The Secondary One (Special/Express) Mathematics Syllabus covers topics in arithmetic including whole numbers, fractions, decimals, approximation, estimation, and use of a scientific calculator. It also includes squares, square roots, cubes, cube roots and number sequences. Key areas of focus are the four arithmetic operations, ordering of numbers, factors and multiples, and rounding numbers to a specified degree of accuracy. The syllabus aims to develop students' conceptual understanding and skills in calculating with whole numbers, fractions, decimals and real numbers.























![NORMAL ACADEMIC PART B
27
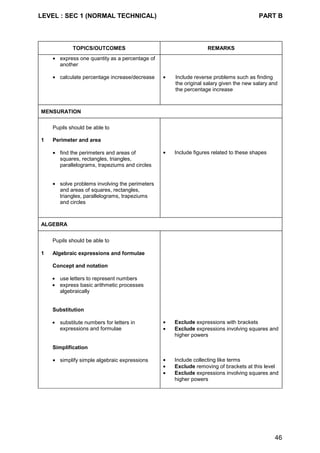
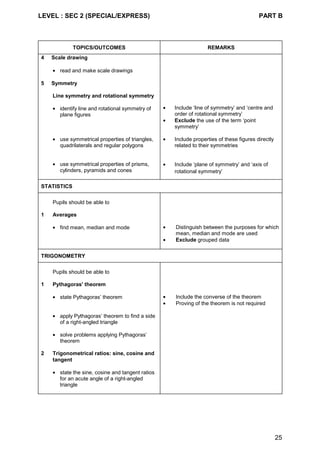
Content Chart - Secondary One & Two (Normal [Academic] Course)
Secondary One Secondary Two
1 Whole numbers
• the four operations
• ordering
• factors and multiples
2 Fractions and decimals
• concept and notation
• ordering
• the four operations
3 Approximation and estimation
• rounding off
• estimation
4 Use of a scientific calculator
5 Squares, square roots, cubes and
cube roots
6 Number sequences
7 Measures and money
8 Ratio, proportion and rate
9 Percentage
10 Real numbers
• integers
• rational and irrational numbers
1 Simple financial transactions
2 Arithmetic problems
3 Standard form
4 Number sequences
1 Perimeter and area
• square, rectangle, triangle,
parallelogram, trapezium, circle
2 Volume and surface area
• cube, cuboid, prism, cylinder
1 Volume and surface area
• sphere, pyramid and cone
2 Arc length and sector area
1 Algebraic expressions and
formulae
2 Simple algebraic manipulation
1 Algebraic manipulation and
formulae
2 Solutions of equations
• simple linear equations
• simultaneous linear equations
• simple fractional equations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singaporemathssyllabus-181018083734/85/Singapore-maths-syllabus-27-320.jpg)
![NORMAL ACADEMIC PART B
28
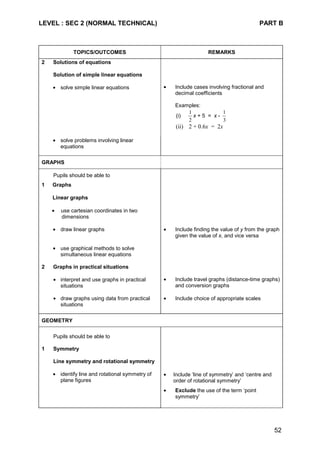
Content Chart - Secondary One & Two (Normal [Academic] Course)
Secondary One Secondary Two
1 Graphs of linear and quadratic
functions
2 Graphs in practical situations
1 Simple plane figures
2 Simple solid figures
3 AngIe properties
• angles formed with a common
vertex
• angles formed with parallel lines
• angle properties of triangles
• angle properties of squares,
rectangles, parallelograms and
rhombuses
4 Geometrical construction of
simple geometrical figures
1 Similar and congruent figures
2 Angle properties of polygons
3 Scale drawing
4 Symmetry
• line symmetry
• rotational symmetry
1 Handling data
• table and chart
• pictogram
• dot diagram
• bar graph
• line graph
• pie chart
• stem and leaf diagram
• histogram
1 Averages
• mean
• mode
• median
1 Problem solving heuristics
2 Practical uses of Mathematics
1 Problem solving heuristics
2 Practical uses of Mathematics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singaporemathssyllabus-181018083734/85/Singapore-maths-syllabus-28-320.jpg)










![NORMAL TECHNICAL PART B
41
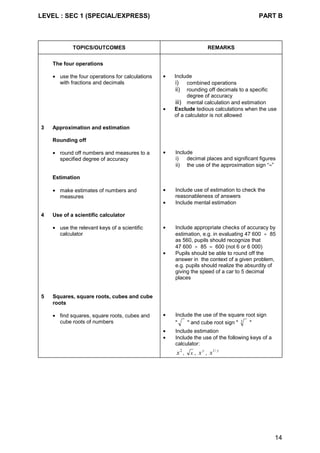
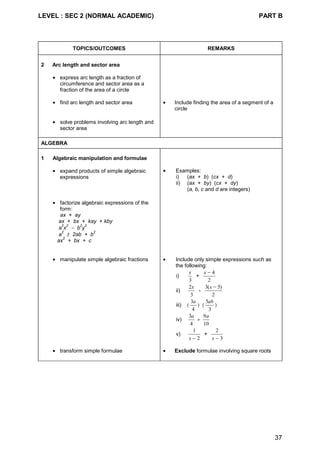
Content Chart - Secondary One & Two (Normal [Technical] Course)
Secondary One Secondary Two
1 Whole numbers
• the four operations
• ordering
• factors and multiples
2 Fractions and decimals
• concept and notation
• ordering
• the four operations
3 Approximation and estimation
• rounding off
• estimation
4 Use of a scientific calculator
5 Squares, square roots, cubes and
cube roots
6 Measures and money
7 Ratio, proportion, scale, rate and
speed
8 Percentage
1 Simple financial transactions
2 Arithmetic problems
3 Directed numbers
• concept and notation
• ordering
• the four operations
4 Number sequences
1 Perimeter and area
• square
• rectangle
• triangle
• parallelogram
• trapezium
• circle
1 Volume and surface area
• cube
• cuboid
• prism
• cylinder
1 Algebraic expressions and
formulae
• concept and notation
• substitution
• simplification
1 Algebraic expressions and
formulae
• substitution
• manipulation
2 Solutions of simple linear
equations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singaporemathssyllabus-181018083734/85/Singapore-maths-syllabus-41-320.jpg)
![NORMAL TECHNICAL PART B
42
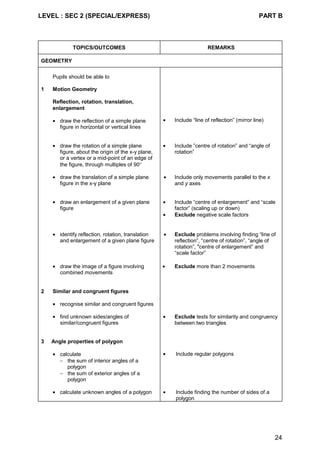
Content Chart - Secondary One & Two (Normal [Technical] Course)
Secondary One Secondary Two
1 Linear graphs
2 Graphs in practical situations
1 Simple plane figures
2 Simple solid figures
3 AngIe properties
• angles formed with a common
vertex
• angles formed with parallel
lines
• angle properties of triangles
• angle properties of squares,
rectangles, parallelograms and
rhombuses
4 Construction of triangles
1 Symmetry
• line symmetry
• rotational symmetry
2 Angle properties of polygons
3 Geometrical construction
• simple four-sided figures
• scale drawing
1 Handling data
• table and chart
• pictogram
• dot diagram
• bar graph
• line graph
• pie chart
• histogram
1 Averages
• mean
• mode
• median
1 Problem solving heuristics
2 Practical uses of Mathematics
3 Mathematics for leisure and
recreation*
1 Problem solving heuristics
2 Practical uses of Mathematics
3 Mathematics for leisure and
recreation*
*Non-examination topic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singaporemathssyllabus-181018083734/85/Singapore-maths-syllabus-42-320.jpg)