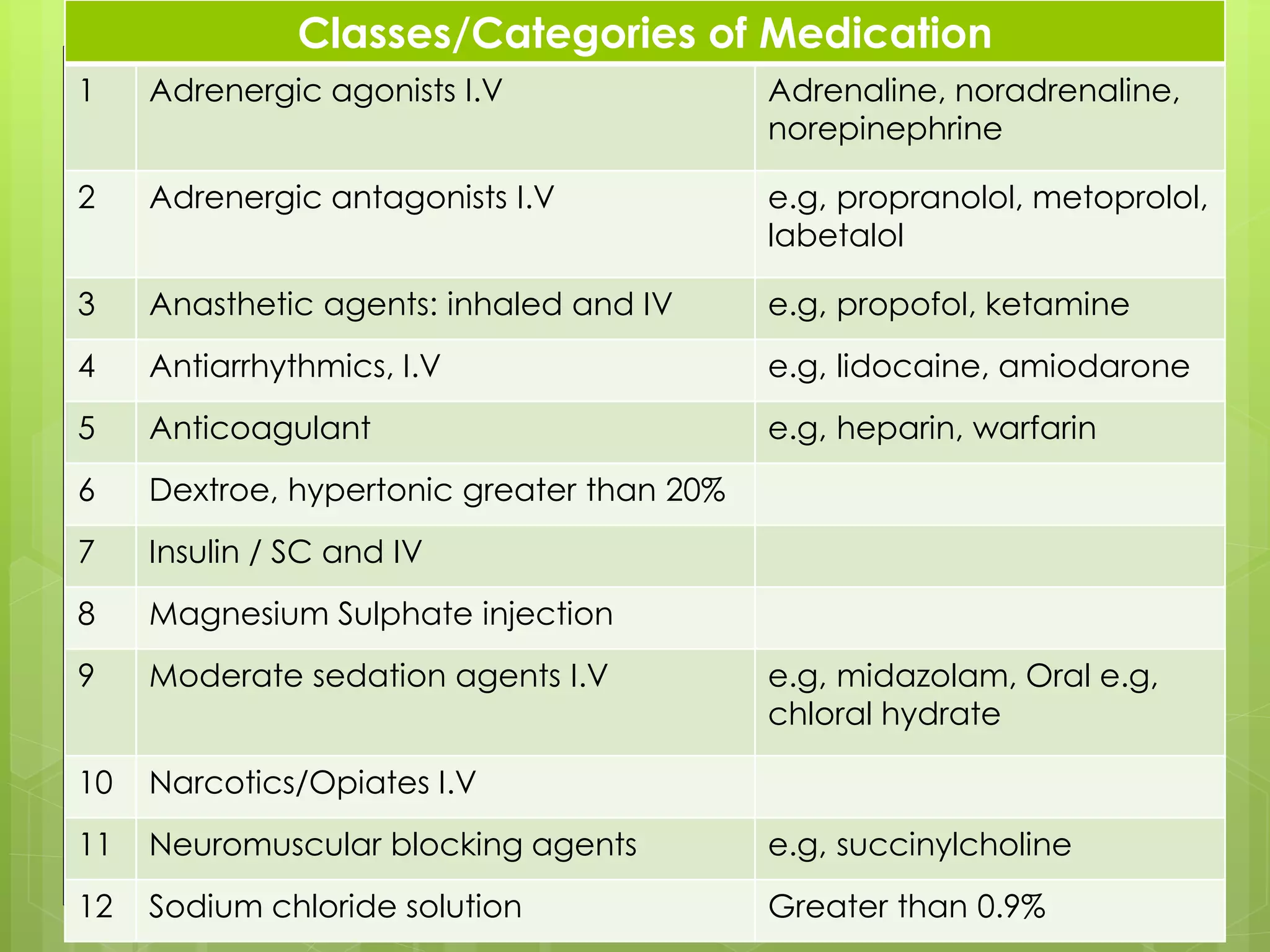
High-alert medications are drugs that pose a significant risk of patient harm when errors occur, necessitating strict safety protocols. The document outlines various drug classes identified as high-alert, common risk factors for errors, and strategies to prevent mistakes in their use including procurement, storage, prescribing, preparation, administration, and monitoring. Effective management of high-alert medications involves clear labeling, limiting available drug strengths, thorough training, and proper documentation.