1. The document analyzes factors that lead to content going viral on social media, such as emotions, author influence, and content type.
2. Models like random forests and support vector machines were used to predict popularity based on features like title sentiment and LIWC analysis. These achieved over 84% accuracy.
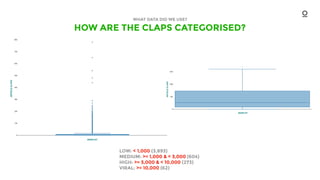
3. Causality analysis through randomized experiments found that altering article tone to induce more negative emotions increased likes and comments, but decreased shares, indicating anger may provoke reaction but not widespread sharing.