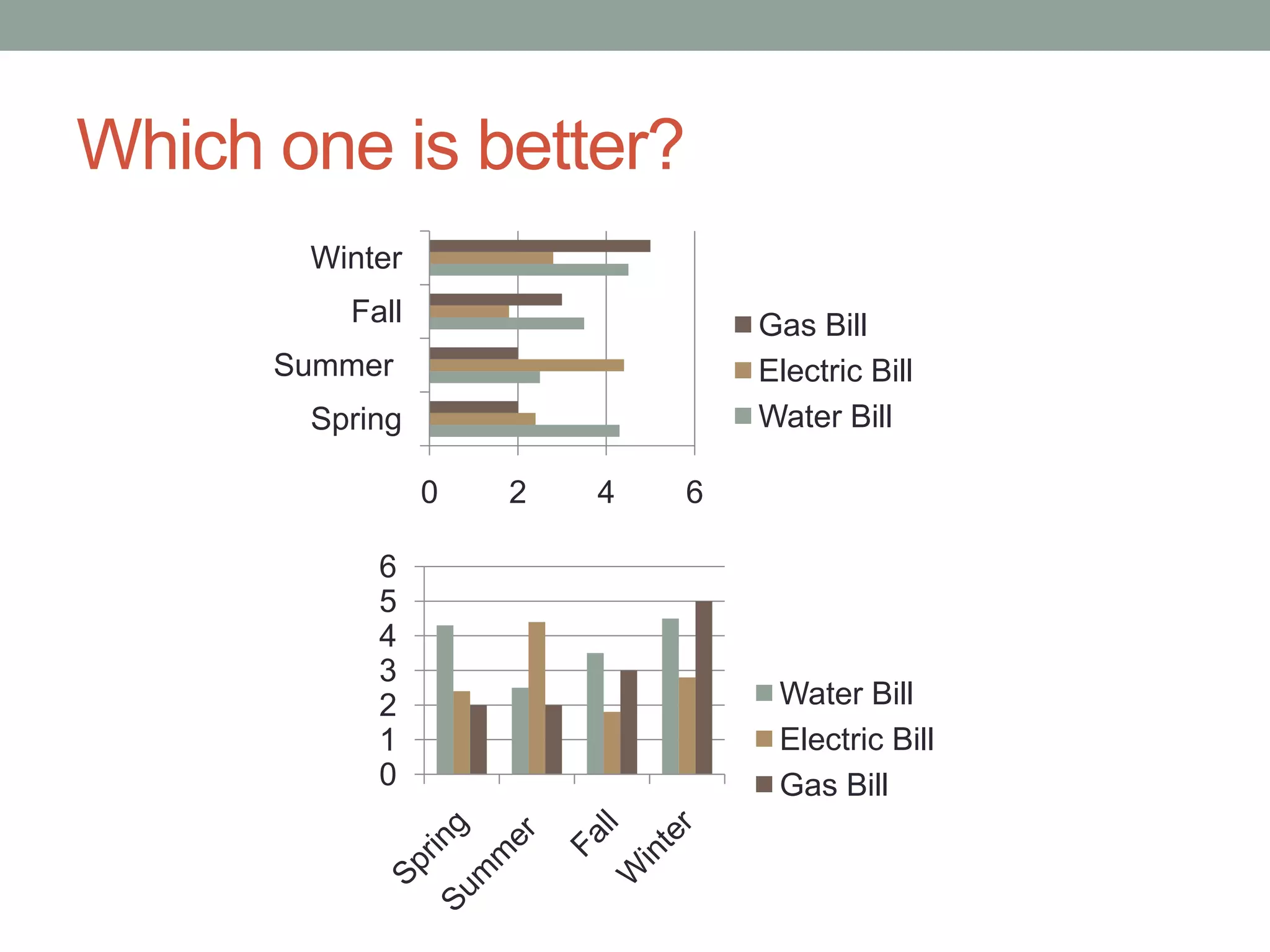
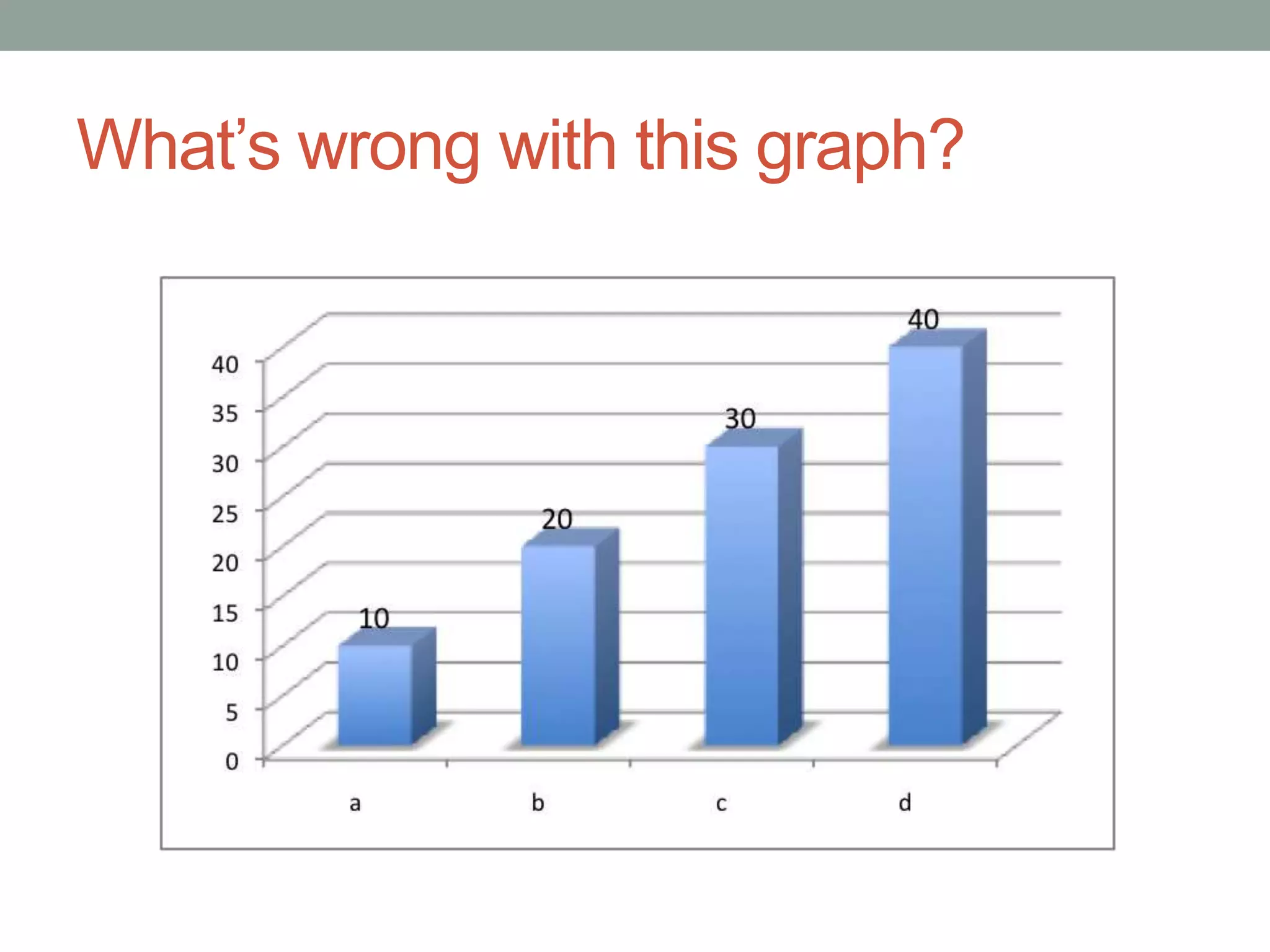
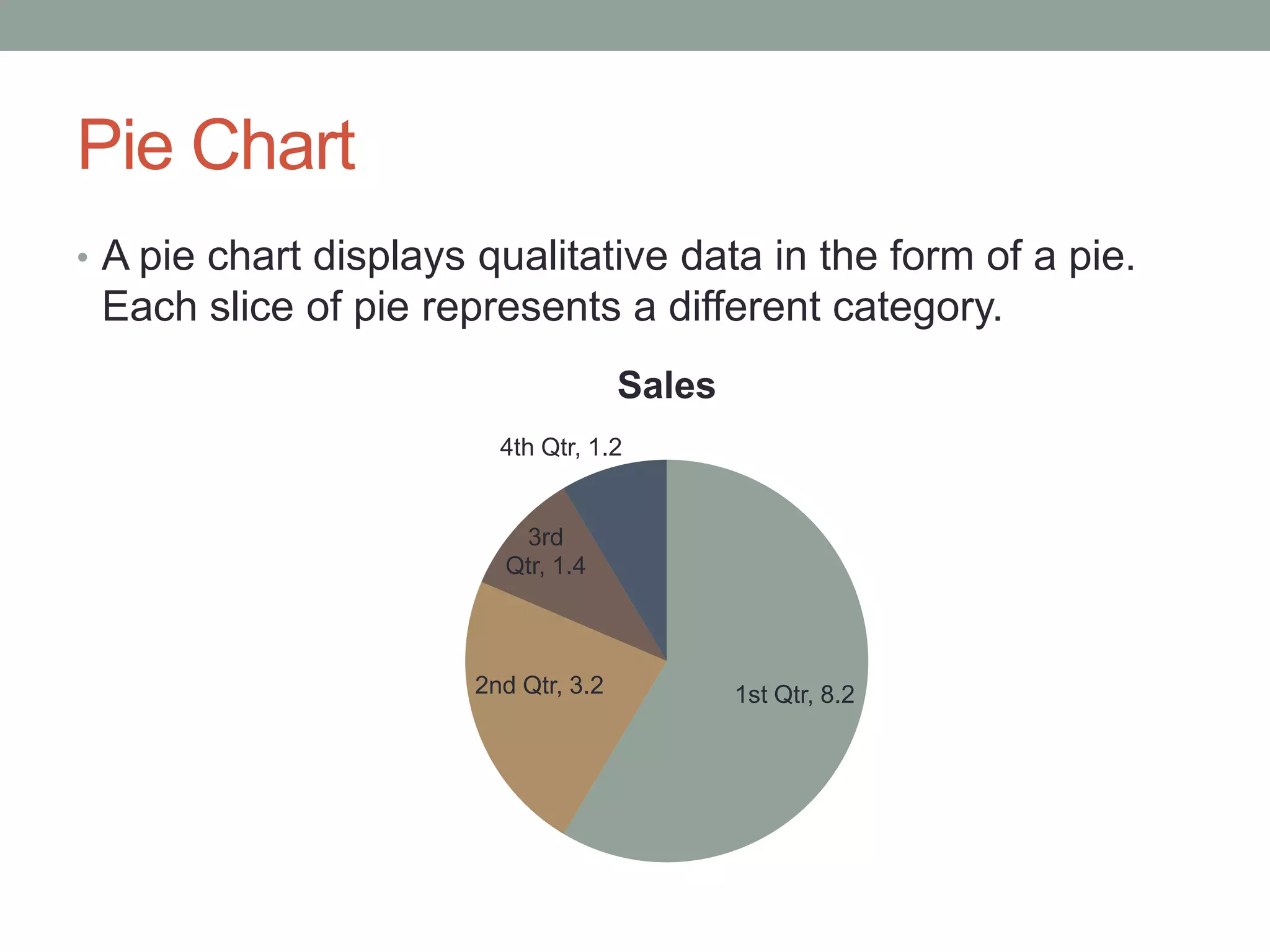
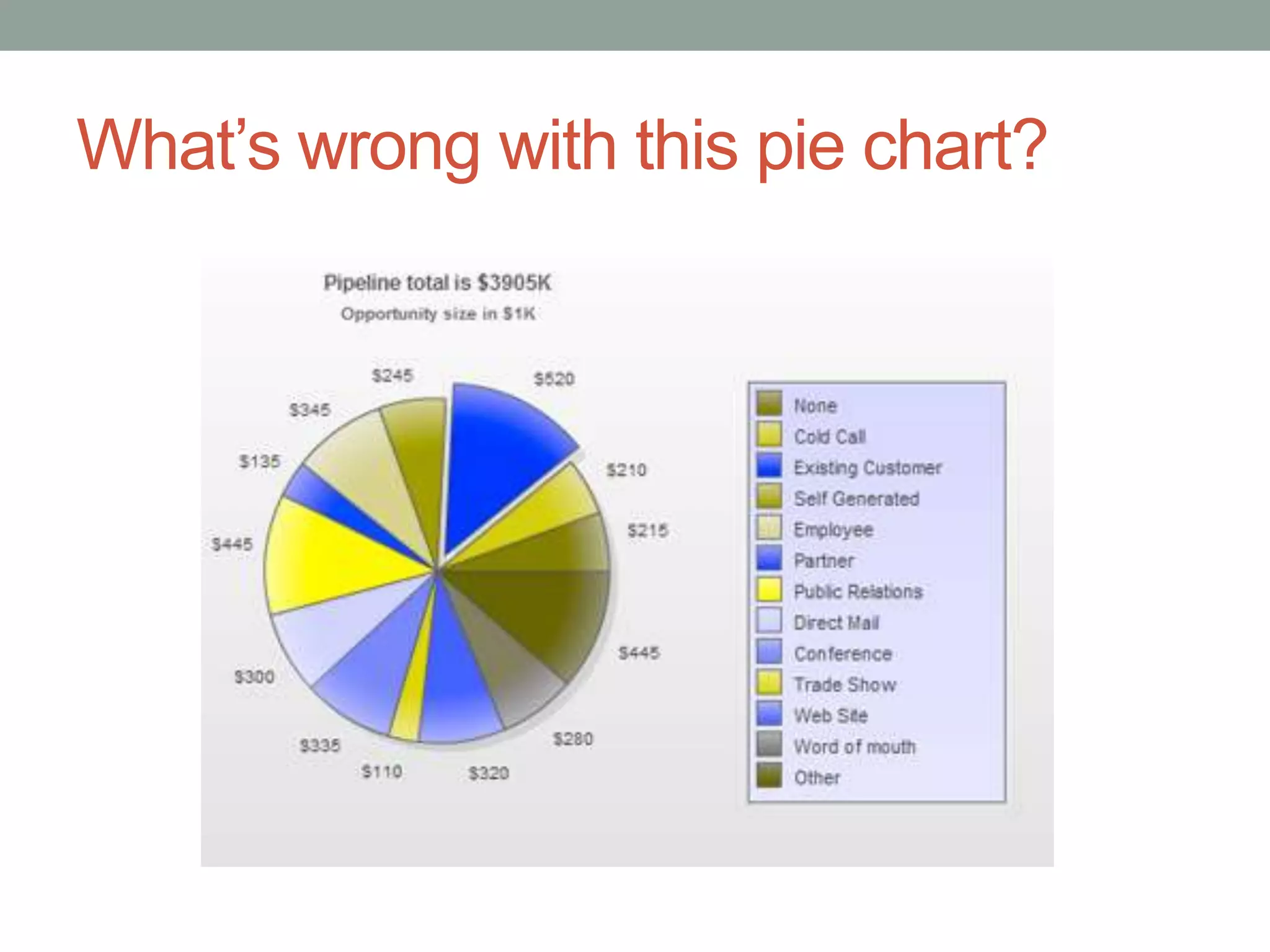
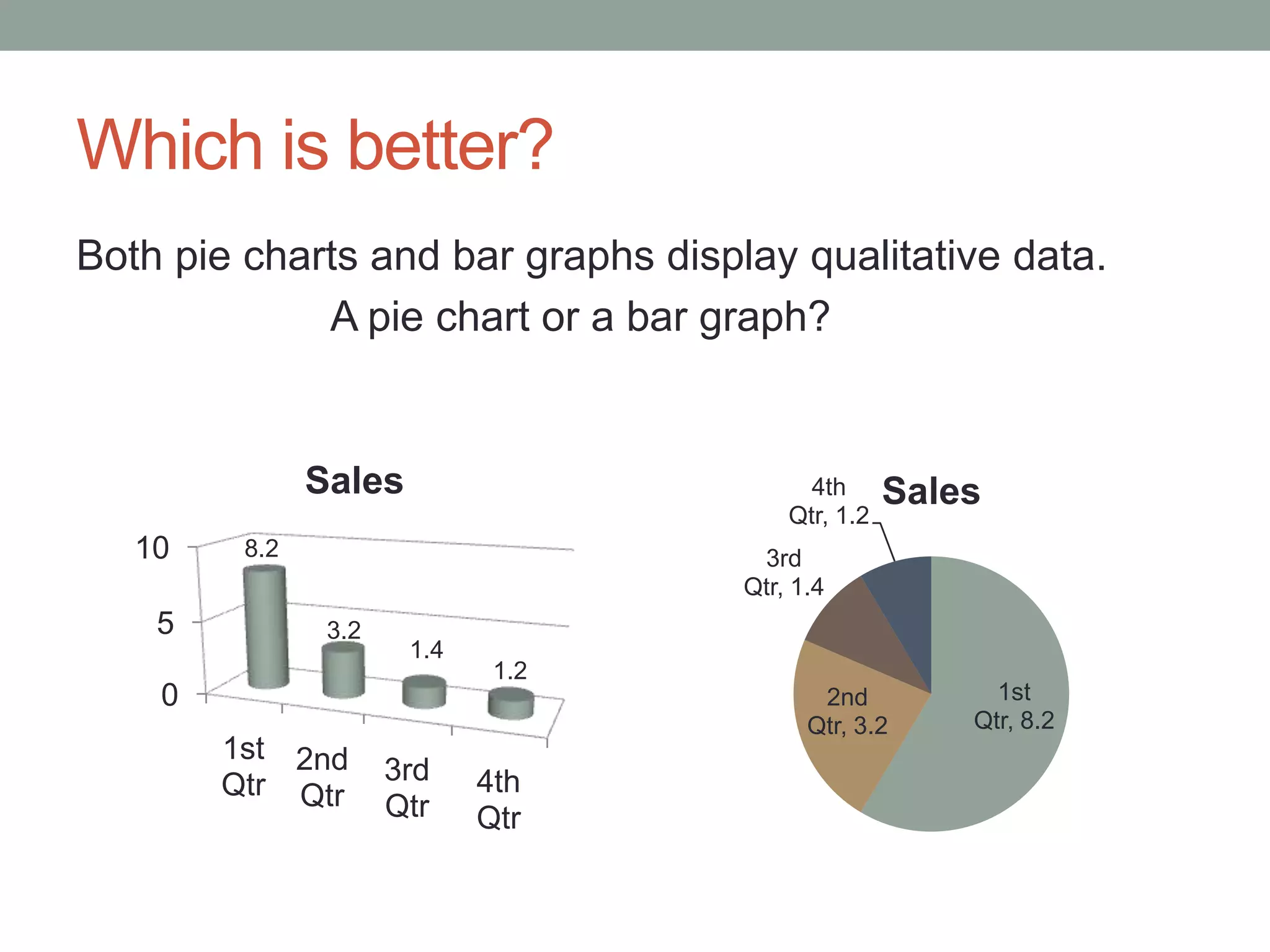
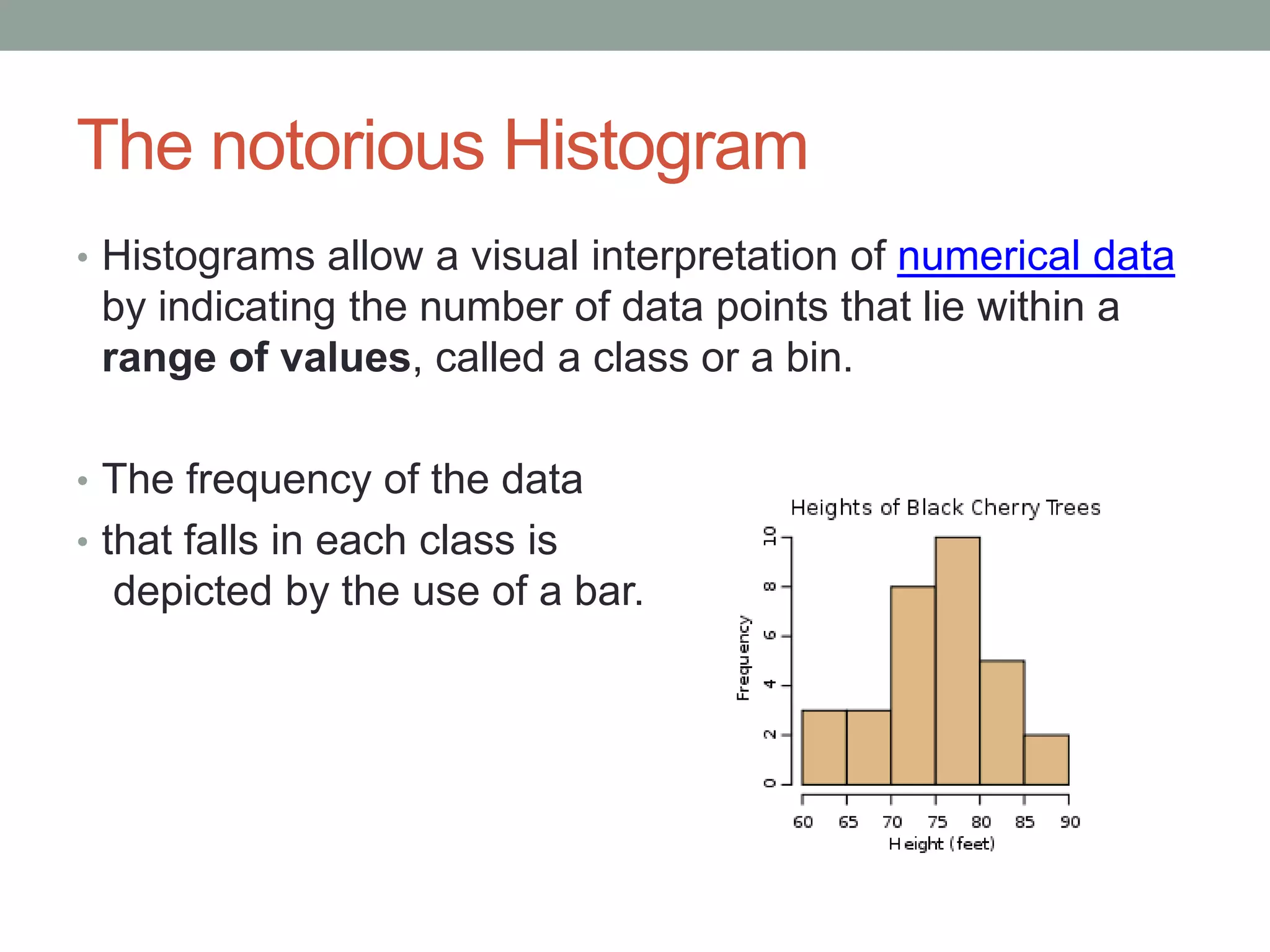
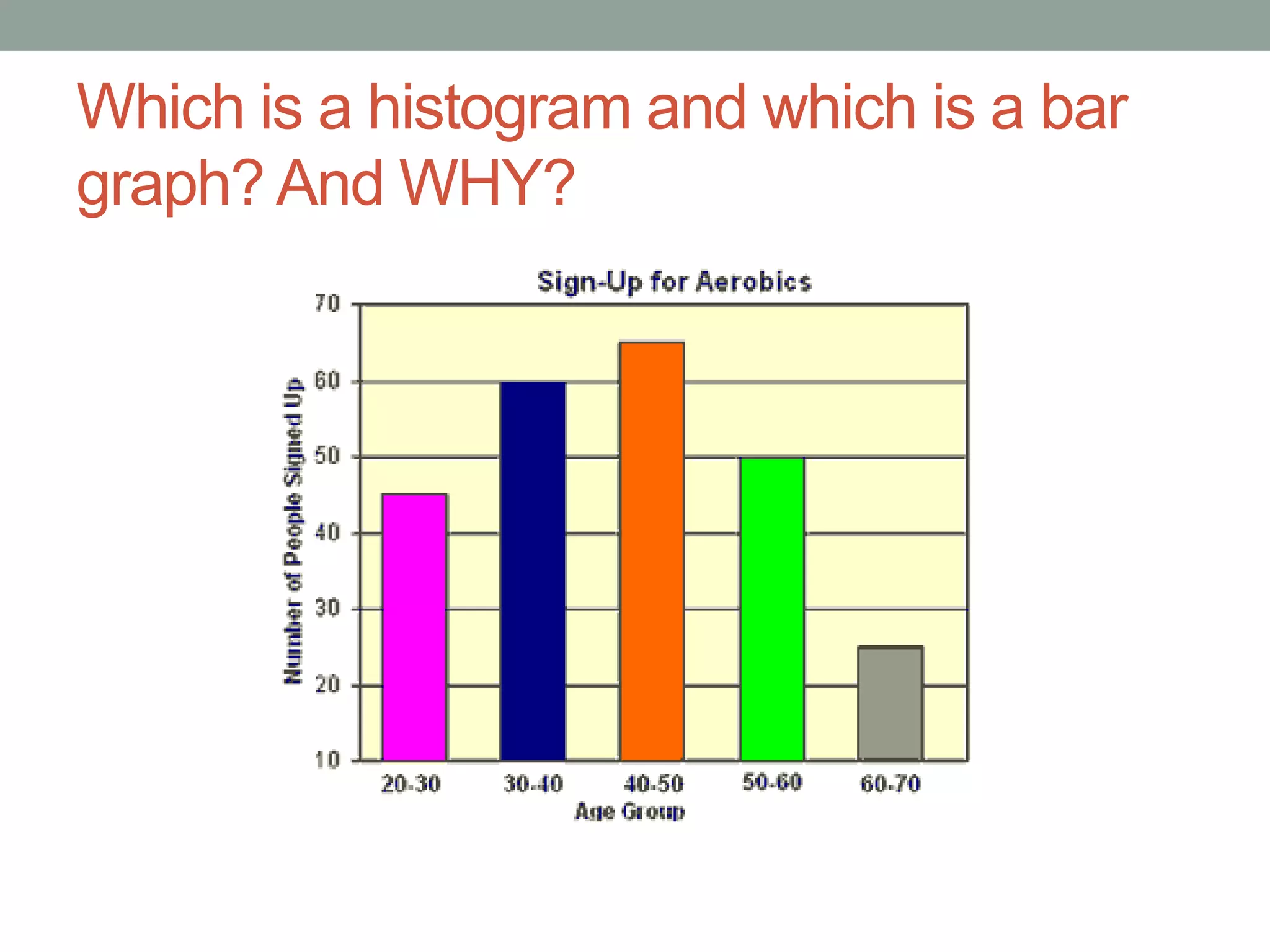
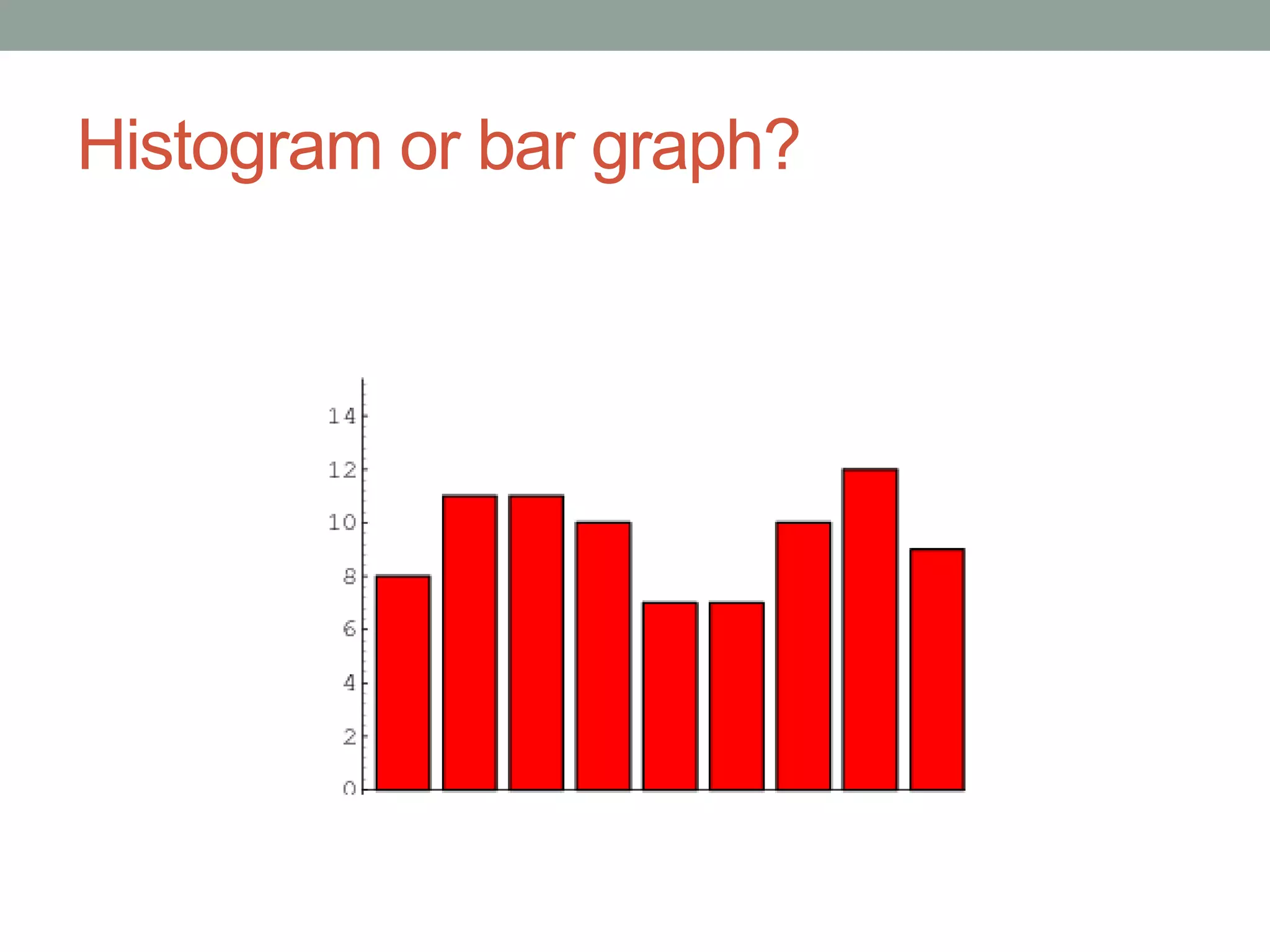
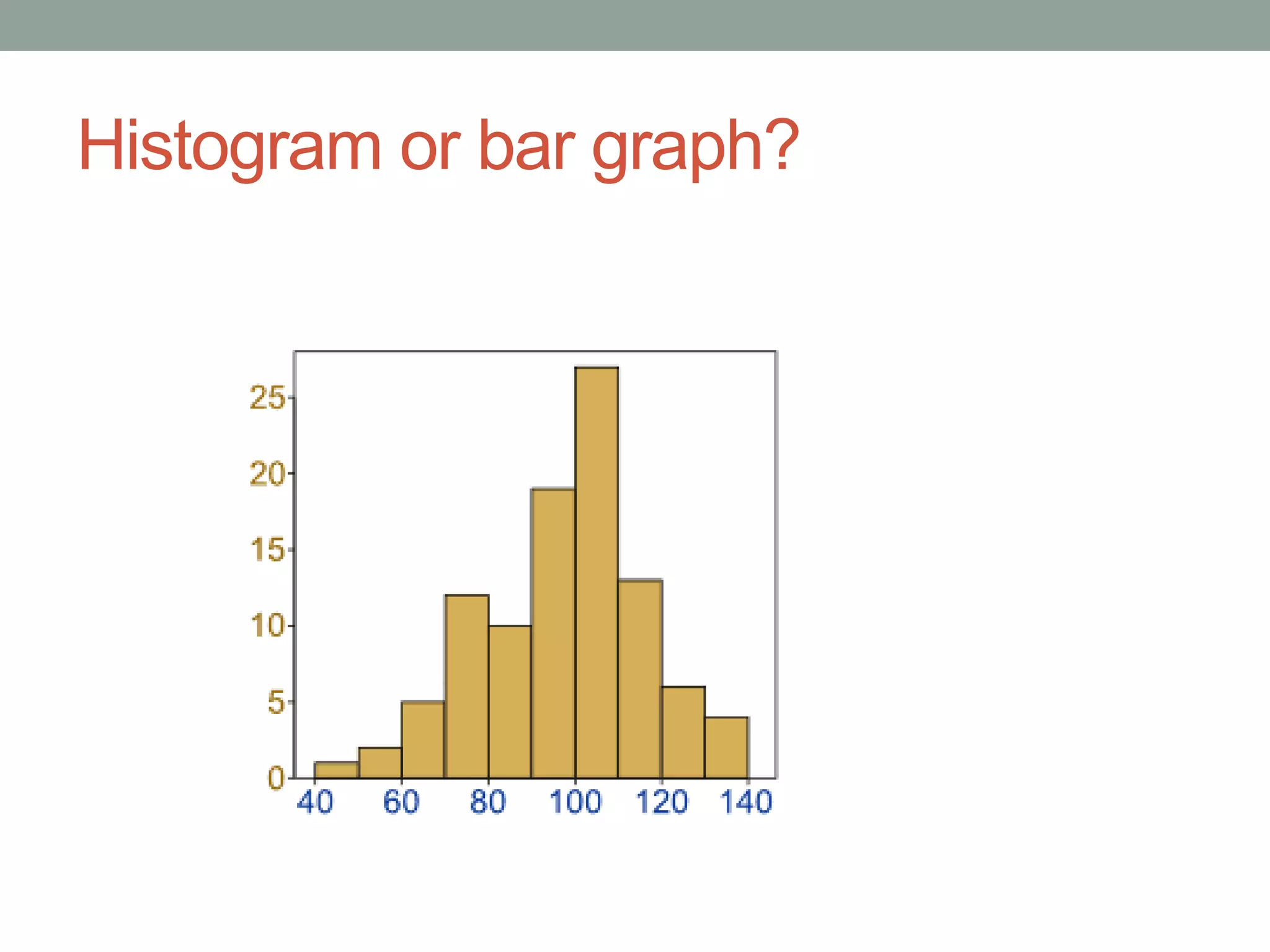
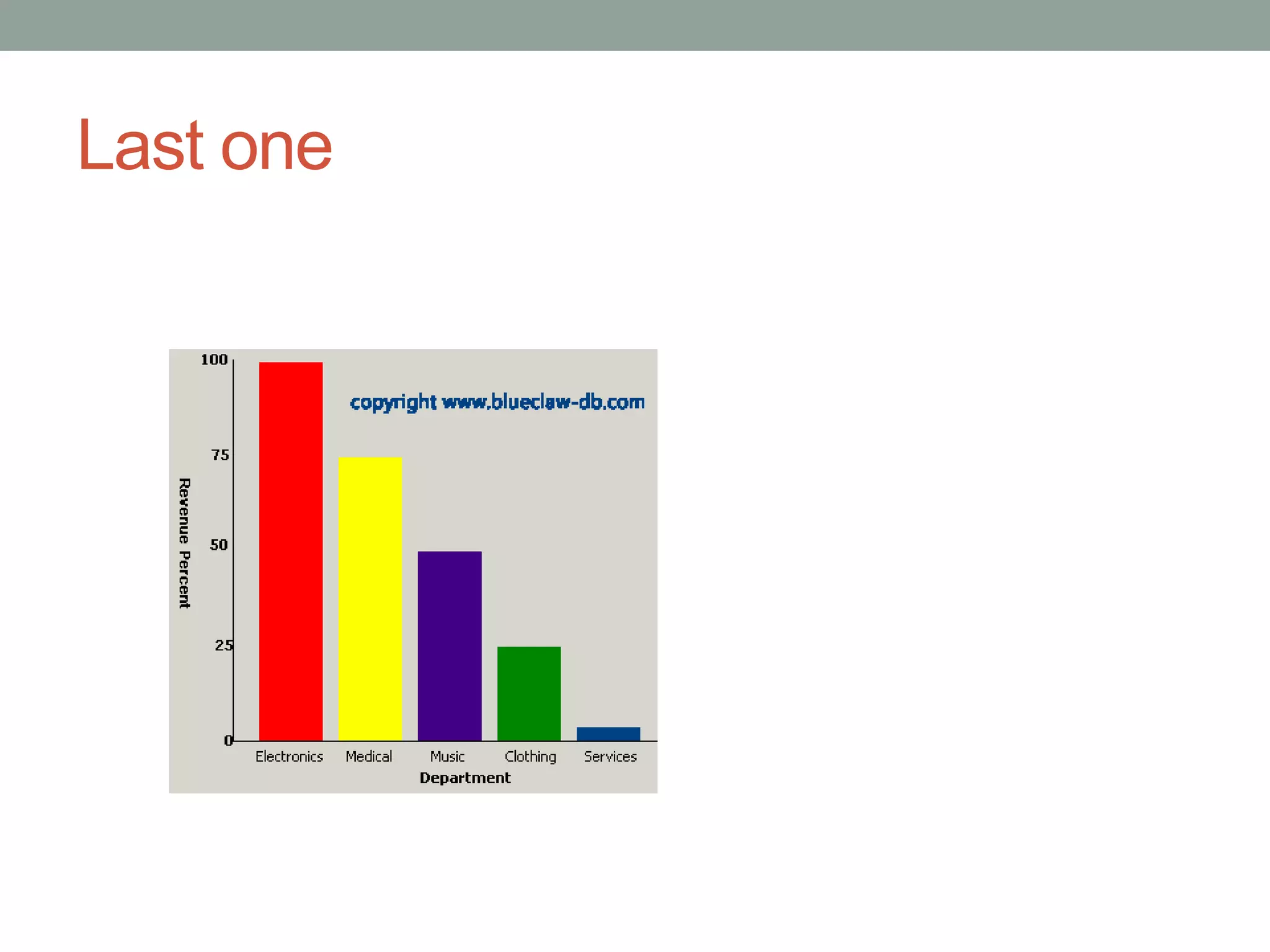
This document provides an introduction to different types of data displays used in statistics, including bar graphs, pie charts, histograms, and when each is most appropriate. Qualitative data that can be sorted into categories is best displayed using bar graphs or pie charts, while quantitative numerical data is best shown using histograms. Key factors in determining the best graph include whether the data is qualitative or quantitative, paired, categorical, or measured on a numerical scale. Histograms depict the distribution of numerical data by frequency across ranges or "bins".