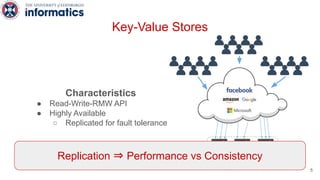
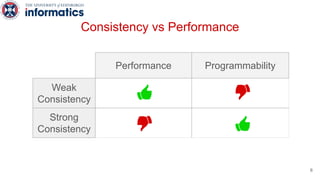
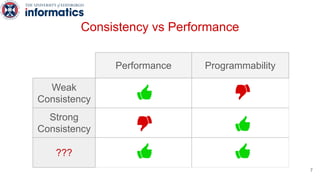
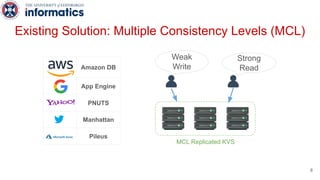
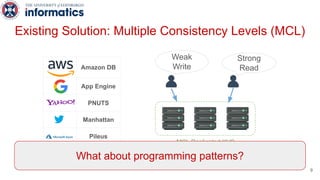
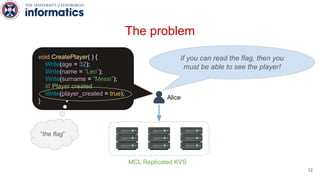
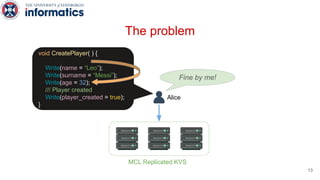
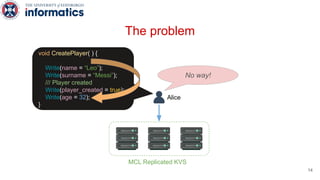
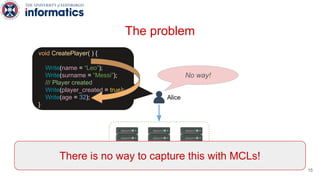
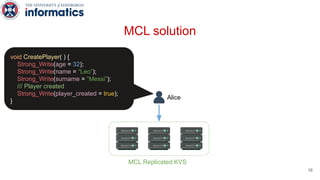
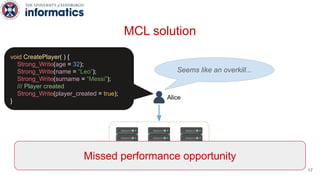
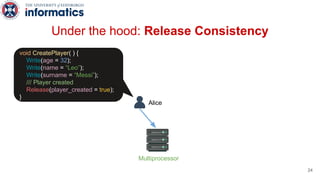
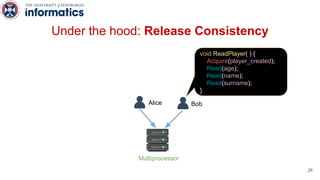
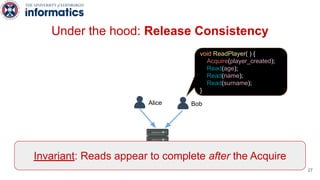
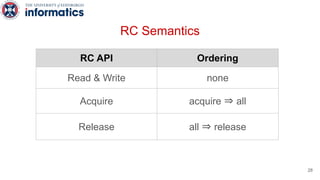
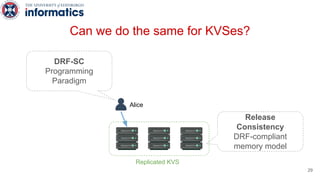
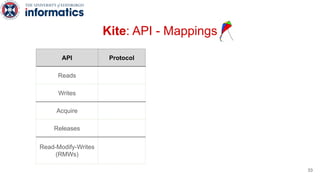
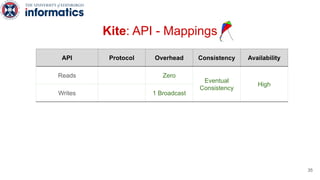
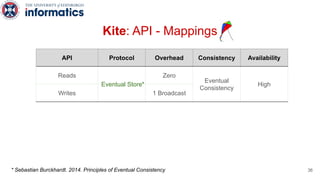
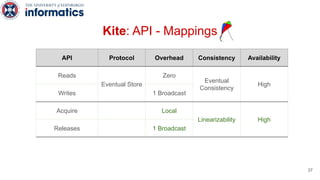
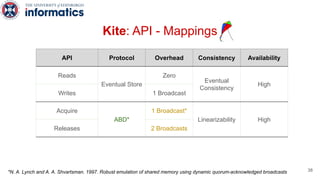
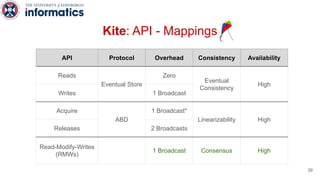
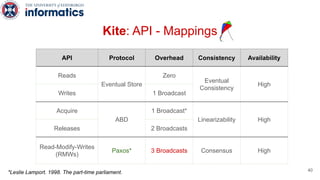
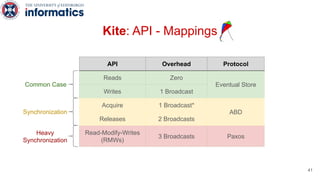
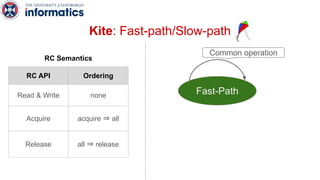
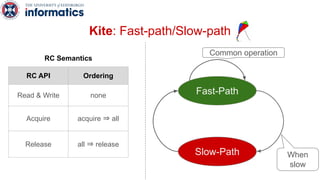
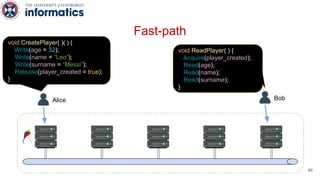
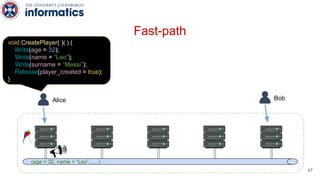
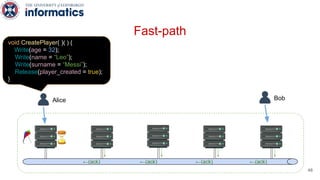
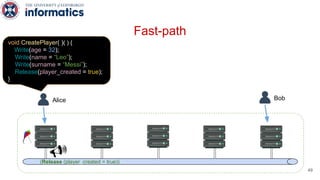
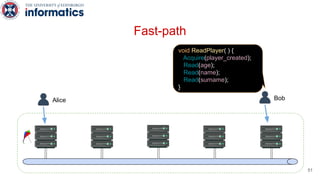
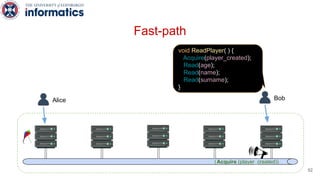
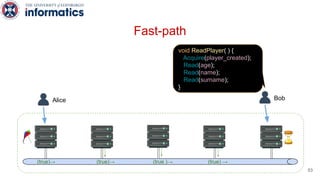
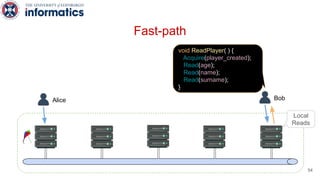
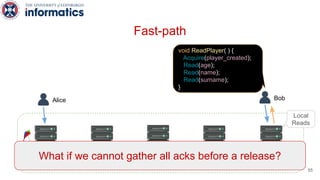
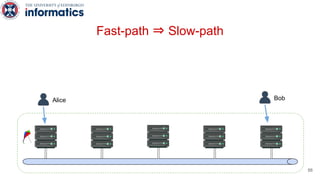
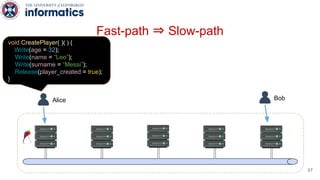
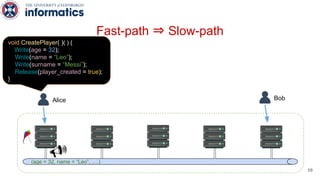
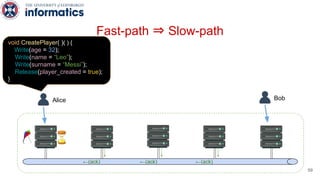
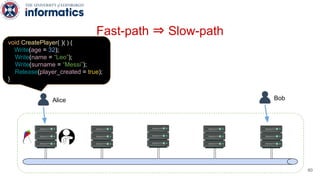
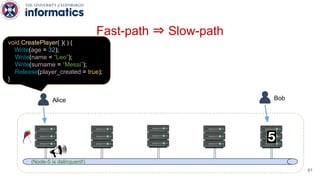
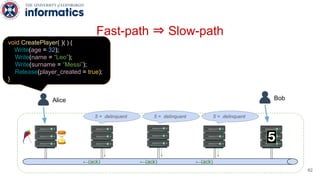
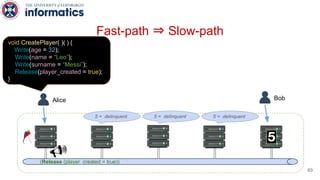
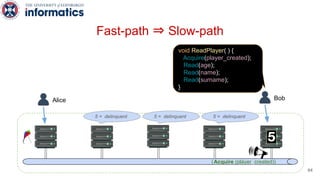
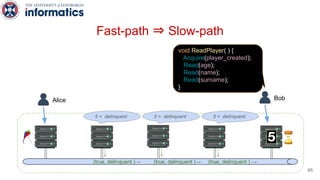
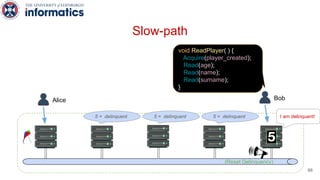
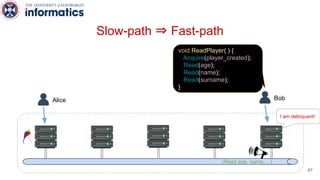
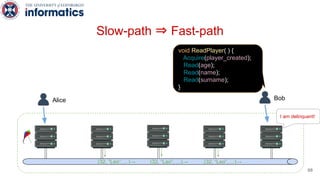
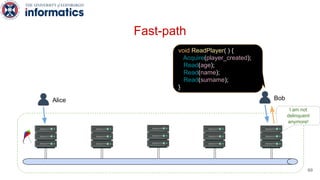
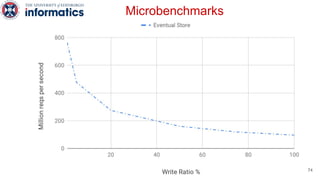
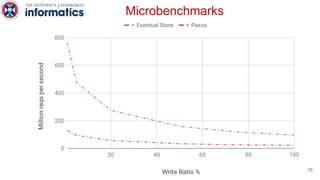
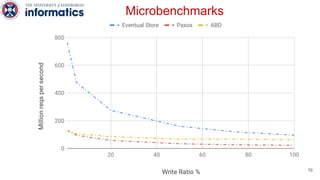
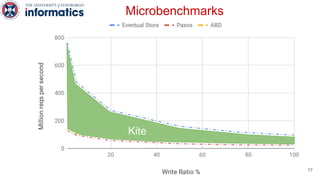
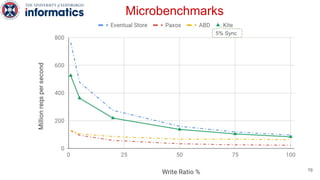
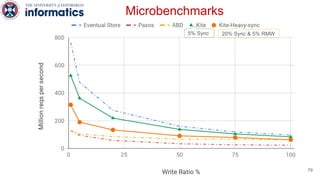
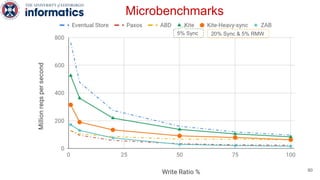
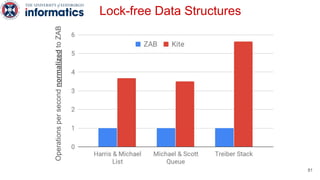
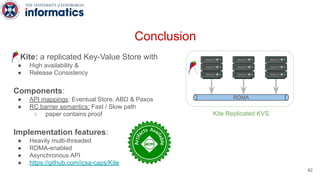
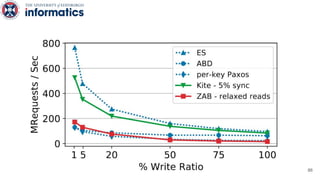
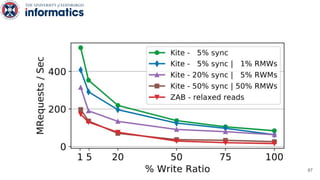
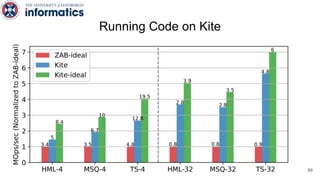
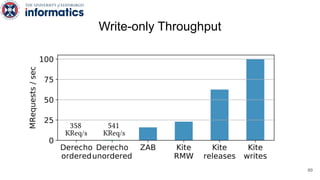
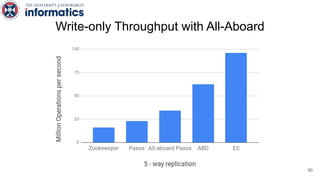
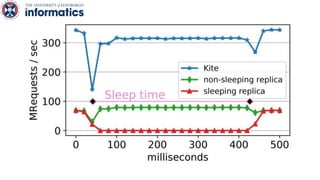
Kite is a replicated key-value store that provides release consistency and high availability. It uses an efficient fast-path/slow-path mechanism to provide release consistency semantics while minimizing synchronization overhead. The fast path uses eventual consistency for common reads and writes, while acquiring locks for synchronization operations like acquires and releases. The slow path is used when the fast path times out, adding a broadcast round to restore consistency. Microbenchmarks and experiments with lock-free data structures show that Kite outperforms a baseline implementation by up to 3x for workloads with synchronization operations.