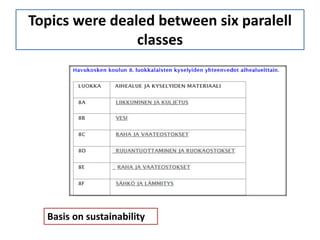
This document contains summaries of several topics discussed in classes at Havukosken koulu Spring 2015, including:
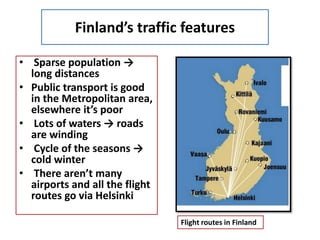
- Finland's sparse population and long distances require extensive transportation infrastructure and energy usage.
- Ways to reduce traffic emissions include lowering car taxes, biking/walking for short trips, public transit for long trips, and ridesharing.
- Wood is Finland's most important domestic source of energy as burning wood releases the stored chemical energy and is renewable.