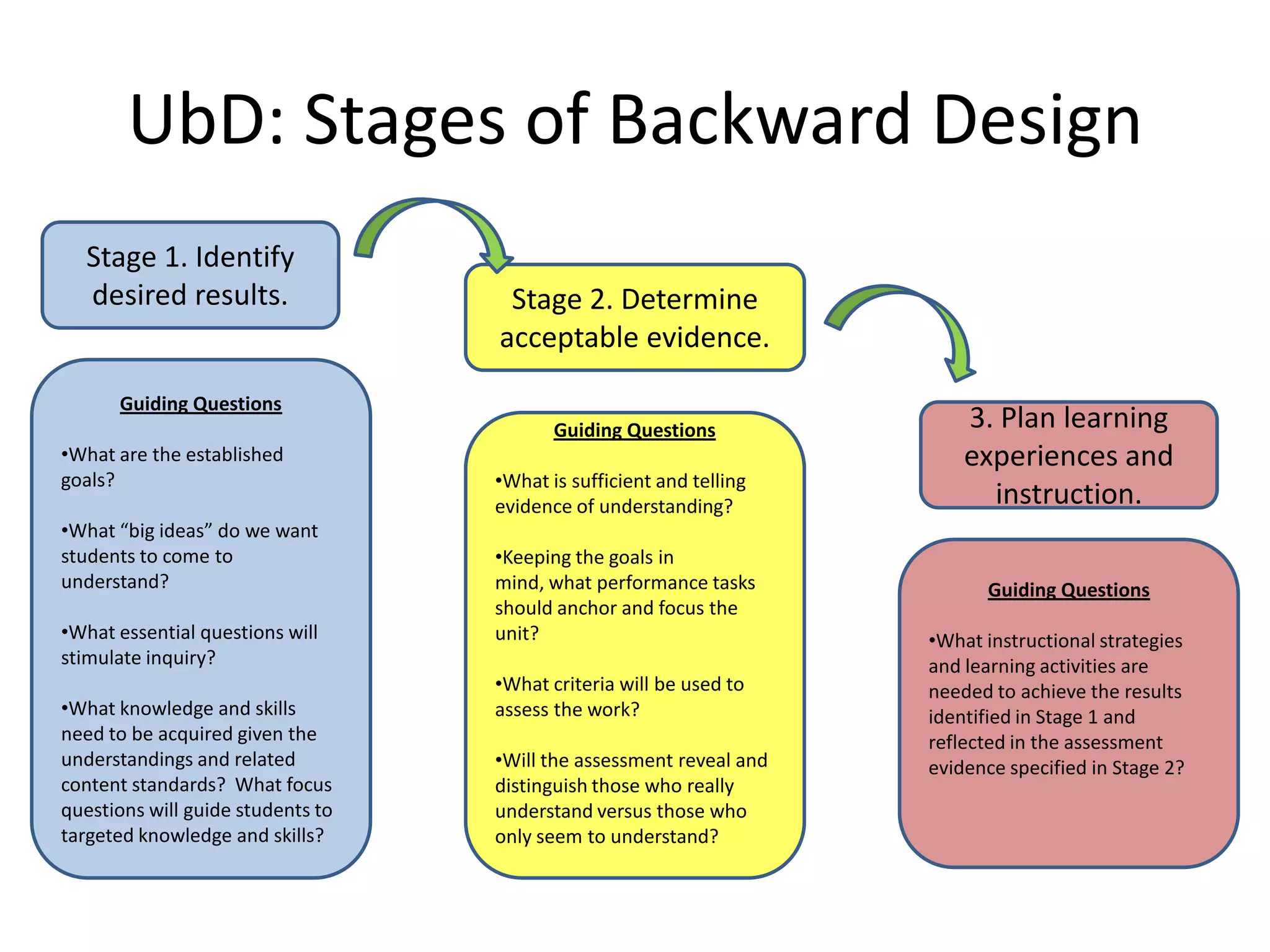
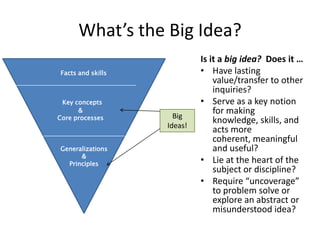
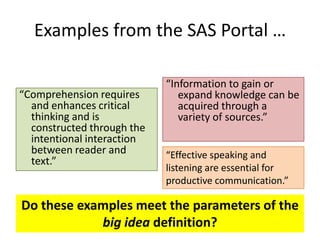
1. A big idea is "information literacy enhances lifelong learning."
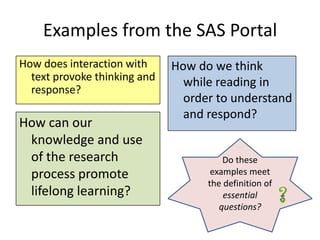
2. An essential question is "How can we evaluate information from different sources to expand our understanding?"
3. A concept is "research is a process of gathering, analyzing, and communicating information to answer questions."