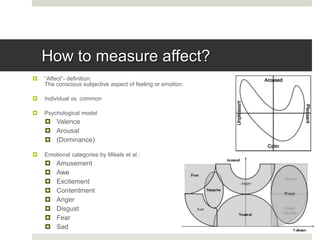
This document discusses affective image classification using features inspired by psychology and art theory. It summarizes the context and motivation, contributions, and system flow of the research. The research aims to classify images into emotional categories defined by psychological studies using features designed to capture emotional aspects. The system extracts color, texture, composition and content features from images and uses a naive Bayes classifier to classify images from three datasets into emotional categories like amusement, awe, excitement, and sadness. Evaluation shows the emotion-specific features perform better than general features at classifying images, though humans also disagree on emotional categories for abstract images without context.