Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX







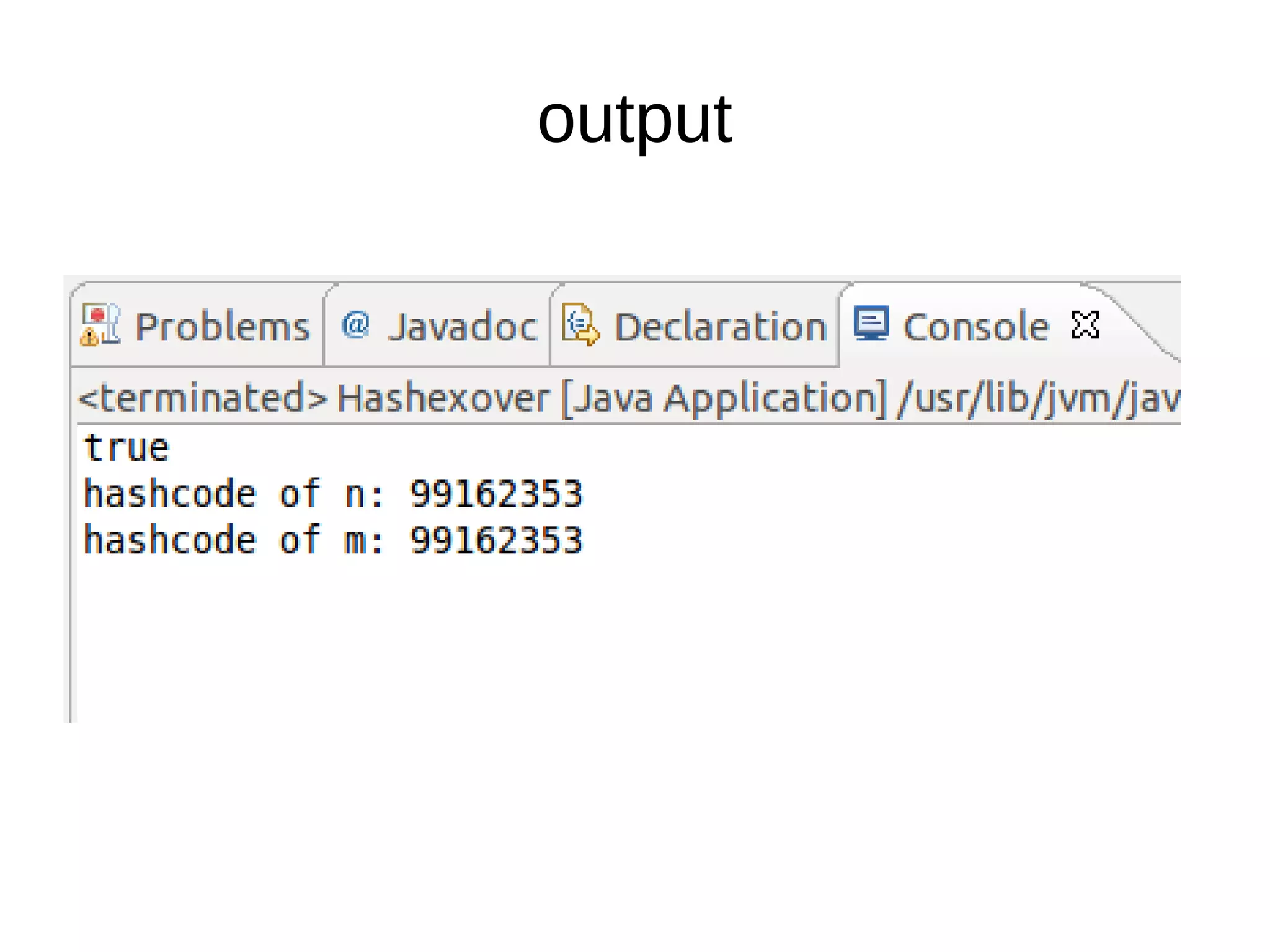


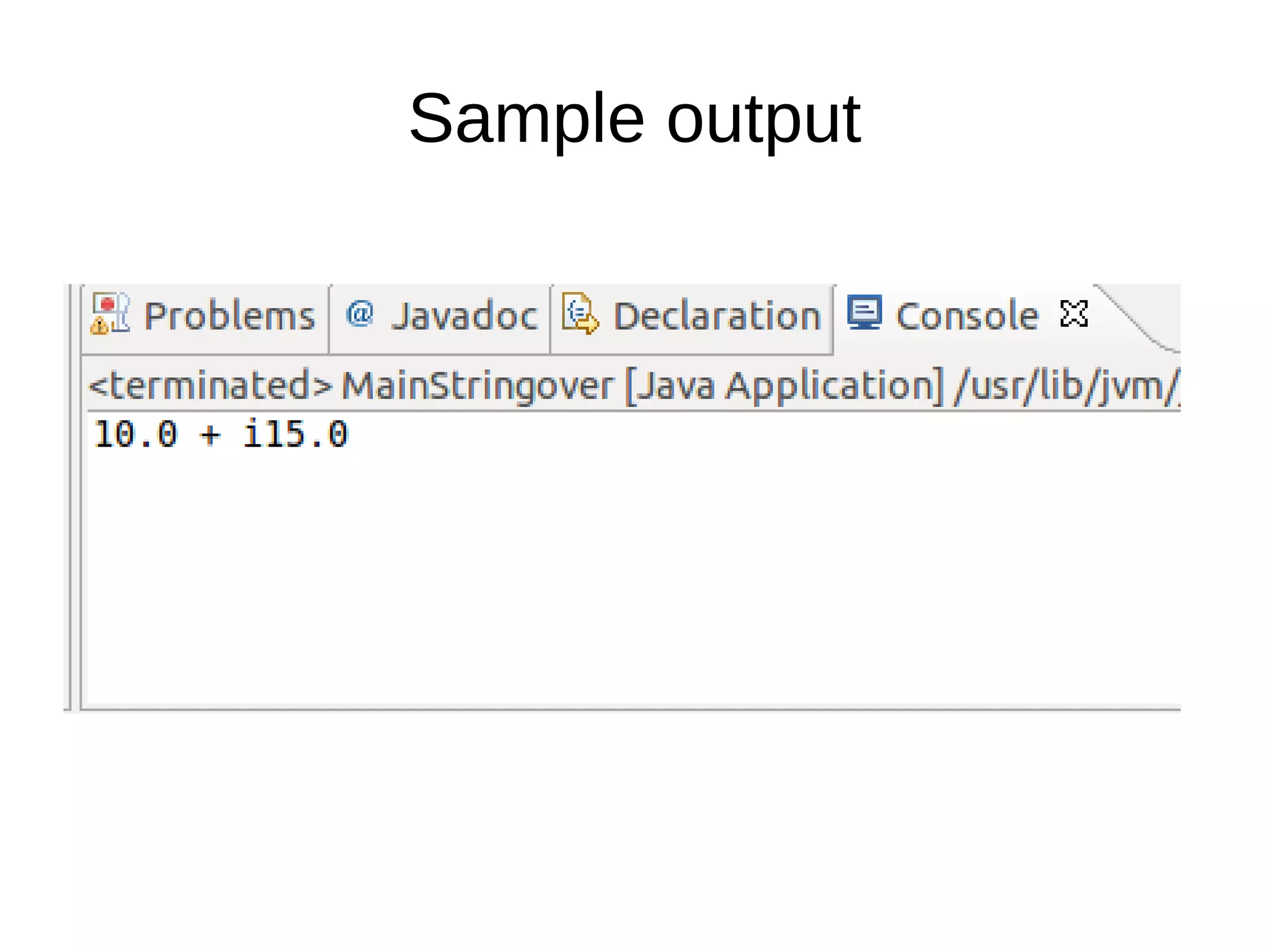

To override the equals() method: 1. Do null and type checks 2. Type cast objects and compare individual attributes starting with numeric ones using short-circuit logic 3. Both equals() and hashCode() should be overridden together for collections to work properly 4. Override toString() to print objects in a custom format










