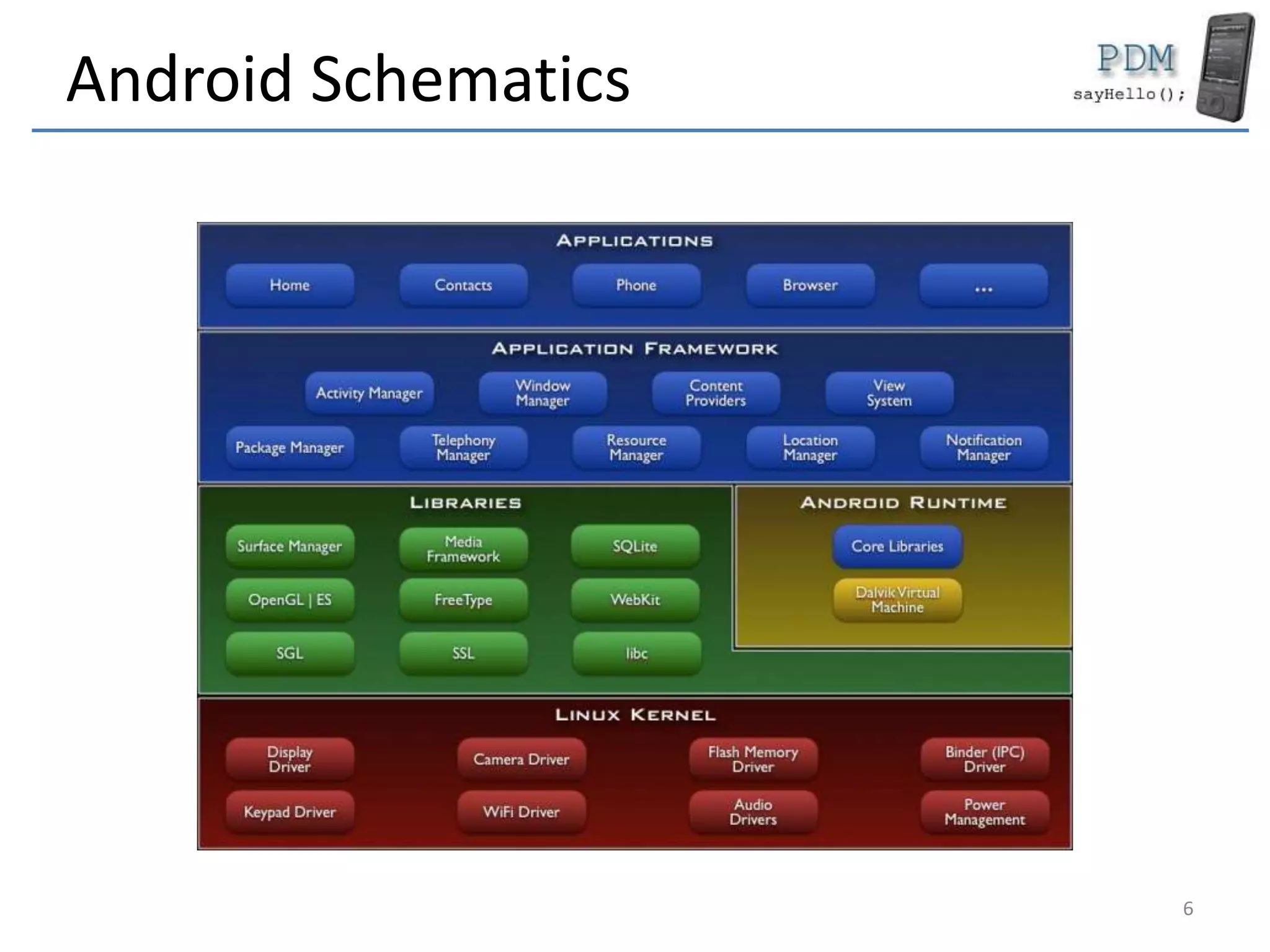
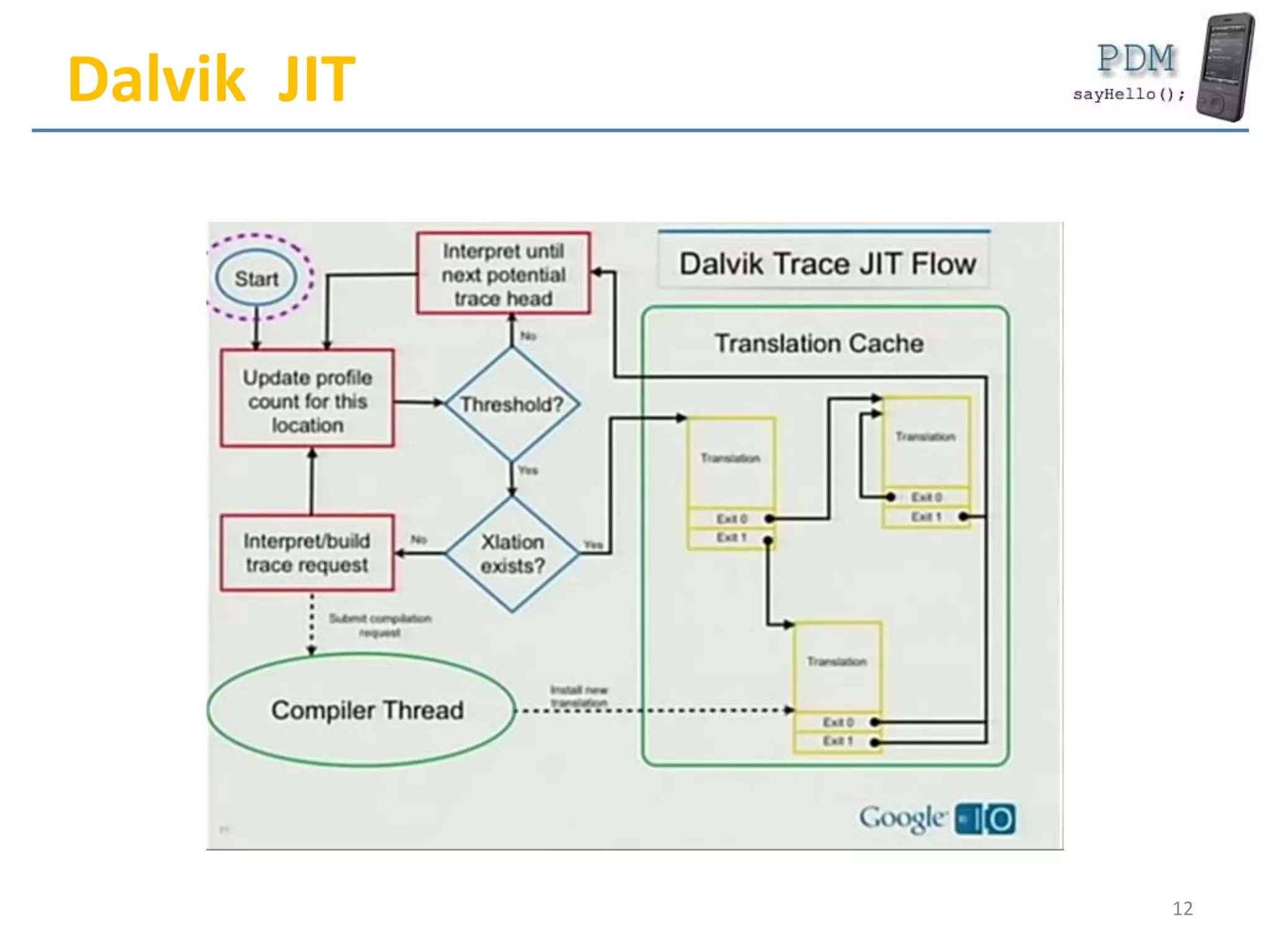
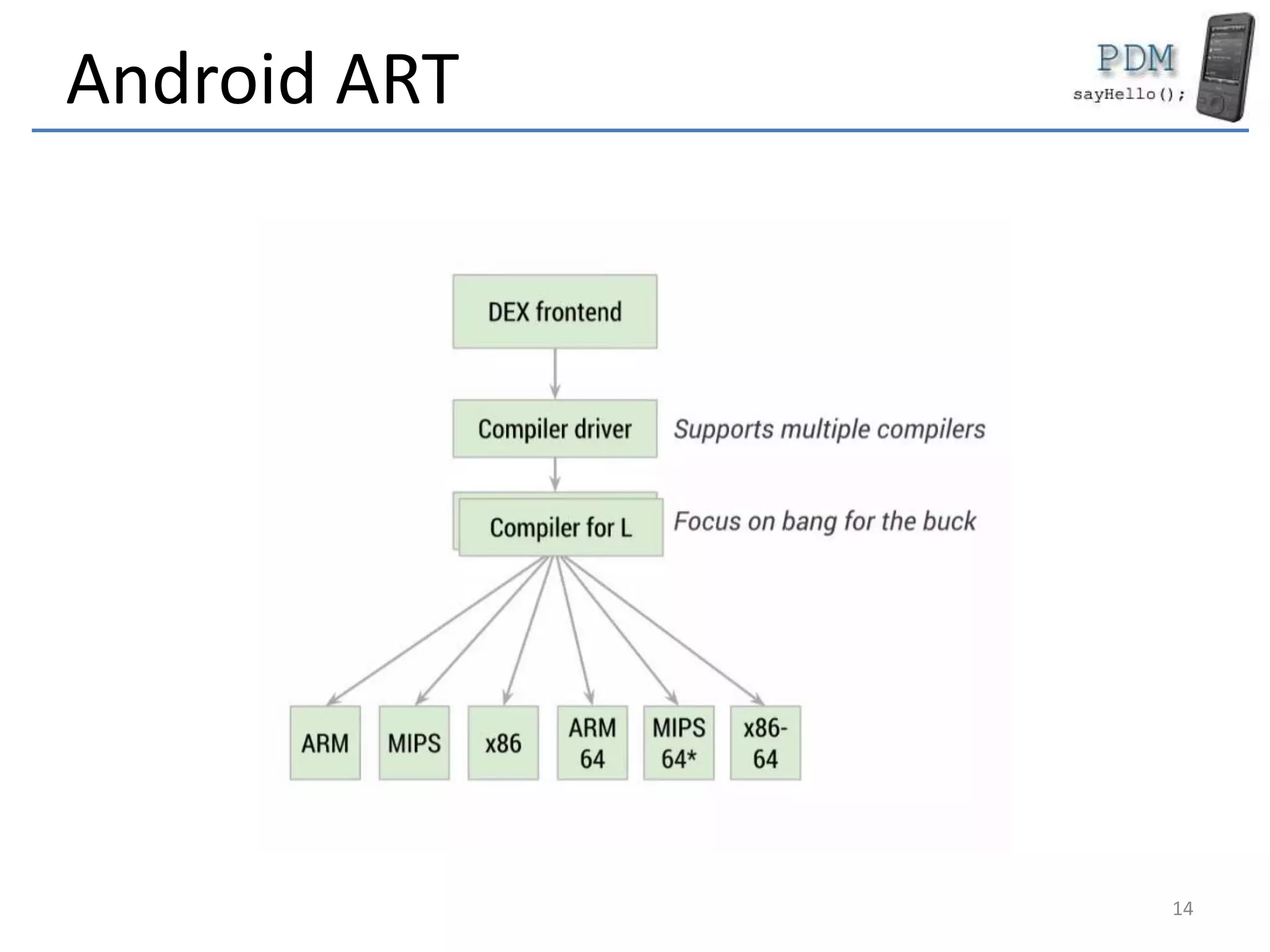
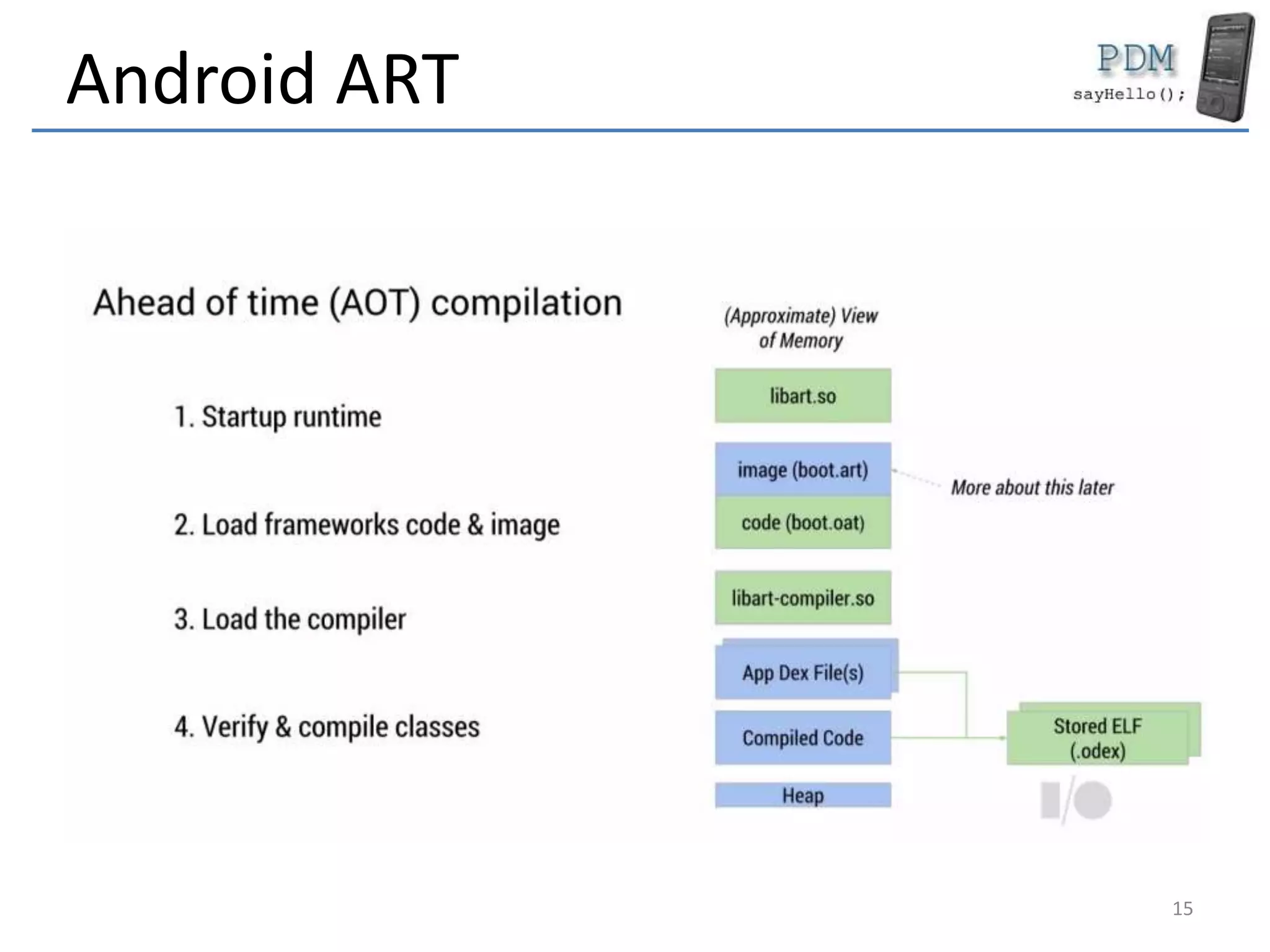
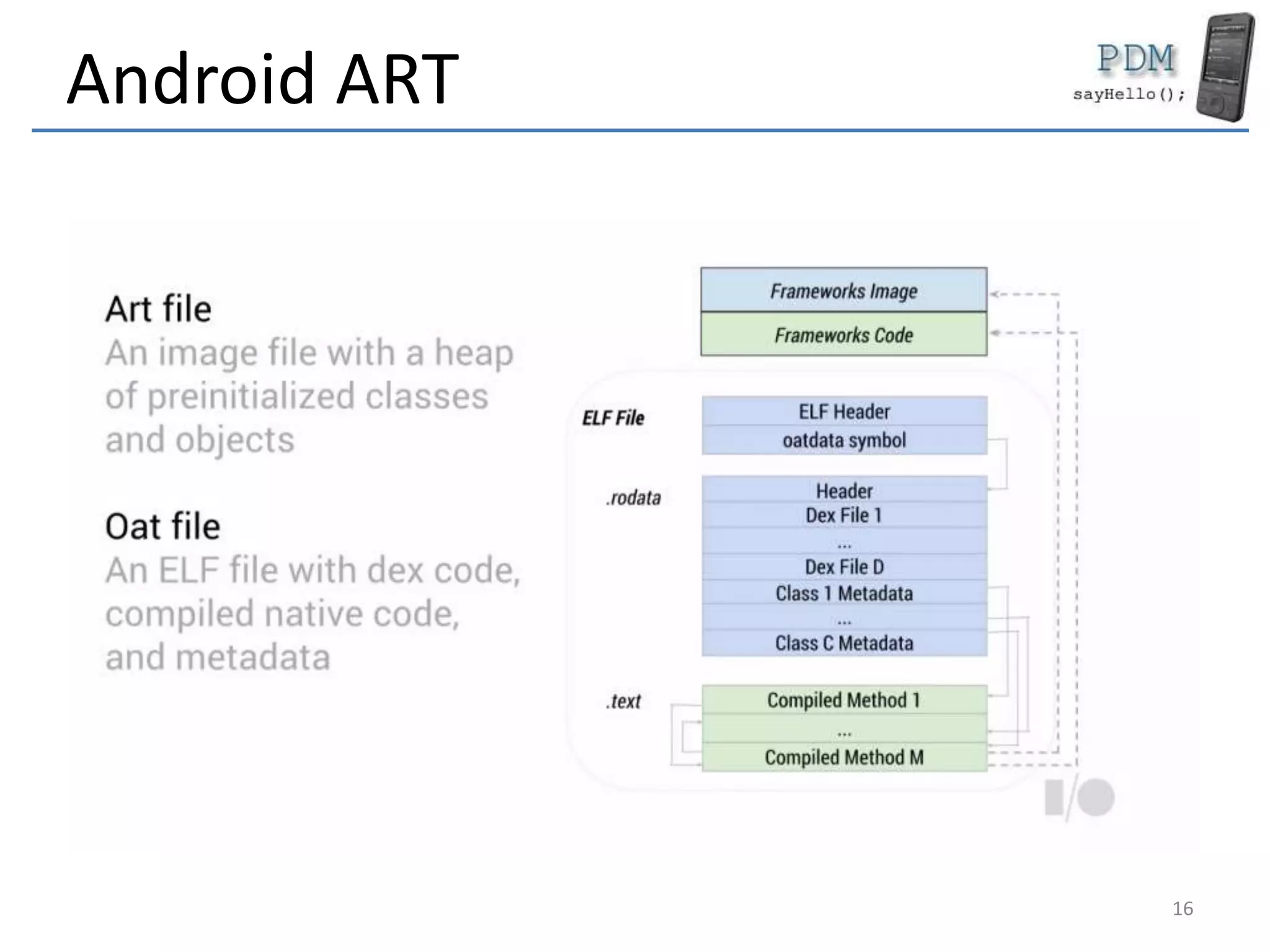
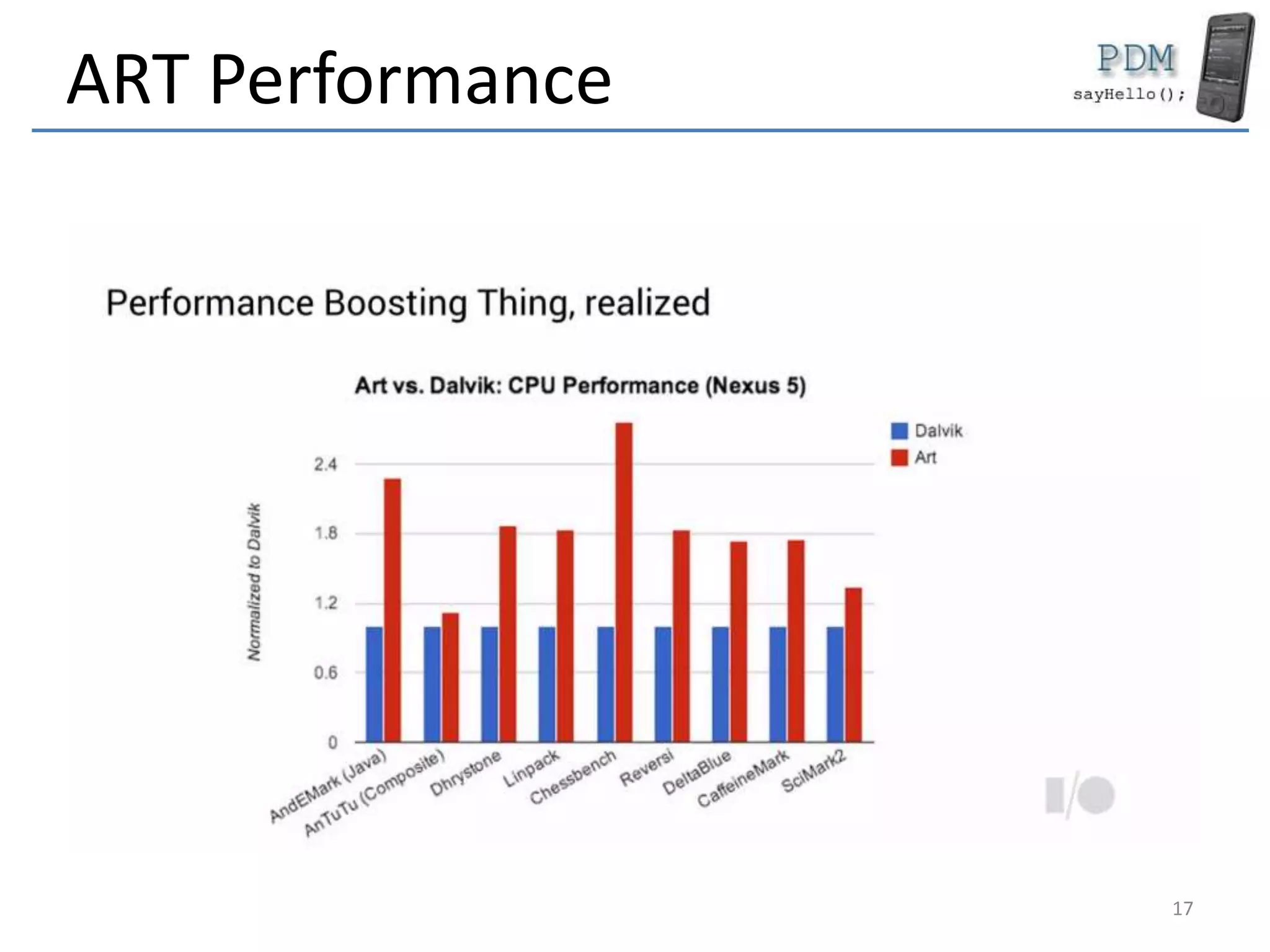
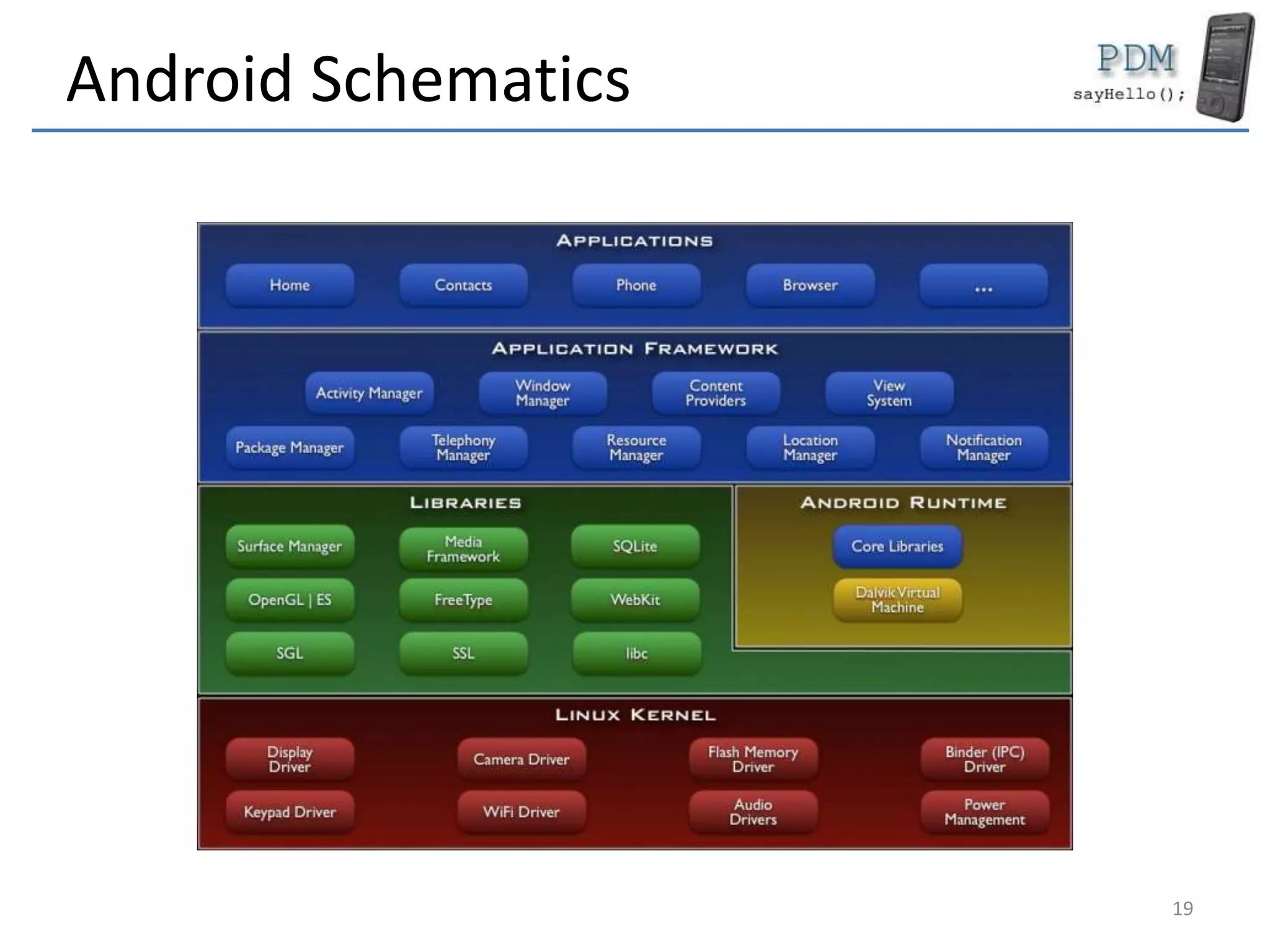
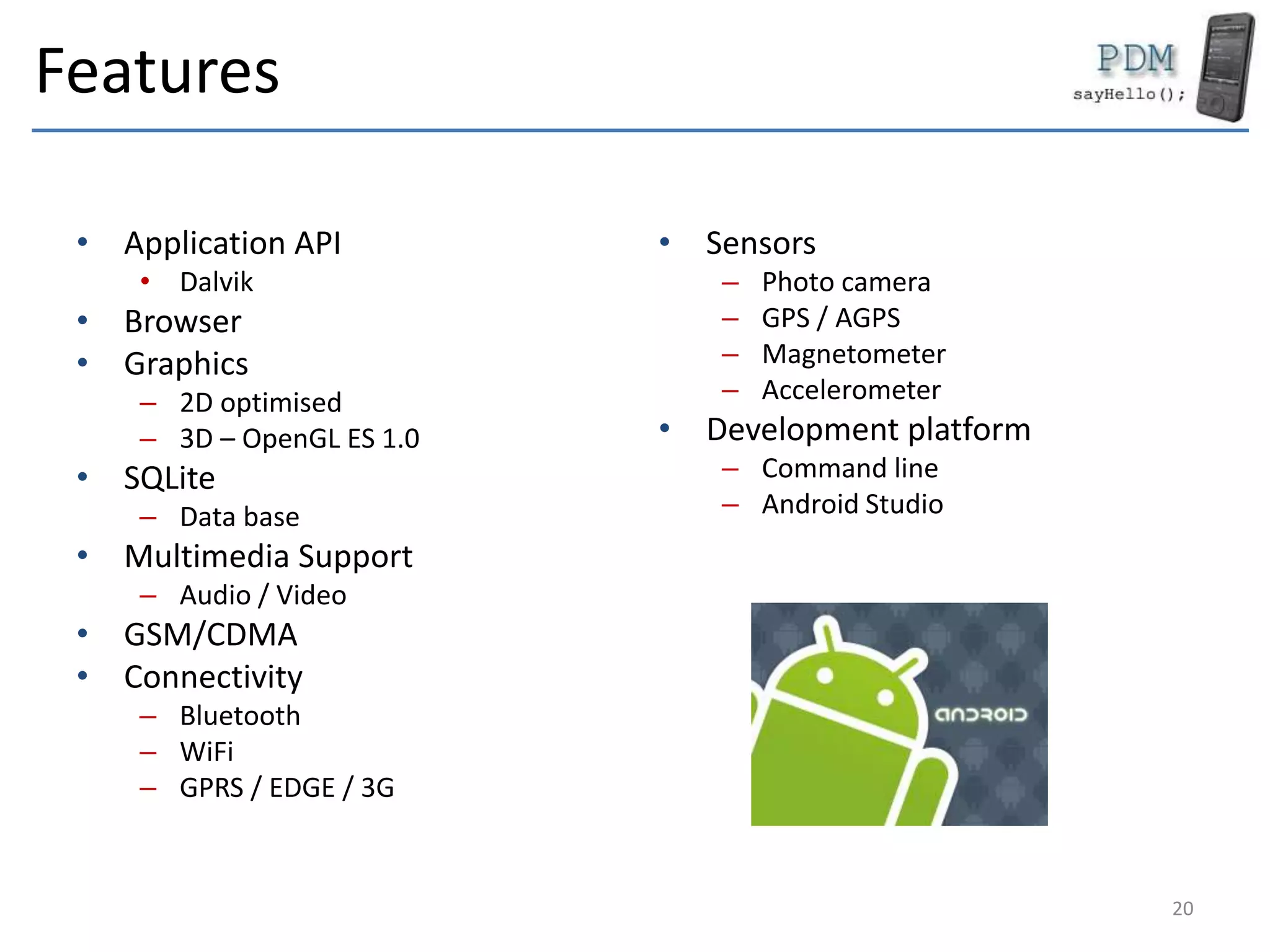
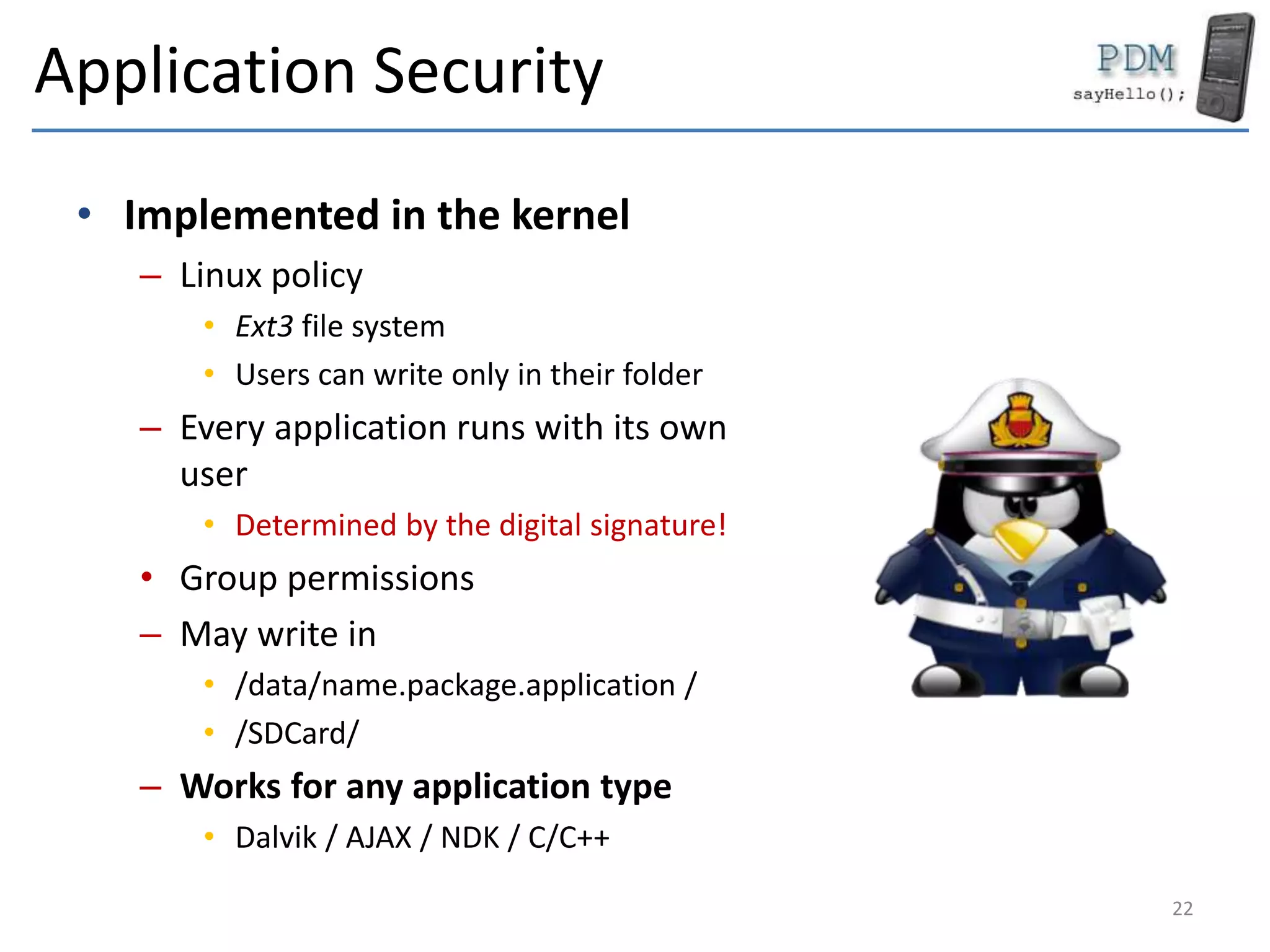
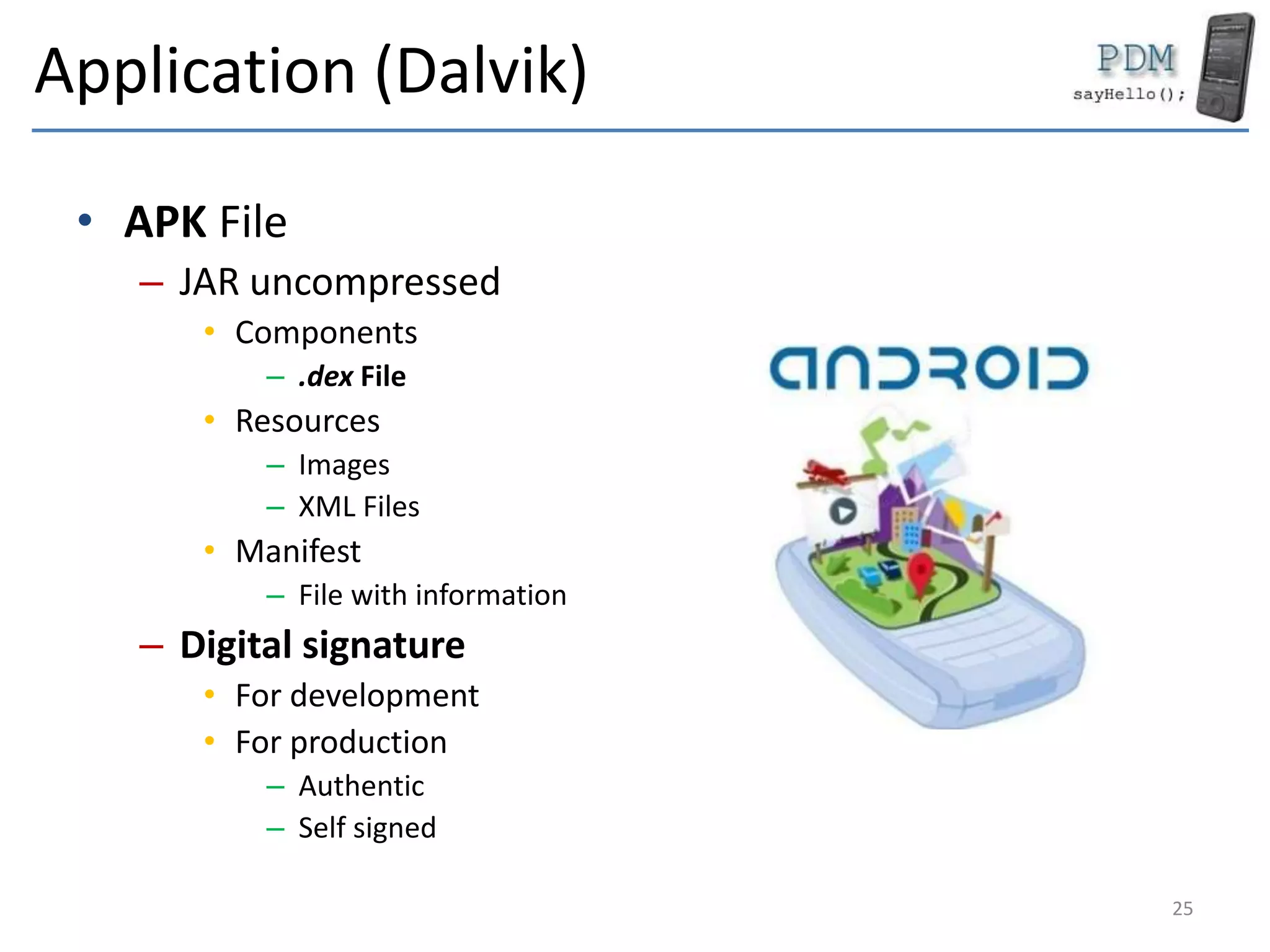
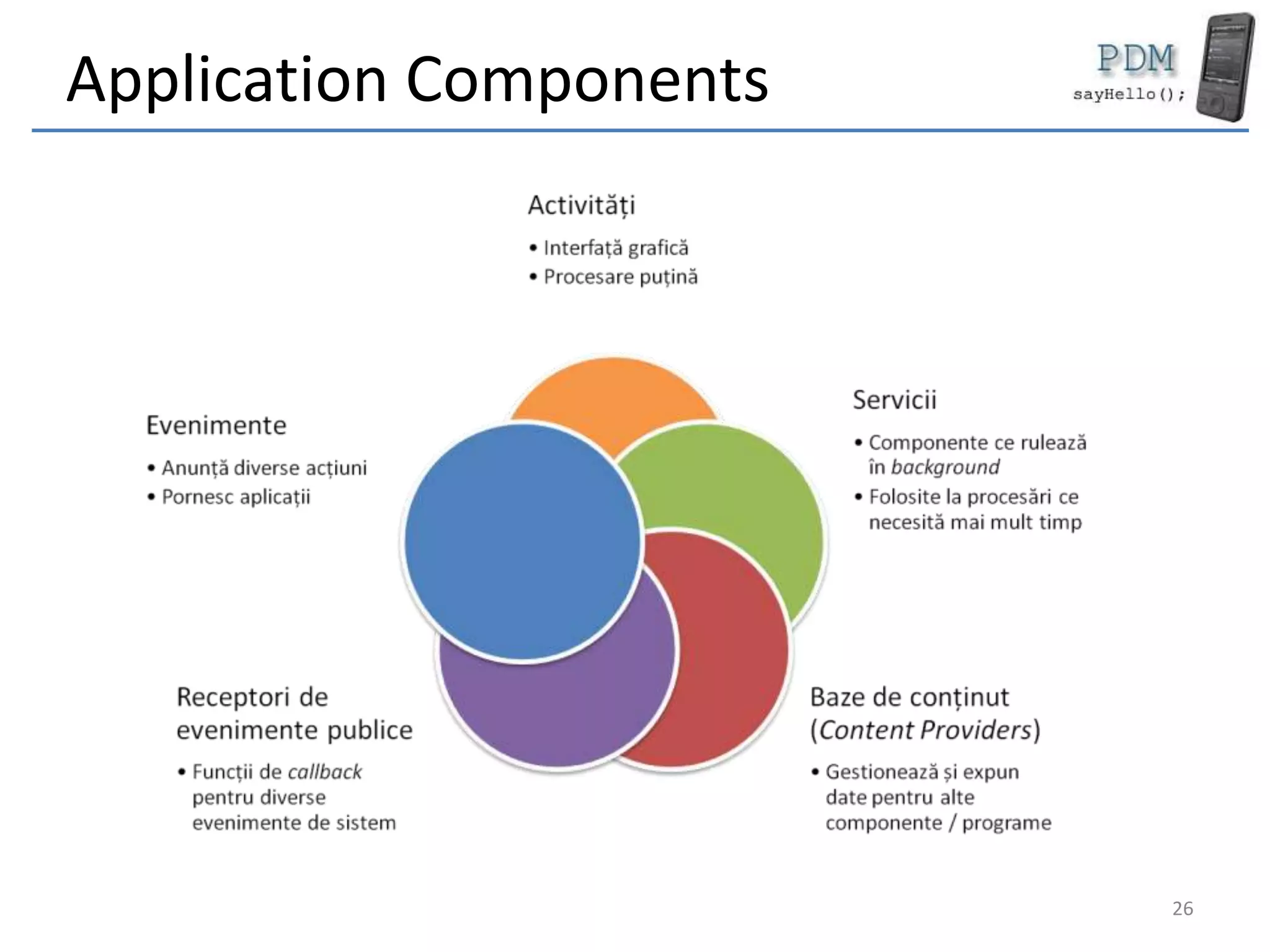
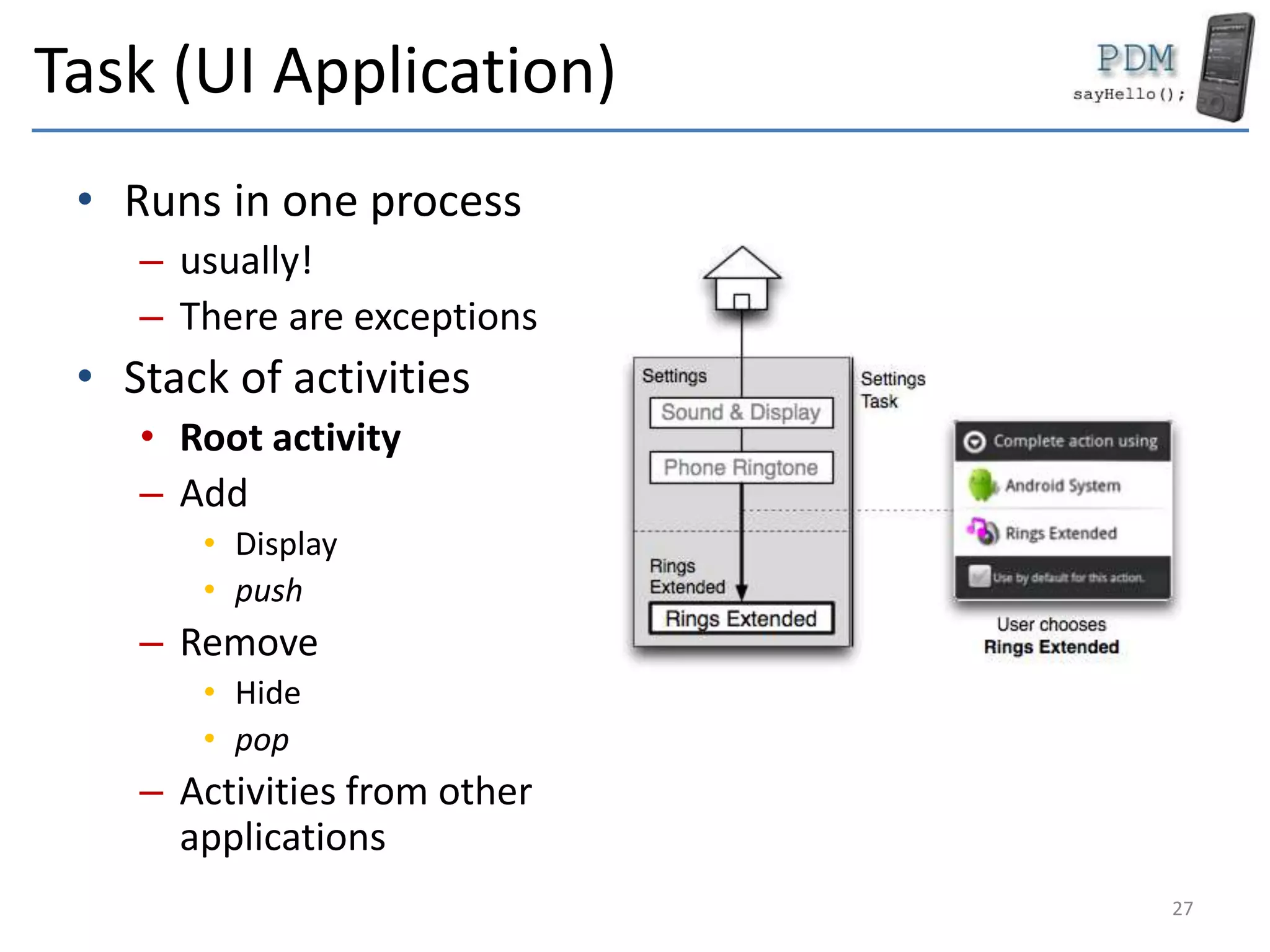
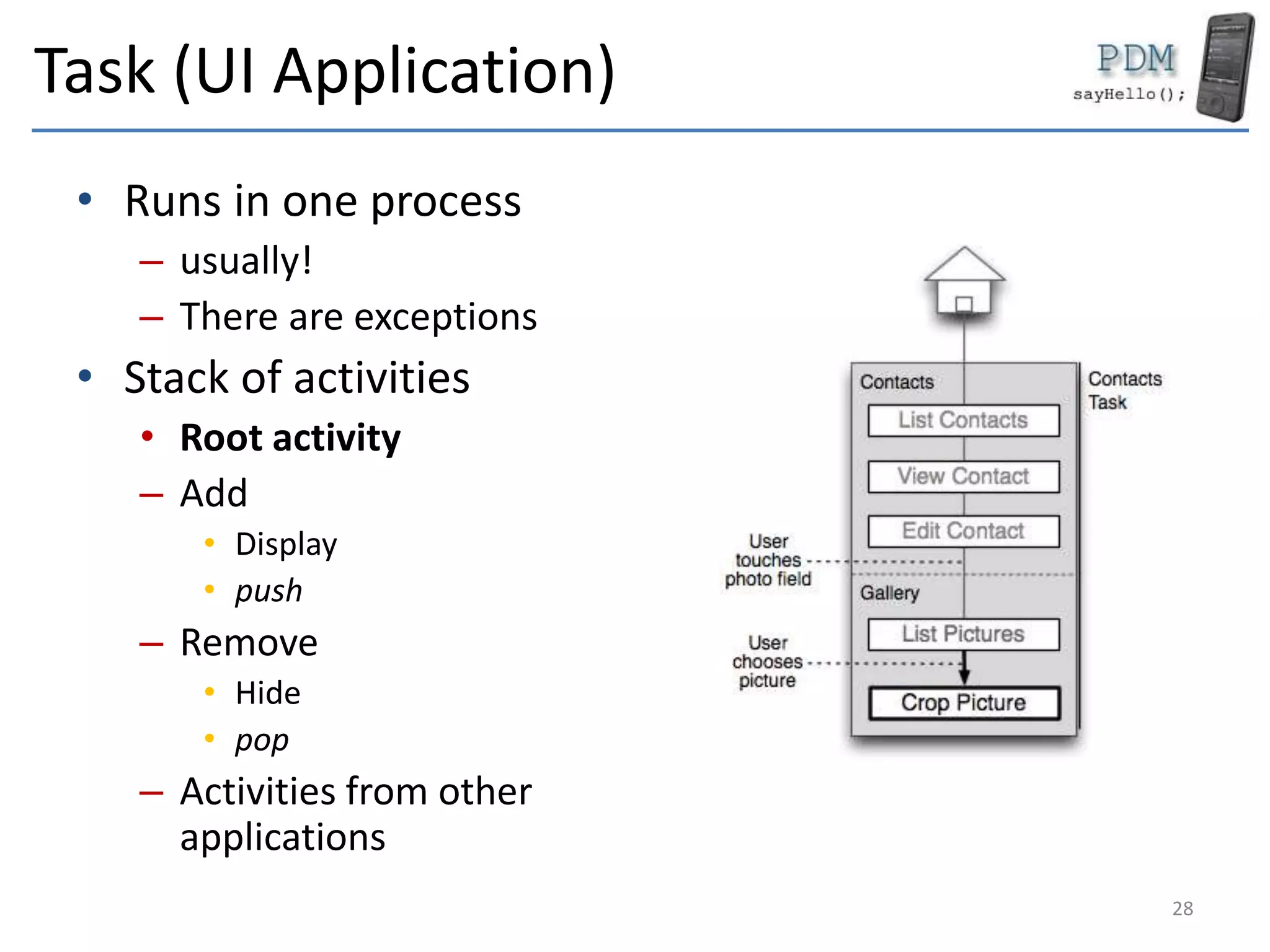
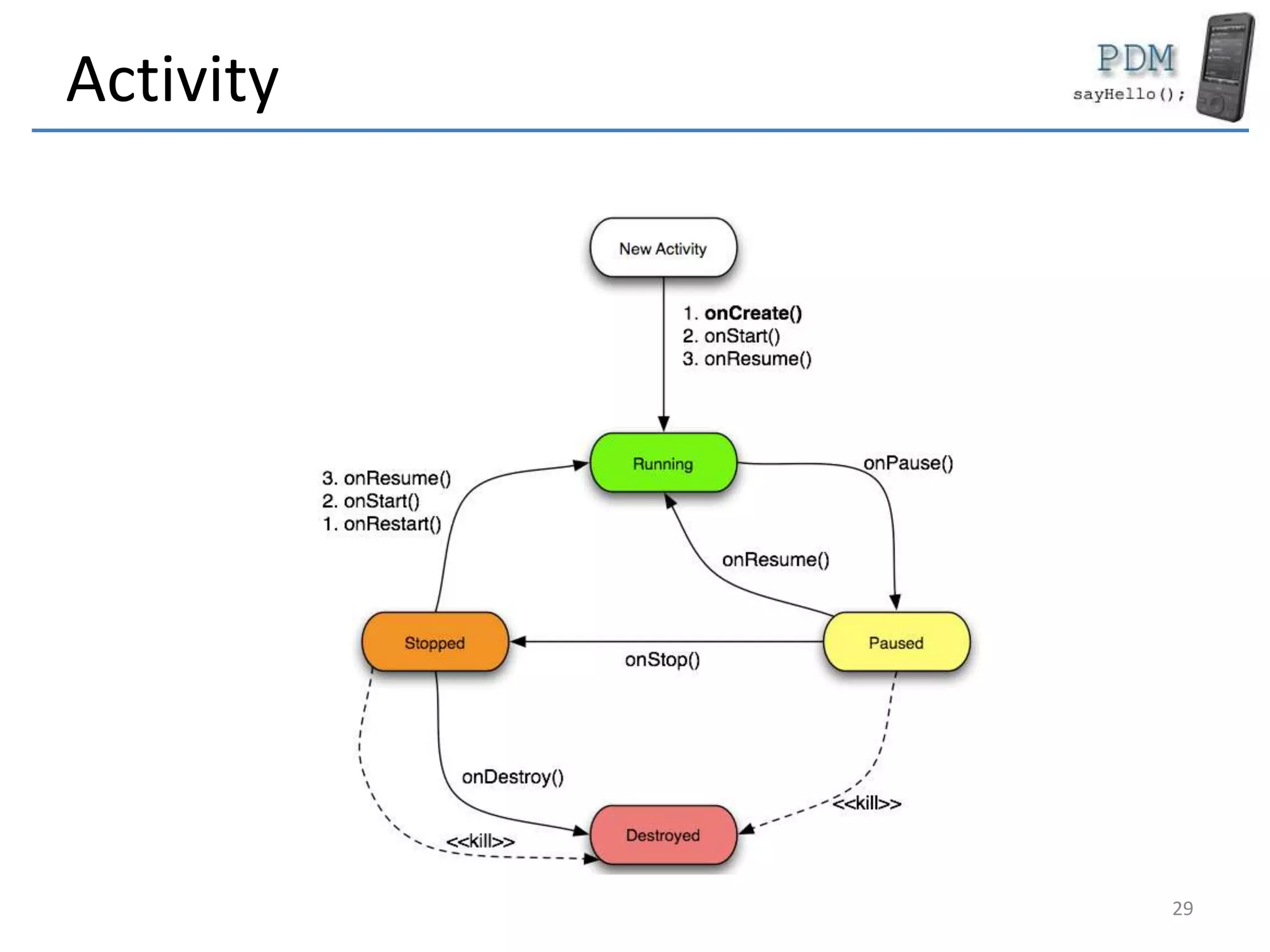
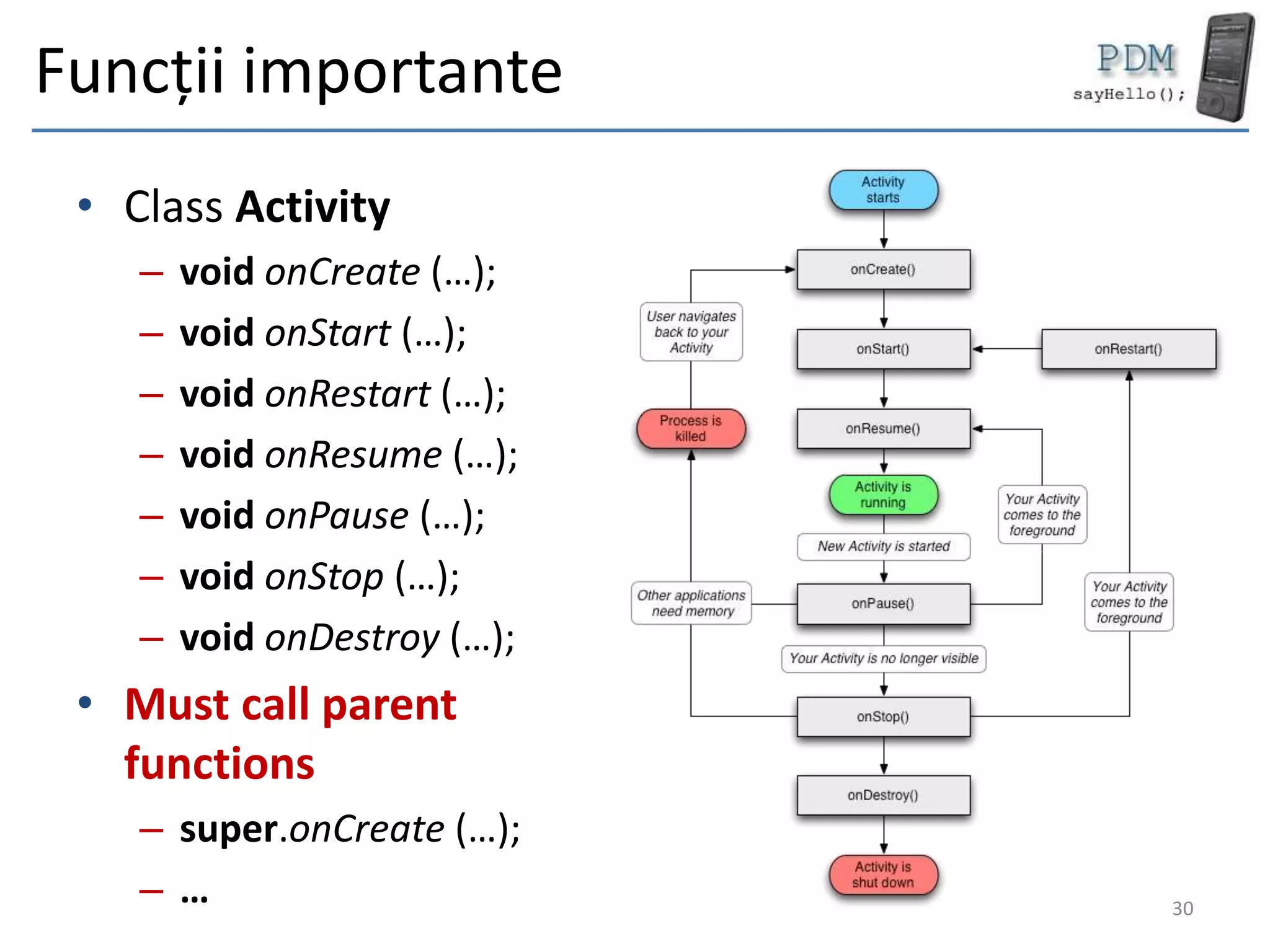
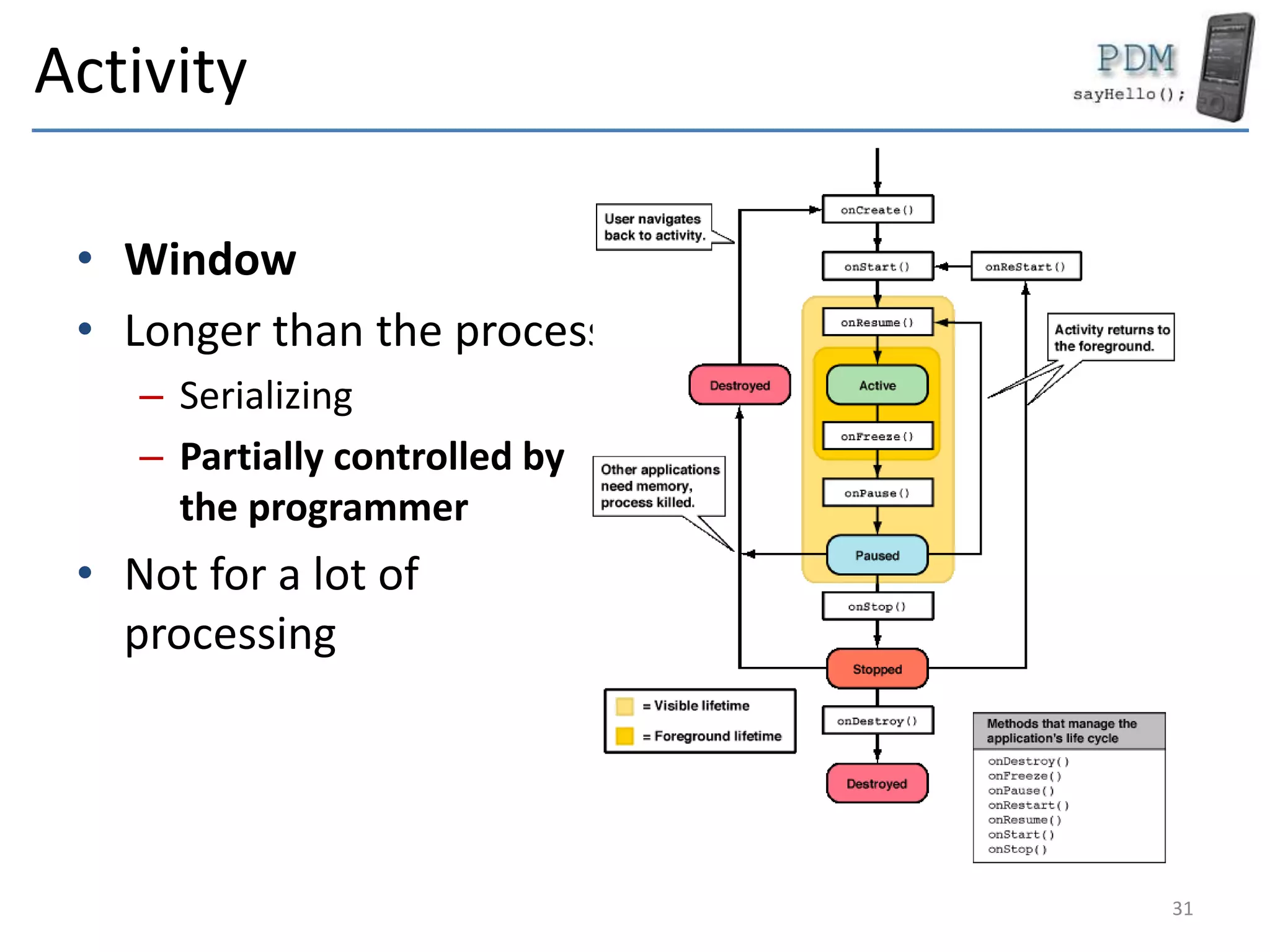
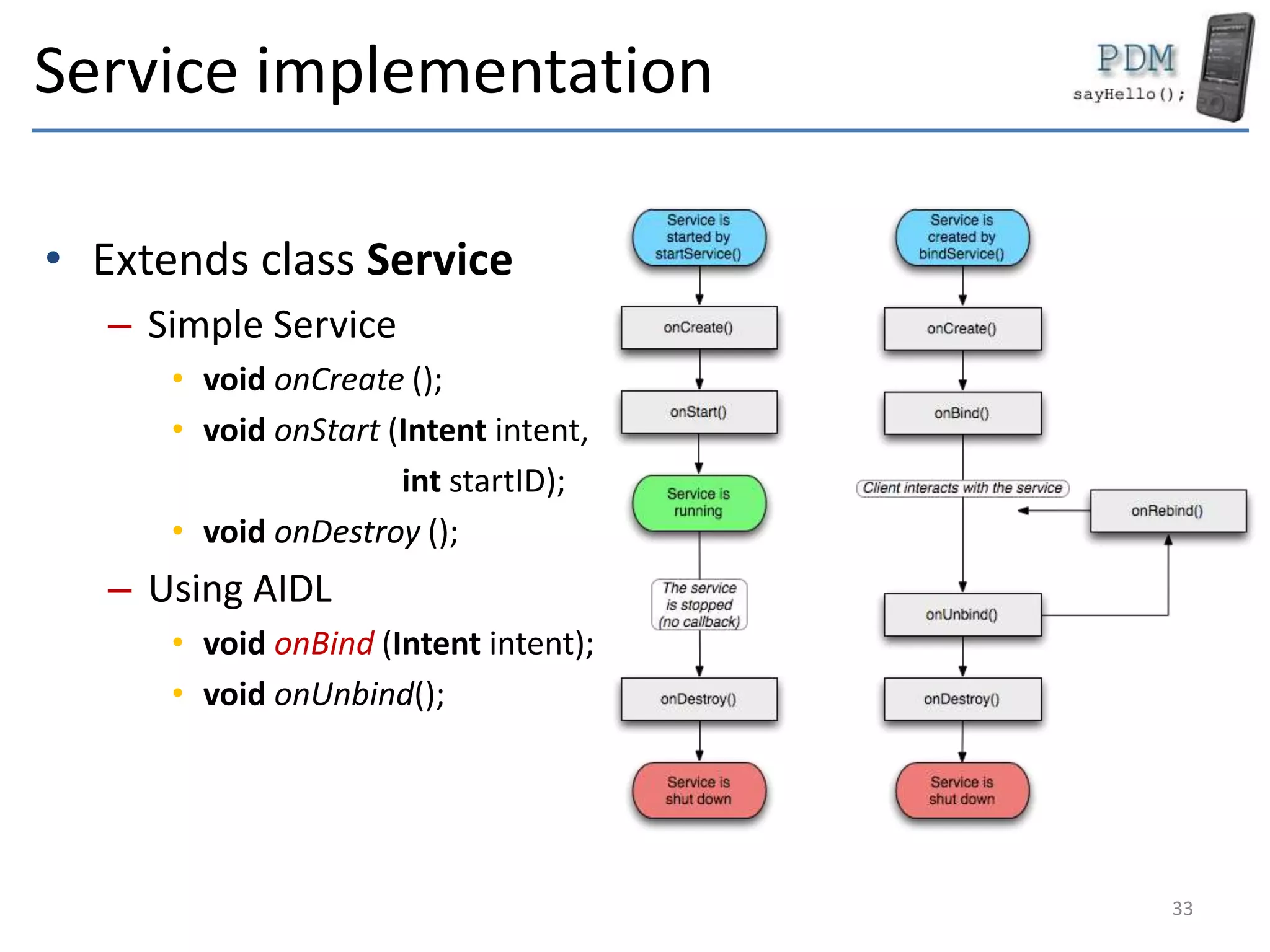
Android is an open source platform based on a modified version of the Linux kernel. It includes native libraries and virtual machine optimizations for mobile devices. Android applications are composed of reusable components like activities, services, content providers and broadcast receivers that can run independently of each other. The Android runtime environment Dalvik uses a just-in-time compiler to optimize apps for performance, while the newer ART runtime uses ahead-of-time compilation.