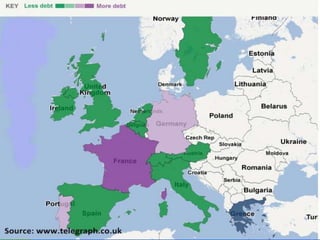
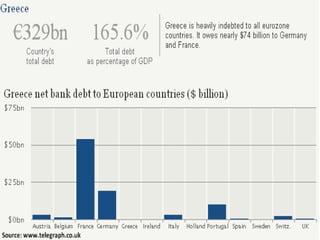
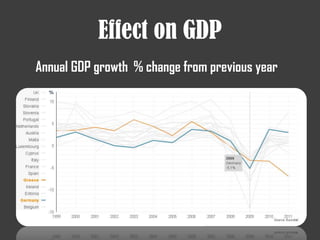
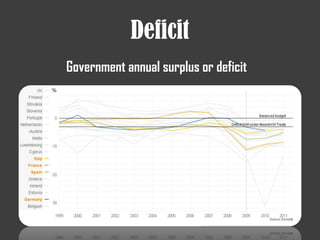
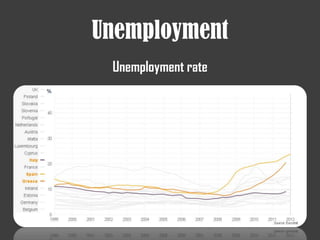
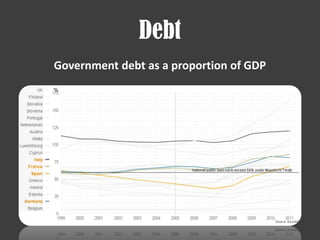
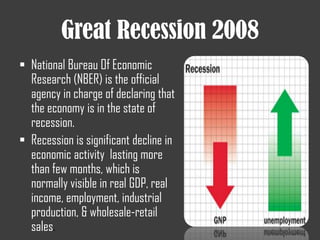
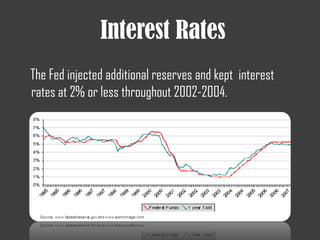
The document discusses several financial crises throughout history including:
- The 1973 oil crisis caused by OPEC oil export restrictions which led to energy conservation policies.
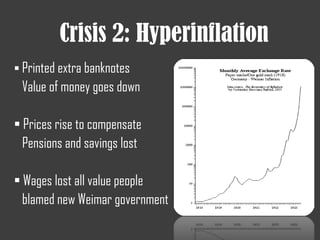
- Hyperinflation in Germany after WWI due to the French invasion of the Ruhr and printing of extra banknotes to pay reparations. This caused people's pensions and savings to lose value.
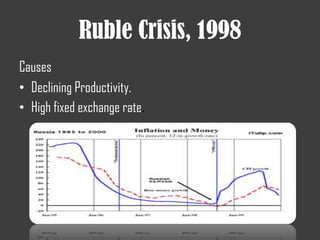
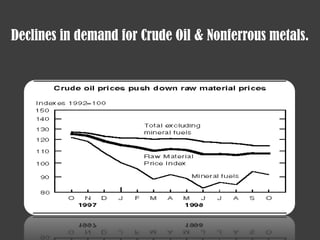
- The 1998 Russian financial crisis caused by declining productivity, a fixed exchange rate, and falling oil prices which led to a political crisis and currency collapse.
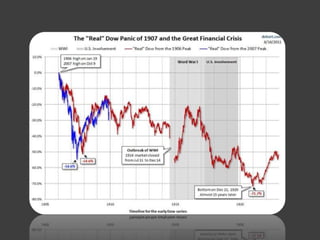
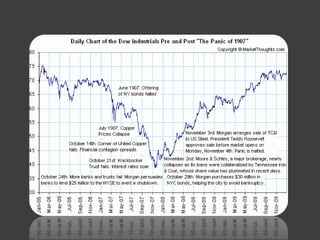
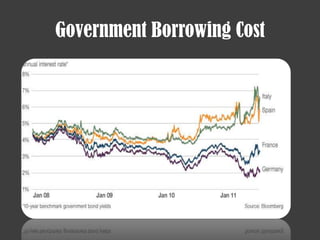
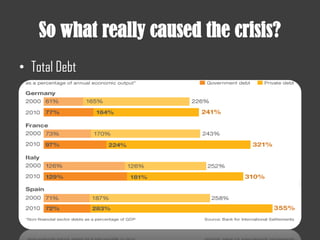
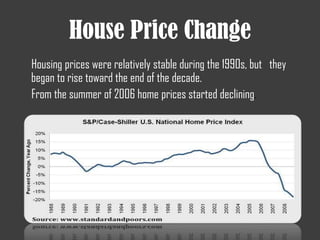
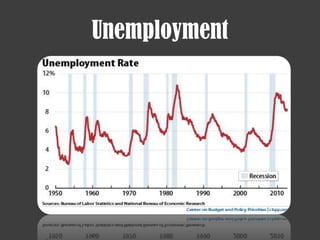
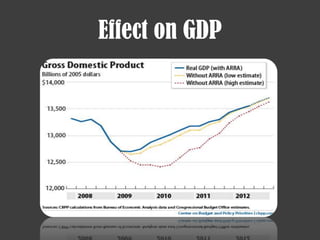
- The 2007-2008 global financial crisis triggered by the bursting of the US housing bubble, subprime mortgage crisis, and failure/bailout of Lehman Brothers which caused a recession