 2
- 5. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Unit 5, Lessons 4, 5
Unit 9, Lesson 1
Assessed as
SC.5.N.2.1.
(experimenting) 5. Analyzing and
synthesizing the data (graphing) 6.
Explaining the results (drawing
conclusions) and 7. Sharing the results
(communicating with other scientists)
Do all science investigations follow the
exact steps of the scientific method? not
really - modern scientists find the
traditional method too linear and
frequently back-track forming new
predictions and tests before gathering the
data they need to confirm their results.
(But scientists still emphasize the need for
precise, accurate empirical evidence and
replication.)
Polygon
Park
Unit 1, Lesson 1
Unit 3, Lesson 5
Unit 8, Lessons 1, 2
Unit 10, Lesson 2
SC.5.N.1.6
Recognize and explain
the difference
between personal
opinion/interpretation
and verified
observation.
Assessed as
SC.5.N.2.1.
32 - 33 What kind of questions can be
investigated scientifically? only questions
that can be tested by experimentation,
collecting data and making observations
What kind of questions cannot be
answered by science investigations
answer? questions that ask about an
opinion or belief
3
C.T.
Item – 6
Frankenchicken
Grow Toys
Introducing The
Process of
Investigative
Science
- 6. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Jay Wilder's
Snorkeling
Adventures MEA
Styrofoam
Eliminators
Wild Wind
Unit 1, Lessons 1, 2
Unit 2, Lesson 2
Unit 3, Lesson 1, 3
Unit 5, Lessons 2, 3
Unit 6, Lessons 1, 2
Unit 10, Lesson 2
SC.5.N.2.1
Recognize and explain
that science is
grounded in empirical
observations that are
testable; explanation
must always be linked
with evidence. AA
Also assesses
SC.3.N.1.7, SC.4.N.1.3,
SC.4.N.1.7, SC.5.N.1.5,
and SC.5.N.1.6.
32 -33 What is a claim? a statement about why
or how something happens
What is evidence? any observations or
data that justifies a claim
What is a conclusion? a statement that
tells what an investigation showed, based
on claims and evidence
1 & 3
C.T.
Item – 14
Demonstrating
How To Conduct
Controlled
Investigations
Using Sound
Introducing The
Process of
Investigative
Science
Mission to Mars: A
Comprehension
Instructional
- 7. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Sequence (CIS)
Lesson Plan
What It's Made Of:
A Solute to Mixture
or Solution
Unit 1, Lesson 1
Unit 4, Lesson 3
Unit 7, Lesson 3
SC.5.N.2.2
Recognize and explain
that when scientific
investigations are
carried out, the
evidence produced by
those investigations
should be replicable
by others. AA
Also assesses
SC.3.N.1.2, SC.3.N.1.5,
SC.4.N.1.2, SC.4.N.1.5,
and SC.5.N.1.3.
34 - 35 What is replication? repeating a trial
exactly the same way more than one time
(or increasing the samples within one trial
to more than one)
Why is repeating an experiment and
getting the same results important? it
justifies the results of the trial (test)
1,2, & 6
C.T.
Item – 36
Bridge to
Perfection
Introducing The
Process of
Investigative
Science
Unit 4, Lesson 1
SC.5.P.8.1
Compare and contrast
the basic properties of
solids, liquids, and
51 - 52 What is a physical property of matter? a
characteristic that can be observed,
measured, or changed without changing
the substance itself
15
C.T.
Physical Science:
matter
state of matter
- 8. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
gases, such as mass,
volume, color,
texture, and
temperature. AA
Also assesses
SC.3.P.8.1, SC.3.P.8.2,
SC.3.P.8.3, and
SC.4.P.8.1.
What is a chemical property of matter?
the ability of a substance to change into a
new substance with different properties
What are the physical properties of a
solid? solids keep their shape and volume
What are the physical properties of a
liquid? liquids take the shape of their
container, keep the same volume in a
container or not and can flow
What are the physical properties of a gas?
a gas will take the shape and volume of its
container and can flow
Which tools can measure the mass of
matter in grams (g)? a pan balance with
metric weights or spring scale which
measures in metric units, grams and
kilograms
Which tools can measure the volume of a
liquid or irregular solid in milliliters (mL)?
measuring cups or graduated cylinders
which measure in metric units, milliliters
or liters
What tool can measure the temperature
of matter? thermometers that measure in
degrees Celsius
Item – 20
3 Methods for
Measuring
Volume
Properties of
Matter
Rava's Florida
Fusion Catering
temperature
volume
mass
weight
texture
gas
liquid
solid
physical change
chemical change
condensation
evaporation
reaction
mixture
solution
atom
atomic theory
element
compound
* SSA Tested
Vocabulary
- 9. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Unit 4, Lesson 4, 5
SC.5.P.8.2
Investigate and
identify materials that
will dissolve in water
and those that will not
and identify the
conditions that will
speed up or slow
down the dissolving
process. AA
Assessed as
SC.5.P.8.3.
53 - 54
What is a solution? a mixture in which one
substance is dissolved in another
substance. but looks like a single
substance with the same properties
throughout
What common materials will and will NOT
dissolve in water? Salt, sugar, baking soda,
baking powder, corn syrup, Kool-Aid, and
carbon dioxide will easily dissolve in
water. Oil, sand, rice, iron fillings etc. do
not dissolve.
What conditions will speed up or slow
down the dissolving process? heating or
pressurizing the liquid will speed up
dissolving and allow the liquid to hold
more
17
From Trash
to Treasure
Icky, Icky,
No More
Slicky
- 10. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Unit 4, Lesson 4
SC.5.P.8.3
Demonstrate and
explain that mixtures
of solids can be
separated based on
observable properties
of their parts such as
particle size, shape,
color, and magnetic
attraction. AA
Also assesses
SC.5.P.8.2.
53 - 54
What is a mixture? two or more
substances physically combined together
without forming any new substances (if
the combination did form a new
substance, it would be called a
compound)
How can a mixture be separated? each
substance in a mixture keeps its own
physical and chemical properties, so their
properties can be used to separate the
mixture relatively easily back into each
substance by sifting larger substances
from smaller ones, filtering solid
substances from liquid ones, separating
iron substances from non-magnetic
substances using a magnet, by dissolving a
substance in water then evaporating the
water
16
C.T.
Item – 23
From Trash to
Treasure
Physical
Properties of
Solids
Separating Solid
Mixtures
To Dissolve or
Not to Dissolve
Part 1
What It's Made
Of: A Solute to
Mixture or
Solution
- 11. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Unit 4, Lessons 2, 3
SC.5.P.9.1
Investigate and
describe that many
physical and chemical
changes are affected
by temperature. AA
Also assesses
SC.3.P.9.1 and
SC.4.P.9.1.
55 What is heat? heat is the energy of the
moving particles in matter
What is temperature? temperature is the
average speed of the motion of the
particles in matter as measured by a
thermometer
How can heating a substance change it's
physical properties? as a substance is
heated the particles that make up the
matter in the substance move faster,
increasing the temperature until the
matter physically changes from one state
(phase) of matter to another (i.e., solid to
liquid, liquid to gas). Because most
substances can exist in all three states of
matter, adding heat melts solids into
liquid and liquids boil into gas If the
original physical and chemical properties
stay the same, only a physical change has
occurred.
How can heating a substance change it
chemically? Sometimes adding heat to
one or more substances will change them
into a something new with different
18
C.T.
Item – 28
Cooking in the
Chemical
Kitchen
Getting the Top
Mini-Fridge not
a "Small" Deal
Inventions and
Innovations
MEA
Shady Day MEA
- 12. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
physical and chemical properties from the
original substances. This type of change is
called a chemical change.
Unit 5, Lesson 1
SC.5.P.10.1
Investigate and
describe some basic
forms of energy,
including light, heat,
sound, electrical,
chemical, and
mechanical. AA
Also assesses
SC.3.P.10.1,
SC.3.P.10.3,
SC.3.P.10.4,
SC.3.P.11.1,
SC.3.P.11.2,
SC.4.P.10.1, and
SC.4.P.10.3.
56 - 57 What are some common forms of energy?
light - a form of energy that travels in long
and very short waves; some waves (long)
are visible to humans and others (short)
are not visible. Common sources of light
energy include a candle, light bulb, fire,
and the Sun. No matter what the source,
light always travels in a straight line (ray)
in all directions from the source. Many
sources of visible light also include heat
(thermal energy) see SC.5.P.9.1. Sound is
a form of wave energy produced by
vibrating objects. Sound waves need a
medium (matter) to travel through. Larger
vibrations cause loud sound, smaller
vibrations cause soft sounds. The type of
medium sound travels through changes
how fast it travels. The pitch of a sound is
how high or low its tone sounds. Electrical
energy is the flow of charged particles
from one place to another. Static
electricity is the build-up of electric
charges on an object, i.e. a balloon near
19
C.T.
Item – 9
All Sorts of
Energy
Enlightening
Explorations, Part
I
Exploring Forms
of Energy
Not that Hot
Anymore
Sail Away - An
Engineering
Design Challenge
Soccer Team
Uniform Decision
Physical Science:
energy
potential energy
kinetic energy
chemical energy
mechanical energy
electrical energy
static electricity
electric current
electric motor
electromagnet
generator
absorb
* SSA Tested
Vocabulary
- 13. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
your hair, lightning. Chemical energy is
the energy stored in matter, i.e. a wood
fire making heat, burning candle making
light. Mechanical energy is the energy of
moving objects and machines, i.e. bike,
car, train.
Solar Energy QR
Hunt
Transformation
of Electrical
Energy
Transformation
of Energy:
Constructing an
Electromagnet
Unit 5, Lessons 1, 2
SC.5.P.10.2
Investigate and
explain that energy
has the ability to
cause motion or
create change. AA
Also assesses
SC.3.P.10.2,
SC.4.P.10.2, and
SC.4.P.10.4.
58 How can energy produce motion?
Different forms of energy can produce
forces (vibrations, flowing particles, build-
up of charges) that cause pushes and pulls
and motion, i.e. magnets attract iron and
repel other magnets, a vibrating tuning
fork splashes water, a comb attracts
pieces of paper, etc.
How can energy create change? Different
forms of energy such as heat, light,
chemical and mechanical can create
chemical and physical changes (camp fire -
wood to heat to light, burning candle -
wax to heat to light, glow sticks - chemical
19
C.T.
Item – 21
Keeping Your
Cool With Your
Lunch Bag
Marbelous Pool
Noodle Ramps
Pop Goes the
Balloon, a Rube
- 15. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Unit 5, Lessons 1, 5
Unit 6, Lessons 1, 2
SC.5.P.10.4
Investigate and
explain that electrical
energy can be
transformed into
heat, light, and sound
energy, as well as the
energy of motion. AA
Also assesses
SC.3.E.6.1,
SC.4.P.11.1,
SC.4.P.11.2,
SC.5.P.10.3,
SC.5.P.11.1, and
SC.5.P.11.2.
59 - 60 How can one energy change into other
energy? Because different forms of
energy can produce forces, motion and
chemical changes, energy is continually
changing form one form to another and
one type to another.
19 & 21
C.T.
Item – 58
Enlightening
Explorations,
Part I
Sammy's Solar
Fountains
Inventions and
Innovations
MEA
Unit 6, Lessons 1, 2
SC.5.P.11.1
Investigate and
illustrate the fact that
the flow of electricity
requires a closed
circuit (a complete
loop).
59 -60 What is a electrical circuit? a pathway that
electrical energy can flow through
What are the parts of a simple circuit? a
battery or other source of electricity,
wires or other pathway for the electricity
to flow, a switch that can 'open' or 'close'
the flow of electricity to a lamp & light
21
C.T.
Item – 4
Circuit Circus
Physical Science:
conductor
insulator
circuit
series circuit
parallel circuit
- 16. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Assessed as
SC.5.P.10.4.
bulb or other electrical device.
What is an 'open' electrical circuit? an
electrical pathway with the switch open
so the electricity does not flow to the
device, turning the light bulb off.
What is a 'closed' electrical circuit? an
electrical pathway with the switch closed
so the electricity flows to the device,
turning the light bulb on.
How Does
Electricity
Flow?
Let It Flow
Let There Be
Light!
Making
Connections!
Short Circuit
* SSA Tested
Vocabulary
Unit 6, Lessons 1, 2
SC.5.P.11.2
Identify and classify
materials that conduct
electricity and
materials that do not.
Assessed as
SC.5.P.10.4.
59 - 60 What is a conductor of electricity? any
material that allows electricity to flow
(pass) through it easily, i.e. metal matter
(solids, liquids, gases) such as copper,
iron, gold, and silver, air, and water
What are insulators of electricity? any
material that does not allow electricity to
flow through it easily, i.e. non-metal
matter such as wood, plastic, rubber, and
ceramic
22
C.T.
Item – 35
Let It Flow
Let There Be
Light!
Making
Connections!
- 17. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Wire We All
Wet?
Unit 7, Lessons 1,
2, 3
SC.5.P.13.1
Identify familiar forces
that cause objects to
move, such as pushed
or pulls, including
gravity acting on
falling objects. AA
Also assesses
SC.3.E.5.4 and
SC.4.P.8.4.
61 - 62 What causes an object to move? If the
forces are unbalanced in strength (have a
'net force' other than zero) then the
object must be moving in the direction of
the stronger force pushing or pulling on it.
Why do most objects fall to the ground?
Gravity is an invisible force created by the
Earth's mass. Because the Earth is more
massive than most other objects, they are
pulled toward Earth (one exception might
be a 'helium balloon' - helium gas has less
mass than air, a mixture of nitrogen &
oxygen gases, so the air pushes the
helium balloon up, away from Earth).
23
C.T.
Item – 45
Balanced or Nah (Not)
Blast Off - An
Engineering Design
Challenge
Bottling Rockets
Clean Dat "SPACE" Inc.
Forces and Movement
Hoverama
Lunar Landers:
Exploring Gravity
Magnets 1: Magnetic
Pick-Ups
Newton's First Law of
Motion Part 1 of 3
Pendulum Inquiry
Physical Science:
force
mass
weight
gravity
friction
balanced forces
unbalanced forces
speed
* SSA Tested
Vocabulary
- 18. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Pendulum Inquiry -
Wrecking Balls
The Coasta with the
Mosta
X-treme Roller Coasters
Unit 7, Lessons 1, 2
SC.5.P.13.2
Investigate and
describe that the
greater the force
applied to it, the
greater the change in
motion of a given
object. AA
Also assesses
SC.4.P.12.1,
SC.4.P.12.2,
SC.5.P.13.3, and
SC.5.P.13.4.
63 - 64 What makes an object move faster and/or
change directions? Forces usually act in
pairs, opposite in direction to each other.
If one force is greater in strength than the
other force acting on an object, the object
will move in the direction of the greater
force. The greater the force, the faster the
the object will move and/or change
direction.
23
C.T.
Item – 27
Blast Off - An
Engineering Design
Challenge
Bottling Rockets
Forces and Movement
Newton's First Law of
Motion Part 1 of 3
- 19. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Pendulum Inquiry -
Wrecking Balls
We're Curious!—An
Engineering Design
Challenge
Wondrous Water Parks
Unit 7, Lessons 1, 2
SC.5.P.13.3
Investigate and
describe that the
more mass an object
has, the less effect a
given force will have
on the object's
motion.
Assessed as
SC.5.P.13.2.
63 - 64 Why can some objects be moved easily
while others are harder to move? For one
force to move, change the speed or
direction of an object, it has to be greater
than the mass (inertia) of that object as
well as any other force(s) acting on the
object. The more massive the object, the
more force is needed to move it.
23
Bottling Rockets
Forces and Movement
Hoverama
Newton's Second Law
of Motion Part 2 of 3
Sunshine Beach Hotel
MEA
Unit 7, Lessons 1, 3
SC.5.P.13.4
Investigate and
explain that when a
force is applied to an
object but it does not
63 - 64 What causes an object to stop?
Remember forces usually act in pairs,
opposite direction to each other. If the
forces acting on an object are balanced
23
C.T.
Item – 5
- 22. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Unit 2, Lessons 1, 2
SC.5.E.5.2
Recognize the major
common
characteristics of all
planets and
compare/contrast the
properties of inner
and outer planets.
Assessed as
SC.5.E.5.3.
38 - 39 What are the "inner planets"? the inner
planets are closer to the Sun and include
Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. They
are "terrestrial" (Earth-like) with rocky
surfaces, solid cores (centers) and
cratered surfaces. Venus, Earth and Mars
have atmospheres so their surface
experiences weather and erosion. Earth
and Mars have moons (Earth-1/Mars-2)
What are the "outer planets"? the outer
planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and
Neptune are "gas giants" much larger than
all the inner planets and further away
from the Sun. Their surface is made of a
kind of slush (not solid) that forms their
gaseous atmospheres. Evidence also
suggests they have a solid core (mostly
iron). All outer planets have lots of moons
(10 or more each).
What about Pluto? Pluto is classified as a
dwarf planet (planetoid) not a terrestrial
or a gas giant. It is smaller than all the
other planets with a surface made of
frozen gas. Pluto has a large moon (close
8
C.T.
Item – 15
A Closer Look of
the Inner and
Outer Planets
Designing a Scale
Model of the
Solar System
Margot's Venus
One of these
days… Right to
the Solar System!
Planets In Space
What's in a
Name? Where
am I in the
Universe?
Researching the
Planets
- 26. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
reservoirs via
evaporation and
precipitation
processes.
Assessed as
SC.5.E.7.1.
surface and enters the atmosphere as
water vapor.
What other bodies of water influence the
amount of water evaporating into the
atmosphere as water vapor? other fresh
water bodies on the surface of the Earth
include lakes, rivers, streams, canals,
swamps, wetlands and ponds
How else are bodies of water on the
surface of the Earth connected to the
water cycle? low lying areas on the Earth's
surface are re-charged with liquid water
every time it rains or snow melts and
runs-off back into oceans, lakes, rivers,
canals, swamps, streams and ponds
Cycling Water
Through the
Environment
Model Magic!
Water Cycle Model
The Water Cycle -
Back and Forth
Why Does Rain
Fall?
Unit 3, Lessons 3,
4, 5
SC.5.E.7.3
Recognize how air
temperature,
barometric pressure,
humidity, wind speed
and direction, and
precipitation
determine the
weather in a
particular place and
time. AA
48 -50 What is the weather? the conditions in
the atmosphere in a certain place for a
short period of time
What is the atmosphere and what role
does it play in the weather? The
atmosphere is the air around and above
you. The Earth's atmosphere has five
distinct layers, each with different
11
C.T.
Item – 8
Feeling the
Pressure —
- 27. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Also assesses
SC.5.E.7.4, SC.5.E.7.5,
and SC.5.E.7.6.
temperatures and air pressure.
What is air temperature, how is it
measured, and what does it tell us about
the weather? Air temperature is the
amount of heat in the atmosphere as
measured by a thermometer. When the
air gets warmer it can hold more moisture
(water vapor); as it gets colder it holds
less moisture.
What is air pressure, how it is measured
and what does it tell us about the
weather? Air pressure is the weight of the
air pressing down on everything around it
as measured by a barometer. A move to
lower air pressure means more
precipitation, i.e. rain/stormy; a move to
higher air pressure means clearing
weather, i.e. fair/dry
What conditions affect air pressure? 1)
Water vapor - air that is more moist has a
lower air pressure; dryer air has a higher
air pressure. 2) Air temperature - as air
gets warmer, the air pressure goes down;
as air gets colder the air pressure goes up.
An
Engineering
Design
Challenge
Go Fly A Kite
MEA
Hey
Weatherpers
on, What's
the Weather
Vacation, All I
Ever Wanted-
Weather
Conditions
MEA
Weather and
Pressure
Systems
- 28. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
3) Altitude - air at higher altitudes is
thinner and more spread out, so as the
altitude gets higher, the air pressure goes
down.
What is wind, how does it move, how is
wind speed measured, and what does it
tell us about the weather? Wind is moving
air. Air moves because Earth's surface is
heated unevenly (the land heats up faster,
water slower). The wind's speed is
measured using an anemometer (the
wind pushes against cups spinning the
anemometer around; the faster the wind
is blowing the faster it spins). The wind
pushes cold and hot air masses together
causing storm fronts (changes in the
weather).
How is wind direction shown and what
does it tell us about the weather? The
wind's direction is shown by a wind vane.
Arrows point to the direction the wind is
coming from, i.e. an arrow pointing north
means the wind is moving from the north
to the south. Wind direction tells us
where a storm may come or go next.
Weather
Tools
International
When
Weather is
Right…We
Camp!
Wild Wind
- 29. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Unit 3, Lessons 3, 5
SC.5.E.7.4
Distinguish among the
various forms of
precipitation (rain,
snow, sleet, and hail),
making connections to
the weather in a
particular place and
time.
Assessed as SC.5.E.7.3
48 - 50 What is precipitation and how is it
measured? Precipitation is water that falls
to the Earth's surface as rain, snow, sleet,
or hail. Rainfall is measured with a rain
gauge (a clear container with marks
showing centimeters/inches).
What are the different forms of
precipitation and what determines the
type of precipitation in a weather
forecast? rain - liquid water, snow - ice
crystals, sleet - frozen rain, hail - ice balls.
Air temperature, as measured by a
thermometer, determines the type of
precipitation (rain, sleet, hail or snow) in a
particular place and time. As the air
temperature falls below 0o
C (32o
F) the
forecast changes form rain to sleet or
snow. Hail forms in freezing temperatures
higher in the atmosphere and falls to the
surface as balls of ice.
11
C.T.
Item – 33
Catch Me if You
Can:
Engineering
Design
Challenge
Making it Rain
Water Cycle
You're Moving
Where?
Unit 3, Lesson 6
SC.5.E.7.5
Recognize that some of
the weather-related
differences, such as
48 - 50 What is climate and what are the three
basic climate zones on Earth? Climate is
the general weather of an area over a
long period of time, such as years. The
12
- 30. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
temperature and
humidity, are found
among different
environments, such as
swamps, deserts, and
mountains.
Assessed as SC.5.E.7.3.
three basic climate zones on Earth are
tropical (warm/wet or dry), temperate
(cool/seasons), and polar (cold/dry).
How do weather-related conditions
change from one place to another (i.e.
swamp to desert to mountain)? Different
environments in different climates have
different weather-related conditions
depending on the temperature and
annual precipitation, i.e. swamps in a
tropical climate change from wet (rain) to
dry seasonally but stay warm year round
where as swamps in temperate climates
are cooler and wetter (rain) year round.
Deserts in tropical climates are dry year
round, have very little rainfall but change
from warm to very hot seasonally where
as deserts in polar climates are drier (less
rain) and much colder (dry snow).
Temperate mountains are cooler,
experience four seasons ranging from wet
(rain) to dry and warm to cold (snow)
where as polar mountains are much
colder (snow) and drier year round.
Banana
Bonanza
- 31. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Unit 3, Lesson 6
SC.5.E.7.6
Describe characteristics
(temperature and
precipitation) of
different climate zones
as they relate to
latitude, elevation, and
proximity to bodies of
water.
Assessed as SC.5.E.7.3.
48 - 50 What causes the climate zones and the
differences in weather within different
zones? Earth's tilt on its axis is mainly
responsible for the climate zones, i.e. in
December the North Pole is tilted away
from the Sun.
What else can affect the weather in
different climate zones? The available
sunlight at different latitudes isn't the only
thing that affects the weather in different
climate zones. Elevation and bodies of
water can also influence the weather
within these regions. Because elevation
affects the air pressure, it changes the
amount of moisture the air can hold and
depending on the temperature can
change the amount of local precipitation.
Likewise any local body of water can
change the amount of moisture that can
be recycled (evaporation, condensation
and precipitation) into the region
depending on the temperature.
12
C.T.
Item – 51
Anita Balance:
Climate
Catch Me if You
Can:
Engineering
Design
Challenge
Weathering
Weather
Unit 8, Lessons 1,
2, 3, 4
SC.5.L.14.1
Identify the organs in
the human body and
describe their functions,
67 What is a body organ? A structure made
of two or more different tissues which has
a specialized job (function), such as the
lungs which help you breathe or the
25
C.T.
Life Science:
organism
organ
- 32. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
including the skin, brain,
heart, lungs, stomach,
liver, intestines,
pancreas, muscles and
skeleton, reproductive
organs, kidneys, bladder,
and sensory organs. AA
stomach which helps you digest food.
What are the five human sensory organs
and their functions? The five human
sense organs are the eyes (which help you
see), ears (help hear), nose (help smell),
tongue (helps taste), and the skin (which
helps you feel and responds to stimulus).
What is the main function of the skeletal
system? The skeletal system supports the
body (with bones), give it shape, and
protects some of the vital organs inside
the body. It also can move because it has
joints.
What is the main function of the muscular
system? The muscular system moves your
body (skeletal muscles), moves food
through your digestive system (smooth
muscles), and pumps blood through your
circulatory system (cardiac muscle).
What is the main function of the
respiratory system? The respiratory
system inhales oxygen from the air you
breathe and exhales carbon dioxide and
Item -32 &
65
Beating On
and On
Are We Like
Robots?
Are you
Inspiring?
Body
Swatter
Is My
Epidermis
Showing?
organ system
brain
skin
bones
muscles
exoskeleton
lungs
heart
stomach
liver
pancreas
kidneys
bladder
ovary
reproduction
* SSA Tested
Vocabulary
- 33. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
water vapor out of the body. Your
respiratory system includes the mouth,
nose, trachea, bronchi and lungs.
What is the main function of the
circulatory system? The circulatory
system moves blood throughout your
body, delivers food nutrients and oxygen
to all your body's cells, removes carbon
dioxide and other wastes from the cells,
and helps fight infections in the blood
(white blood cells). The circulatory system
includes the heart, arteries, veins, and
capillaries.
What is the main function of the digestive
system? The digestive system breaks
down food into simpler substances that
your cells can use and gets rid of wastes
resulting from digestion. The digestive
system includes the mouth, esophagus,
stomach, small intestine, liver, gall
bladder, pancreas, large intestine, rectum
and anus.
What is the main function of the excretory
system? The excretory system removes
Kidney
Filtering
Making the
Cut!
Mechanical
Hands
Name That
Organ!
Systems of
the human
body
The Three
Main
Sections of
the Brain
- 34. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
liquid and gas wastes. The excretory
system includes the kidneys, bladder,
urethra, skin, and lungs.
What is the main function of the nervous
system? The nervous system controls all
the other systems of your body, receives
information (stimulus) from the
environment, stores memories and
enables thinking. The nervous system
includes the brain, spinal cord, nerves,
and sense organs.
Walk, Run,
Jump
Work that
Body-
Human
Organs
MEA
Unit 8, Lessons 1,
3, 4
SC.5.L.14.2
Compare and contrast
the function of organs
and other physical
structures of plants and
animals, including
humans, for example:
some animals have
skeletons for support --
some with internal
skeletons others with
exoskeletons -- while
some plants have stems.
AA
Also assesses SC.3.L.15.1
and SC.3.L.15.2.
68 - 69 How are vertebrate animals classified?
Vertebrate animals (those with
backbones) are classified by scientists into
five groups: amphibians, fish, reptiles,
birds and mammals. Each group has its
own unique characteristic structures
(body parts) and behaviors (life cycles).
How are plants classified? Plants are
grouped into two major groups, flowering
and nonflowering according to their life
cycles.
24
C.T.
Item – 25
Are We Like
Robots?
Frankenchicken
- 35. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Unit 10, Lessons 1,
2, 3, 4
SC.5.L.17.1
Compare and contrast
adaptations displayed by
animals and plants that
enable them to survive
in different
environments such as
life cycles variations,
animal behaviors and
physical characteristics.
AA
Also assesses
SC.3.L.17.1, SC.4.L.16.2,
SC.4.L.16.3, SC.4.L.17.1,
SC.4.L.17.4, and
SC.5.L.15.1.
72 - 73 What is survival? In terms of wild
organisms, survival is living long enough to
reproduce more of your own kind in large
numbers.
What is a trait? A physical characteristic
or condition passed by genes (DNA
segments) from parent to offspring. Some
traits are observable (dominant), others
are not (recessive).
What is a behavior? An activity or action
that generally helps an organism survive
in its environment. Many behaviors are
learned from experience over a lifetime;
others are innate (inborn, or coded for in
the genes) like animal survival instincts.
How can traits help organisms survive?
Traits determine an organisms body type
and structures, i.e. scales or fur, hooves or
claws, legs or fins, teeth or beak, eggs or
live-birth, flowers or cones, leaves or
needles. In most cases these body
structures help the organism compete
with other organisms in the same habitat.
21
C.T.
Item – 7
A Tasty Experiment
Adaptations: Will
You Survive?
Amazing
Adaptations!—An
Engineering Design
Challenge
Arctic Animals and
a Changing Climate
Be very, very
quiet... Hunting
MEA
Bird Beaks
Bird Buffet (Animal
Survival)
Cicada Invasion
Exploring
Adaptations!
Life Science:
habitat
adaptation
behavior
characteristic
instinct
grassland
desert
taiga
polar
wetland
intertidal zone
* SSA Tested
Vocabulary
- 36. 5th
Grade Science Fusion, Test Specification, Key Questions, & Florida Coach Correlation Chart
Mennecke – 2016 (Some info taken from PB S&S and CPALMS
ScienceFusion
Lesson
Number/s
NGSS Standard Test
Specificati
on Page
Number/s
Key Questions Florida Coach
Lessons &
CPALMS
Lessons
Vocabulary by
Strand
Can behaviors help organisms survive?
Behaviors like physical traits can give
organisms a edge in surviving i.e.,
swimming or flying, running or climbing,
hibernating or migrating and responding
to light (phototropism) and responding to
gravity (gravitropism) in plants.
Exploring Habitats!
Florida Animals
and Plants
Research
Interplanetary Zoo
Introduction To The
Nature Journal
It's All Happening at
the Zoo
Unit 9, Lessons 1, 2 SC.5.L.15.1
Describe how, when the
environment changes,
differences between
individuals allow some
plants and animals to
survive and reproduce
while others die or move
to new locations.
Assessed as SC.5.L.17.1.
72 - 73 What is an adaptation? A body part or
behavior that helps a living thing survive.
Why do organisms adapt? Organisms
need to adapt (change) to their
environment to compete for food, water,
shelter and living space and then
reproduce offspring in order to survive.
What is natural selection? Natural
selection is the process by which
organisms change over many generations
and those best suited to their
environment survive to pass their traits
26
Adaptations:
Will You
Survive?
Animal Tracks
Arctic Animals
and a Changing
Climate
Life Science:
environment
ecosystem
population
community
species
pollution
conservation
extinct species
endangered species
* SSA Tested
Vocabulary