1. Computer networks allow for the interconnection of independent computers to share information and resources. ARPANET, developed in 1967, was one of the first computer networks and connected four nodes through the use of IMPs (Interface Message Processors).
2. Computer networks provide advantages like central storage of data, sharing of information and resources, reliability, and reduced costs. However, they also present disadvantages such as requiring specific setups and introducing security and cost issues.
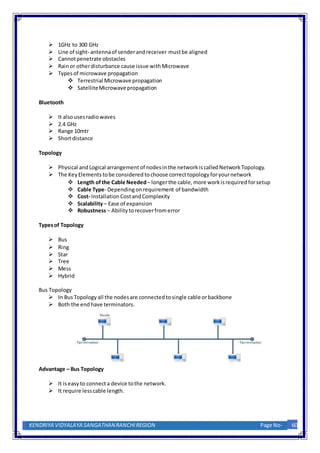
3. Common network topologies include bus, ring, and star configurations. A bus topology connects all nodes to a single cable or backbone but a failure of one node can shutdown the entire network. Ring topologies connect all nodes in a closed loop but also

![MM : MM : MM : SS : SS : SS
Full Duplex –Communicationsisbi-directional simultaneouslyi.e.bothsenderand
receivercanbe send data at same time.
NetworkTerminology
Node- The device connected toanetwork.
Client–The device thatrequestforaservice
Server– The Device thatrender the services
Client-Server- Inthismodel,the data are storedon powerful computerscalled
Server that can be accessedbya much simplercomputercalled Clientthatare
connected by a network.
NetworkInterface CardorUnit (NetworkAdapterorLAN card) - It is hardware that
allows acomputer(or device) to connecttonetwork.
MAC (MediaAccessControl) address –Each NICis assignedaunique 12 digit
hexadecimalnumber,knownaMAC address,isusedasnetworkaddressin
communication. The formatforthe MACaddress is
Manufacturer ID Card Id
IP Address:Everydevice onnetworkhasunique identifiercalledIPaddress.It
consistsof 4 bytes(IPv4) decimal number(between0to 255) separatedby‘.’
(Period).
Channel –It is communication paththroughwhichdataisactually transmitted.
CommunicationMedia- Itisallowsdataorsignal to be communicatedacrossthe
devices. Itismeansof communication.
Data – Information storedwithinthe computersysteminform of ‘0’ and‘1’
Signal- Itiselectricor electromagneticencodingof datatobe transmitted.Itcanbe
categorized into:
o AnalogSignal – that hasinfinitelymanylevel of intensityoveraperiodof
time.
o Digital Signal –that can have only a limitednumberof definedvalues.
Bit rate – It definesthe amountof datatransferred.Itisdefinedasnumberof bits
persecond (bps).[Bps – BytesperSecond]
Baud – The numberof changes insignal persecond.
Bandwidth – Itis difference betweenthe highestandthe lowestfrequencies
containedin the signal.
Mode of Transmission
Analog or Broadband Transmission
It usesanalogsignalstotransmitthe information
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHANRANCHI REGION Page No- 54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computernetworks-220606092239-c8cbe549/85/Computer-Networks-docx-2-320.jpg)