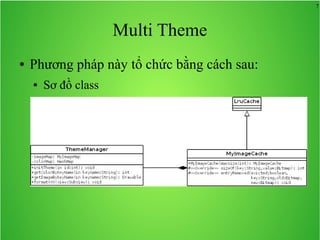
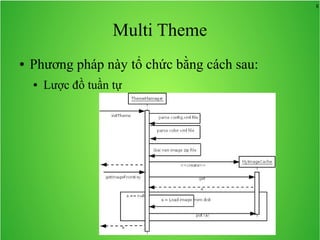
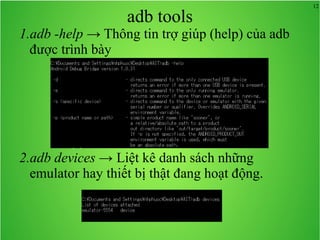
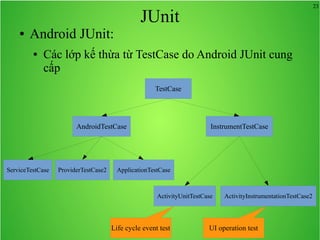
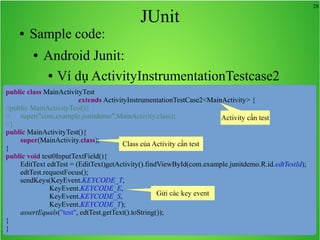
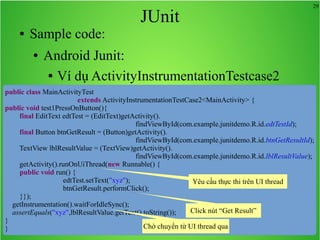
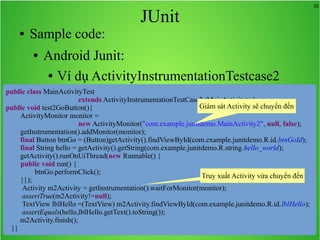
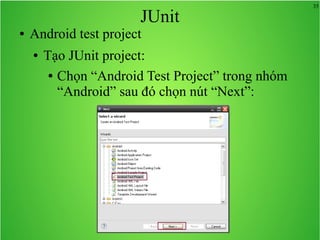
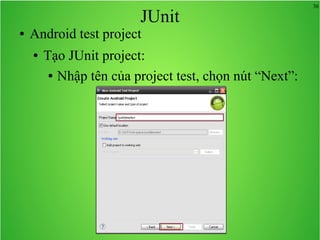
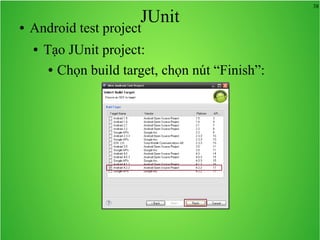
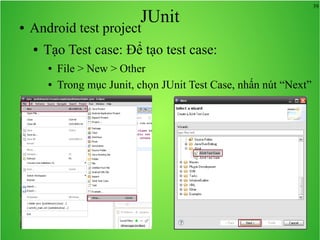
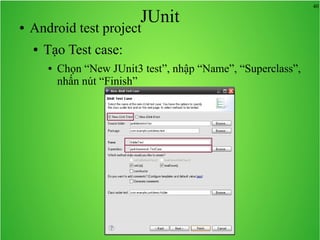
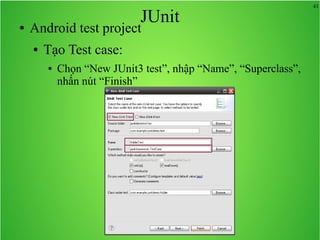
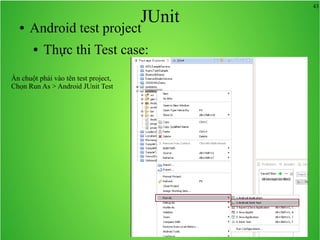
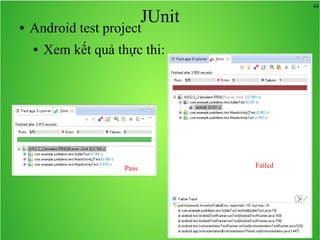
Bài học này bao gồm ba chủ đề chính: multi theme, adb tool và junit. Multi theme hướng dẫn cách tổ chức và sử dụng nhiều theme cho ứng dụng Android, trong khi adb tool là công cụ hỗ trợ quản lý thiết bị Android và emulator. Junit được giới thiệu như một framework để phát triển unit test cho các chương trình Java, đặc biệt trong môi trường Android.