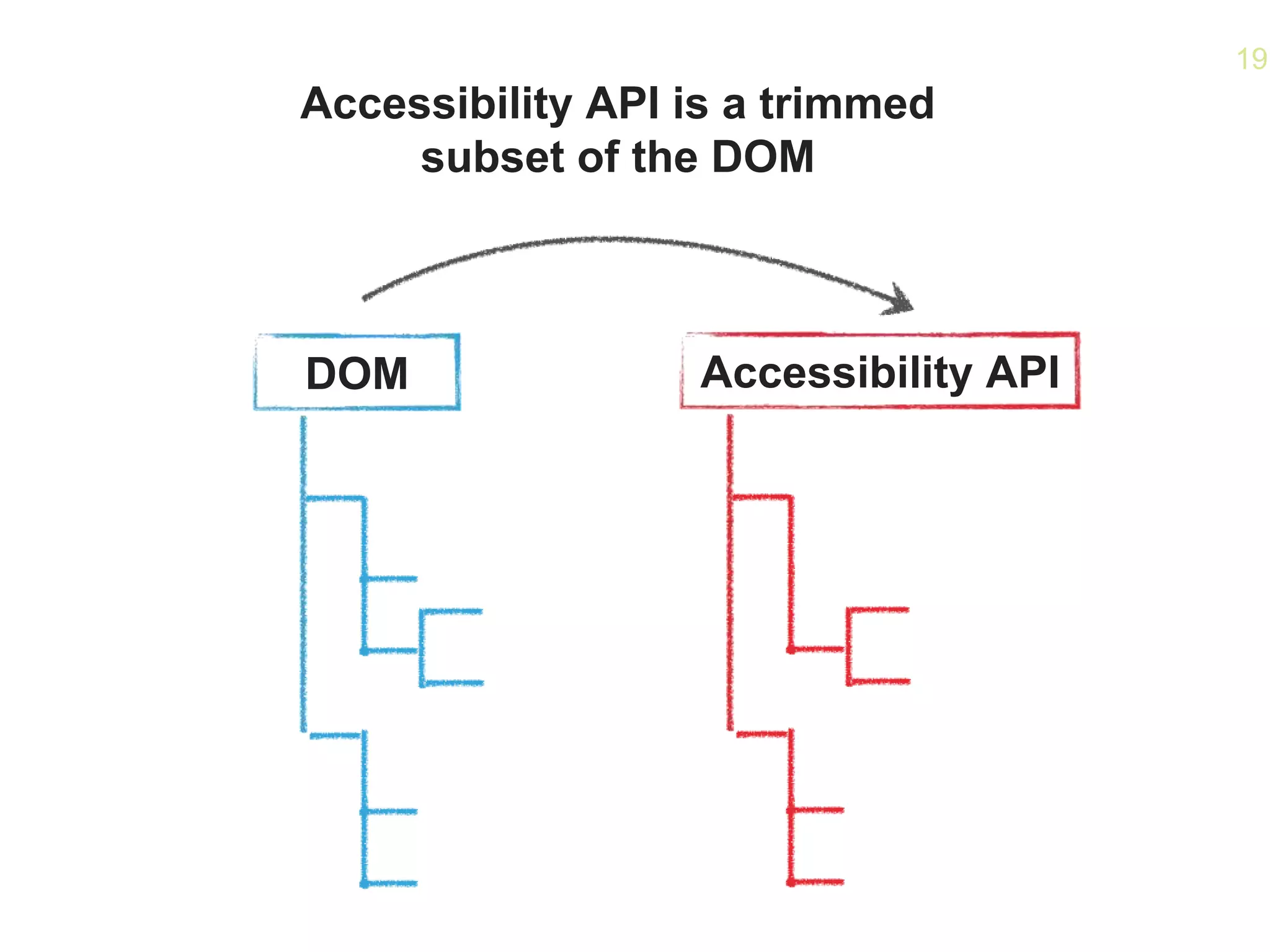
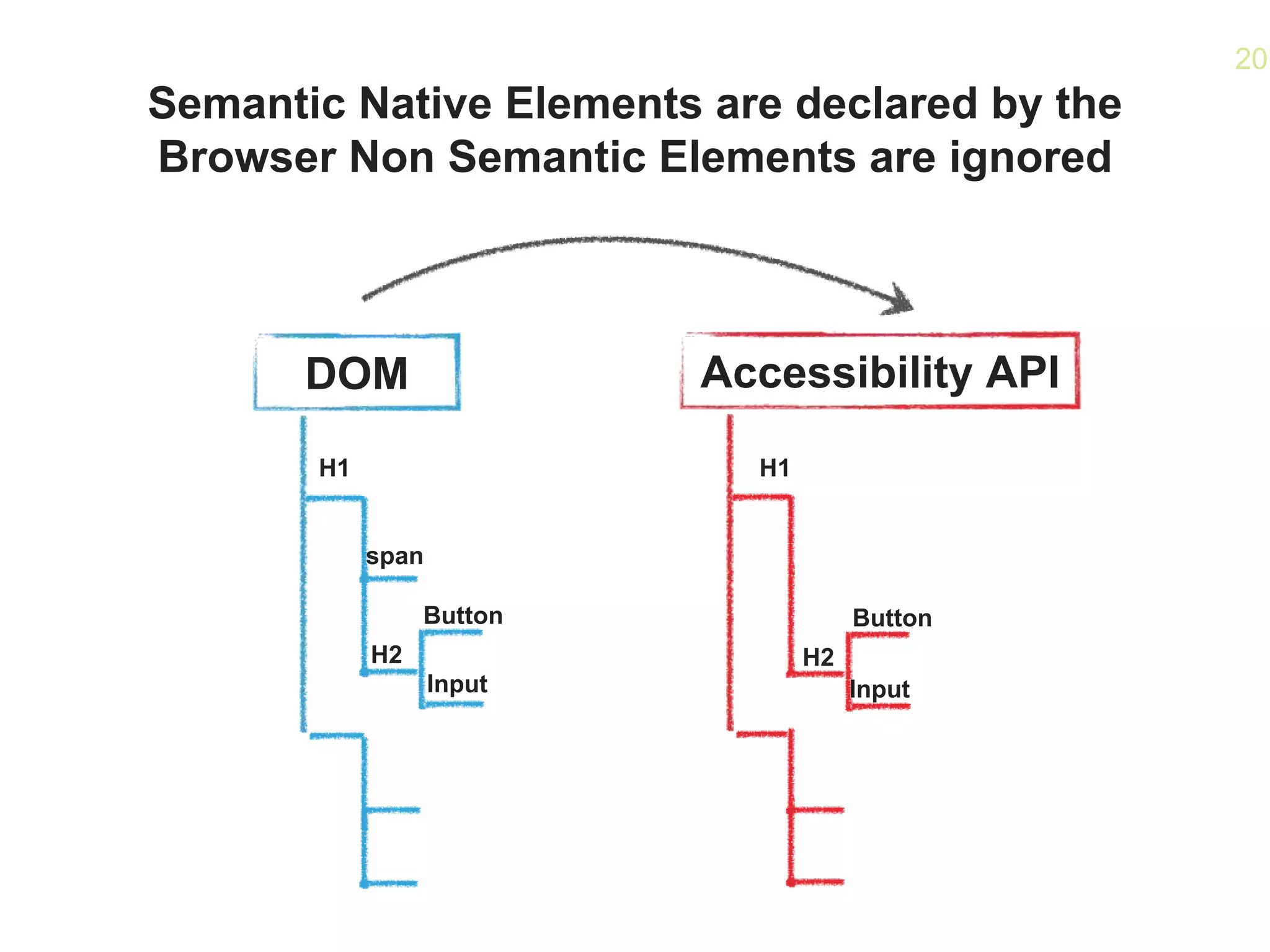
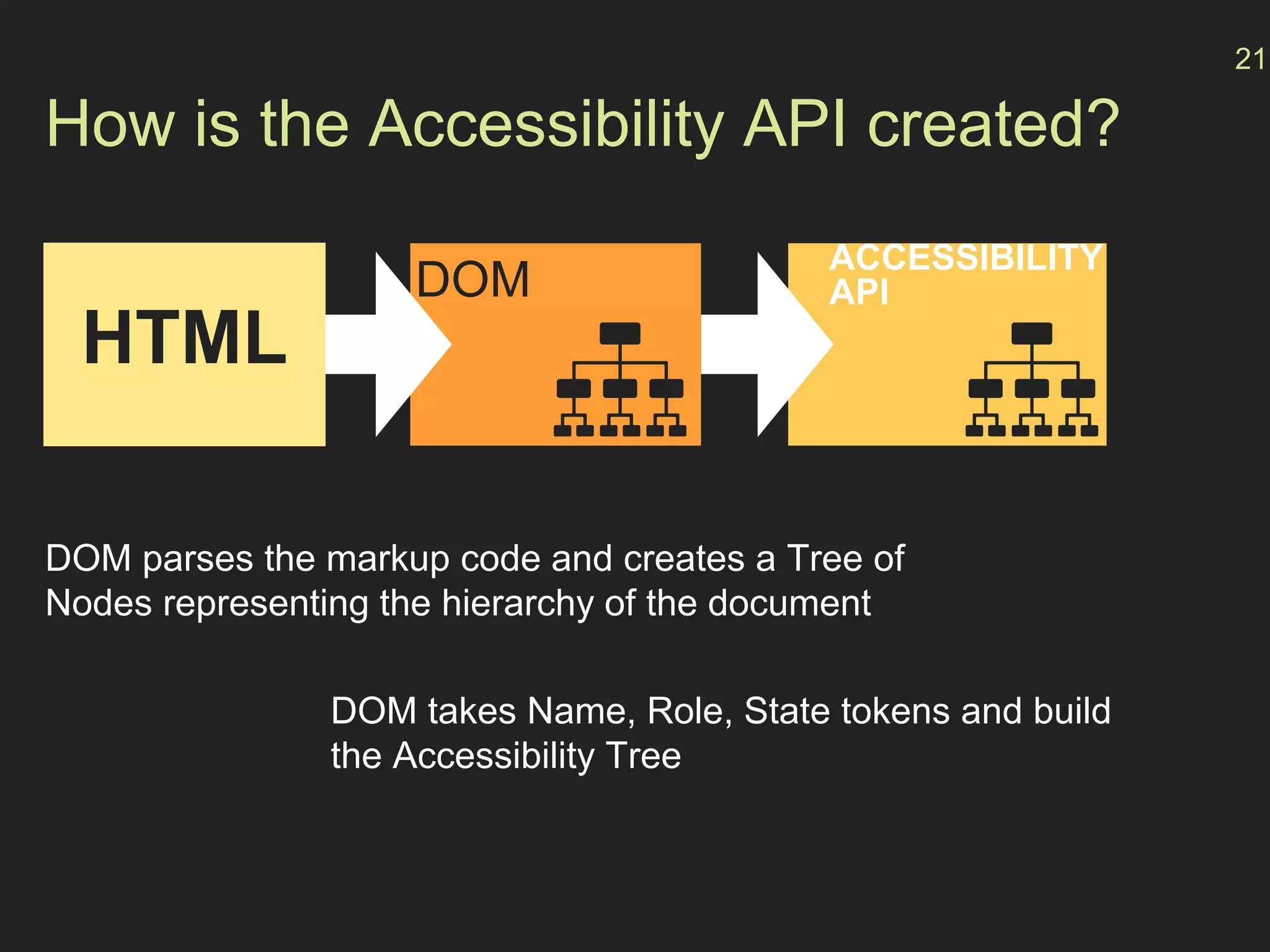
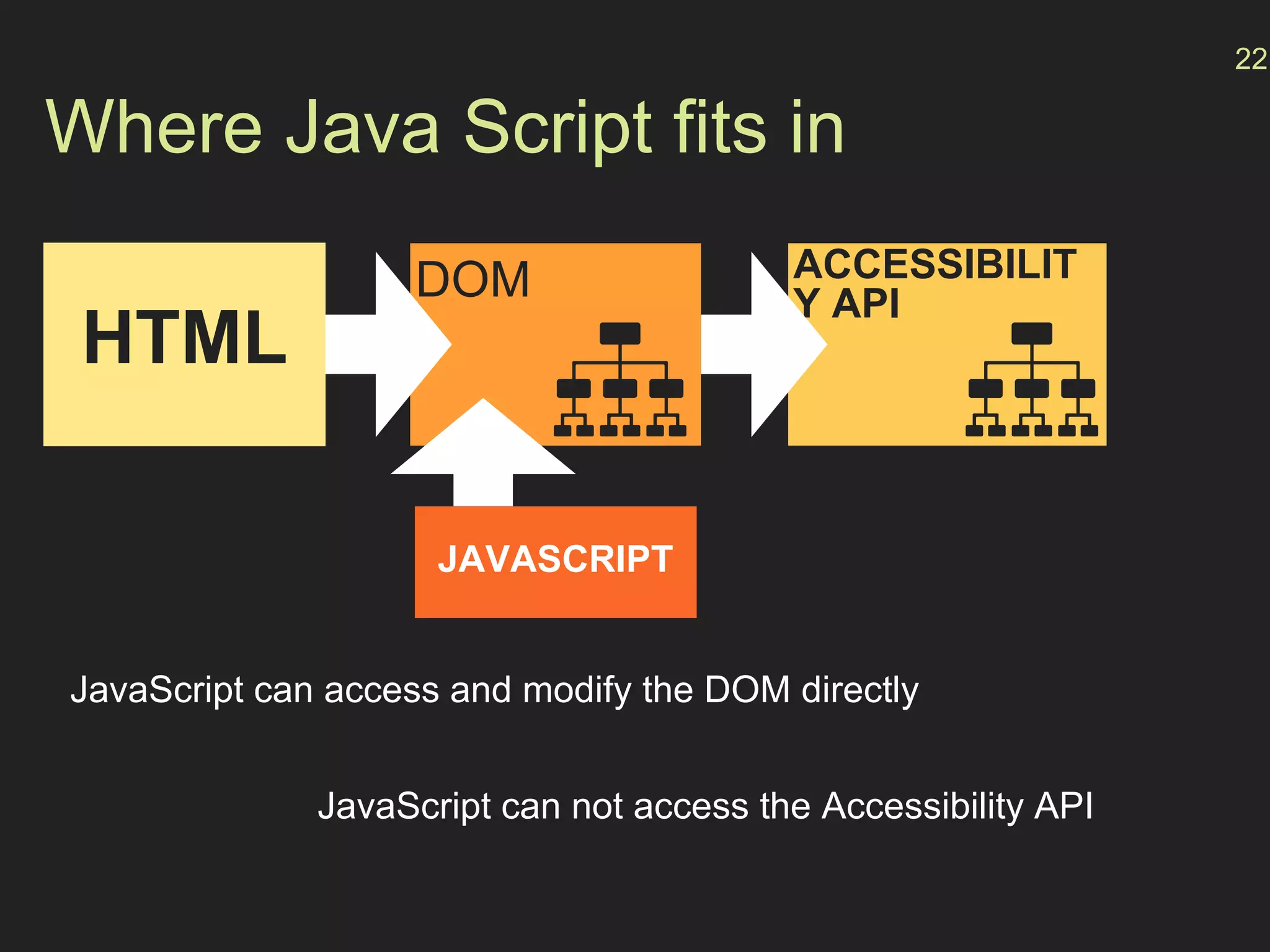
The document provides an overview of how accessibility is implemented on the web. It discusses:
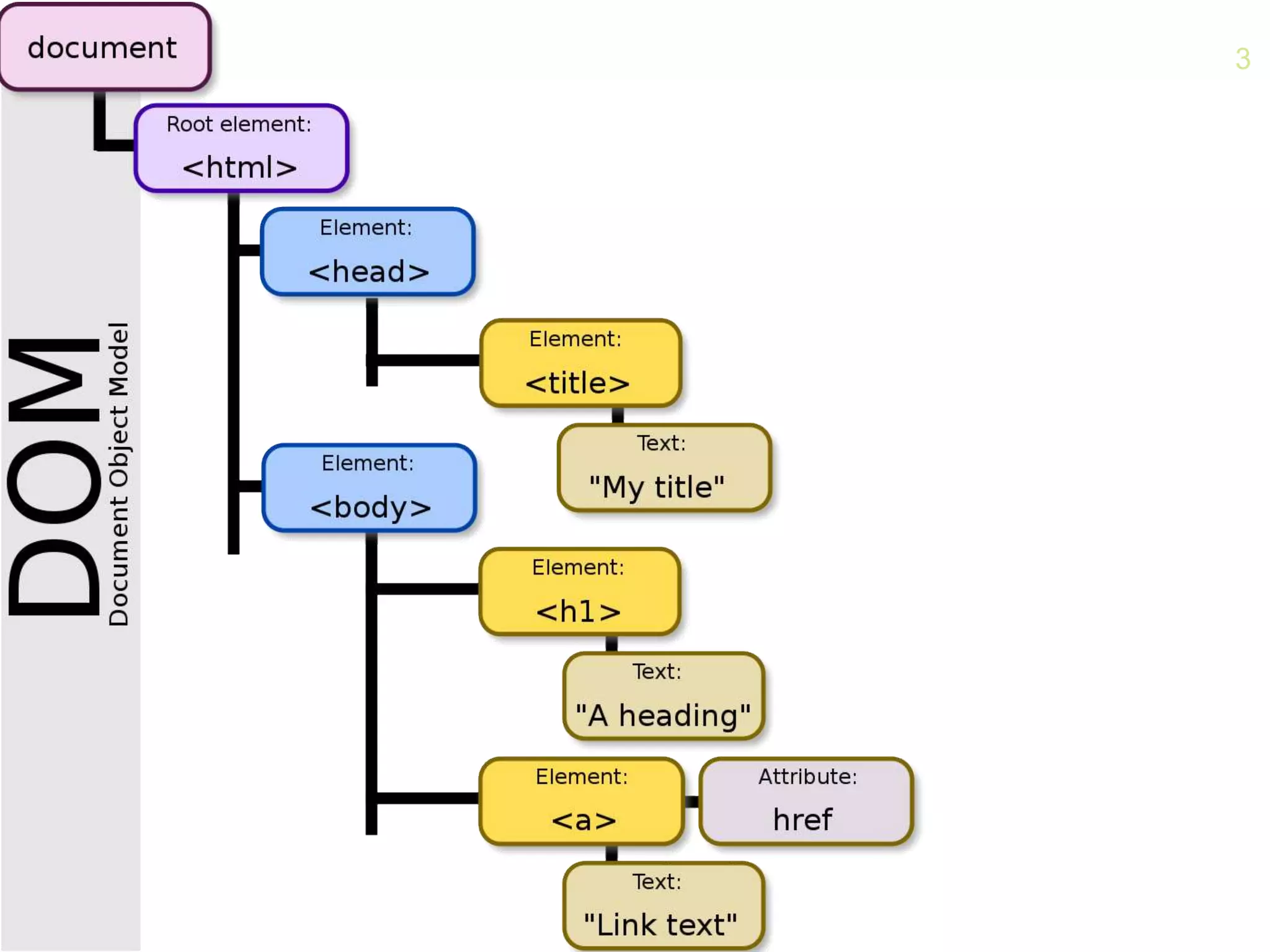
- The origins of the DOM and Accessibility API in the 1990s to provide interfaces for scripts and assistive technologies to interact with web pages.
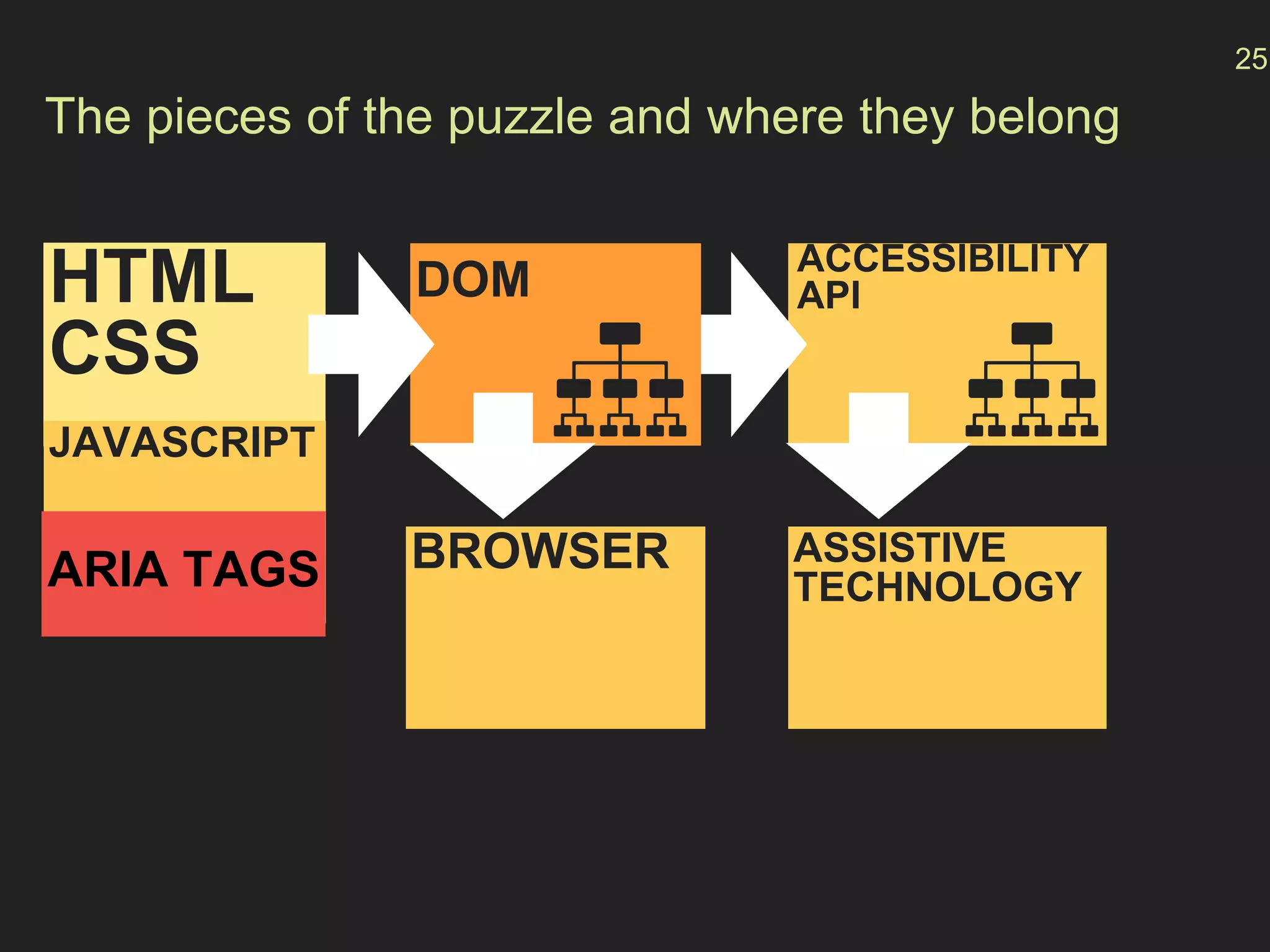
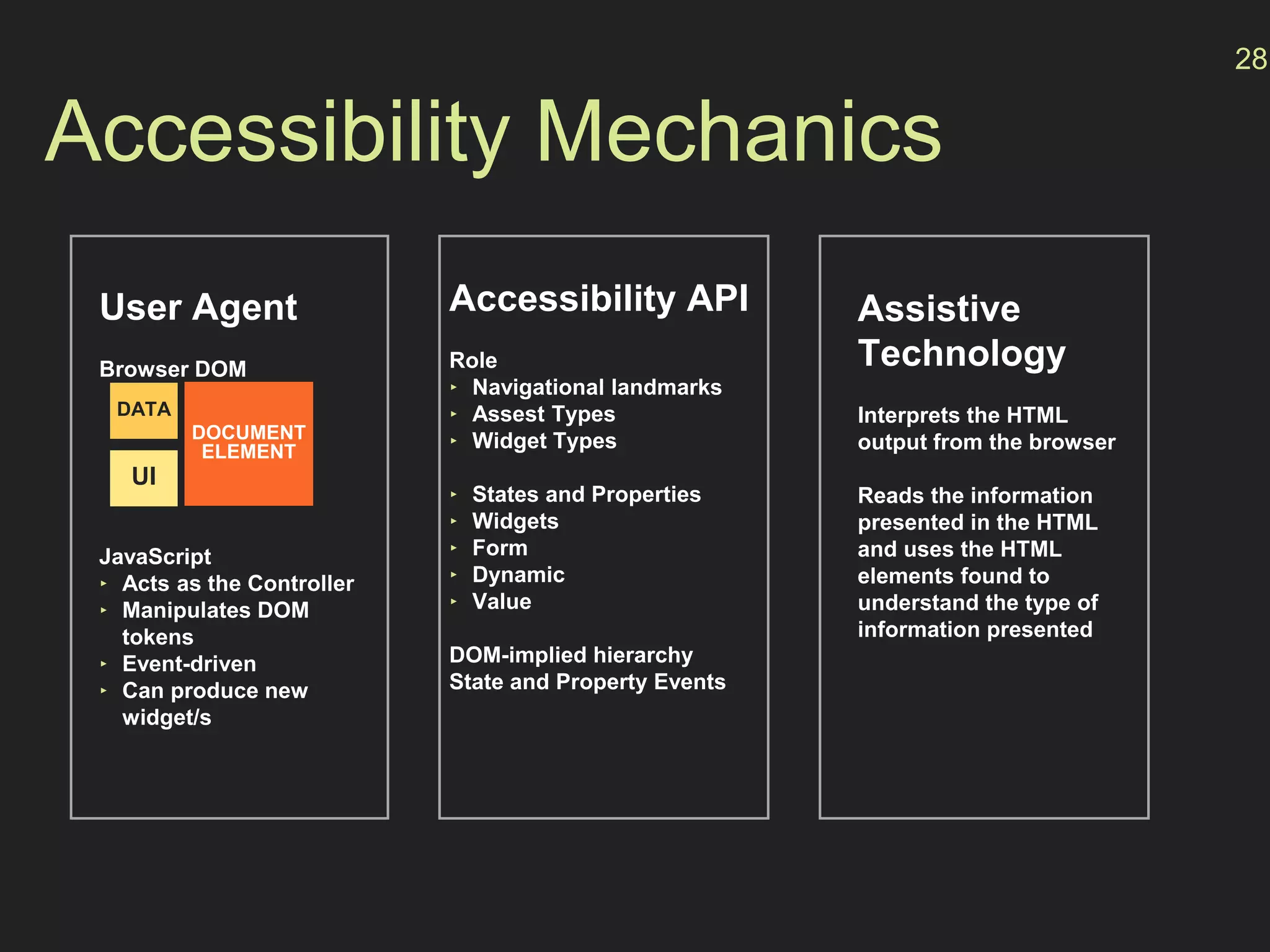
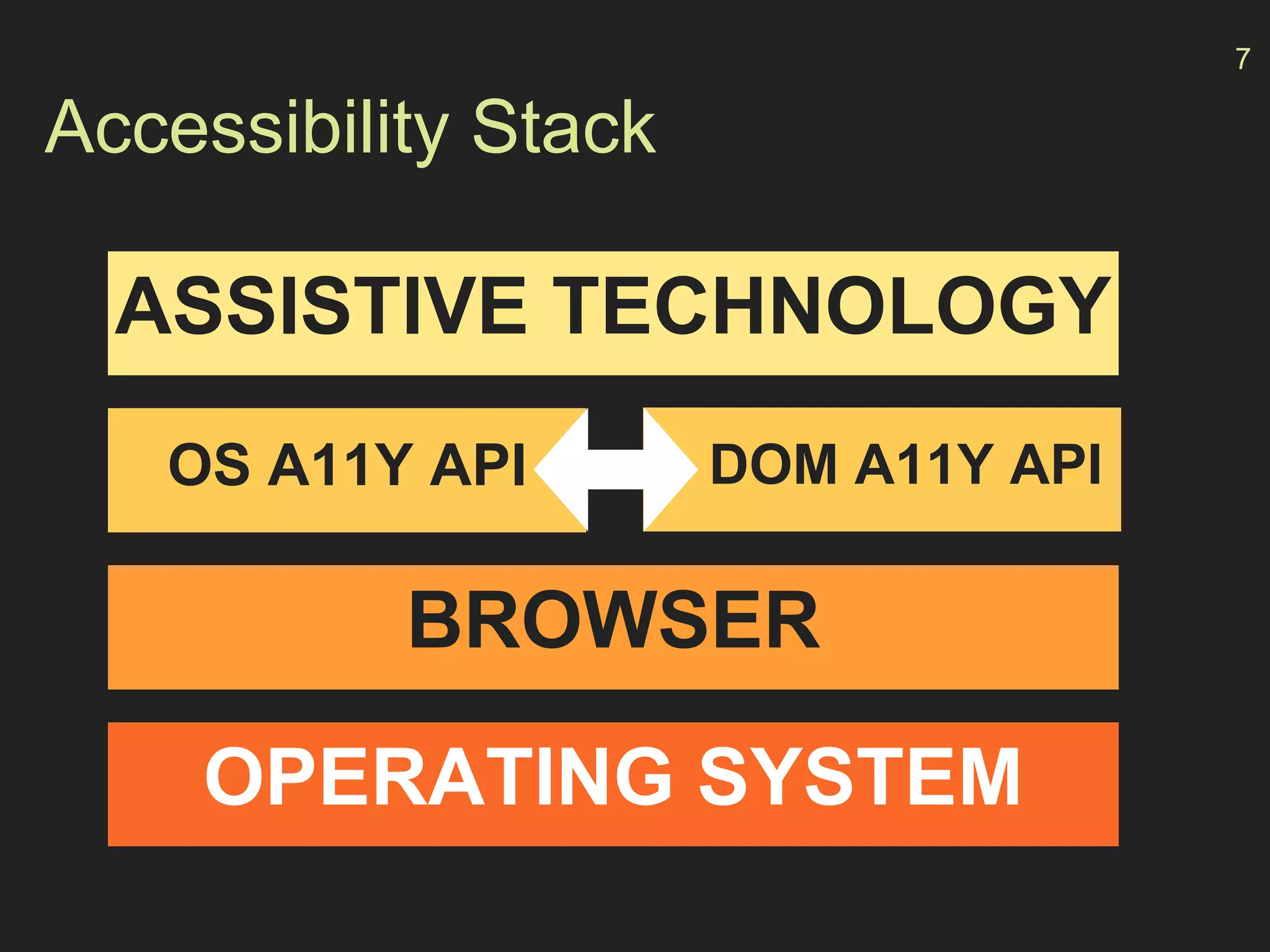
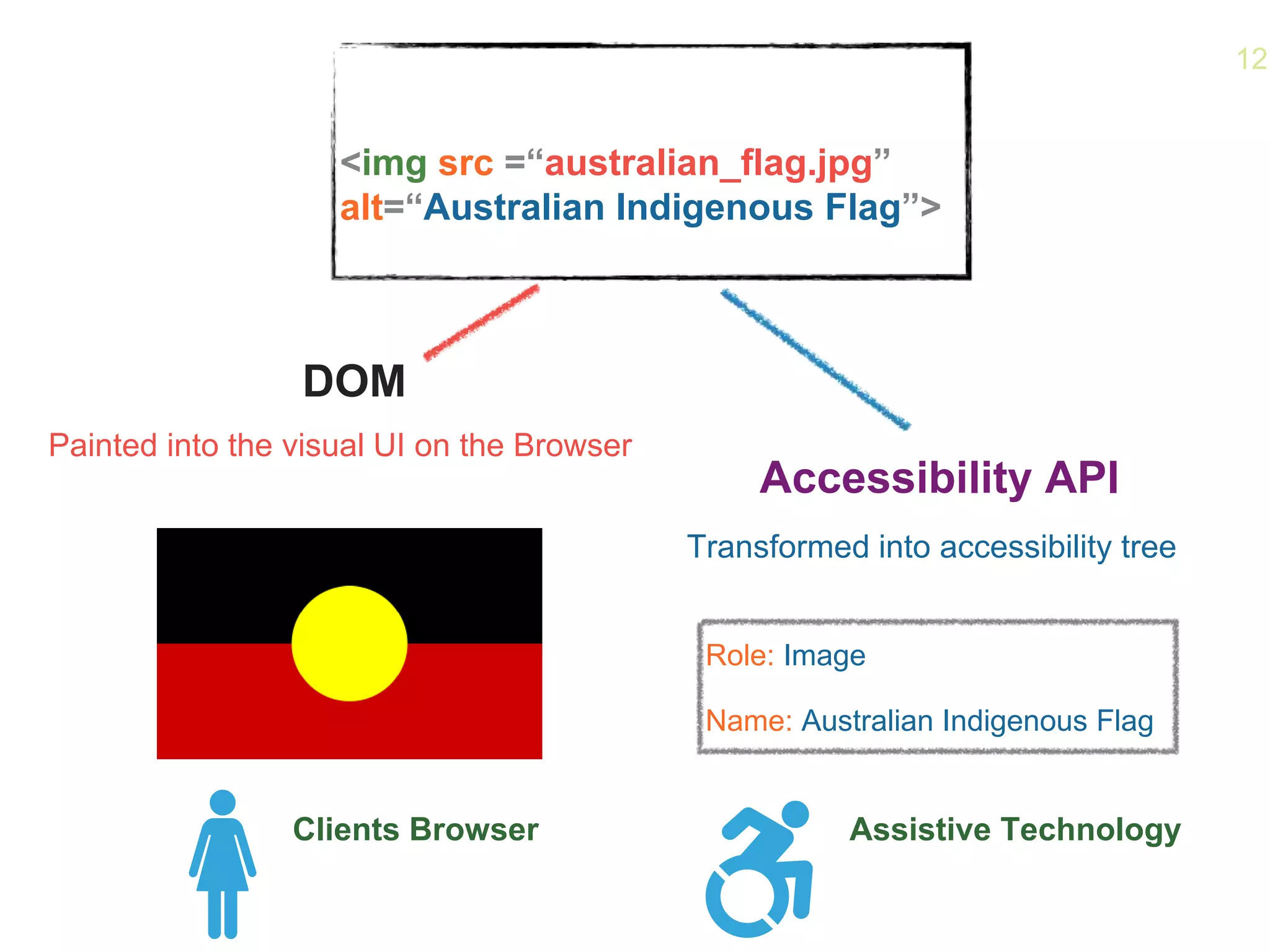
- How the Accessibility API maps HTML elements to operating system elements, allowing for a seamless experience across devices.
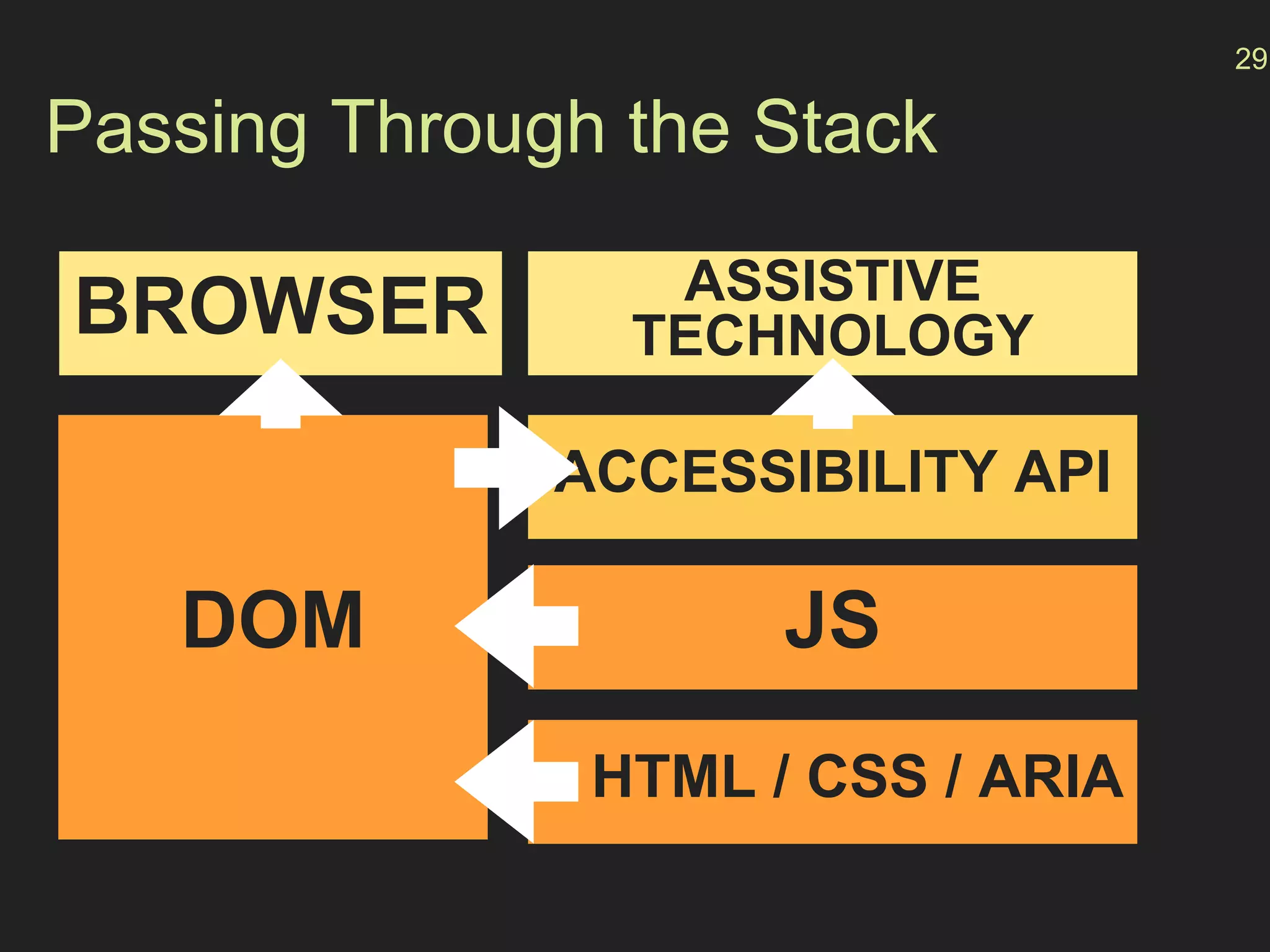
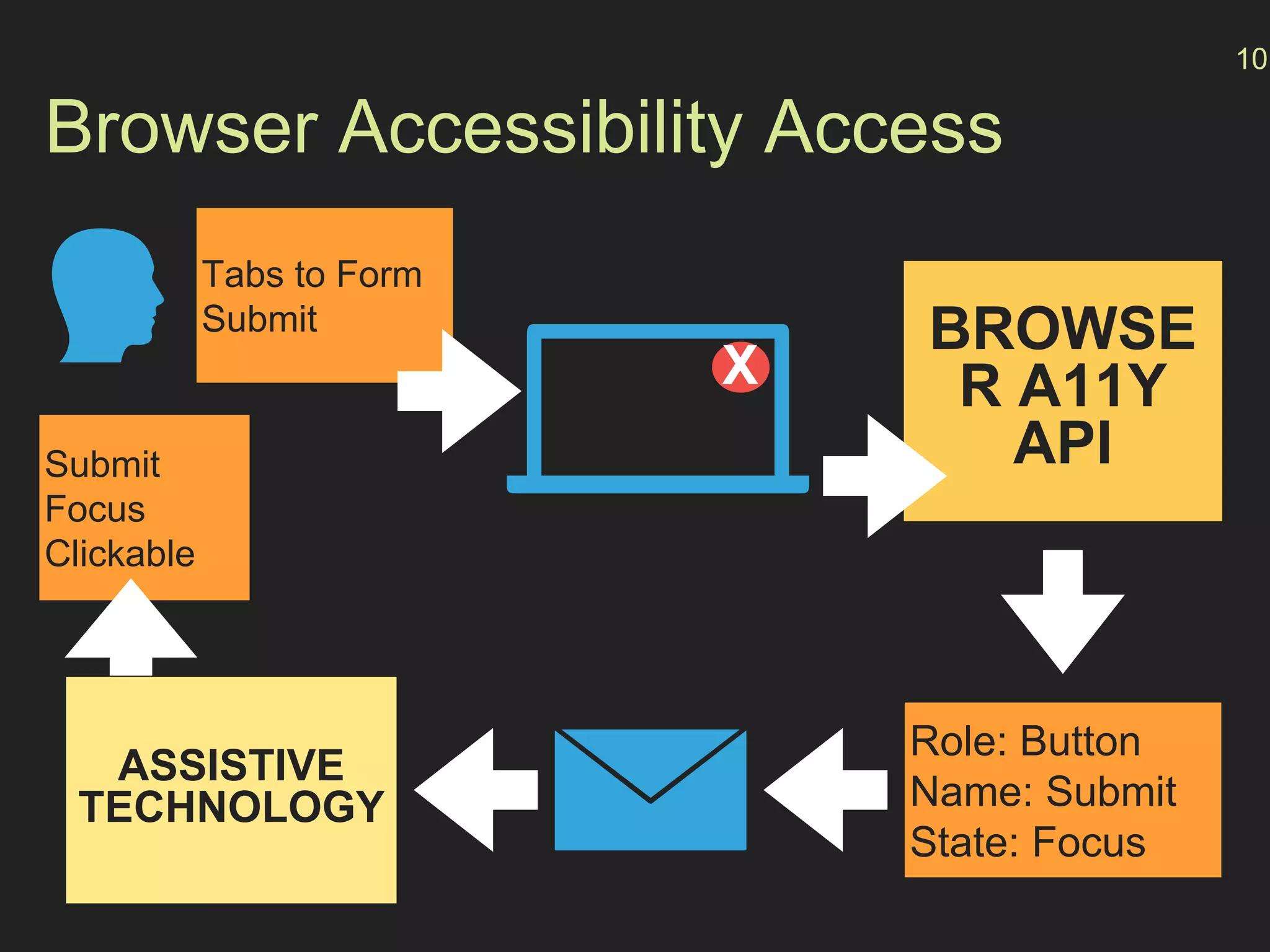
- The "accessibility stack" with assistive technologies interacting with the OS and browser accessibility APIs to interpret web pages.
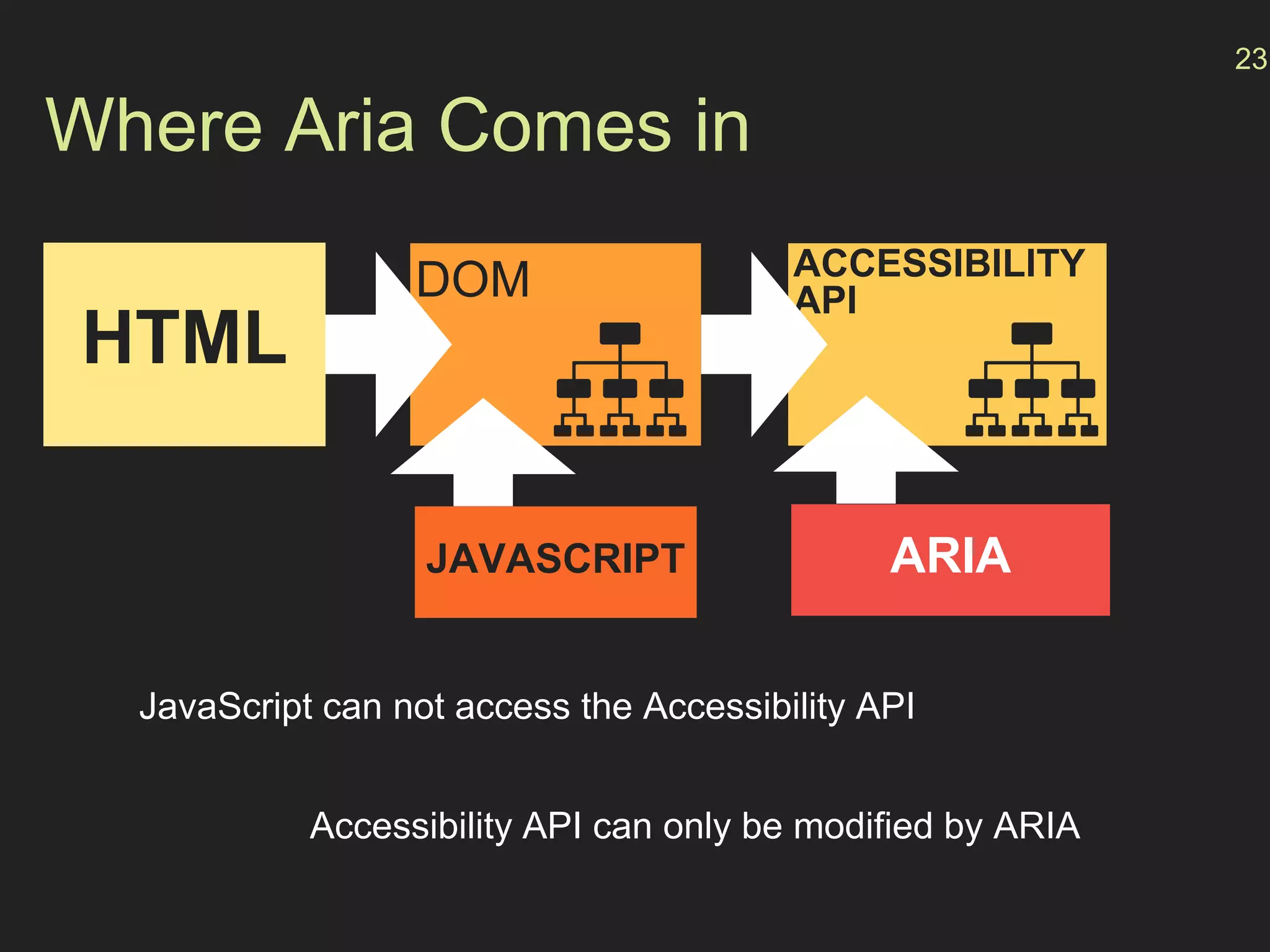
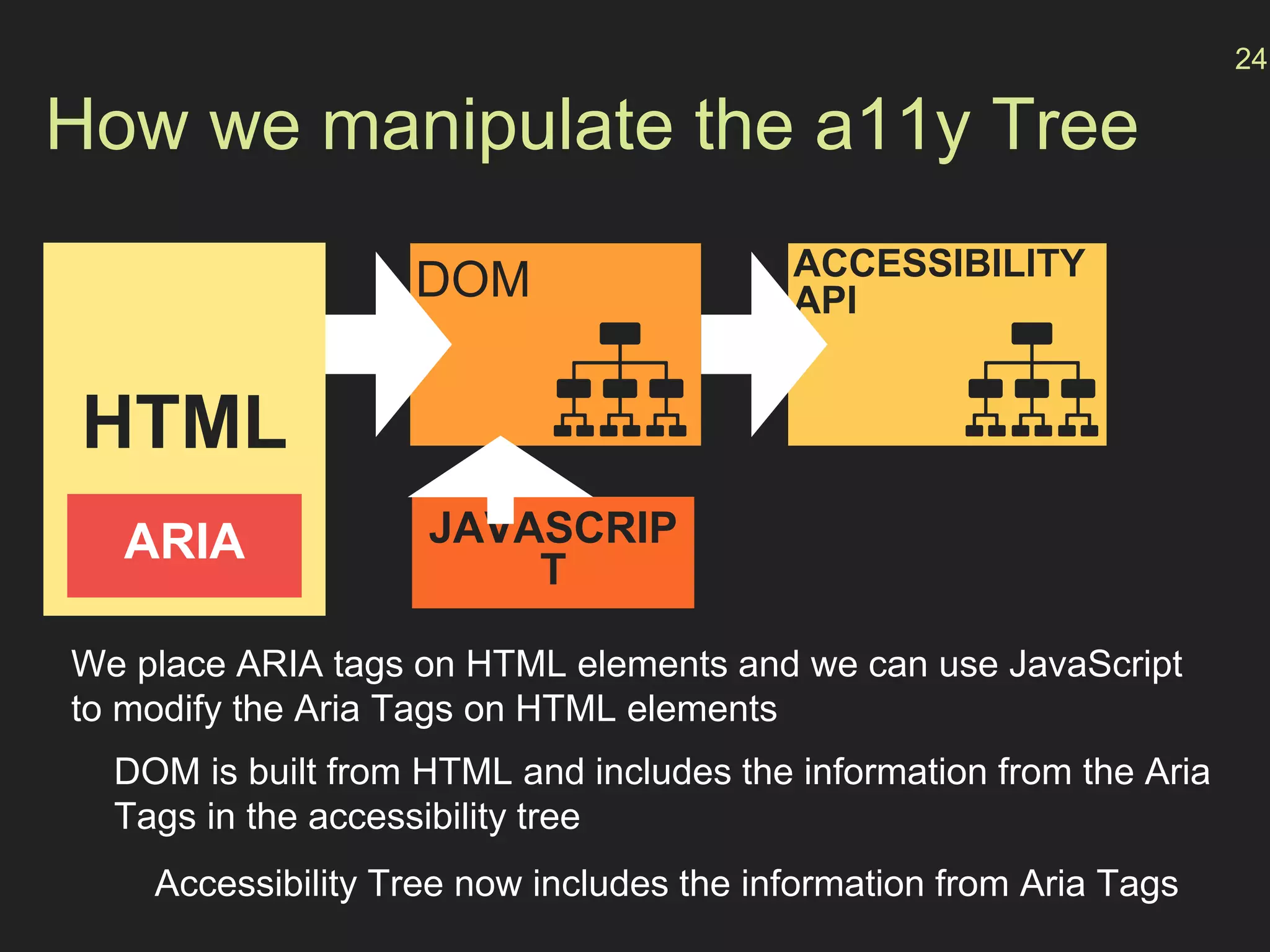
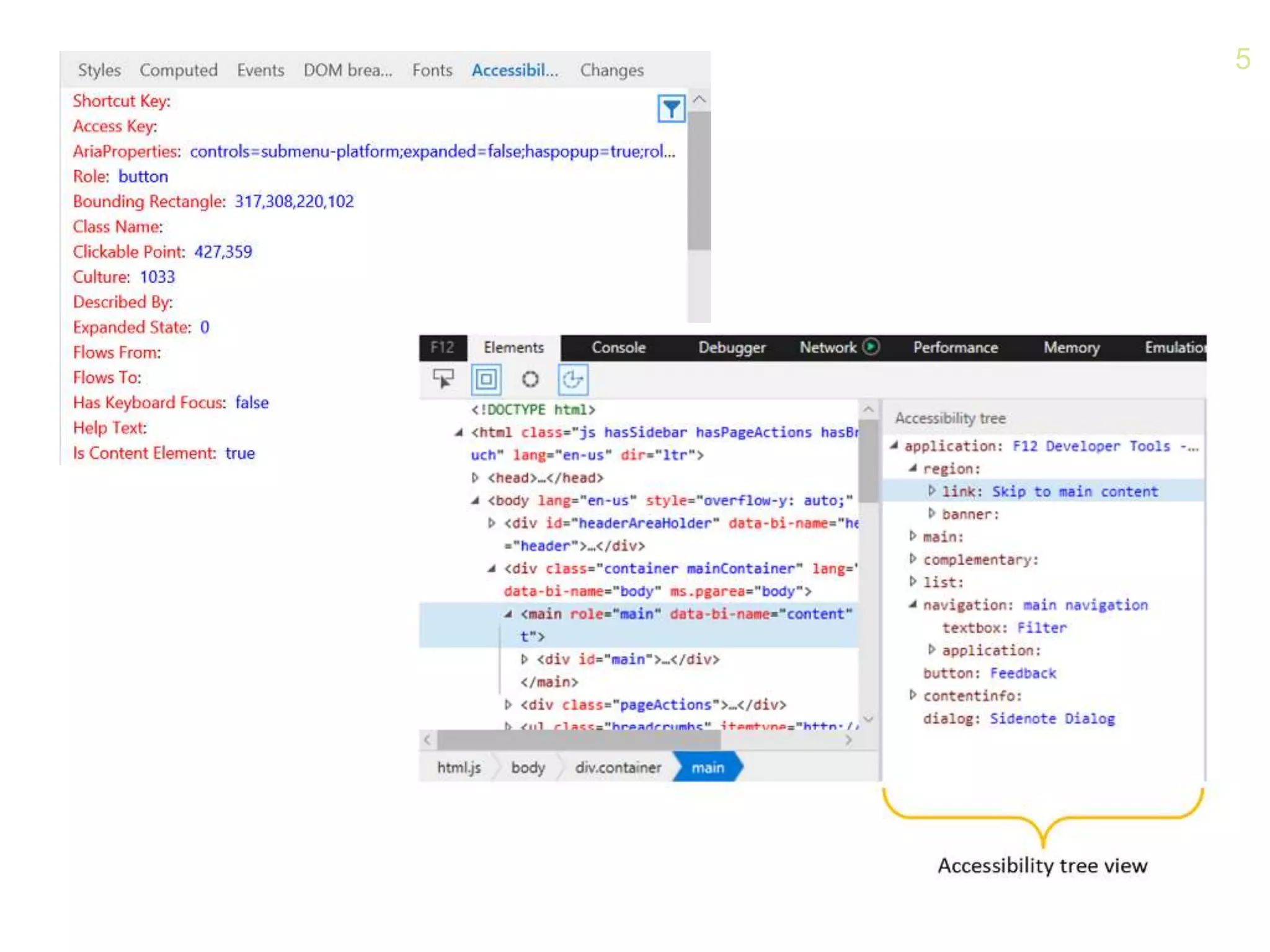
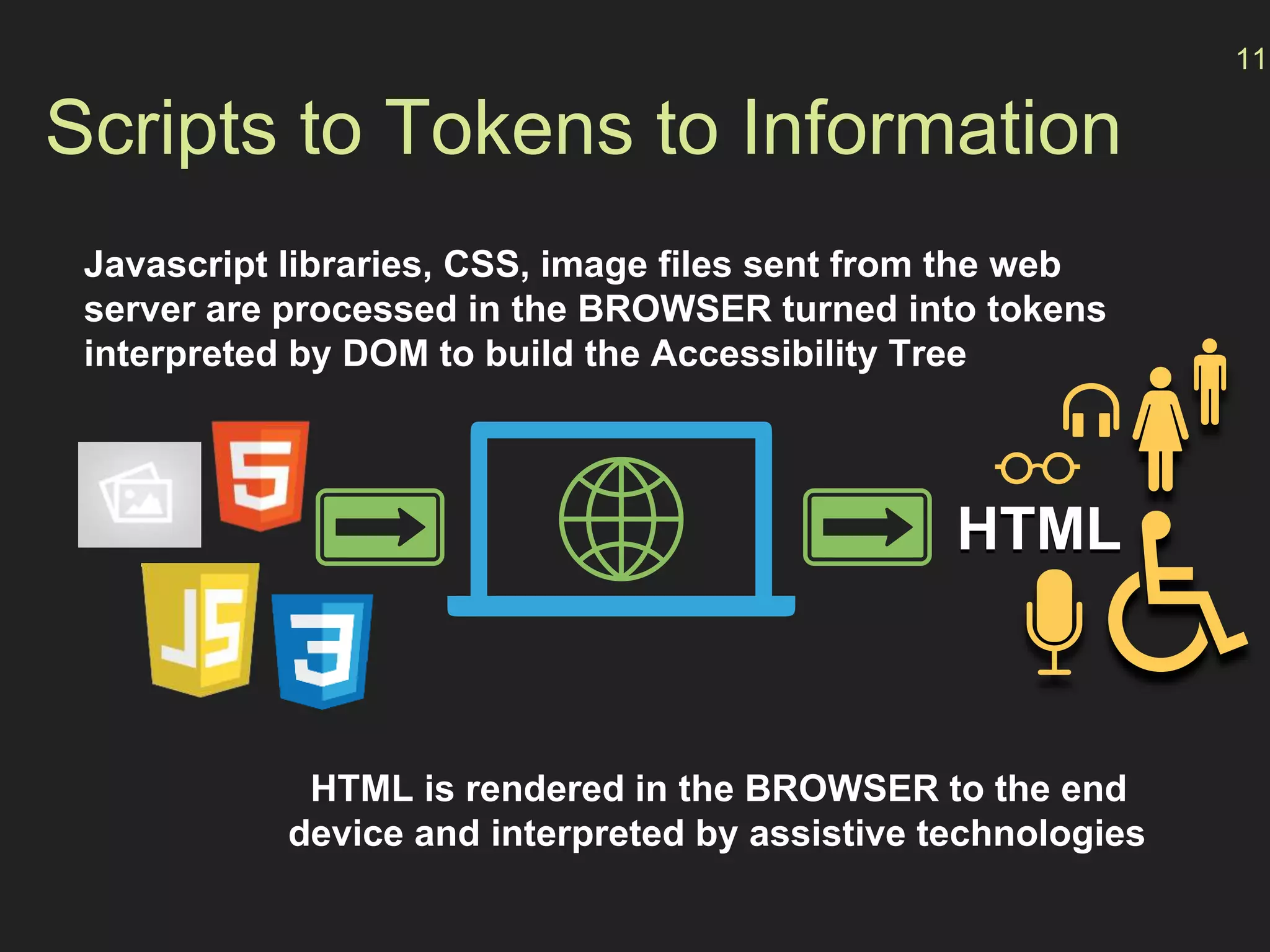
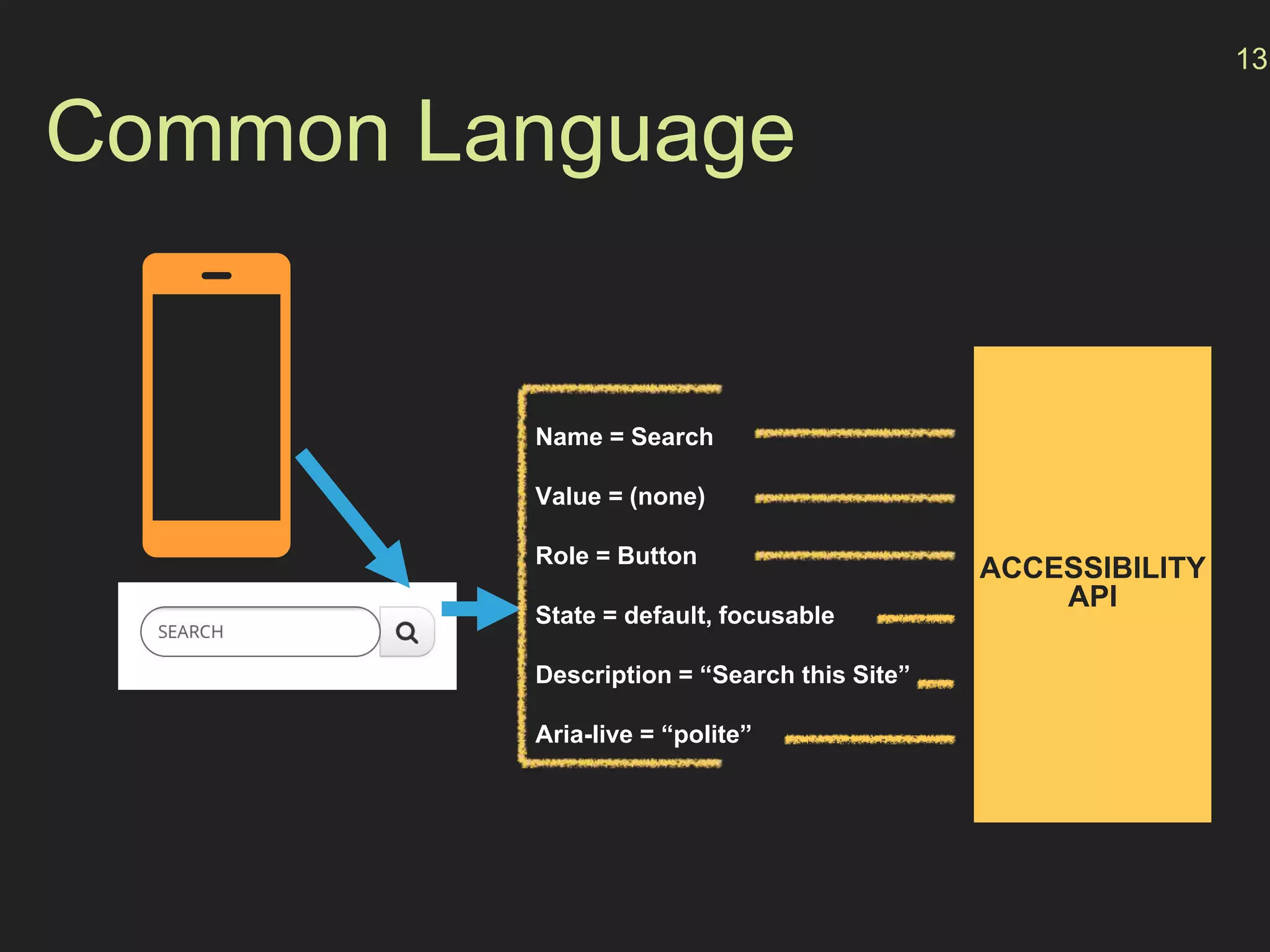
- How the browser processes HTML, CSS and JavaScript to build the accessibility tree from the DOM, with ARIA roles, properties and states providing additional semantics.
- Best practices like using native HTML semantics and communicating state changes









![State
Conveys the current state of the element
Dynamic property expressing characteristics of an object that
may change in response to an action [user or script]
Represent associated data or user interaction
States declare interactions and grouped by Widget types, Live
region, drag and drop
<input type=“checkbox” id=“happy" checked>
<label for=“happy”>Code 2017 makes me happy</label>
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a11ycampapi-101-191114221928/75/DOM-and-Accessibility-API-Communication-17-2048.jpg)