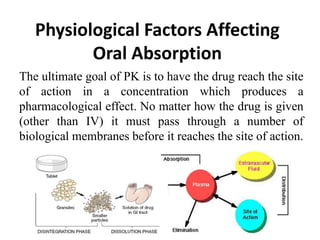
Pharmacokinetics / Biopharmaceutics - physiological factors affecting oral absorption
- 1. Physiological Factors Affecting Oral Absorption The ultimate goal of PK is to have the drug reach the site of action in a concentration which produces a pharmacological effect. No matter how the drug is given (other than IV) it must pass through a number of biological membranes before it reaches the site of action.
- 2. Pharmacokinetics of Drug Absorption • The systemic drug absorption from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract or from any other extravascular site is dependent on: 1) The physicochemical properties of the drug. 2) The dosage form used. 3) The anatomy and physiology of the absorption site.
- 3. Factors Affecting Absorption • Formulation factors –Tablet disintegration –Inert ingredient / solvent effects –Solubility –Drug pka –Concentration • Patient factors –Absorbing surface –Blood flow –pH –Disease states –Interactions with food, other drugs
- 4. The physicochemical properties of the drug • pH - partition theory – For a drug to cross a membrane barrier it must normally be soluble in the lipid material of the membrane to get into membrane, also it has to be soluble in the aqueous phase as well to get out of the membrane. – Most drugs have polar and non-polar characteristics or are weak acids or bases. – For drugs which are weak acids or bases the pKa of the drug and the pH of the GI tract fluid and the pH of the blood stream will control the solubility of the drug and thereby the rate of absorption through the membranes, lining the GI tract.
- 5. Formulation factors • A drug must be in solution to be absorbed from the GI tract. • The bioavailability of a drug decrease in the order: solution > suspension > capsule > tablet > coated tablet This order may not always be followed but it is a useful guide.
- 6. Pharmacokinetics of Drug Absorption • For oral dosing, such factors affect the rate and the extent of drug absorption: i. surface area of the GI tract. ii. stomach-emptying rate. iii. GI mobility. iv. blood flow to the absorption site.
- 7. pH Membrane Blood Supply Surface Area Transit Time By-pass liver BUCCAL approx 7 thin Good, fast absorption with low dose small Short unless controlled yes ESOPHAGUS 5 - 6 Very thick, no absorption - small short - STOMACH 1 - 3 decomposition, weak acid unionized normal good small 30 - 40 minutes, reduced absorption no DUODENUM 6 - 6.5 bile duct, surfactant properties normal good very large very short (6" long), window effect no SMALL INTESTINE 7 - 8 normal good very large 10 - 14 ft, 80 cm 2 /cm about 3 hours no LARGE INTESTINE 5.5 - 7 - good not very large 4 - 5 ft long, up to 24 hr rectum yes GI Physiology and Drug Absorption
- 11. Gastric emptying and motility • Generally drugs are better absorbed in the small intestine (because of the larger surface area) than in the stomach, therefore increasing stomach emptying will increase drug absorption. • The quicker the stomach emptying the higher the plasma concentration. • Also slow stomach emptying can cause increased degradation of drugs in the stomach's lower pH; e.g. L-dopa.
- 12. Food • Food can effect the rate of gastric emptying. • For example fatty food can slow gastric emptying and retard drug absorption. Generally the extent of absorption is not greatly reduced. • Occasionally absorption may be improved. Griseofulvin absorption is improved by the presence of fatty food. Apparently the poorly soluble griseofulvin is dissolved in the fat and then more readily absorbed.
- 13. • Propranolol plasma concentrations are larger after food than in fasted subjects. This may be an interaction with components of the food. The Effect of Fasting versus Fed on Propranolol Concentrations
- 14. Passage of Drugs across Biological membrane • Transport across the membranes Transcellular transport Passive diffusion Carrier-mediated transport Facilitated diffusion Active transport Ion-pair transport Endocytosis or Pinocytosis Paracellular transport Bulk flow Filtration
- 15. Transcellular transport Passive diffusion Most (many) drugs cross biologic membranes by passive diffusion. Diffusion occurs when the drug concentration on one side of the membrane is higher than that on the other side. Drug diffuses across the membrane in an attempt to equalize the drug concentration on both sides of the membrane. Drugs that can passively diffuse through cell membrane must be: • Lipid soluble • Unionized form • Move according to concentration gradient
- 17. Carrier-mediated transport 1. Facilitated diffusion Carrier needed Can be saturated No energy required Move along conc. Gradient e.g. vitamin B12 transport. 2. Active transport Carrier needed Can be saturated Energy required Move against conc. Gradient competitive inhibition is possible E.g. glucose and amino acids
- 18. 3. Carrier-mediated intestinal transport (P-gp) • P-glycoprotein (P-gp, MDR-1) is a 170 kDa membrane-bound protein. • P-gp transporters are present throughout the body including liver, brain, kidney and the intestinal tract epithelia. • This is an active, ATP-dependent process which can have a significant effect on drug bioavailability. • They appear to be an important component of drug absorption acting as reverse pumps generally inhibiting absorption. They work as efflux transporters and provide a defense mechanism against harmful substances. They transport certain hydrophobic substances in the following direction: Into the gut Out of the brain Into bile Into urine Out of the gonads Out of other organs
- 19. • P-glycoprotein works against a range of drugs such as cyclosporin A, digoxin, β-blockers, antibiotics and others. This process has been described as multi-drug resistance (MDR). • Additionally P-glycoprotein has many substrates in common with cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP 3A4) thus it appears that this system not only transports drug into the lumen but causes the metabolism of substantial amounts of the drug as well (e.g. cyclosporin). • Clinically significant substrates of P-gp include digoxin, cyclosporine, fexofenadine, paclitaxel, nortriptyline and phenytoin. • A number of compounds can act as P-gp inhibitors including atorvastatin, ketoconazole or erythromycin (digoxin AUC increased) and grapefruit juice (increased paclitaxel absorption). • Rifampin has been reported to induce P-gp expression.
- 20. Vesicular Transport Pinocytosis and phagocytosis Macromolecules are transported by endocytosis or exocytosis e.g. Vitamin A, D, E, and K, Ion-pair transport e.g. Propranolol and Quinine For example, the formation of ion pairs to facilitate drug absorption has been demonstrated for propranolol, a basic drug that forms an ion pair with oleic acid
- 21. Paracellular Transport Pore (convective) Transport Bulk flow and Filtration • Very small molecules (such as urea, water, and sugars) are able to cross cell membranes rapidly, as if the membrane contained channels or pores. • Filtration is an important way to excrete drugs
- 22. Passage of Drugs across Biological membrane • Drug properties Molecular weight, shape and size Small molecules – more chance of crossing membrane
- 23. Passage of Drugs across Biological membrane • Lipid solubility • Movement directly through the lipid bilayer requires that the substance dissolve into the lipid bilayer Increase lipid solubility causes increased partition coefficient Increase in partition coefficient causes increased permeability. Permeability Kp
- 24. Ionization General rules A drug usually exists in 2 forms – unionized and ionized forms. Unionized drug can passively diffuse across membrane The ratio of unionized drug will indicate direction of passive diffusion Factors affecting ionization are pH of the medium pKa (acid dissociation constant) of the drug Acidic drug tend to ionize in more basic medium pH – pKa = log (ionized / nonionzized) Basic drug tend to ionize in more acidic medium pH – pKa = log (nonionized / ionized)24
- 25. Ionization • Henderson-Hasselbach Equations for calculations pH = pK + log [H+ acceptor] [H+ donor] 25
- 26. Stomach fluid pH 2 Plasma pH 7 More non-ionized Ionized Less non-ionized Ionized Example Acidic drug pKa 6 pH – pKa = log (ionized / non-ionized) 26
- 27. Some data for practice calculation pH Plasma 7.4 CSF 7.4 Stomach 1.4 Small Intestine 8.0 Acidic drug pKa Basic drug pKa Ampicillin 2.5 Strychnine 8.0 Sulfadiazine 6.5 Aminopyrine 5.0 Aspirin 3.4 Procaine 9.0 27
- 28. Routes of Drug Administration • The route of administration (ROA) that is chosen may have a profound effect upon the speed and efficiency with which the drug acts. • Appropriate administration route depends on: the dosage form in which the drug is available the patient’s age the patient’s condition, e.g. level of consciousness
- 29. Sublingual/buccal • Some drugs are taken as smaller tablets which are held in the mouth or under the tongue. • Advantages: rapid absorption drug stability avoid first-pass effect Ideal for lipid soluble drugs Absorption favored of acids with high pka and bases with low pka • Disadvantages inconvenient small doses unpleasant taste of some drugs
- 30. Rectal • Advantages: unconscious patients and children if patient is nauseous or vomiting Bypassing first pass effect (partially) good for drugs affecting the bowel such as laxatives • Disadvantages absorption may be variable irritating drugs contraindicated discomfort
- 31. Intravenous (IV) • Advantages: complete bioavailability precise, accurate and almost immediate onset of action, large quantities can be given, fairly pain free • Disadvantages greater risk of adverse effects high concentration attained rapidly (anaphylaxis) risk of embolism Cost Drug suspensions cannot be used
- 32. Subcutaneous slow and constant absorption absorption is limited by blood flow, affected if circulatory problems exist concurrent administration of vasoconstrictor will slow absorption Intramuscular rapid absorption of drugs in aqueous solution depot and slow release preparations pain at injection sites for certain drugs
- 33. Inhalation • Gaseous and volatile drugs may be inhaled and absorbed by the pulmonary epithelium and mucous membranes of respiratory tract. -almost instantaneous absorption, -large surface area of alveoli (~72 m2) -high permeability of alveolar membrane -avoids first-pass metabolism • Local application (mainly) • Difficulties in regulating the exact amount of dosage. • Sometimes patient having difficulties in giving themselves a drug by inhaler.
- 34. Oral Administration • Advantages: Generally the safest route Convenient - can be self- administered, pain free, easy to take Absorption - takes place along the whole length of the GI tract Cheap - compared to most other parenteral routes No need for sterile equipment Variety: tablets, capsules, fast, slow release …..
- 35. Oral Administration • Disadvantages Sometimes inefficient - only part of the drug may be absorbed. First-pass effect - drugs absorbed orally are initially transported to the liver via the portal vein Irritation to gastric mucosa - nausea and vomiting Destruction of drugs by gastric acid and digestive juices, gut flora, mucosal enzymes Onset of effect is slow unpleasant taste of some drugs unable to use in unconscious patient Food interaction and G-I motility can affect drug absorption
- 40. Physiological Factors – Gastric motility – Gastric emptying time – pH at the absorption site – Area of absorbing surface – Blood flow – Disease states – Ingestion with or without food 40
- 41. Oral drug absorption Oral cavity: Saliva is the main secretion (1500 mL/day) Saliva contains amylases The pH is 6-7 Highly vascular area Esophagus: pH of 5-6 No drug absorption from this site Very little dissolution
- 42. Stomach : The surface area for absorption of drugs is relatively small in the stomach due to the absence of macrovilli & microvilli. Extent of drug absorption is affected by variation in the time it takes the stomach to empty, i.e., how long the dosage form is able to reside in stomach. Drugs which are acid labile must not be in contact with the acidic environment of the stomach. pH of 1.5 -2 (fed-state) or 2 – 6 (fasted-state). HCl secretion of the stomach is stimulated by gastrin and histamine. High-density foods generally are emptied from stomach more slowly.
- 43. Small Intestine: Include duodenum, jejunum and ileum. Major site for absorption of most drugs due to its large surface area. The Folds in small intestine called as folds of kerckring, result in 3 fold increase in surface area. These folds possess finger like projections called Villi which increase the surface area 30 times. From the surface of villi protrude several microvilli which increase the surface area 600 times. Blood flow is 6-10 times that of stomach. pH Range is 6–7.5 , favorable for most drugs to remain unionised.
- 44. Small Intestine: Peristaltic movement is slow, while transit time is long. Permeability is high. The drugs which are predominantly absorbed through the small intestine, the transit time of a dosage form is the major determinant of extent of absorption. the transit time in small intestine for most healthy adults is between 3 to 4 hours, and a drug may take about 4 to 8 hours to pass through the stomach & small intestine during fasting state. During the fed state, the small intestine transit time may take about 8 to 12 hours.
- 45. Large intestine: Include colon and rectum Lack villi Limited absorption from colon The major function of large intestine is to absorb water from ingestible food residues which are delivered to the large intestine in a fluid state, & eliminate them from the body as semi solid feces. pH ranging from 5.5-7 Colon contains microorganisms Only a few drugs are absorbed in this region.
- 46. Influence of drug pKa and GI pH on drug absorption Drugs Site of absorption Very weak acids (pKa > 8.0) Unionized at all pH values Absorbed along entire length of GIT Moderately weak acids (pKa 2.5 – 7.5) Unionized in gastric pH Ionized in intestinal pH Better absorbed from stomach Strong acids (pKa <2.5) Ionized at all pH values Poorly absorbed from GIT Very weak bases (pKa < 5) Unionized at all pH values Absorbed along entire length of GIT Moderately weak bases (pKa 5 – 11 ) Ionized in gastric pH Unionized in intestinal pH Better absorbed from intestine Strong bases (pKa >11) Ionized at all pH values Poorly Absorbed from GIT
- 47. GIT motility and Gastric Emptying • GI motility tends to move the drug through the alimentary canal. • For each drug there is an optimal absorption window. • Physiologic movement of drug within the GIT depends on fed/fasted state. • The time a dosage form takes to leave the stomach is usually termed: the gastric residence time, gastric emptying time.
- 48. • Rapid Gastric Emptying Advisable when : – Rapid onset of action is desired eg. Sedatives – Dissolution occurs in the intestine eg. Enteric coated tablets – Drugs not stable in GI fluids eg. penicillin G – Drug is best absorbed from small intestine eg. Vitamin B12 • Delay in Gastric Emptying recommended when – Food promotes drug dissolution and absorption e.g. Gresiofulvin – Disintegration and dissolution is promoted by gastric fluids
- 49. Factors affecting Gastric Emptying Volume of Ingested Material Bulky material tends to empty more slowly than liquids Type of Meal Gastric emptying rate: carbohydrates > proteins > fats Temperature of Food Increase in temperature, increase in emptying rate Body Position Lying on the left side decreases emptying rate and right side promotes it GIT pH Retarded at low stomach pH and promoted at higher alkaline pH Emotional state Anxiety and stress promotes where as depression retards it Disease states gastric ulcer, diabetes and hypothyroidism retards it, while duodenal ulcer, hyperthyroidism promotes it.
- 50. Effect of Food: - The presence of food in the GIT can influence the rate and extent of absorption, either directly or indirectly via a range of mechanisms. - As a general rule, drugs are better absorbed under fasting conditions. Presence of food may retard or prevent drug absorption. - Generally the extent of absorption is not greatly reduced. Occasionally absorption may be improved - Food does not significantly influence absorption of a drug taken half an hour or more before meals and two hours or more after meals.
- 51. Effect of Food: • Increased drug absorption following a meal can be due to the following reasons: a) Increased time for dissolution of poorly soluble drug. b) Enhanced solubility due to GI secretions like bile. c) Prolonged residence time and absorption site contact of the drug e.g. water-soluble vitamins.
- 52. Effect of Food: • Delayed or decrease drug absorption by food can be due to one or more of the following reasons: a) Delayed gastric emptying, affecting the drugs unstable in the stomach e.g. penicillin, erythromycin. b) Preventing the transit of enteric tablets into the intestine which may be as long as 6 – 8 hrs. c) Formation of poorly soluble, unabsorbable complex e.g. tetracycline- calcium complex. d) Alteration of pH e) Competition between food components and drugs for specialized absorption mechanisms
- 53. Effect of Food: • Types of meal a) Meals high in fat aid solubilisation of poorly aqueous soluble drugs like griseofulvin. b) Food high in proteins increases oral availability of propranolol because such a meal promotes blood flow to the GIT helping in drug absorption. increases hepatic blood flow due to which the drug can bypass first-pass hepatic metabolism (propranolol is a drug with high hepatic metabolism)
- 54. Effect of Fasting versus Fed on Metaxalone Concentrations
- 55. A comparison of the effects of different types of food intake on the serum griseofulvin levels following 1.0 g oral dose
- 56. Effect of water volume and meal on the bioavailability of some drugs F aspirin (650-mg) tablets, erythromycin stearate (500- mg) tablets, amoxicillin (500-mg) capsules, and theophylline (260-mg) tablets, together with large and small accompanying volumes of water.
- 57. Theophylline serum concentrations in an individual subject after a single 1500 mg Theo-24 Theophylline serum concentrations in an individual subject after a single 1500-mg dose of Theo-24 taken during fasting and after breakfast. The shaded area indicates the period during which this patient experienced nausea, repeated vomiting, or severe throbbing headache. The pattern of drug release during the food regimen is consistent with "dose dumping."
