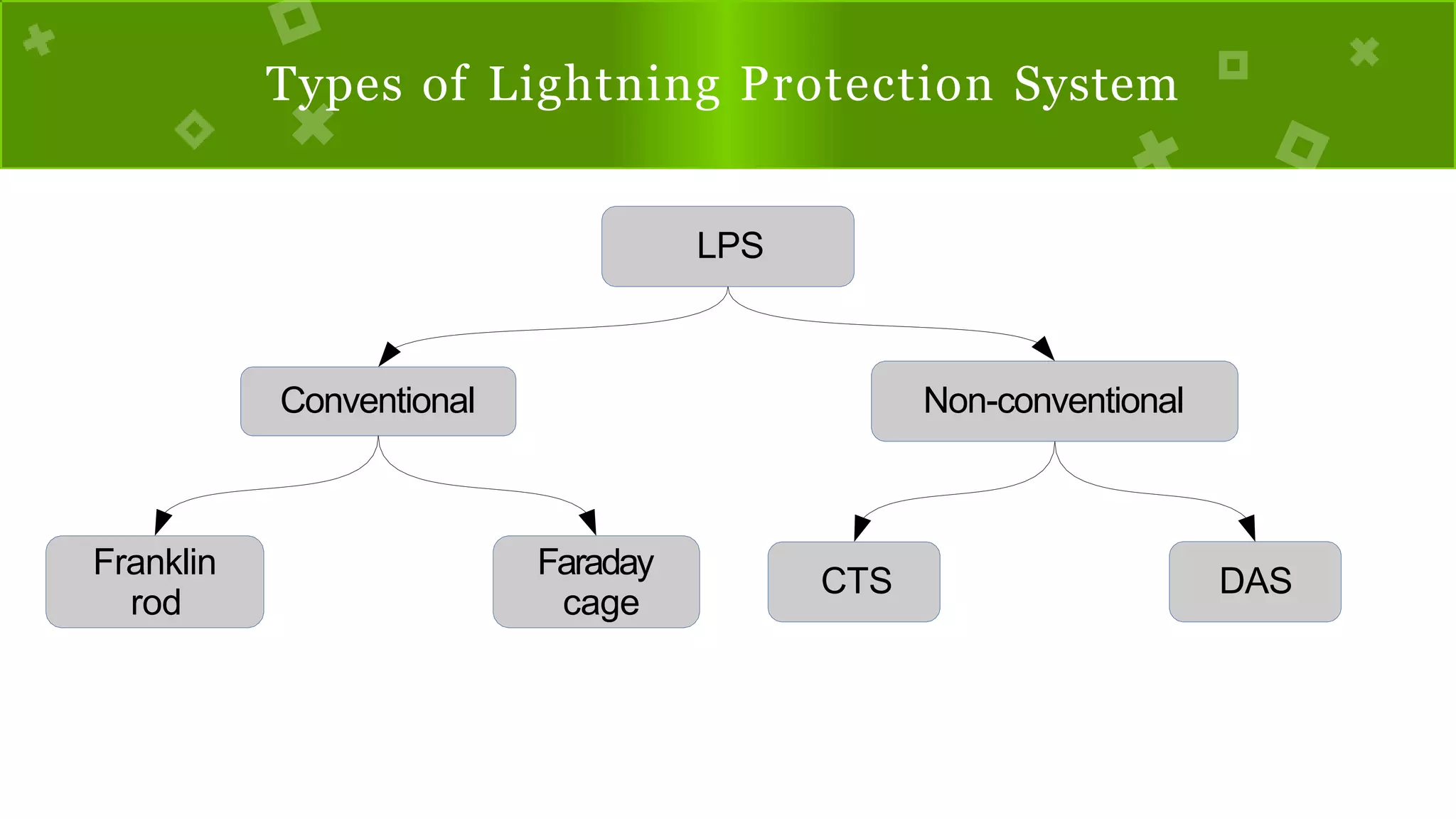
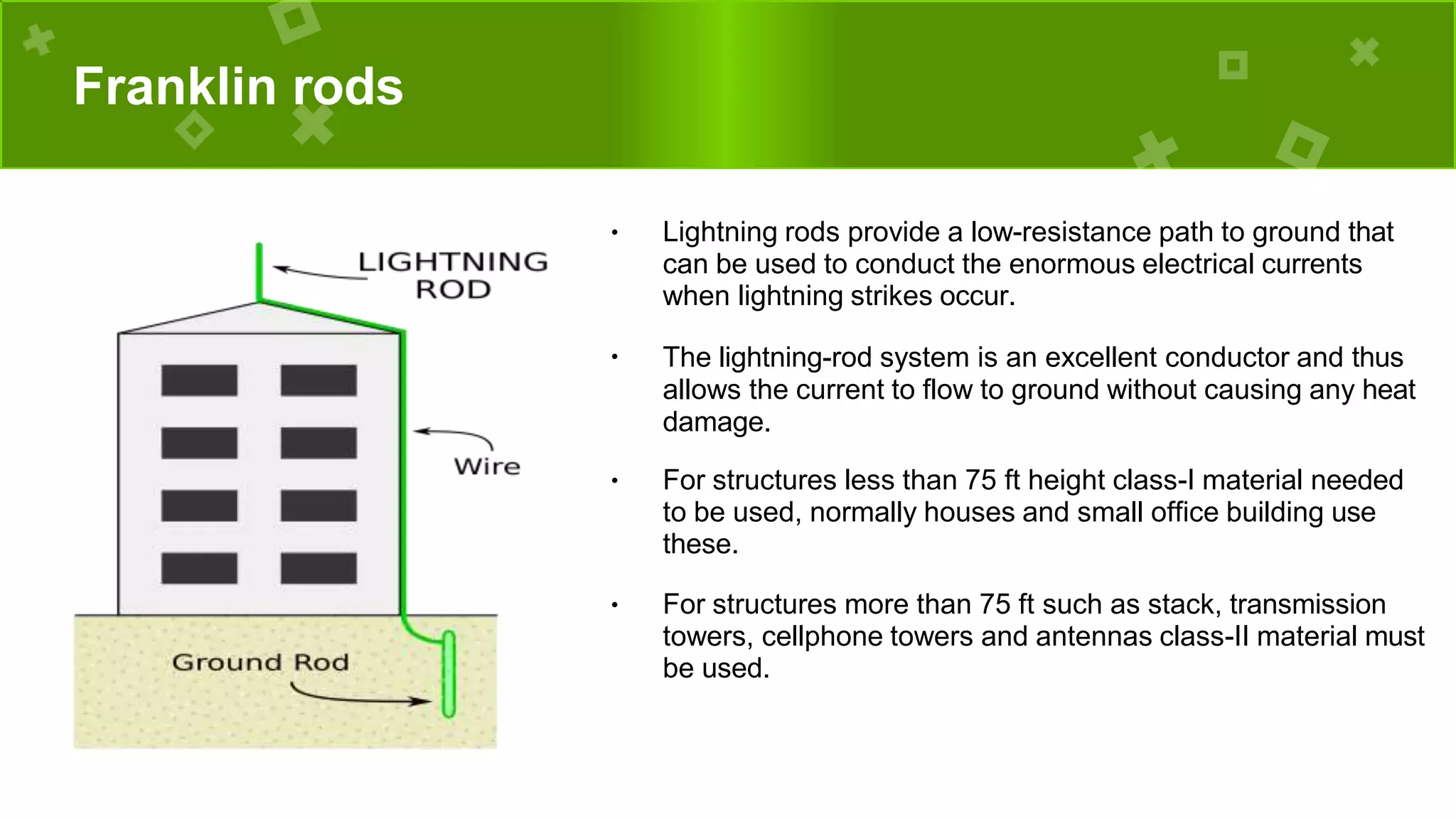
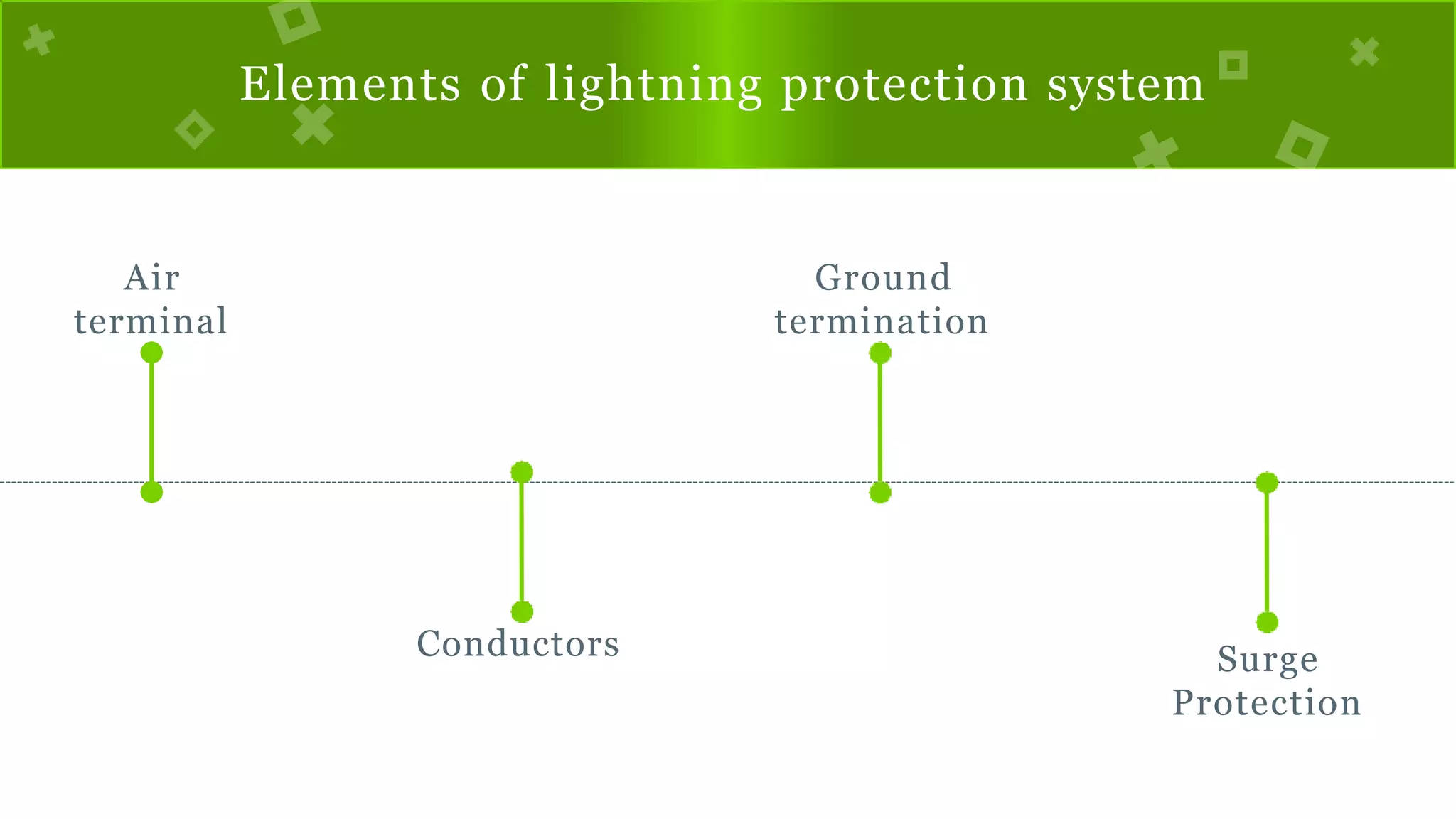
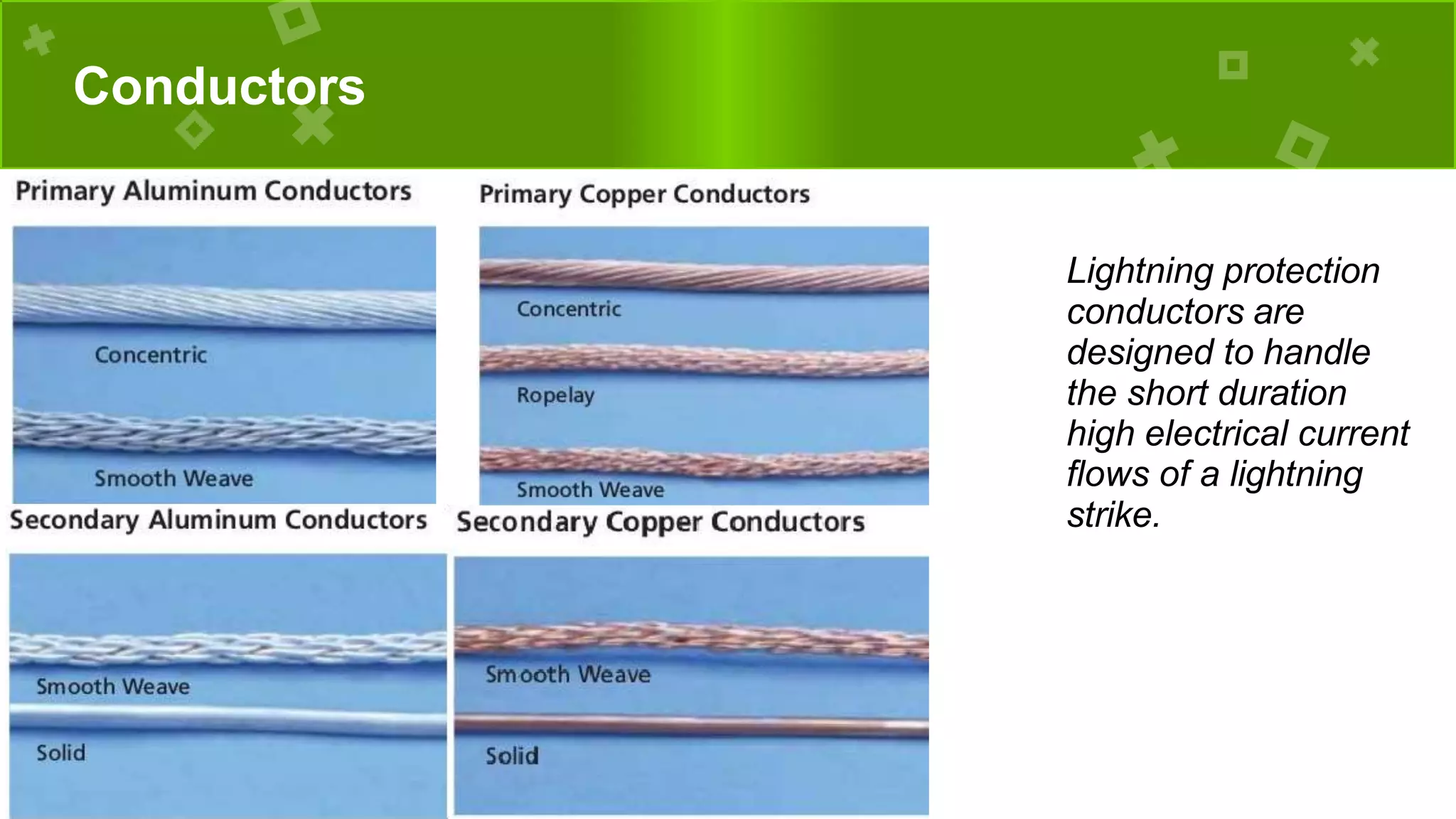
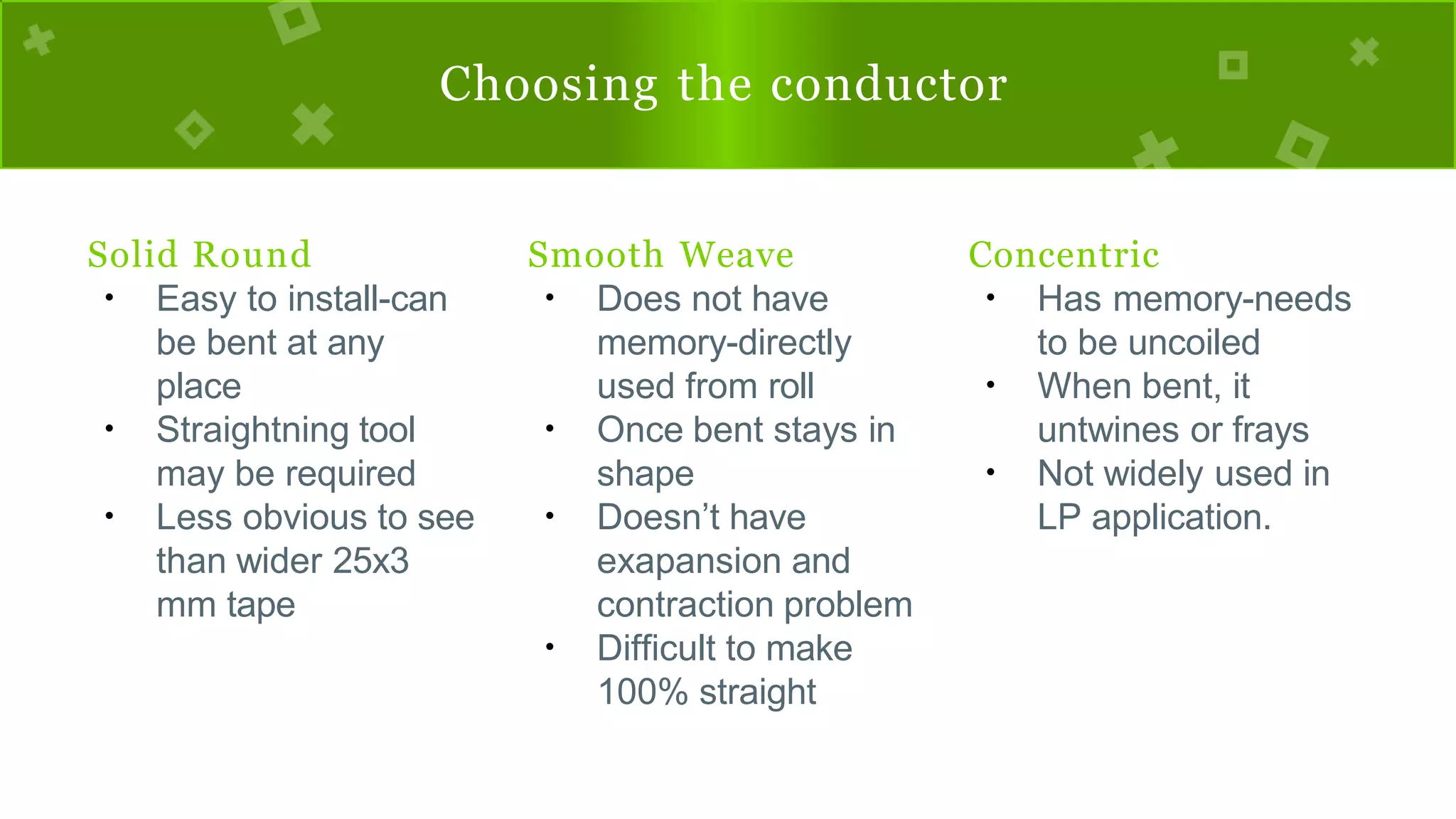
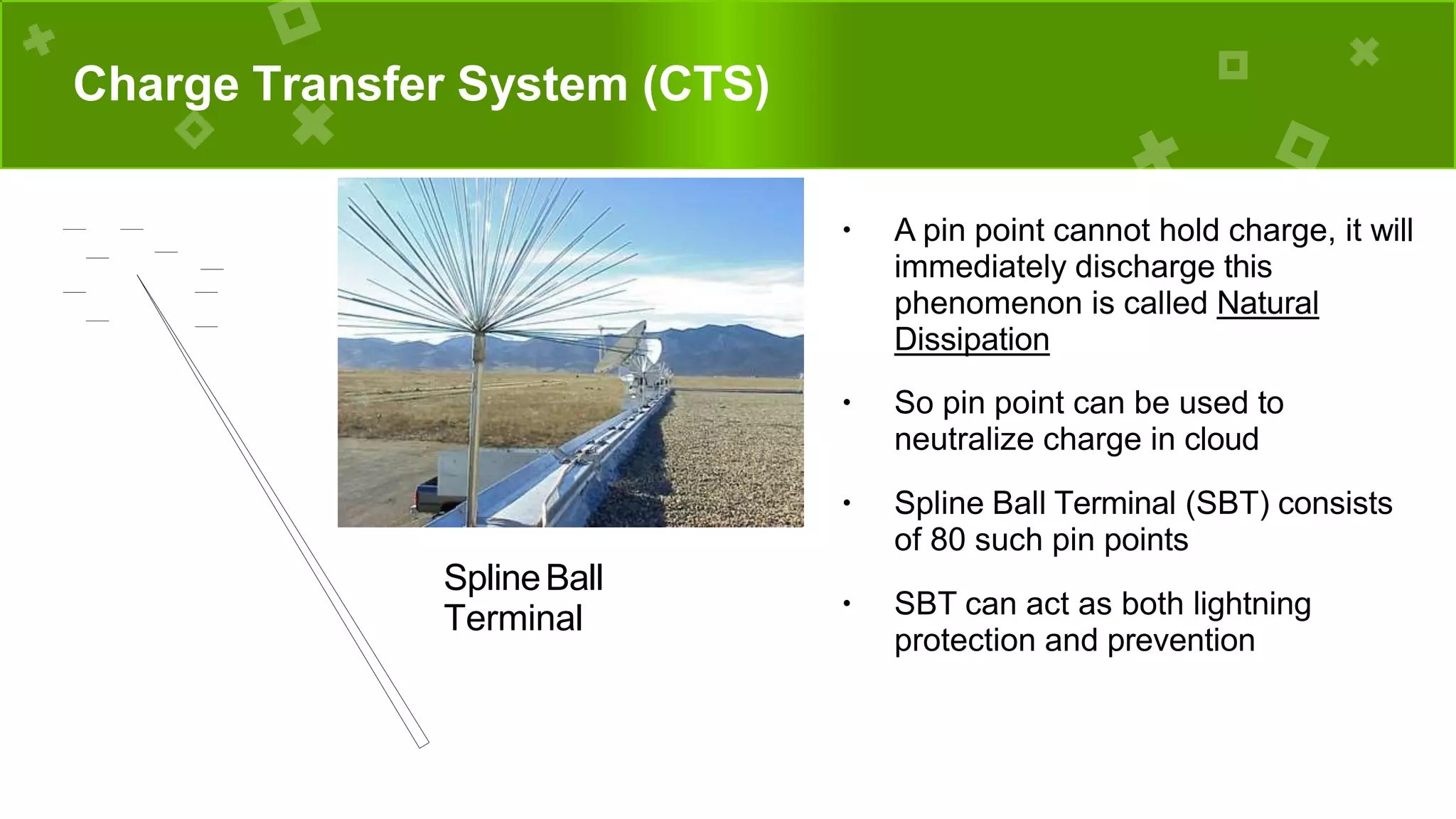
The document discusses lightning, its formation, and important facts about lightning strikes, such as their high temperature and voltage. It elaborates on lightning protection systems (LPS), detailing types including conventional methods like Franklin rods and Faraday cages, and their components such as air terminals and surge protective devices (SPDs). Additionally, it explains technical aspects of conductors and the Charge Transfer System (CTS) and Dissipation Array System (DAS) to enhance lightning protection.