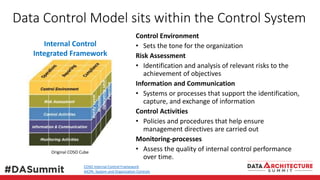
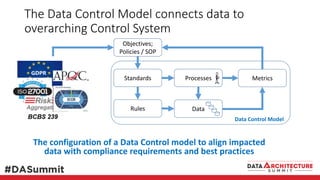
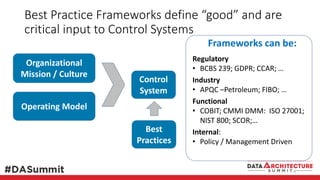
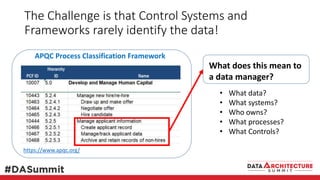
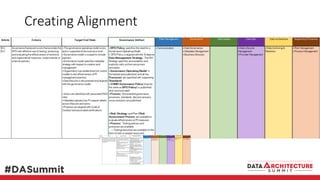
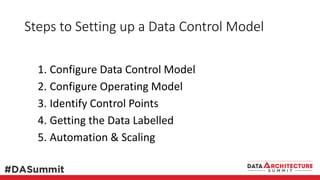
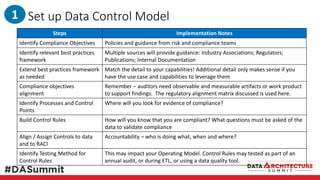
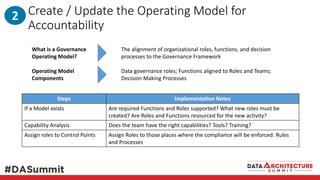
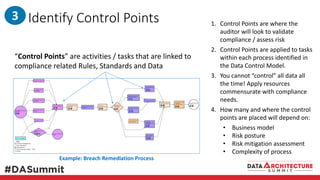
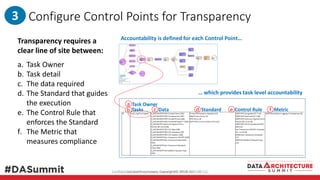
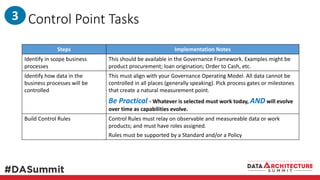
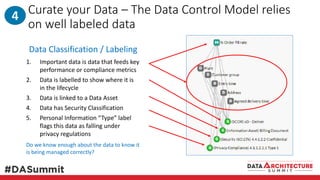
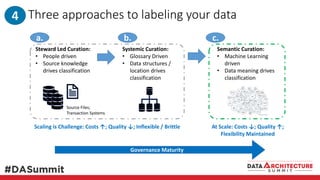
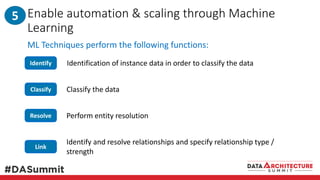
The document outlines the framework for compliance and risk management in data governance, emphasizing the importance of establishing robust data control models that link data with compliance requirements. It provides detailed steps for creating and implementing these models, including identifying control points, labeling data, and ensuring accountability through defined roles and processes. The overall goal is to enhance audit defensibility and manage compliance risks effectively across various organizational processes.