Ecosystem Types.pptx
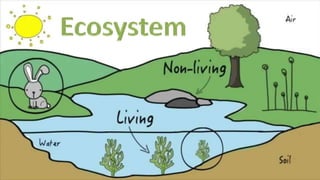
- 2. Ecosystem An ecosystem includes all of the living things (plants, animals and organisms) in a given area, interacting with each other, and also with their non-living environments (weather, earth, sun, soil, climate, atmosphere).
- 3. Types of ecosystems • Forest ecosystem • Grassland ecosystem • Desert ecosystem • Aquatic ecosystem
- 5. Forests • Forests are formed by a community of plants which predominantly includes trees, shrubs, climbers and ground cover.
- 6. Forest ecosystem • A forest ecosystem is the community formed by plants and animals of that particular area that interact with the chemical and physical features of the environment in which they live. Example: Amazon rainforest ecosystem • This ecosystem is home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, which include producers, consumers, and decomposers. These organisms are interdependent on each other for survival.
- 7. The forest ecosystem has two parts: • The non-living or abiotic aspects: Forests on mountains and hills differ from those along river valleys. Vegetation type depends on: – Rainfall – Temperature – Latitude – Altitude – Soil type • The living or the biotic aspects: The plants and animals form communities that are specific to each forest type. – Plants (trees, shrubs, climbers, grasses, and herbs ) – Animals including species of mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, insects and other invertebrates. Forest ecosystem
- 8. Structure of Forest Ecosystems • Different organisms exist within the forest layers and interact with each other and their surroundings. Each organism has a role or niche in sustaining the ecosystem. • Some provide food for other organisms; others provide shelter or control populations through predation. Producers • In a forest ecosystem, plants get their energy from sunlight. • They produce their own food through • photosynthesis. • Plants are called the primary producers since they produce the basic foodstuffs for other organisms within food chains and food webs.
- 10. Structure of Forest Ecosystems Consumers – Animals cannot produce their own food. All animals, including mammals, insects, birds and others are called consumers. – Consumers rely on plants and other animals as a food source. – Primary consumers only eat plants and are referred to as herbivores. (Rabbit, Deer) – Secondary consumers are referred to as carnivores and feed on herbivores. (Mongoose, Wild cat) – Tertiary consumers are carnivores that feed on other carnivores. (Tiger, Lion) – Omnivores eat both plant and animal matter.
- 11. Forest Ecosystem Animals • Tropical rain forest provides both shelter and food for huge number of animals which include: – birds like cuckoo bird, parrot, swallows, humming bird, eagles – mammals like orangutans ,monkeys, gibbons, tiger, foxes, hippopotamus, jaguar – reptiles like crocodiles, alligators, anaconda, flying gecko • Tropical deciduous forest contains animals like: – Mammals including deer, elephants, sambars, cheetahs, wild buffaloes, tiger, leopard – Birds – Reptiles – Amphibians • Coniferous forests consists of rich and varied animal life which includes: – mammals like mouse deer, musk, rat, porcupine, rabbit, squirrels etc. – insectivorous birds like grouse, jay cross bill – reptiles like snakes and lizards
- 12. Decomposers – Eventually all plants and animals die. These materials are decomposed by microbes. – Decomposers break down these complex organic matters into simpler forms which can then be used again. Decomposers are important in that they sustain the nutrient cycle of ecosystems. Structure of Forest Ecosystems
- 15. Desert • A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and consequently living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. About one third of the land surface of the world is arid or semi-arid. • The most typical desert landscape in India is seen in the Thar Desert, Rajasthan. • There are cold deserts such as in Ladakh, which are located in the high plateaus of the Himalayas. • The Great and Little Rann of Kutch are highly specialized arid ecosystems. In the summer they are similar to a desert landscape. However, as these are low-lying areas near the sea, they get converted to salt marshes during the monsoons • A desert ecosystem is defined by interactions between organism populations, the climate in which they live, and any other non-living influences on the habitat.
- 16. Different components of a desert ecosystem • Abiotic Component: – The abiotic component includes the nutrients present in the soil and the aerial environment. – The characteristic feature of the abiotic component is lack of organic matter in the soil and scarcity of water. – Extreme temperatures
- 17. Biotic Component: Producers – Mainly shrubs or bushes, some grasses and rarely trees. – Most of them are succulents which store water. – Others have seeds that lay dormant until a rain awakens them. – These plants are adapted to survive under extreme temperatures and acute water scarcity (xerophytic adaptation). – The most famous desert plant is the cactus. – Xerophytes can hold water inside its soft tissue, has a thick, waxy layer that minimize transpiration (water loss). Leaves are reduced to spines and roots are highly developed to search for water. Stems contains chlorophyll and modified to perform photosynthesis. Different components of a desert ecosystem
- 19. Biotic Component: Consumers These include animals such as insects and reptiles. Besides them, some rodents, birds and some mammalian vertebrates are also found. • Desert Insects and Arachnids: – There are plenty of insects in the desert. – One of the most common and destructive pests is the locust. – The yucca moth is very important to the yucca plant, and helps in pollination. – There are also several species of ants in the desert. The harvester ants gather seeds and store them for use during the dry season. The honey pot ants eat large amounts of sugar. – There are also arachnids in the desert. Spiders are the most notable arachnids. Some scorpions have poison in their sharp tails. They sting their predators and their prey with the piercing tip. Different components of a desert ecosystem
- 20. Yucca plant and Yucca Moth
- 21. Biotic Component: Consumers These include animals such as insects and reptiles. Besides them, some rodents, birds and some mammalian vertebrates are also found. • Desert Reptiles: – Reptiles can withstand the extreme temperatures because they can control their body temperatures very easily. The desert reptiles belong to two categories: snakes and lizards. – Snakes: Rattlesnakes, cobra, king snake and the hognose. – Lizards: They are probably the most bizarre looking animals in the desert. While some change colors and have sharp scales for defense, others change their appearance to look threatening. – Example: Frilled hazard, gila monster (poisonous) Different components of a desert ecosystem
- 22. Different components of a desert ecosystem Biotic Component: Consumers These include animals such as insects and reptiles. Besides them, some rodents, birds and some mammalian vertebrates are also found. • Desert Birds: – Birds come up with interesting ways to survive in the harsh climate. – The sand grouse has special feathers that soak up water. It can then carry the water to its young ones in the nest. – Gila woodpecker depends on the giant saguaro (cactus) as its home. The cool, damp inside is safe for the babies. – Others include roadrunners, ostriches and galahs.
- 23. Different components of a desert ecosystem Biotic Component: Consumers These include animals such as insects and reptiles. Besides them, some rodents, birds and some mammalian vertebrates are also found. • Desert Mammals: – Mammals also have to find ways to stay cool and drink plenty of water. – Many desert mammals are burrowers. They dig holes in the ground and stay there during the hot days. They return to the surface at night to feed. Hamsters, rats . – The kangaroo and spiny anteater both are non-burrowers. Spiny anteaters are unusual mammals because they lay eggs. – Others include foxes, jackals.
- 24. Different components of a desert ecosystem Biotic Component: Consumers These include animals such as insects and reptiles. Besides them, some rodents, birds and some mammalian vertebrates are also found. • Desert Mammals: – Another interesting mammal found in the deserts is camel. – There are two types of camels: Bactrian and dromedary. – Dromedaries have one hump, and Bactrian have two. – Camels can withstand very high temperatures without sweating. They also store fat in their humps for food.
- 25. Different components of a desert ecosystem Biotic Component: Decomposers • Due to poor vegetation the amount of dead organic matter is very less. As a result the decomposers are very few. • The common decomposers are some bacteria and fungi, most of which are thermophile.
- 28. Grassland • Grasslands are areas where the vegetation is dominated by grasses and other herbaceous (non-woody) plants. • Grasslands occupy about 24% of the earth’s surface. • They occur in regions too dry for forests and too moist for deserts. • The annual rainfall ranges between 25-75 cm, usually seasonal. • The principal grasslands includes: – Prairies (Canada, USA) – Pampas (South America) – Steppes (Europe and Asia) – Veldts (Africa) • The highest abundance and greatest diversity of large mammals are found in these ecosystems.
- 29. Different components of grassland ecosystem Biotic Components: • Producer Organisms: – In grassland, producers are mainly grasses; though, a few herbs and shrubs also contribute to primary production of biomass. – Some of the most common species of grasses are: Cynodon sp., Desmodium sp., Digitaria sp.
- 30. Different components of grassland ecosystem Biotic Components: • Consumers: In grassland, consumers are of three main types: • Primary Consumers: – The primary consumers are herbivores feeding directly on grasses. – These are grazing animals such as Cows, Buffaloes, Sheep, Goats, Deer, and Rabbits etc. – Besides them, numerous species of insects, termites, etc. are also present. • Secondary Consumers: – These are carnivores that feed on primary consumers (Herbivores). – These include Frogs, Snakes, Lizards, Birds, Foxes, Jackals etc. • Tertiary Consumers: – These include hawks etc. which feed on secondary consumers.
- 31. Different components of grassland ecosystem Biotic Components: • Decomposers: – These include wide variety of saprotrophic microorganism like: Bacteria; Fungi; Actinomycetes. Abiotic Components: • These include basic inorganic and organic compounds present in the soil and aerial environment. • The essential elements like C, H, N, O, P, S etc. are supplied by water, nitrogen, nitrates, sulphates, phosphates present in soil and atmosphere. • The structure of the grassland ecosystem will depend on: – Temperature – Rainfall – Soil chemistry
- 32. Types of grasslands Tropical Grasslands • Tropical grasslands are warm all year round with established rainy and dry seasons. • During the rainy season, they receive 50-130 cm of rain. • Most notable of the tropical grasslands is the African savanna, which is home to elephants, giraffes, lions, and zebras. • They make excellent grazing area. Temperate Grasslands • Temperate grasslands also have two seasons, growing and dormant. • During the dormant season, no grass or crops grow because it's too cold. • These grasslands make for excellent farming because of their deep and nutrient-rich soils. • Temperate grasslands receive 25-75 cm of rain a year. • The most notable temperate grasslands are the North American prairies, which are home to a wide variety of wildlife, including jackrabbits, foxes, and snakes. Grass here can grow quite tall, reaching up to seven meters in height. Trees are restricted to where there is a large concentration of water such as a river or lake.
- 33. Types of grasslands • Polar or tundra grasslands – They occur in high to subarctic regions. – These grasslands consist mainly of shrubs and have a very short growing season.
- 34. Types of grasslands • Montane grasslands – – These are high-altitude grasslands located on high mountain ranges and valleys. A notable example of montane grasslands is the paramo of the Andes. • Xeric or desert grasslands – These are very sparse grasslands located in and on the outskirts of deserts. – Grass here is highly resistant to disease and drought.
- 37. Aquatic ecosystem • Communities of plants and animals living in water are known as aquatic ecosystems. • They are divided into two main groups: – Freshwater ecosystems: Found in water containing low concentrations of salts, from ponds to estuaries. – Marine ecosystems: Found in the saltwater of seas and oceans. • The nature of an aquatic ecosystem is controlled by: – Availability of food – Dissolved Oxygen – Temperature – Salinity – Sunlight penetration • Aquatic ecosystems in shallow waters, where there is plenty of sunlight, generally tend to be the most productive.
- 38. Lake and Pond ecosystem • A pond ecosystem refers to fresh water ecosystem. • Usually ponds are shallow water bodies with a depth of 12-15 feet in which the sun rays can penetrate to the bottom permitting the growth of plants there. Abiotic components: – The abiotic substances of Pond ecosystem are formed as a result of the mixture of some organic and inorganic materials. – The basic components are • Water • Oxygen • carbon dioxide • salts of calcium and nitrogen etc. – Only a small amount of these elements are present in soluble state in pond water, but a large amount is held in reserve solid form in the bottom sediments as well as within the organisms. – The rate of release of reserve nutrients ,the solar input and the cycle of temperature, day length and other climatic conditions regulate the function of the Pond ecosystem.
- 39. • Lakes and ponds are also known as lentic ecosystems and are characterized by a lack of water movement. • They are divided into four distinct zones: – Littoral – Limnetic – Profundal – Benthic. • Light penetrates the uppermost of these, the littoral, which contains floating and rooted plants. • The other zones also each play unique roles in the ecosystem. Lake and Pond ecosystem
- 40. Lake and Pond ecosystem Biotic components: • Producers: – The producers are of two types: • Larger rooted and floating vegetation together termed macrophytes • Phytoplanktons which are microscopic floating algae. – Phytoplanktons are available upto the depth of water where light penetrates. These are filamentous alga like Oedogonium, Spirogyraand minute floating plants – The macrophytes include Typha, submerged plants plants like Pistia. marginal emergent plants like like Hydrilla, surface floating
- 41. Biotic components: • Consumers: – Consumers of the Pond ecosystem are heterotrophs which depend for their nutrition on other organisms. – Zooplankton form primary consumers including dinoflagellates, crustaceans, chordates, and molluscs who feed on phytoplankton. – Neritic animals like insects and fishes form secondary consumers as they feed on zooplanktons. – Benthic animals like snakes a n d big fishes live on neritic animals and are termed tertiary consumers. Lake and Pond ecosystem
- 42. Biotic components: • Decomposers: – Most of the decomposers also found. of Pond ecosystem are saprophytes but some parasites are – Bacteria as well as fungi like Saprolegnia are decomposers. – Generally the decomposers either live in the soil layer beneath water or in the mud. – They act on dead and decayed organic matter of plants and animals and supply raw materials to the producers. Lake and Pond ecosystem
- 43. River and stream ecosystem • River and stream ecosystems can be characterized by: – flowing water that is mostly unidirectional – a state of continuous physical change – many different and changing microhabitats – variability in the flow rates of water – plants and animals that have adapted to live within water flow conditions. • Biotic components are similar to pond ecosystem.
- 44. River and stream ecosystem Abiotic components: • Water flow – Water flow is the main factor that makes river ecology different from other water ecosystems. – This is known as a lotic (flowing water) system. – The strength of water flow varies from torrential rapids to slow backwaters. – The speed of water also varies and is subject to chaotic turbulence. – Water flow can alter the shape of riverbeds through erosion and sedimentation, creating a variety of changing habitats. • Substrate – The substrate is the surface on which the river organisms live. – It may be inorganic, consisting of geological material from the catchment area such as boulders, pebbles, gravel, sand or silt, or it may be organic, including fine particles, decomposed leaves, wood, moss and plants. – Substrate is generally not permanent and is subject to large changes during flooding events. • Light • Temperature • Waterchemistry
- 45. Ocean ecosystem • The ocean ecosystem is unique among aquatic ecosystems because of saline water. • While ocean ecosystems do have much in common with other aquatic ecosystems, such as freshwater lakes, rivers or estuaries, they are unique in many ways, especially because of the high salt water levels. • The plants, animals and microorganisms are specially adapted to saline environment.