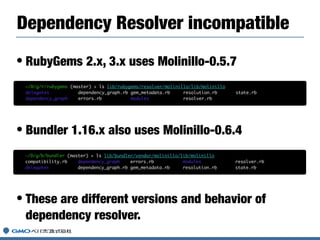
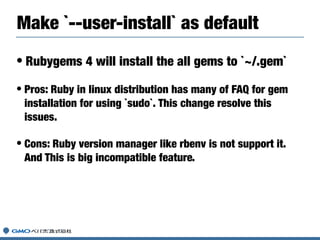
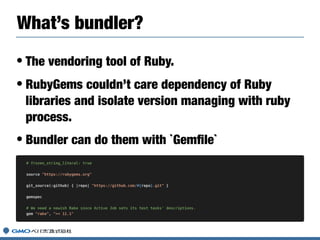
Hiroshi Shibata gave a presentation on Ruby, RubyGems, and Bundler. He discussed his work on the Ruby core team maintaining Ruby versions like 2.6. He then covered updates to RubyGems including version 3 and the upcoming version 4. Finally, he talked about Bundler 2 and efforts to better integrate RubyGems and Bundler.


![self.introduce
=> {
name: “SHIBATA Hiroshi”,
nickname: “hsbt”,
organizations: [“ruby”, “rubygems”, “bundler”,
“asakusarb”, “railsgirls”, “pepabo”, …],
commit_bits: [“ruby”, “rake”, “rubygems”, “bundler”,
“rdoc”, “psych”, “json”, “ruby-build”, “railsgirls”,
“railsgirls-jp”, …],
sites: [“hsbt.org”, “ruby-lang.org”, “rubyci.org”,
“railsgirls.com”, “railsgirls.jp”],
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20181026-rubyconfmy-2018-181025080830/85/Gems-on-Ruby-3-320.jpg)

















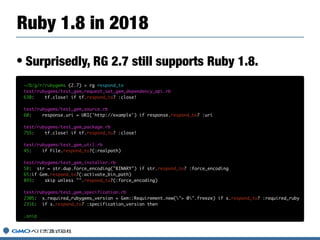
![• Removed deprecated methods.
• Removed to support for < Ruby 2.2.
• Added warnings of deprecated methods.
• Removed deprecated options.
• [CAUTION] `--ri` and `--rdoc` options
What’s new in RubyGems3?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20181026-rubyconfmy-2018-181025080830/85/Gems-on-Ruby-26-320.jpg)


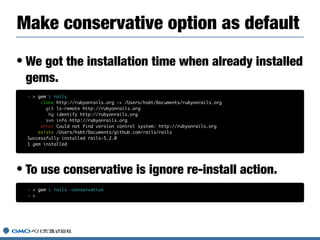




![• Bundler was located rubygems repository as git
submodule
Bundler Integration(rubygems.rb)
if USE_BUNDLER_FOR_GEMDEPS
ENV["BUNDLE_GEMFILE"] ||= File.expand_path(path)
require 'rubygems/user_interaction'
Gem::DefaultUserInteraction.use_ui(ui) do
require "bundler"
@gemdeps = Bundler.setup
Bundler.ui = nil
@gemdeps.requested_specs.map(&:to_spec).sort_by(&:name)
end
else
rs = Gem::RequestSet.new
@gemdeps = rs.load_gemdeps path
rs.resolve_current.map do |s|
s.full_spec.tap(&:activate)
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20181026-rubyconfmy-2018-181025080830/85/Gems-on-Ruby-38-320.jpg)