Report
Share
Recommended
Magnificent work in the field of Nano drug deliveryTumor Microenvironment-Mediated Construction and Deconstruction of Extracellu...

Tumor Microenvironment-Mediated Construction and Deconstruction of Extracellu...S KANDAKUMAR CUDDALORE
Recommended
Magnificent work in the field of Nano drug deliveryTumor Microenvironment-Mediated Construction and Deconstruction of Extracellu...

Tumor Microenvironment-Mediated Construction and Deconstruction of Extracellu...S KANDAKUMAR CUDDALORE
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (17)
Cells undergoing morphological changes during apoptosis

Cells undergoing morphological changes during apoptosis
Chimeric virus like particles made using GAG and M1 Capsid prteins providing ...

Chimeric virus like particles made using GAG and M1 Capsid prteins providing ...
The Effect of Oflactomedin1 and Latrophilin2 in Glioblastoma Metastasis

The Effect of Oflactomedin1 and Latrophilin2 in Glioblastoma Metastasis
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (15)
Booking open in Shankra Residency Jaipur Flats @7503367689

Booking open in Shankra Residency Jaipur Flats @7503367689
Similar to poster for 2014 KSPST_revision
Presentation by: Santiago Giraldo Rodas. III Semester. Medicine UPB.Identification of a new way to induce differentiation of dermal fibroblasts i...

Identification of a new way to induce differentiation of dermal fibroblasts i...Santiago Giraldo Rodas
Similar to poster for 2014 KSPST_revision (20)
Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...

Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...
Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...

Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...
Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...

Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...
Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...

Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...
Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...

Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...
Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...

Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...
Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...

Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...
Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...

Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...
Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...

Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...
Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...

Functional Disparity of Carcinoma Associated Fibroblasts in Different Stages ...
Identification of a new way to induce differentiation of dermal fibroblasts i...

Identification of a new way to induce differentiation of dermal fibroblasts i...
poster for 2014 KSPST_revision
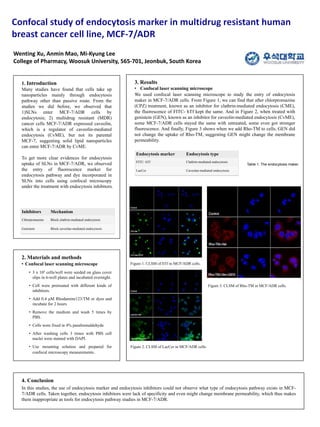
- 1. 1. Introduction Many studies have found that cells take up nanoparticles mainly through endocytosis pathway other than passive route. From the studies we did before, we observed that 1)SLNs enter MCF-7/ADR cells by endocytosis; 2) multidrug resistant (MDR) cancer cells MCF-7/ADR expressed caveolin, which is a regulator of caveolin-mediated endocytosis (CvME), but not its parental MCF-7, suggesting solid lipid nanoparticles can enter MCF-7/ADR by CvME. To get more clear evidences for endocytosis uptake of SLNs in MCF-7/ADR, we observed the entry of fluorescence marker for endocytosis pathway and dye incorporated in SLNs into cells using confocal microscopy under the treatment with endocytosis inhibitors. 2. Materials and methods • Confocal laser scanning microscope • 3 x 105 cells/well were seeded on glass cover slips in 6-well plates and incubated overnight. • Cell were pretreated with different kinds of inhibitors. • Add 0.4 μM Rhodamine123/TM or dyes and incubate for 2 hours • Remove the medium and wash 5 times by PBS. • Cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde • After washing cells 3 times with PBS cell nuclei were stained with DAPI. • Use mounting solution and prepared for confocal microscopy measurements. 3. Results • Confocal laser scanning microscope We used confocal laser scanning microscope to study the entry of endocytosis maker in MCF-7/ADR cells. From Figure 1, we can find that after chlorpromazine (CPZ) treatment, known as an inhibitor for clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME), the fluorescence of FITC- hTf kept the same. And in Figure 2, when treated with genistein (GEN), known as an inhibitor for caveolin-mediated endocytosis (CvME), some MCF-7/ADR cells stayed the same with untreated, some even got stronger fluorescence. And finally, Figure 3 shows when we add Rho-TM to cells, GEN did not change the uptake of Rho-TM, suggesting GEN might change the membrane permeability. Wenting Xu, Anmin Mao, Mi-Kyung Lee College of Pharmacy, Woosuk University, 565-701, Jeonbuk, South Korea 4. Conclusion In this studies, the use of endocytosis marker and endocytosis inhibitors could not observe what type of endocytosis pathway exists in MCF- 7/ADR cells. Taken together, endocytosis inhibitors were lack of specificity and even might change membrane permeability, which thus makes them inappropriate as tools for endocytosis pathway studies in MCF-7/ADR. Inhibitors Mechanism Chlorpromazine Block clathrin-mediated endocytosis Genistein Block caveolae-mediated endocytosis Endocytosis marker Endocytosis type FITC- hTf Clathrin-mediated endocytosis LacCer Caveolae-mediated endocytosis Figure 1. CLSM of hTf in MCF/ADR cells. Figure 2. CLSM of LacCer in MCF/ADR cells. Figure 3. CLSM of Rho-TM in MCF/ADR cells. Table 1. The endocytosis maker.
Editor's Notes
- Copyright Colin Purrington (http://colinpurrington.com/tips/academic/posterdesign).
