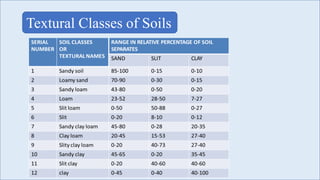
Soil texture refers to the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles that make up a soil. Particle size is determined based on international standards, with clay being less than 0.002 mm and sand between 0.02 and 2.0 mm. Soil texture influences properties like water and nutrient holding capacity. A soil texture pyramid is used to describe the textures based on varying amounts of sand, silt and clay. Soil texture plays an important role by affecting water retention, aeration, root growth, ecology, and nutrient status.