natural science lithosphere.pptx
- 2. Lesson objectives After this lesson, learners will be able to : • Define lithosphere • Differentiate between Earth’s layers. • Identify different types of rocks • Value the importance of the lithosphere
- 3. The Lithosphere The lithosphere is considered the outer layer of the Earth. It consists of all the mountains, rocks, stones, top soil and sand found on the planet. It also includes all the rocks under the sea and under the surface of the Earth. The lithosphere is found all around us and we interact quite closely with it everyday.
- 4. Continue OCEANIC: Which is associated with oceanic crust and exists in the ocean basins. Continental: This is associated with continental crust (mountains, plateaus, plains). The lithosphere is important because it provides us forests, grasslands for grazing, land for agriculture and human settlements and I also a rich source of minerals. Lithosphere is where the living things on Earth thrive and strive.
- 5. Lithosphere
- 6. What is inside the earth? This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY
- 7. This how earth look like inside
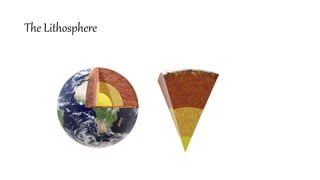
- 8. There are three(3) layers of the earth. Lithosphere is considered as the outer layer of the earth. Inside the earth there are three layers. Namely; crust, mantle, and core. Each layer is divided into two.
- 9. Crust The earth’s outmost layer. The crust is made of solid rocks and minerals 0- 45 km Crust is divided into two; Oceanic crust Continental crust
- 10. Mantle Mantle is the mostly – solid bulk of the earth’s interior . 45- 2900 km The mantle lies between Earth’s dense, super-heated core and its thin outer layer crust. The mantle is about 2 900 km thick and makes up a whopping 84% of Earth’s total volume. It is divided into two; The lower mantle The upper mantle
- 11. Core Earth’s core is the very hot, very dense centre of our planet. 2900- 6371 km The core has two parts; Inner core (solid); The temperature of the Earth’s inner core is about the same temperature as the surface of the sun. Outer core ( liquid)
- 12. The Rock Cycle
- 13. The rock cycle The rock cycle is a natural continuous process in which rocks form, are broken down and re-form again over long periods of time. Wind, water, heat and cold cause the weathering of rocks on the surface of the Earth. The rocks are broken up into smaller and smaller pieces and form sand Wind and water wash the sand and small stones away and deposit them as sediments into lakes and the ocean. This process is called deposition.
- 14. Continue The sediments settle at the bottom of the oceans, lakes and rivers. Over time they get covered with more layers of sediment. The pressure from the additional layers causes the sediments to compact and solidify to form sedimentary rock. The sedimentary rock may be buried deeper and deeper beneath the surface of the Earth through movement in the Earth's crust (where oceanic plates and continental plates meet). The rocks can also be pushed deeper (subducted) into the Earth. As the rocks move deeper into the Earth, temperature and pressure increase.
- 15. CONTINUE Rocks become more compact as processes of compaction and cementation occur. As the chemical compounds in the rocks change, due to heat and pressure, metamorphic rock is formed. Over time the metamorphic rock can move deeper into the Earth, melt and become magma. Magma moves towards the surface of the Earth through volcanic pipes. The hot magma cools slowly on its way to the surface and forms igneous rock. Magma can also break through the surface as lava in volcanoes. In this case, the lava will solidify quickly on the surface to form igneous rocks. Igneous rock can form in the crust or on the surface. Igneous rocks get eroded by wind and water and the whole process starts again.
- 17. TYPES OF ROCKS
- 18. THERE ARE THREE TYPES OF ROCKS 1. SEDIMENTARY ROCK 2. METAMORPHIC ROCK. 3. IGNEOUS ROCK.
- 20. -Sedimentary refers to “ small pieces” -Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of small particles and organic particles on the floor of oceans at the earth’s surface. -They are made from other rocks , once living things and the precipitates. -Examples includes, limestone, sandstone, and shale.
- 21. METAMORPHI C ROCKS • They form when rocks are substantially changed from their original igneous, sedimentary, or earlier metamorphic form. • It is a type of rock which has been changed by extreme heat and pressure. • They are often found in mountain ranges. • Examples includes, slate and marble. This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY
- 22. IGNEOUS ROCK
- 23. -It is the type of rock that is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. - They are used in flooring, landscaping and construction projects. -Their examples includes granite, basalt etc.
- 25. CONCLUSION Lithosphere is the outer part of the earth. Upper portion of the mantle and the crust. Rock cycle Rock formation Heat causes expansion of rocks a cold causes contraction. Types of rocks, Sedimentary(layered), metamorphic (Sedimentary and Igneous) and igneous rocks(molten rock).
