The document is a presentation on getting started with C++ by Michael P. Redlich, covering its definition, evolution, features, and object-oriented programming principles. It includes information on C++ classes, inheritance, memory management, and popular compilers, along with live demos and resources for further learning. Upcoming events and further reading materials are also mentioned.
















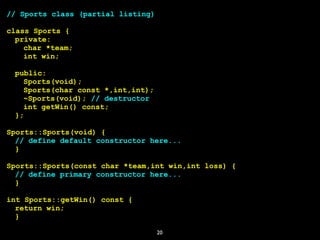




![Operator new (2)
int *var = new int; // int();
Sports *sports = new Sports();
// initializes an array of pointers
to type int
int *var = new int[10]
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettingstartedwithc-180318221834/85/Getting-Started-with-C-26-320.jpg)

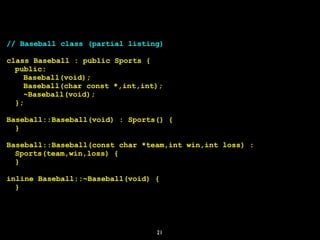
![Operator delete (2)
int *var = new int;
delete var;
int *var = new int[10]
delete[] var;
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettingstartedwithc-180318221834/85/Getting-Started-with-C-28-320.jpg)