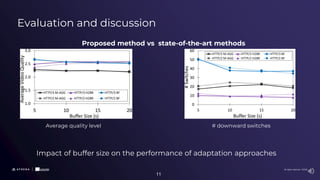
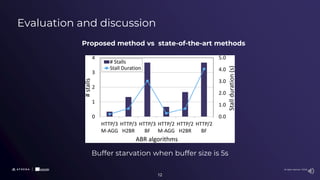
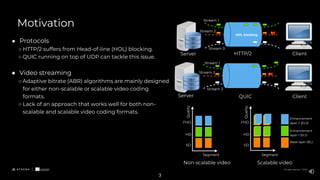
The document presents a comparative study of scalable high-efficiency video coding over HTTP/3 using QUIC and its advantages over HTTP/2 with TCP, addressing issues like head-of-line blocking. It proposes a novel adaptive bitrate algorithm combining non-scalable and scalable video streaming techniques for improved video quality and adaptability. The findings indicate that while QUIC enhances performance during packet loss, the proposed method can risk buffer starvation under certain conditions.



![All rights reserved. ©2020
Proposed method
● State-of-the-art ABR algorithms
○ Non-scalable based method: Aggressive ABR (AGG)
○ Scalable based method: Backfilling
● Proposed method for Scalable Video Streaming
○ Modified AGG + HTTP/2-Based Retransmission technique (H2BR)
○ Modified AGG
■ Choosing the number of layers for each segment based on the
network condition,
■ Downloading sequentially from low to high layers of each segment.
○ H2BR [PV’20]
■ Filling quality gaps in the buffer,
■ Downloading concurrently next layers and the additional layer with
priority and multiplexing features,
■ Terminating layers with termination feature.
Scalable based Backfilling
Modified non-scalable based
AGG
Modified non-scalable based
AGG + H2BR
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/epiq-presentationscalablehighefficiencyvideocodingbasedhttpadaptivestreamingoverquic-200815140339/85/Scalable-High-Efficiency-Video-Coding-based-HTTP-Adaptive-Streaming-over-QUIC-Using-Retransmission-5-320.jpg)