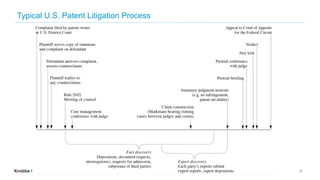
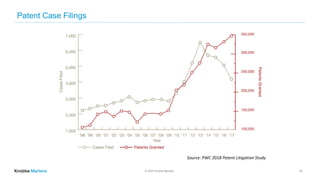
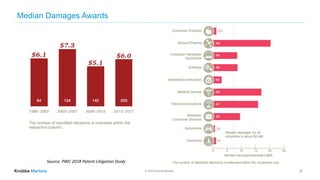
This document outlines the scope and services of Knobbe Martens, a law firm specializing in intellectual property (IP) procurement and protection in the United States. It details various types of IP, including patents, trademarks, trade secrets, and copyrights, and emphasizes the importance of legal protection and strategic management for businesses. Additionally, it discusses the patent litigation process, common mistakes made by applicants, and the enforcement mechanisms for trademarks and trade secrets.