Mcom summer training report on GST
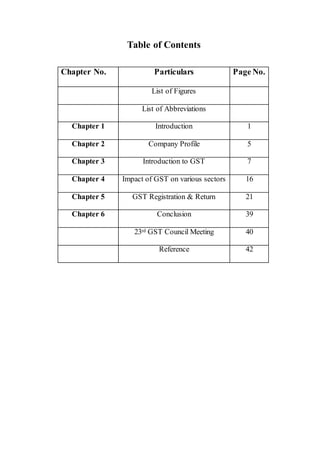
- 1. Table of Contents Chapter No. Particulars Page No. List of Figures List of Abbreviations Chapter 1 Introduction 1 Chapter 2 Company Profile 5 Chapter 3 Introduction to GST 7 Chapter 4 Impact of GST on various sectors 16 Chapter 5 GST Registration & Return 21 Chapter 6 Conclusion 39 23rd GST Council Meeting 40 Reference 42
- 2. List of Figures Figure Title Page No. 3.1 Present Taxation System 9 3.2 Indirect Taxation System in India 10 3.3 GST Model 11 4.1 How GST Work 17 4.2 Effect on IT Sector 18 4.3 Effect on Home use ProductRates 18 4.4 Effect on Home use Products Rates 18 4.5 Effect on Automobile ProductPrice 19 4.6 Effect on Mobile Rates 19 5.1 GST Registration Page 22 5.2 GSTIN 22 5.3 Types of GST Return 25 5.4 GSTR-1Registration 26 5.5 Challenges faced during Return filing 31
- 3. List of Abbreviations GST : Goods and Services Tax SGST : State Goods and Services Tax CGST : Central Goods and Services Tax IGST : Integrated Goods and Services Tax GSTIN : Goods and Services Tax Identification Number POS : Place of Supply UIN : Unique Identity Code B to B : from one registered person to another registered person B to C : from one registered person to unregistered person VAT : Value Added Tax CST : Central Sales Tax
- 4. 1 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Background Internship is the process of working as an assistant to gain practical experience and skills in an occupation. In order to expose the students to the actual working environment, internship has been included as a compulsory requirement for the successful completion of two-year MCOM (Finance) under Bundelkhand University. MCOM (Finance) is a management program with the provision of four semester comprising of three weeks industrial training. Internship is an opportunity to observe, learn and understand the corporate culture, acquire knowledge and skills in the respective field which helps the students in their further carrier development. It is carried out in the organization which suits the area of specialization. Internship provides the opportunity to understand how the knowledge acquired through the lectures, group discussion and formal study is applied in real working situation. It is the best way of knowledge gaining as it provides as experience. Similarly the assigned responsibilities during the internship period help to enhance the interpersonal and communicative skills and boost up the confidence level as well. Even though the interns are not the employees of the organizations, they are given an opportunity to work as if they are the employees. The interns do what the staffs of the organizations have to do. However, they do not have obligations or authority over anything. The interne did his internship in under M/s Rachit Agarwal & Associates Jhansi The interne was given the opportunity to observe and learn about the GST Registration and Return process.
- 5. 2 1.2 Objectives of the Study The general objective of the study is to get practical insights of Goods and Services Tax . The specific objectives are as follows : a. To learn about the GST Registration process. b. To learn how to file GST Return both online & offline c. To help clients in the Registration process. d. To help clients in downloading the offline return software. 1.3 Rationalof the study In college we learn the organizational structure only in theoretical basis. Internship is the place where how theoretical knowledge are useful in real life scenarios. For that students need to prepare resumes, write cover letters and go through interviews as if they were applying for the job. This gives students valuable experience in preparation for employment. The internship allows opportunities for the development of practical’s skills in contexts where professional criticism is both immediate and constructive. It also furnishes students with opportunities to observe and understand connections between coursework and skills needed to perform effectively in a given profession. Finally, internship aid in the identification of knowledge and skills essential to doing well in a particular profession. 1.4 Scope of the study Generally, an internship consists of an exchange of services for experience between the student and an organization Internship program is a good opportunity to show our learning skills that we get from our school/college. Students can also use an internship to determine if they have an interest in a particular career. It helps to build Curriculum Vitae (CV) for the student.
- 6. 3 1.5 Methodology For the preparation of this report both primary and secondary sources of data are used. The secondary data are collected from annual reports, brochures, website of GST, different financial magazine, published documents. Most of the information in this report is written on the basis of experience gained by the internee in the company during the period of internship. While preparing this report I took help from company staff and group discussion with friends. I have consulted related departmental staff as a primary source. For the secondary data I used gst website, cbec website, financial express website, clear tax website. 1.6 Organization Selection Selection of the organization is one of the most difficult task. However the specialization of the student in finance has made GST a better option for doing internship. Since GST is related to financial transaction, it would be easy to understand various dimensions related to services like registration, quarterly return, monthly return, annual return. Besides this, one should have strong reference to get enrollment in the organizations. So because of the reference of the college, M/s Rachit Agarwal & Associates has been selected for internship on 12-06-2017. 1.7 Duration The duration of internship period has been defined for 7 weeks by the Bundelkhand University. The intern has completed internship from 12th June to 31st July in M/s Rachit Agarwal & Associates.
- 7. 4 1.8 Limitations of the Study Even though great support was provided by the organization and the staff to the intern during the internship period to make the work environment conducive, they had to face variours difficulties during the internship period. Due to various unavoidable constraints, the report could not do complete justice to the study. The interns in the organization are more focused to assist their supervisors. It restricts the amount of information and the level of complex work assigned to its interns owing to the confidentially and competency issues. It is because of this interns get to learn mostly by observation and some amount of discussion with supervisor only. The report is limited to the department in which the intern is placed it might not be able to provide the comprehensive knowledge of the overall functioning of the company.
- 8. 5 Chapter 2 Company Profile About Rachit Agarwal& Associates : We are an Indian chartered accountant firm based in below Union Bank Jhansi. We provide all sort of chartered accountant services related to Accounting, Auditing, Income Tax, Financial Services, Company Law Matters, Foreign Collaborations, Import-Export Consultancy, Sales Tax / Vat Matte, Service Tax, STPL, Transfer Pricing related matters etc. In order to meet the specific requirements of the clients, we provide the best possible solution and consultancy for their respective matters. With the active support we receive from our competent team of professionals, we have manage to provide the effective services to our various esteemed clients. Head office 671, Civil Lines, Bhaskar House, Below Union Bank, Jhansi Jhansi (Uttar Pradesh)
- 9. 6 SERVICES Services No. of Clients Company Registration 1 One Person Company 2 LLP Registration 3 Service Tax Registration 4 GST Registration 5 Project Financing 8 ROC Filling 15 Service Tax Return 16 GST Returns 17 TDS Returns 18 Income Tax (Salaried) 20 Income Tax (Business) 21 Tally Accounting 22 Statutory Audit 25 Tax Audit 26 Internal Audit 27 TAN registration 33
- 10. 7 Chapter 3 Introduction to Goods and Services Tax (GST) 3.1 About GST The Good and services tax (GST) is the biggest and substantial indirect tax reform since 1947. The main idea of GST is to replace existing taxes like value-added tax, excise duty, service tax and sales tax. GST as it is known is all set to be a game changer for the Indian economy. India as world’s one of the biggest democratic country follow the federal tax system for levy and collection of various taxes. Different types of indirect taxes are levied and collected at different point in the supply chain. The centre and the states are empowered to levy respective taxes as per the Constitution of India. The Value Added Tax (VAT) when introduced was considered to be a major improvement over the pre-existing Central excise duty at the national level and the sales tax system at the State level. Now the Goods and Services Tax (GST) will be a further significant breakthrough - the next logical step - towards a comprehensive indirect tax reform in the country. Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax which was launched at midnight on 1 July 2017 by the President of India, Pranab Mukherjee and Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi. The launch was marked by a historic midnight (30 June-1 July) session of both houses of the Parliament convened at the Central Hall of the Parliament. GST is applicable throughout India which replace multiple cascading taxes levied by the central and state governments. It was introduced as The Constitution (One Hundred and First Amendment) Act 2017, following the passage of Constitution 122nd Amendment Act Bill.
- 11. 8 3.2 Key features of GST 1. Dual Goods and Service Tax : CGST and SGST 2. Destination-Based Consumption Tax: GST will be a destination-based tax. This implies that all SGST collected will ordinarily accrue to the State where the consumer of the goods or services sold resides. 3. Computation of GST on the basis of invoice credit method: The liability under the GST will be invoice credit method i.e. cenvat credit will be allowed on the basis of invoice issued by the suppliers. 4. Payment of GST: The CGST and SGST are to be paid to the accounts of the central and states respectively. 5. Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN): A not-for-profit, Non-Government Company called Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN), jointly set up by the Central and State Governments will provide shared IT infrastructure and services to the Central and State Governments, tax payers and other stakeholders. 6. GST on Imports : Centre will levy IGST on inter-State supply of goods and services. Import of goods will be subject to basic customs duty and IGST. 7. Maintenance of Records : A taxpayer or exporter would have to maintain separate details in books of account for availment, utilization or refund of Input Tax Credit of CGST, SGST and IGST. 8. Administration of GST : Administration of GST will be the responsibility of the GST Council, which will be the apex policy making body of the GST. Members of GST Council comprised of the Central and State ministers in charge of the finance portfolio. 9. Goods and Service Tax Council : The GST Council will be a joint forum of the Centre and the States. The Council will make recommendations to the Union and the States on important issues like tax rates, exemption list, threshold limits, etc. One-half of the total number of Members of the Council will constitute the quorum of GST council.
- 12. 9 figure 3.1: Present taxation system Business Organizations Manufacturer Trader Service Goods Services Production Trading Provider Reciver Central Excise VAT , CST Service Tax Entry Tax, Luxury Tax, Entertainment Tax, State Cess, Lottery Tax
- 13. 10 figure 3.2:Indirect Taxation Systemin India Central Levies State Levies Central Excise Duty Additional Excise Duty Countervailing Duty Add. Spl. Duty of Customs Service Tax Vat / Sales Tax Purchase Tax CST Entry Tax Luxury Tax Indirect Taxes
- 14. 11 figure 3.3: GST model 3.3 Dual GST Model India is a federal country where both the Centre and the States have been assigned the powers to levy and collect taxes through appropriate legislation. It has been proposed that there would be a “Dual GST “model in India, taxes will be levied by both centre (Central GST) and state (State GST) on Goods and Services. Hence, a dual GST would be according to the Constitutional requirement of fiscal federalism. 3.4 Commodities not subsumed in GST 3.5 Taxes not subsumed in GST State GSTCentral GST Integrated GST Levied by the Centre This is applicable on supplies within the state. Tax collected will be shared to Centre. Levied by the State This is applicable on supplies within the state. Tax collected will be shared to State. Levied by the Centre & State This is applicable on interstate and import transactions. Tax collected is shared between Centre and State Alcohol for human consumption Petrol Products – Crude, Petrol, High Speed Diesel, Natural Gas and Aviation Turbine Fule Stamp Duty & Property Tax, Toll Tax, Electricity Duty GST
- 15. 12 3.6 GST Rates in India Exempted categories – 0 Commonly used Goods and Services – 5% Standard Goods and Services fall under 1st slab – 12% Standard Goods and Services fall under 2nd Slab – 18% Special category of Goods and Services including luxury - 28% 3.7 GST Council It is set up by president under article 279-A. It is chaired by union finance minister. It will constitute union minister of state in charge of revenue and minister in charge of finance or taxation or of any other field nominated by state governments. The 2/3rd representatives in council are from states and 1/3rd from union. It will make recommendations on : a. Taxes, surcharge, cess of central and states which will be integrated in GST. b. Goods and services which may be exempted from GST. c. Interstate commerce – IGST- proportion of distribution between state and center. d. Registration threshold limit for GST. e. GST floor rates. f. Special rates during calamities. g. Provision with respect to special category states specially north east states. It may also work as Dispute Settlement Authority for GST. The Council would consist of 2/3rd representation of states and 1/3rd representation of the Centre. The GST Council will take all decisions regarding tax rates, dispute resolution, exemptions and so on. Recommendations of the GST Council (75% votes) will be binding on the Centre and the States.
- 16. 13 3.8 Goods and Services TaxNetwork (GSTN) Goods and Services Tax Network has been set up by the Government as a private company under erstwhile Section 25 of the Companies Act, 1956. GSTN would provide three front end services, namely Registration, Payment and Return to taxpayers. It will also assist some State with the development of back end modules. 3.9 GSTIN Goods and Services Identification Number is a 15 digit alphanumeric number. First two digit shows the State code, Another ten digit shows the Permanent Account Number (PAN). Next number shows the entity number of the same PAN holder in a state. Next is alphabet Z by default. Next is the check sum digit. GST Identification Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 State code PAN Entity Code/ Check digit
- 17. 14 3.10 SWOT Analysis Strengths GST provides a comprehensive and a wider coverage of input credit set off service tax credit could be used for the payment of tax on the sale of goods etc. A single GST could be used instead of other indirect taxes at the state and central level. It would end the cascading effects. There would be uniformity of tax rates across the states. It ensures better compliance as the aggregate tax reduces. It helps in the reduction of prices of the goods and services to the consumer with the reduction of tax. It would reduce transaction costs and unnecessary wastage to both government and individuals. It encourages transparency and unbiased tax structure. It brings efficiency in the indirect tax mechanism. Weaknesses It doesn’t include alcohol and petroleum products which would lead to incurring of huge losses. It requires strong IT infrastructure which is not highly developed in India. Single GST rate would be high compared to individual indirect tax rate. In reality, it might result in a dual tax system in which both state and the Centre would collect tax separately. Dealers paying VAT in the state will be required to pay GST at the Centre Sudden implementation of GST might create confusion to the common man.
- 18. 15 Opportunities Reduction in tax burden will increase the competitiveness of Indian products in the international market There would be a gradual increase in the revenues of state and the union Helps reducing corruption as the implementation of GST would result in a gradual decrease of procedures and formalities Threats It is entirely dependent on the efficiency and effectiveness of the system Beneficiaries of the system are uncertain. It could be either state or the Centre. This would create a chaos while preparing budgets and financing polices Lack of co-ordination between the Centre and the state might affect the system and also the revenues generated Interpretation of the SWOT Analysis From the above SWOT analysis it is clear that GST would create uniformity of taxes and also reduce tax burden. This in turn would increase revenues of the state and the union at the country level and increase competition at the international level. But this in reality might appear to be a dual tax system and would also require a strong IT infrastructure. Besides this, it is entirely dependent on the efficiency of the system. Co-ordination between the Centre and the state only can help in its implementation and execution of the proposed plan. Therefore before implementation of such a tax regime, it should be carefully examined at every levels to benefit all the stakeholders.
- 19. 16 Chapter 4 Impact of GST on various sectors IT Currently IT sector is paying 14 percent of tax to the authority and subjected to 18-20 percent after the imposition of GST. Also an important point to notice here, that the long disputed issue of canned software taxation will also come to end as their will no difference arise between goods and services after the GST. Overall impact could be suggested here is neutral or slightly negative. Telecom In the current stage, the Telecom sector is paying 14 percent of tax to the government body, but the scenario takes the shift after the imposition of GST. The rate arise to 18 percent and the companies expect to pass the burden on the post-paid customers. There is also a lower input tax credit in this sector's capex cost. Overall, it seems that this regime will be negative to the industry and the sector will also be in state where they can't pass the entire tax burden to the customers especially their prepaid segment. Automobiles Currently, automobile sector pays around 30 to 47 percent tax to the Government which is now expected to range between 20-22 per cent, after the implementation of GST. And the overall cost cutting can be expected for the end user by around 10 per cent. Transportation time should also be reduced as the check points and octroi is cleared hands before. Overall GST will bring a smile into the automobile sector. Cement In the current scenario, cement sector is presenting 27 to 32 per cent of their share to the tax authority. After the rolling out of GST, this will improve the sector growth in various terms, like transportation by 20-25 per cent and in the warehouse scheme as the rationalization would be easy in terms of state wise fragmentation and also in the transportation cost as reduced transit time.
- 20. 17 Pharmacy Here, the impact could be neutral as the sector only shares 6 per cent of his share to the tax authority. The sector also avails the incentives in tax benefits of location wise. There are various concessional benefits and exemptions held for this sector and will extend till the expiry of the period. The implications of GST would also try to reduce the logistics cost and would also try to see in to the matter of inverted duty structure. Banking and Financial Institutions The sector is paying 14 percent right now, but not on the interest part of transaction. After the GST implied, the tax horizon can expand up to 18 to 20 percent on the fee based transactions. Overall input expense of operations will likely to increase and also hike in the transactions of financial in nature such as loan processing fees, debit/credit charges, insurance premiums etc. 4.1 Result Analysis Basic conceptofGST Importer to wholesaler Gold 100000 100000 Sales Tax (14%) 14000 - duty (12.5%) 12500 - Excise Duty (1%) 1000 - CGST (18%) - 18000 Grand Total 127500 118000 wholesaler to retailers Price 127500 118000 Add margin (10%) 12750 11800 other charges (rent, transport) 15000 15000 Sub Total 155250 144800 Sales Tax (14%) 21735 - SGST (18%) - 26064 Total Price 176985 170864 figure 4.1: How GST work
- 21. 18 Effect on IT Industrial M&G LTD. Software for school uses 9500 9500 Service Tax (14%) 1330 - GST (5%) - 475 Grand Total 10830 9975 figure 4.2: Effect on IT Sectors Effecton ManufactoryIndustrial Whirlpool 6.5 kg Fully Automatic Top Load Washing Machine Price (exclusive Tax) 15490 15490 Sales Tax (14.5%) 2168.6 - GST (12%) - 1858.8 Grand Total 17658.6 17348.8 figure 4.3: Effect on Home use Products Rates Effecton LED T.V. Price SONY BRAVIA 32" KLV 32R306 Price (exclusive tax) 20700 20700 Sales Tax (14.5%) 3001.5 - GST (18%) - 3726 Grand Total 23701.5 24426 figure 4.4: Effect on Home use Product Rates
- 22. 19 Effecton Spare Parts Price Motor vehicle spare parts Names Qt Per Unit Price Total Price Throttle Body Cleaning 5 750 3750 3750 AC Disinfectant 4 700 2800 2800 AC Servicing of Maruti Car Including Gas Refill and Labour Charges 10 2500 25000 25000 Sub-Total 31550 31550 Sales Tax (14.5%) 4574.8 - Surcharges (2%) 631 - GST (12%) - 3786 Grand Total 36756 35286 figure 4.5: Effect on Automobile Product Price Effecton mobile company Description Qt MRP VAT/CST KKC Net Amount (exclusive of taxes) Net Amount (in GST) Redmi 3S Grey 32G 1 8.999 5.50% - 8530 8530 Mi Protect 1 599 14.50% 0.50% 521 521 Sub Total 9051 9051 VAT/CST 469 - ST 76 - GST (18%) - 1629 KKC 3 - Grand Total 9598 10680 figure 4.6: Effect on Mobile Rates
- 23. 20 4.2 Impact of GST on Indian Economy Reduce tax burden on producers and foster growth through more production. This double taxation prevents manufacturers from producing to their optimum capacity and retards growth. GST would take care of this problem by providing tax credit to the manufacturer. Various tax barriers such as check posts and toll plazas lead to a lot of wastage for perishable items being transported, a loss that translated into major costs through higher need of buffer stocks and warehousing costs as well. A single taxation system could eliminate this roadblock for them. A single taxation on producers would also translate into a lower final selling price for the consumer. Also, there will be more transparency in the system as the customers would know exactly how much taxes they are being charged and on what base. GST would add to government revenues by widening the tax base. GST provides credits for the taxes paid by producers earlier in the goods/services chain. This would encourage these producers to buy raw material from different registered dealers and would bring in more and more vendors and suppliers under the purview of taxation. GST also removes the custom duties applicable on exports. Our competitiveness in foreign markets would increase on account of lower cost of transaction. The proposed GST regime, which will subsume most central and state-level taxes, is expected to have a single unified list of concessions/exemptions as against the current mammoth exemptions and concessions available across goods and services The introduction of Goods and Services Tax would be a very noteworthy step in the field of indirect tax reforms in India. By amalgamating a large number of Central and State taxes into a single tax, it would alleviate cascading or double taxation in a major way and pave the way for a common national market.
- 24. 21 Chapter 5 GST REGISTRATION & RETURN 1) Every person who is liable to be registered under Schedule III of this Act, shall apply for registration in every such State in which he is liable within 30 days from the date of which he becomes liable to registration, in such manner and subject to such conditions as may be prescribed. 2) Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-section (1), a person having multiple business verticals in a State may obtain a separate registration for each business vertical, subject to such conditions as may be prescribed. 3) A person, though not liable to be registered under Schedule III, may get himself registered voluntary, and all provisions of this Act, as are applicable to a registered taxable person, shall apply to such person. 4) Every person shall have a Permanent Account Number issued under the Income Tax Act, 1961 (43 of 1961) in order to be eligible for grant of registration under sub- section (1), (2) or (3). 5) Where a person who is liable to be registered under this Act fails to obtain registration, the proper officer may, without prejudice to any action that is, or may be taken under this Act, proceed to register such person in the manner as may be prescribed. 6) The registration or the Unique Identity Number, shall be granted or, as the case may be, rejected after due verification in the manner and within such periods as may be prescribed. 7) A registration or an Unique Identity Number shall be deemed to have been granted after the period prescribed under sub-section (7), if no deficiency has been communicated to the applicant by the proper officer within that period. 8) Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-section (7), any rejection of application for registration under the CGST/SGST Act shall be deemed to be a rejection of application for registration under the CGST/SGST Act. 9) The Central or State Government may, on the recommendation of the Council, by notification, specify the category of persons who may be a exempted from obtaining registration under this Act.
- 25. 22 figure 5.1 GST registrationpage figure 5.2: GST Identification Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 State code PAN Entity Code/ Check digit
- 26. 23 5.1 Amendment of Registration Every registered taxable person shall inform the proper officer of any changes in the information furnished at the time of registration, or that furnished subsequently, in the manner and within such period as may be prescribed. The proper officer may, on the basis of information furnished under sub-section (1) or as ascertained by him, approve or reject amendments in the registration particulars in the manner and within such period as may be prescribed, provided that approval of the proper officer shall not be required in respect of amendment of such particulars as may be prescribed. The proper officer shall not reject the request for amendment in the registration particulars without giving a notice to show cause and without giving the person a reasonable opportunity of being heard. Any rejection or approval of the amendments under the CGST/SGST Act shall be deemed to be rejection or approval of amendments under the CGST/SGST Act.
- 27. 24 5.2 Tax Invoice : A registered taxable person supplying – i. taxable goods shall issue, at the time of supply, a tax invoice showing the description, quantity and value of goods, the tax charged thereon and such other particulars as may be prescribed; ii. taxable service shall issue a tax invoice, within the prescribed time, showing the description, the tax charged thereon and such other particulars as may be prescribed; Provided that a registered taxable person may issue a revised invoice against the invoice already issued during the period starting from the effective date of registration till the date of issuance of certificate of registration to him; Provided further that a registered taxable person supplying non-taxable goods or services or paying tax under the provision of Section 8 shall issue, instead of a tax invoice, a bill of supply containing such particulars as may be prescribed;
- 28. 25 5.3 GST RETURNS Every registered taxable person shall, for every calendar month or part thereof, furnish, in such form and in such manner as may be prescribed, a return, electronically, of inward and outward supplies of goods or services, input tax credit availed, tax payable, tax paid and other particulars as may be prescribed within 20 days after the end of such month: Provided that a registered taxable person paying tax under the provisions of Section 8 of this Act shall furnish a return for each quarter or part thereof, electronically, in such form and in such manner as may be prescribed, within 18 days after the end of such quarter: Every registered taxable person, who is required to furnish a return under sub-section (1) shall pay to the credit of the appropriate Government the tax due as per such return not later than the last date on which he is required to furnish such return. A return furnish under the sub-section (1) by a registered taxable person without payment of full tax due as per such return shall not be treated as a valid return for allowing input tax credit in respect of supplies made by such person. Every registered taxable person shall furnish a return for every tax period under sub-section (1), whether or not any supplies of goods or services have been effected during such tax period. Note: Subject to the provisions of Section 25 and 26, if any taxable person after furnishing a return discovers any omission or incorrect particulars therein, other than as a result of scrutiny, audit, inspection or enforcement activity by the tax authorities, he shall rectify such omission in the return to be filed for the month or quarter, as the case may be, during which such omission are noticed, subject to the payment of interest, where applicable and as specified in the Act:
- 29. 26 figure 5.3 Types of GST Returns S.No. Return Particulars 1 GSTR-1 Details of outward supplies of taxable goods or services. 2 GSTR-2 Details of inward supplies of taxable goods or services. 3 GSTR-3 Monthly return on the basis of details of inward and outward supplies along with the payment of amount of tax. 4 GSTR-4 Quarterly Return for compounding taxable persons. 5 GSTR-5 Return for Non-Resident foreign taxable persons. 6 GSTR-6 Input Service Distributor return. 7 GSTR-7 Return for authorities deducting tax at source. 8 GSTR-8 Details of supply affected through e-commerce operator. 9 GSTR-9 Annual Return
- 30. 27 1) What is GSTR-1? GSTR-1 is a monthly return that should be filed by every registered dealer by the 10th of the following month. It is the first or the starting point for passing input tax credit to the dealers. It contains details of all outward supplies i.e. sales. GSTR-1 has to be filed by "all" taxable registered persons under GST. However, there are certain dealers who are not required to file GSTR-1, instead are required to file other different GST returns as the case may be. These dealers are E-Commerce operators, Non-Resident dealers and Tax deductors. It has to be filed even in cases where there is no business conducted during the reporting month. figure 5.4 GSTR-1 Registration
- 31. 28 How to file GSTR-1 ? The Suppliers need to log in to the GSTN portal with the given User ID and Password, following these steps : Search for "Services" and then click on Returns, followed by Returns Dashboard. In the Dashboard, the dealer has to enter the financial year and the month for which the return needs to be filed. Click on Search after that. All returns relating to this period will be displayed on the screen. Dealer has to select the tile containing GSTR-1 After this, he will have the option either to prepare online or to upload the return. The dealer will now Add invoices or upload all invoices directly. Once the entire form is filled up, the dealer shall then Click on Submit and validate the data filled up With the data validated, dealer will now click on FILE GSTR-1 and proceed to either E-Sign or digitally sign the form. Another confirmation pop-up will be displayed on the screen with a yes or no option to file the return. Once Yes is selected, an Acknowledgement Reference Number (ARN) is generated.
- 32. 29 2) What is GSTR-2 ? It is mandatory to furnish details of inward supplies of goods/services received during a tax period for every registered taxable person. These details are furnished based on FORM GSTR-2A which is auto populated on the basis of GSTR 1 filed by your supplier, electronically through the Common Portal, either directly or from a Facilitation Centre. However, GSTR 2A does not in itself auto populates a complete GSTR 2, as there are certain other transactions which are to be mentioned manually in addition to the data which is generated through GSTR 2A, viz. Details of Inward Supplies from an Unregistered Persons on which tax is paid on the Reverse Charge basis and Imports effected during the tax period, etc. Who can file GSTR-2 ? It is mandatory to file a GST Return for each and every entity registered under the GST Act. Even in case where there are no inward supplies during the tax period, NIL return for that period is required to be filed. In case of failure to file the return within due period, the tax payer is penalized with the late fees of INR 100 per day up to a maximum limit of INR 5,000/- When to file GSTR-2 ? Every registered taxable person is required to furnish details of Inward Supply for a tax period i.e. the end of the relevant month. This return has to be filed by the recipient of (goods/services) supplies within 15 days from the end of the relevant tax period. However to facility the ease of payment and return filing for small and medium scale businesses with annual aggregate turnover up to Rs.1.5 crores, it has been decided in the 22nd GST Council meeting dated 06th October 2017, that such tax payers shall be required to file quarterly returns in Form GSTR 1,2 and 3 and pay taxes only on quarterly basis, starting from the third quarter of this financial year, i.e. October to December 2017.
- 33. 30 3) What is GSTR-3 ? GSTR-3 is a return to be filed on monthly basis (compounding and ISD taxpayers are exceptions). GSTR-3 is more like a pooled version of GSTR-1 and GSTR-2. The form captures the information of outward and inward supply information at aggregate level which will be auto populated through GSTR-1, GSTR-1A and GSTR-2.It will comprise of the entire turnover related details, including, local sales turnover, export sales turnover, exempted local sales turnover, turnover except GST and taxable turnover. A taxpayer just has to validate this prefilled information and make modifications if required.
- 34. 31 4) What is GSTR-4 ? Compounding taxpayers would have to file a quarterly return called GSTR-4. Taxpayers otherwise eligible for the compounding scheme can opt against the compounding and file monthly returns and thereby make their supplies eligible for ITC in hands of the purchasers. Compounding taxpayer will also file a simple Annual return (GSTR-9) 5) What is GSTR-5 ? Non –Resident Taxpayers would have to file GSTR-1, GSTR-2 and GSTR-3 returns for the period for which they have obtained registration. The registration of Non–Resident taxpayers will be done in the same manner as that of Regular taxpayers. Non-Resident Taxpayers would be required to file GSTR-5 return for the period for which they have obtained registration within a period of seven days after the date of expiry of registration. In case registration period is for more than one month, monthly return(s) would be filed and thereafter return for remaining period would be filed within a period of seven days as stated earlier. 6) Annual Return Every registered taxable person, other than an input service distributor, a deductor under Section 37, a casual taxable person and a non-resident taxable person, shall furnish an annual return for every financial year electronically in such form and in such manner as may be prescribed on or before the thirty first day of December following the end of such financial year. Every taxable person who is required to get his accounts audited under sub-section(4) of section 42 shall furnish, electronically the annual return along with the audited copy of the annual accounts and a reconciliation statement, reconciling the value of supplies declared in the return furnished for the year with audited annual financial statement, and such other particulars as may be prescribed.
- 35. 32 figure 5.5 Challenges facedduring Return Filing VAT GST Interaction with Government for compliance Once a Quarter or Month 3 times Every Month Return filing Summary of Sales/Purchases needs to be filed Need to upload Every Transaction Invoice Matching Not Monitored extensively Invoices of Supplier and Recipient need to Match Input Credit Availed based on Returns Can be availed only when Invoices are matched and seller pays tax
- 36. 33 ACCOUNTS AND RECORDS Every registered person shall keep and maintain, at his principal place of business, as mention in the certificate of registration, a true and correct accounts of production or manufacture of goods, of inward or outward supply of goods and services, of stocks of goods, of input tax credit availed, of output tax payable and paid, and such other particulars as may be prescribed in this behalf: Provided that where more than one place of business is specified in the certificate of registration, the accounts relating to each place of business shall be kept at such places of business concerned: Provided further that the registered person may keep and maintain such accounts and other particulars in the electronic form in the manner as may be prescribed. The Commissioner may notify a class of taxable persons to maintain additional accounts or documents for such purpose. Every registered taxable person whose turnover during a financial year exceeds the prescribed limit shall get his accounts audited by a chartered accountant or a cost accountant and shall submit to the proper officer a copy of the audited statement of accounts, the reconciliation statement under sub-section (2) of section 30 and such other documents in the form of manner as may be prescribed in this behalf. Period of retention of accounts Every registered taxable person required to keep and maintain books of account or other records under sub-section (1) of section 42 shall retain them until the expiry of sixty months from the last date of filing of Annual Return for the year pertaining to such accounts and records: Provided that a taxable person, who is a party to an appeal or revision or any other proceeding before any Appellate Authority or Tribunal or Court, whether filed by him or by the department, shall retain the books of account and other records pertaining to the subject matter of such appeal or revision or proceeding for a period of one year after final disposal of such appeal or revision or proceeding, or for the period specified under sub-section (1), whichever is later.
- 37. 34 AUDIT Audit by tax authorities : 1. The Commissioner of CGST/SGST or any officer authority by him, may undertake audit of the business transactions of any taxable person for such period, at such frequency and in such manner as may be prescribed. 2. The tax authorities referred to in sub-section (1) may conduct audit at the place of business of the taxable person or in their office. 1. The taxable person shall be informed by way of notice, sufficient in advance, not less than 15 working days, prior to the conduct of audit. 2. The audit under sub-section (1) shall be carried out in a transparent manner and completed within a period of three months from the date of commencement of audit. 3. During the course of audit, the authorized officer may require the taxable person, to afford him the necessary facility to verify the books of accounts or other documents as he may require. to furnish such information as he may require and render assistance for timely completion of the audit. 6. On conclusion of audit, the proper officer shall without delay inform the taxable person, whose records are audited, of the findings, the taxable person's rights and the obligations and the reasons for the findings. 7. Where the audit conducted under sub-section (1) results in detection of tax not paid or short paid, the officer may initiate action under section 51. SpecialAudit If at any stage of scrutiny, enquiry, investigation or any other proceedings before him, any officer not below the rank of [Deputy/Assistant Commissioner] having regard to the nature and complexity of the case and the interest of revenue, is of the opinion that the value has not been correctly declared or the credit availed is not within the normal limits, he may, with the prior approval of the [Commissioner], direct such taxable person by notice in writing to get his records including books of account examined and audited by a chartered accountant or a cost accountant as may be nominated by the [Commissioner] in this behalf.
- 38. 35 OFFENCES AND PENALTIES Offences and penalties : Where a taxable person who – supplies any goods or services without issue of any invoice or issue any false invoice with regard to any such supply ; issue any invoice or bill without supply of goods or services in violation of the provisions of this Act ; collects any amount as tax but fails to pay the same to the credit of the appropriate Government beyond a period of three months from the date on which such payment becomes due ; fails to deduct the tax in terms of sub-section (1) of section 37, or deduct the amount which is less than the amount required to be collected ; fraudulently obtains refund of any CGST/SGST under this Act ; is liable to be registered under this Act but fails to obtain registration ; transport any taxable goods without the cover of documents ; fails to keep, maintain or retain books of account ; issues any invoice by using the identification number of another taxable person ; destroys any material evidence ; fails to furnish information and/or documents called for by a CGST/SGST officer in accordance with the provisions of this Act or rules made there under or furnishes false information and/or documents during any proceedings under this Act; supplies, transports or stores any goods which he has reason to believe are liable to confiscation under this Act; Any person who contravenes any of the provisions of this Act or rules made there under for which no penalty is separately provided for in this Act, shall be liable to a penalty which may extend to Rs. 25,000/-
- 39. 36 STATEMENT ANALYSIS IN EXCEL SHEET Name of the party Bank statement analysis for GST in excelsheet Business Inflow of the Company
- 40. 37 Business Outflow of the Company Personal Inflow of the Company Personal Outflow of the Company
- 42. 39 Chapter 6 Conclusion It can be concluded from the above discussion that GST will provide relief to producers and consumers by providing wide and comprehensive coverage of input tax credit set-off, service tax set off and subsuming the several taxes. Efficient formulation of GST will lead to resource and revenue gain for both Centre and States majorly through widening of tax base and improvement in tax compliance. It can be further concluded that GST have a positive impact on various sectors and industry. Centre has decided to review the existing exemptions from Central Excise Duty so that list of goods exempt from CGST and SGST list and 99 items exempted from VAT are taken off from both the components of GST. VAT has to some extent reduced tax-evasion and frauds. It is encouraging to note that most of the traders and general public are aware of VAT. GST, the major reforms on indirect taxes, will reduce tax burden due to cascading effect. The efficiency in tax administration will be improved, indirect tax revenue will be increased considerably due to inclusion of more goods and services, and at last the cost of compliance will be reduced for the dealers. The implementation of GST will be in favor of free flow of trade and commerce throughout the country. This single most important tax reform initiative by the Government of India since independence provides a significant fillip to the investment and growth of our country’s economy. To get the desired result, it should be assured that the benefit of input credit is ultimately enjoyed by final consumers. Although implementation of GST requires concentrated efforts of all stake holders namely, Central and State Government, trade and industry. GST effect the indirect taxation systems and help reduce the burden on tax payer. GST help to reduce the burden of record make and file maintain. Because GST cover 10-12 Tax. GST reduce the price of various goods and increase the sale. After the implementation of GST indirect taxation systems will remove and it easy to all tax payer to pay the tax to government. Efficient formulation of GST will lead to resource and revenue gain for both Centre and States majorly through widening of tax base and improvement in tax compliance. It can be further concluded that GST have a positive impact on various sectors and industry. Although implementation of GST requires concentrated efforts of all stake holders namely, Central and State Government, trade and industry.
- 43. 40 23rd GST Council Meeting Summary:– Changes in the tax slabs :- Taxes on over 200 items have been squeezed and a whopping 88% of the items from the highest slab of 28% have been switched to 18%. Out of the 228 items in the 28% category, only 50 have been retained and the rest 178 have been slid downwards to different tax brackets. 2 items saw a dip from 28% to 12%, 6 items from 18% to 5%, 8 items from 12% to 5% and 6 items from 5% to nill. Changes in the composition scheme :- - Manufacturers and traders would now operate at a standard rate of 1%. - The threshold to opt GSTR-3B along with payment of tax will now need to be filed by 20th of the next month till March 2018. - Threshold for the composition scheme has been increased to Rs. 1.5 crores from the current limit of Rs. 1 crore. Softened fines on late filing :- - Fine for late returns has been slashed by 90% to a mere Rs. 20 per day from Rs. 200 per day for a taxpayer with nil liability. - Late fine for not submitting the GSTR-3B within due dates for the month of July, August and September 2017 has been waived off.
- 44. 41 Relaxed deadlines for filing returns :- - GSTR-3B along with payment of tax will now need to filed by 20th of the next month till March 2018. - Taxpayers divided into two categories for filing GSTR-1 till March 2018. The categories are :- Businesses with an annual aggregate turnover of upto 1.5 crores will file GSTR-1 quarterly. Period New Due Date July - September 31 – Dec - 2017 October - December 15 – Feb - 2018 January - March 30 – April - 2018 Business with an annual aggregate turnover of above 1.5 crores will file GSTR-1 monthly. Period New Due Date July – October 31 – Dec - 2017 November 10 – Jan - 2018 December 10 – Feb - 2018 January 10 – Mar - 2018 February 10 – Apr - 2018 March 10 – May - 2018
- 45. 42 Reference www.gst.gov.in www.gstn.org www.gstcouncil.gov.in www.cbec.gov.in www.financialexpress.com www.wikipedia.com www.cleartax.com