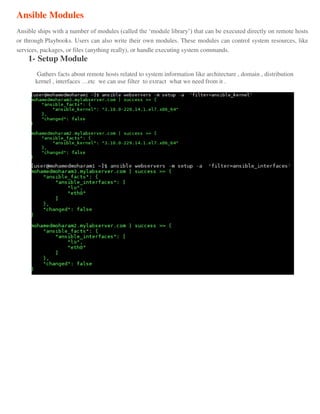
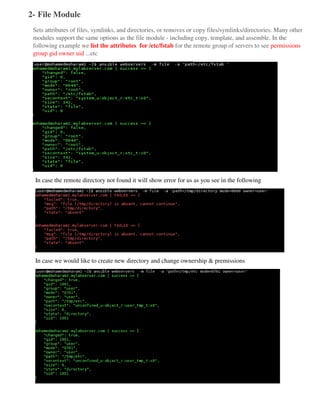
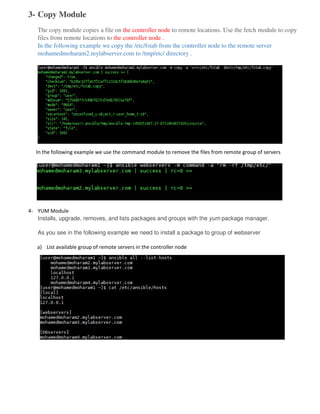
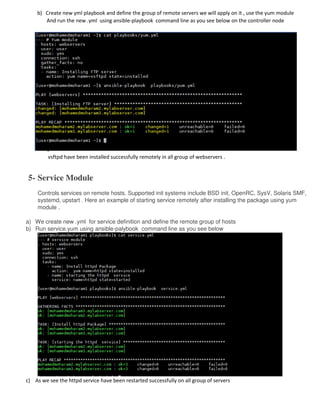
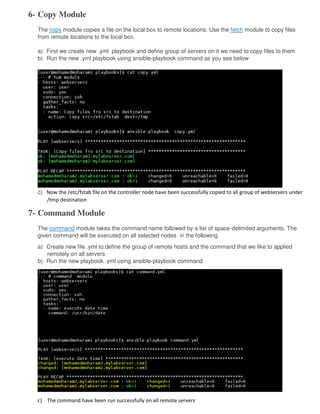
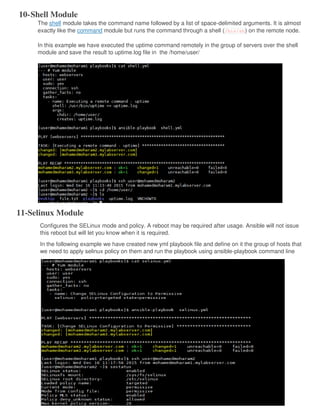
Ansible is an open source automation tool that allows users to configure, manage, and deploy software on remote machines without requiring an agent. It uses SSH to connect to nodes and executes modules written in Python. Playbooks allow users to automate multiple tasks by defining YAML files containing a list of commands. Ansible is agentless and can manage hundreds of nodes with a single command.


![What is YAML ?
YAML (/ˈjæməl/, rhymes with camel) is a human-readable data serialization format that takes concepts from
programming languages such as C, Perl, and Python, and ideas from XML and the data format of electronic mail
YAML syntax was designed to be easily mapped to data types common to most high-level languages: list, associative
array, and scalar.Its familiar indented outline and lean appearance make it especially suited for tasks where humans
are likely to view or edit data structures, such as configuration files, dumping during debugging, and document headers
For more information refer to the following https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YAML
--- # Examples
--- # Sample document
--- # Data structure hierarchy is maintained by outline indentation.
receipt: Oz-Ware Purchase Invoice
date: 2012-08-06
customer:
first_name: Dorothy
family_name: Gale
items:
- part_no: A4786
descrip: Water Bucket (Filled)
price: 1.47
quantity: 4
YAML offers an "in-line" style for denoting associative arrays and lists. Here is a sample of the
components.
Lists: - Conventional block format uses a hyphen+space to begin a new item in list.
--- # Favorite movies comment
- Casablanca
- North by Northwest
- The Man Who Wasn't There
Optional inline format is delimited by comma+space and enclosed in brackets (similar to JSON)
--- # Shopping list comment
[milk, pumpkin pie, eggs, juice]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/785c18bb-35c1-4f14-9208-7fe89859172b-160106093423/85/Ansible-automation-tool-with-modules-3-320.jpg)
![Ansible Documentation: Modules
As we are dealing with an array of modules during using Ansible tutorials. Here we show how to use Ansible
documentation in order to see what modules are available and how to use them. For more information refer to the
following url http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/list_of_packaging_modules.html to know more about available
modules
[root@mohamedmoharam1 ansible]# ansible --version
ansible 1.9.4
configured module search path = None
[root@mohamedmoharam1 ansible]# ansible-doc --help
Usage: ansible-doc [options] [module...]
Show Ansible module documentation
Options:
--version show program's version number and exit
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-M MODULE_PATH, --module-path=MODULE_PATH
Ansible modules/ directory
-l, --list List available modules
-s, --snippet Show playbook snippet for specified module(s)
-v Show version number and exit
System Architecture Diagram
(b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/785c18bb-35c1-4f14-9208-7fe89859172b-160106093423/85/Ansible-automation-tool-with-modules-4-320.jpg)

![Step 3: Creating Inventory File for Remote Hosts
7. Add these three hosts to inventory file. This file hold the host information’s like which host we need to get
connect from local to remote under /etc/ansible/hosts.
# sudo vim /etc/ansible/hosts
Add the following three hosts IP address..
[webservers]
mohamedmoharam2.mylabserver.com
mohamedmoharam3.mylabserver.com
[DBservers]
mohamedmoharam4.mylabserver.com
Note: The ‘webservers‘ in the brackets indicates as group names, it is used in classifying systems and deciding
which systems you are going to controlling at what times and for what reason.
Now time to check our all 3 doing ping from my localhost. To perform the action we need to use the command
‘ansible‘ with options ‘-m‘ (module) and ‘-all‘ (group of servers). ‘WE ARE HERE USING MODULE PING ’
# ansible -m ping webservers
mohamedmoharam2.mylabserver.com | success >> {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
mohamedmoharam3.mylabserver.com | success >> {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/785c18bb-35c1-4f14-9208-7fe89859172b-160106093423/85/Ansible-automation-tool-with-modules-7-320.jpg)
![Ansible Command Line
Now, here we are using another module called ‘command‘, which is used to execute list of commands (like, df,
free, uptim, etc.) on all selected remote hosts at one go, for example watch out few examples shown below.
To check the partitions on all remote hosts
# ansible -m command -a "df -h" webservers
mohamedmoharam2.mylabserver.com | success | rc=0 >>
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/xvda1 20G 4.7G 16G 24% /
devtmpfs 477M 0 477M 0% /dev
tmpfs 497M 84K 496M 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 497M 13M 484M 3% /run
tmpfs 497M 0 497M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
mohamedmoharam3.mylabserver.com | success | rc=0 >>
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/xvda1 20G 4.7G 16G 24% /
devtmpfs 477M 0 477M 0% /dev
tmpfs 497M 0 497M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 497M 13M 484M 3% /run
tmpfs 497M 0 497M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
Installing a package remotely using friendly ansible yum module feature for installing the package httpd on a
remote group of servers
[user@mohamedmoharam1 ansible]$ ansible webservers -s -m yum -a 'pkg=httpd state=installed
update_cache=true'
mohamedmoharam3.mylabserver.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
mohamedmoharam3.mylabserver.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/785c18bb-35c1-4f14-9208-7fe89859172b-160106093423/85/Ansible-automation-tool-with-modules-8-320.jpg)
![System Facts
Using Ansible discovers various system information on remote systems using setup ansible module
[user@mohamedmoharam1 ansible]$ ansible -m setup webservers
mohamedmoharam2.mylabserver.com | success >> {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses": [
"172.31.103.160"
],
"ansible_all_ipv6_addresses": [
"fe80::1042:b8ff:fef2:99"
],
"ansible_architecture": "x86_64",
"ansible_bios_date": "12/07/2015",
"ansible_bios_version": "4.2.amazon",
"ansible_cmdline": {
"BOOT_IMAGE": "/boot/vmlinuz-3.10.0-229.14.1.el7.x86_64",
"LANG": "en_US.UTF-8",
"console": "ttyS0,115200n8",
"crashkernel": "auto",
"ro": true,
"root": "UUID=0f790447-ebef-4ca0-b229-d0aa1985d57f",
"vconsole.font": "latarcyrheb-sun16",
"vconsole.keymap": "us"
},
"ansible_date_time": {
"date": "2015-12-15",
"day": "15",
"epoch": "1450215305",
"hour": "21",
"iso8601": "2015-12-15T21:35:05Z",
"iso8601_micro": "2015-12-15T21:35:05.565977Z",
"minute": "35",
"month": "12",
"second": "05",
"time": "21:35:05",
"tz": "UTC",
"tz_offset": "+0000",
"weekday": "Tuesday",
"year": "2015"
},
"ansible_default_ipv4": {
"address": "172.31.103.160"
"alias": "eth0",
"gateway": "172.31.96.1",
"interface": "eth0",
"macaddress": "12:42:b8:f2:00:99",
"mtu": 9001,
"netmask": "255.255.240.0",
"network": "172.31.96.0",](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/785c18bb-35c1-4f14-9208-7fe89859172b-160106093423/85/Ansible-automation-tool-with-modules-10-320.jpg)
!["type": "ether"
},
"ansible_default_ipv6": {},
"ansible_devices": {
"xvda": {
"holders": [],
"host": "",
"model": null,
"partitions": {
"xvda1": {
"sectors": "41927602",
"sectorsize": 512,
"size": "19.99 GB",
"start": "2048"
}
},
"removable": "0",
"rotational": "0",
"scheduler_mode": "deadline",
"sectors": "41943040",
"sectorsize": "512",
"size": "20.00 GB",
"support_discard": "0",
"vendor": null
}
},
"ansible_distribution": "CentOS",
"ansible_distribution_major_version": "7",
"ansible_distribution_release": "Core",
"ansible_distribution_version": "7.1.1503",
"ansible_domain": "mylabserver.com",](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/785c18bb-35c1-4f14-9208-7fe89859172b-160106093423/85/Ansible-automation-tool-with-modules-11-320.jpg)