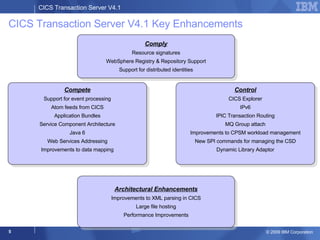
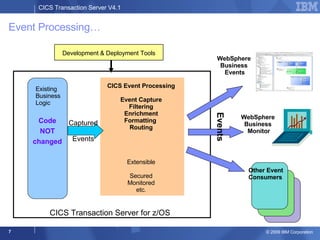
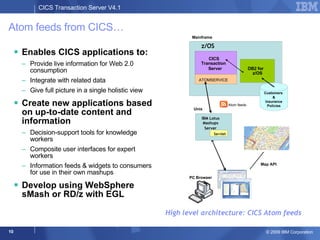
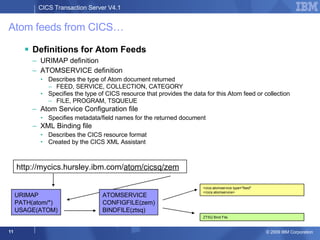
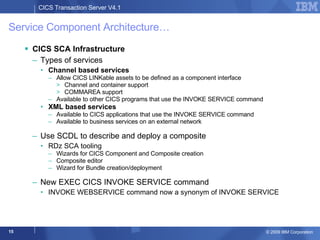
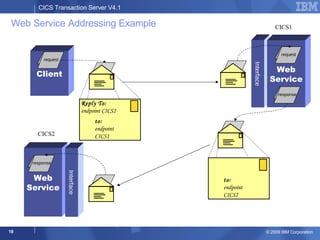
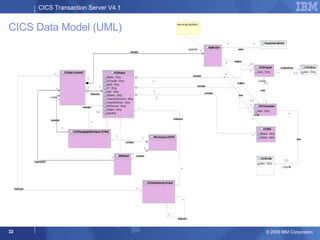
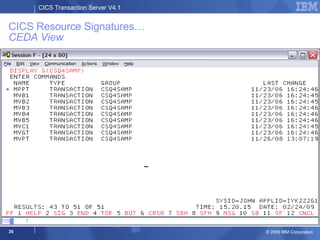
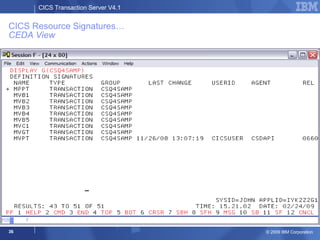
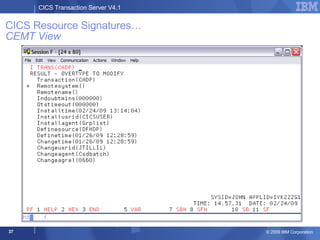
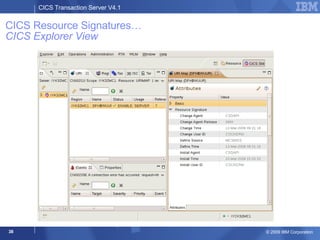
The document provides an overview of new features in CICS Transaction Server V4.1, including enhancements to support event processing, Atom feeds, service component architecture, Java 6, and Web services addressing. Key goals of the new release are to help customers compete by responding quickly to business needs, comply with regulations, and control costs through simplified management and development.
![CICS Transaction Server for z/OS V4.1 Technical Overview Tom Grieve [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cicsts4-1technicaloverview-090417164337-phpapp01/85/Cics-Ts-4-1-Technical-Overview-1-320.jpg)