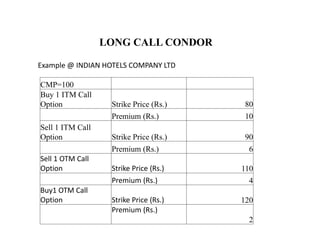
This strategy involves buying one in-the-money (ITM) call, selling one ITM call with a lower strike, selling one out-of-the-money (OTM) call with a higher middle strike, and buying one OTM call with an even higher strike. The maximum loss is limited to the net debit paid to open the position. The maximum gain occurs if the underlying asset closes between the two short call strikes. There are two break-even points: one where the asset closes above the lower long call strike plus premiums paid, and one where it closes below the higher long call strike minus premiums paid.