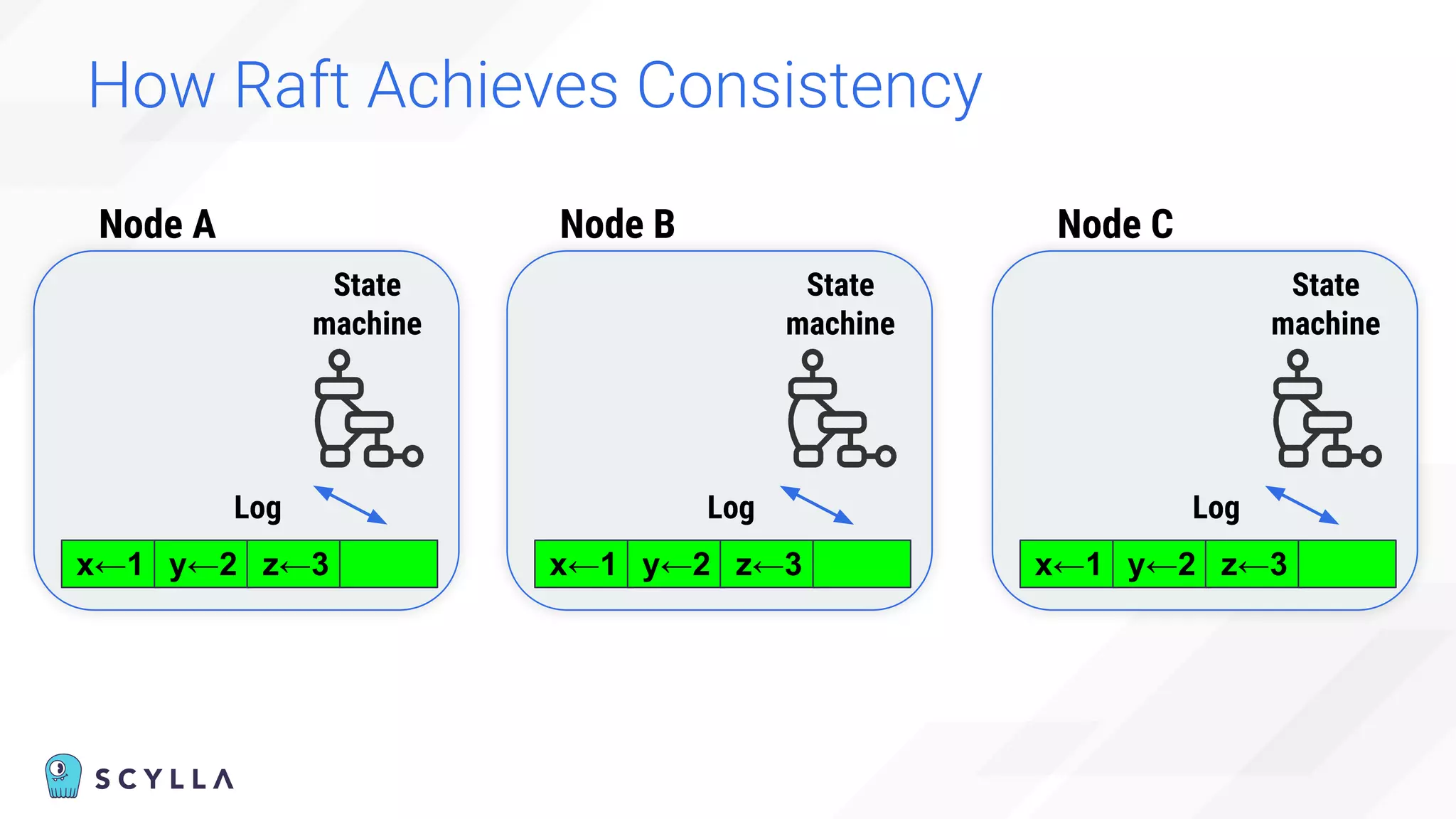
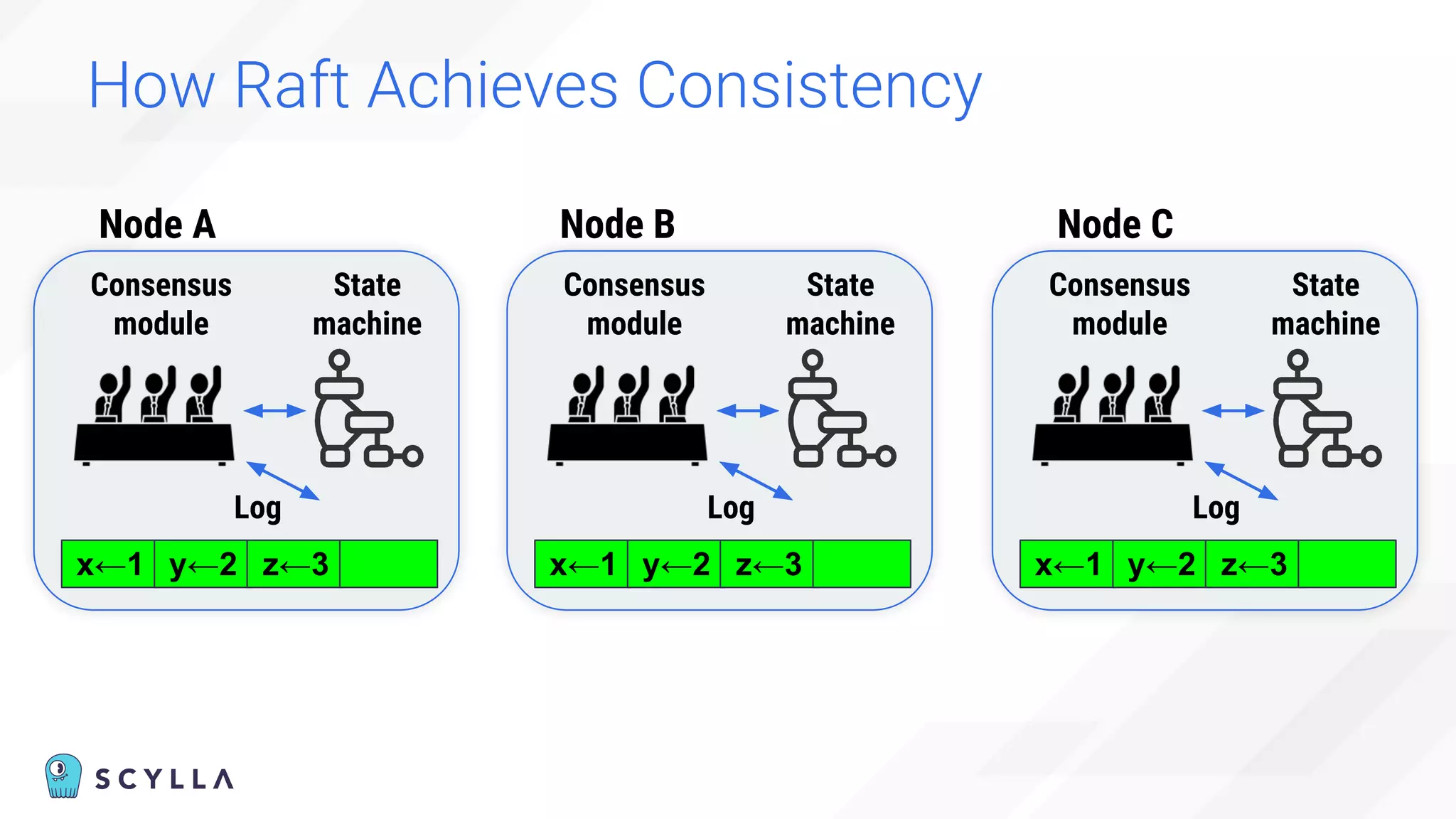
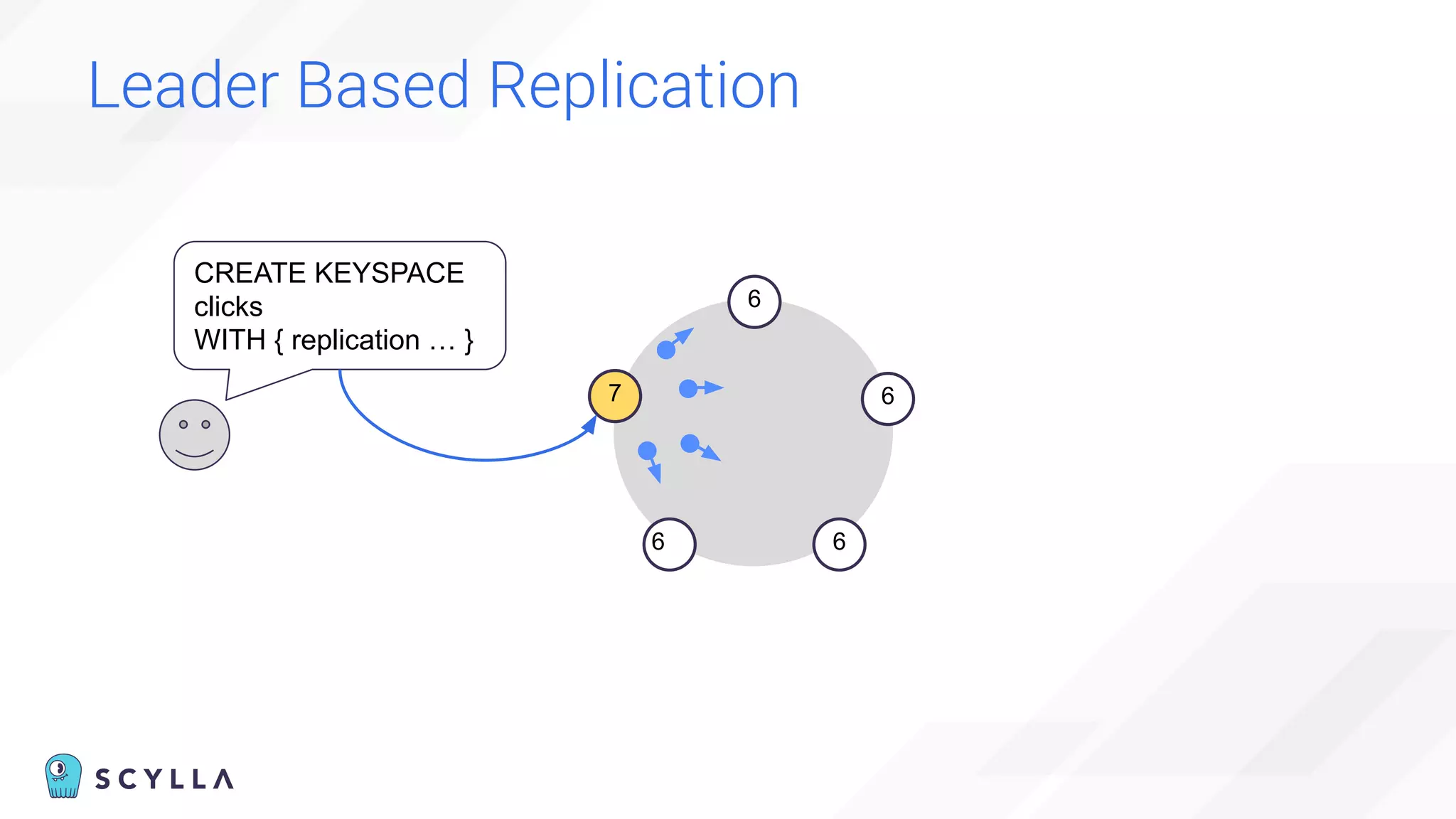
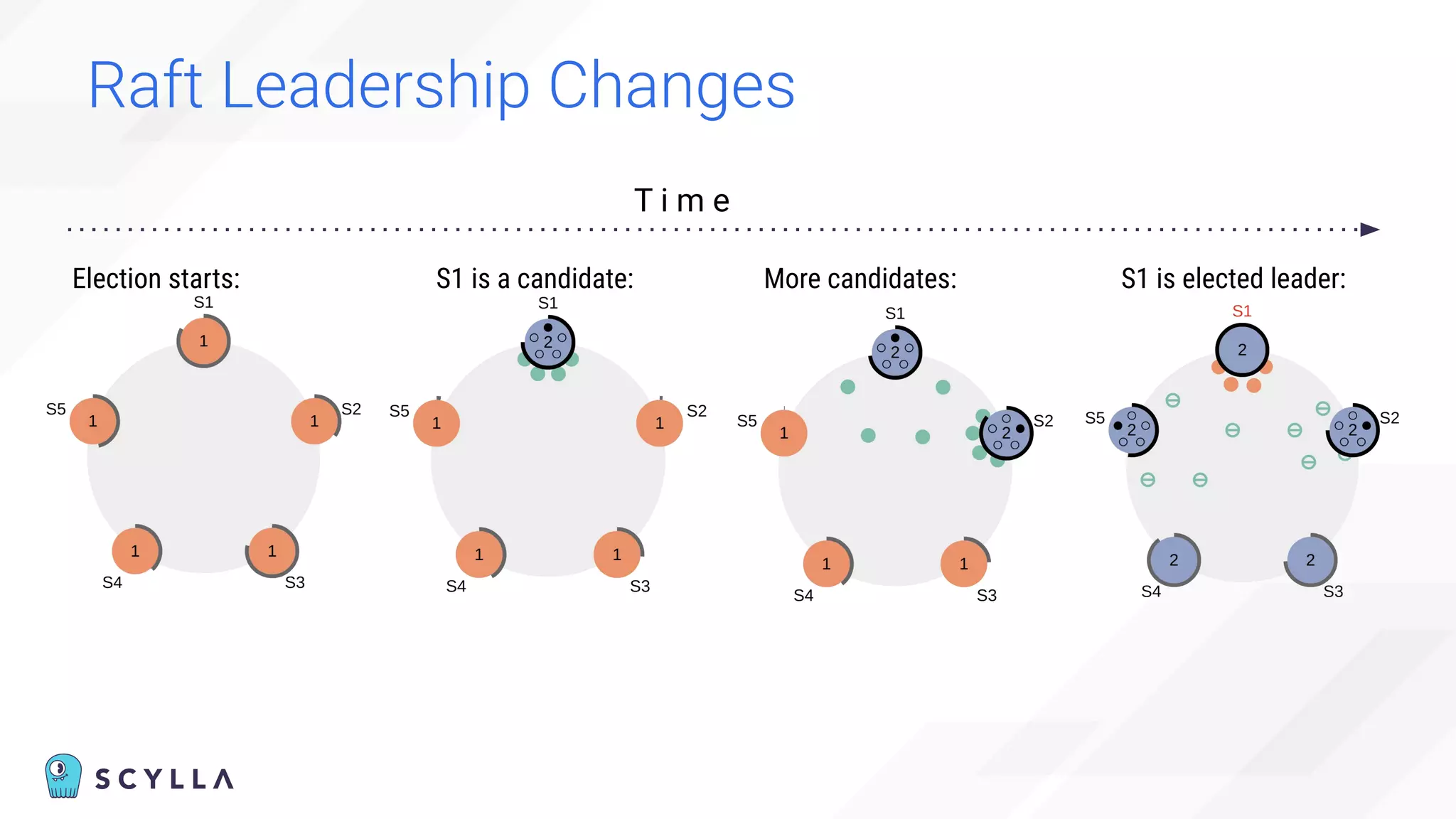
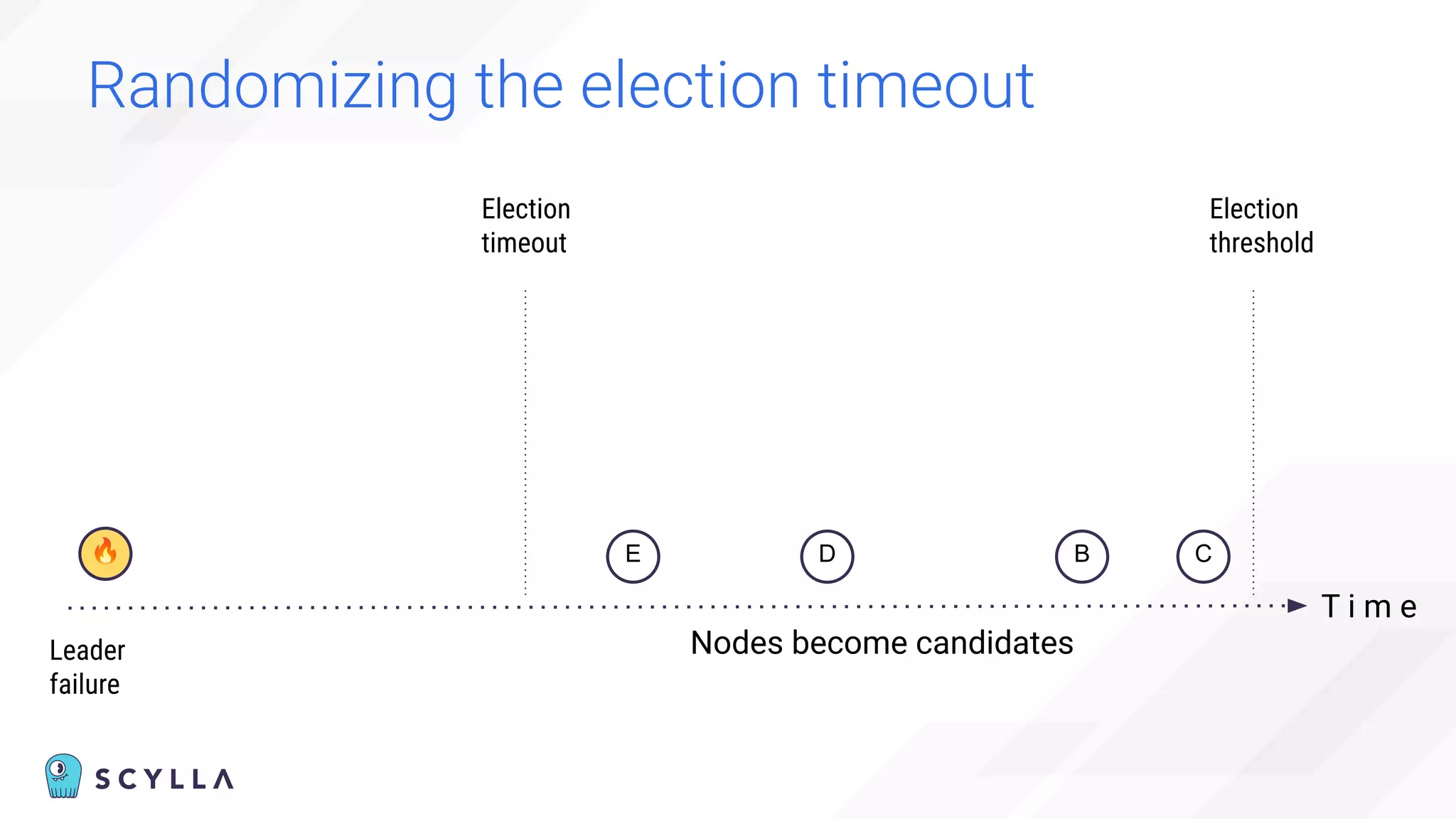
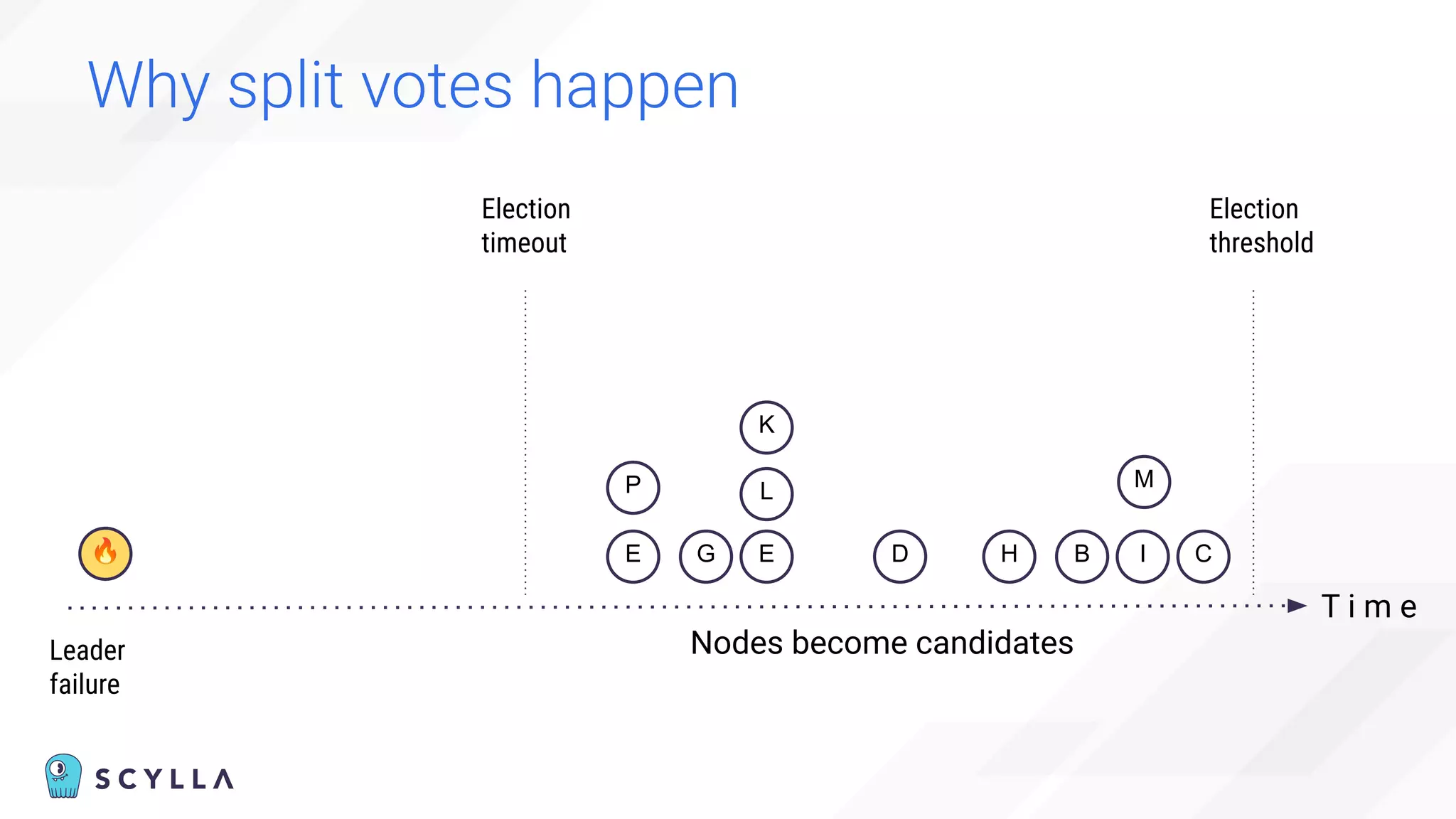
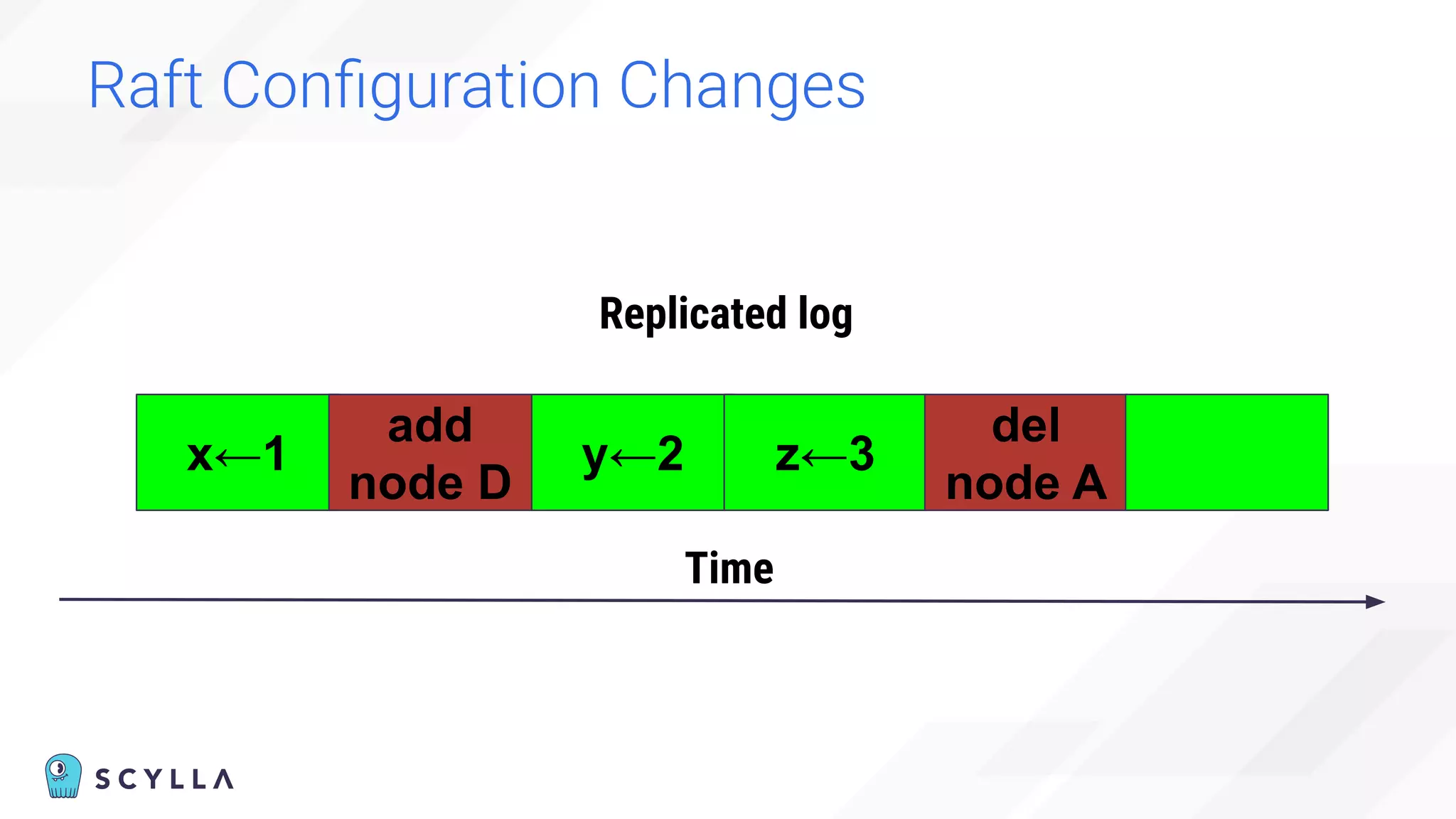
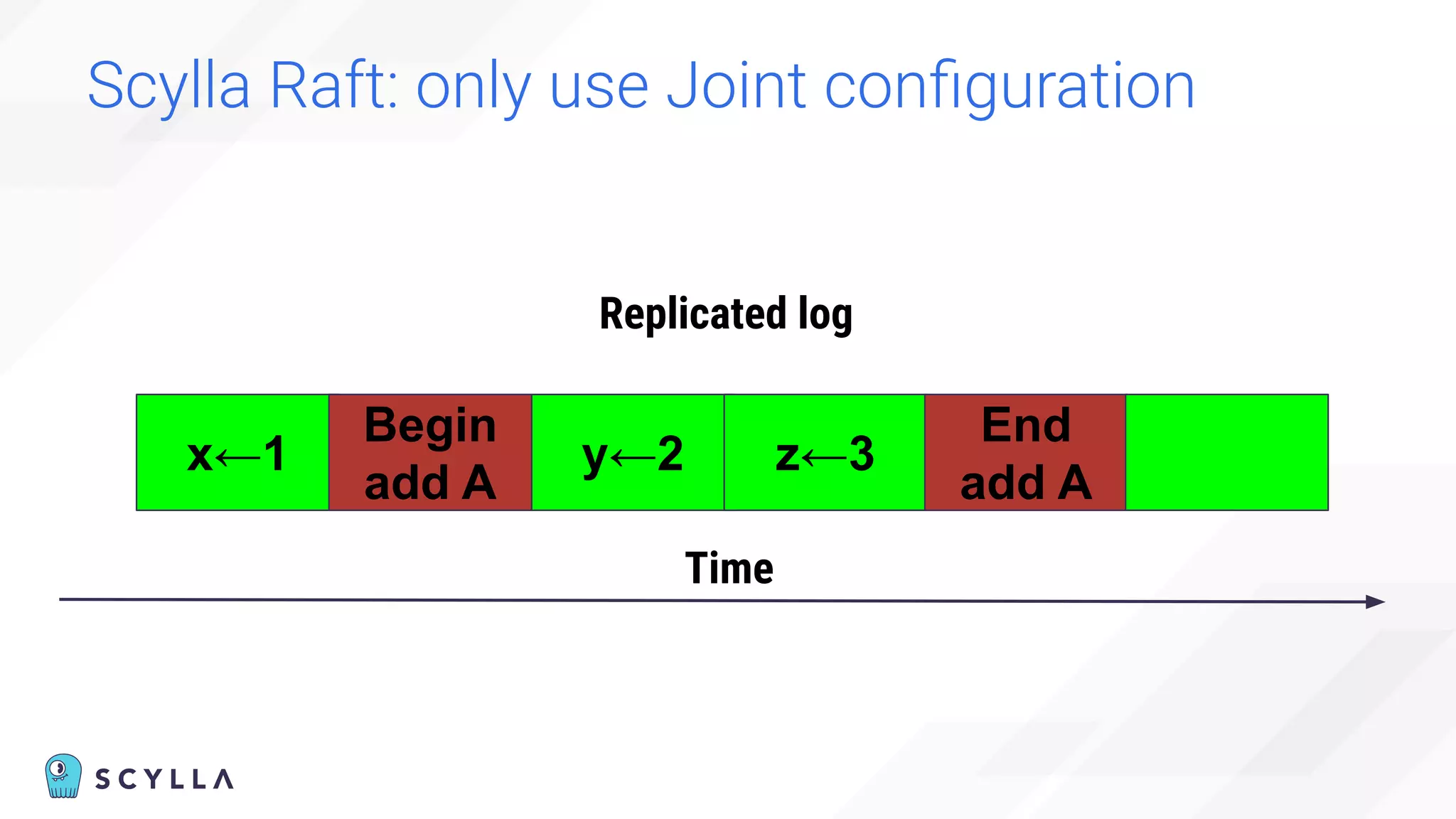
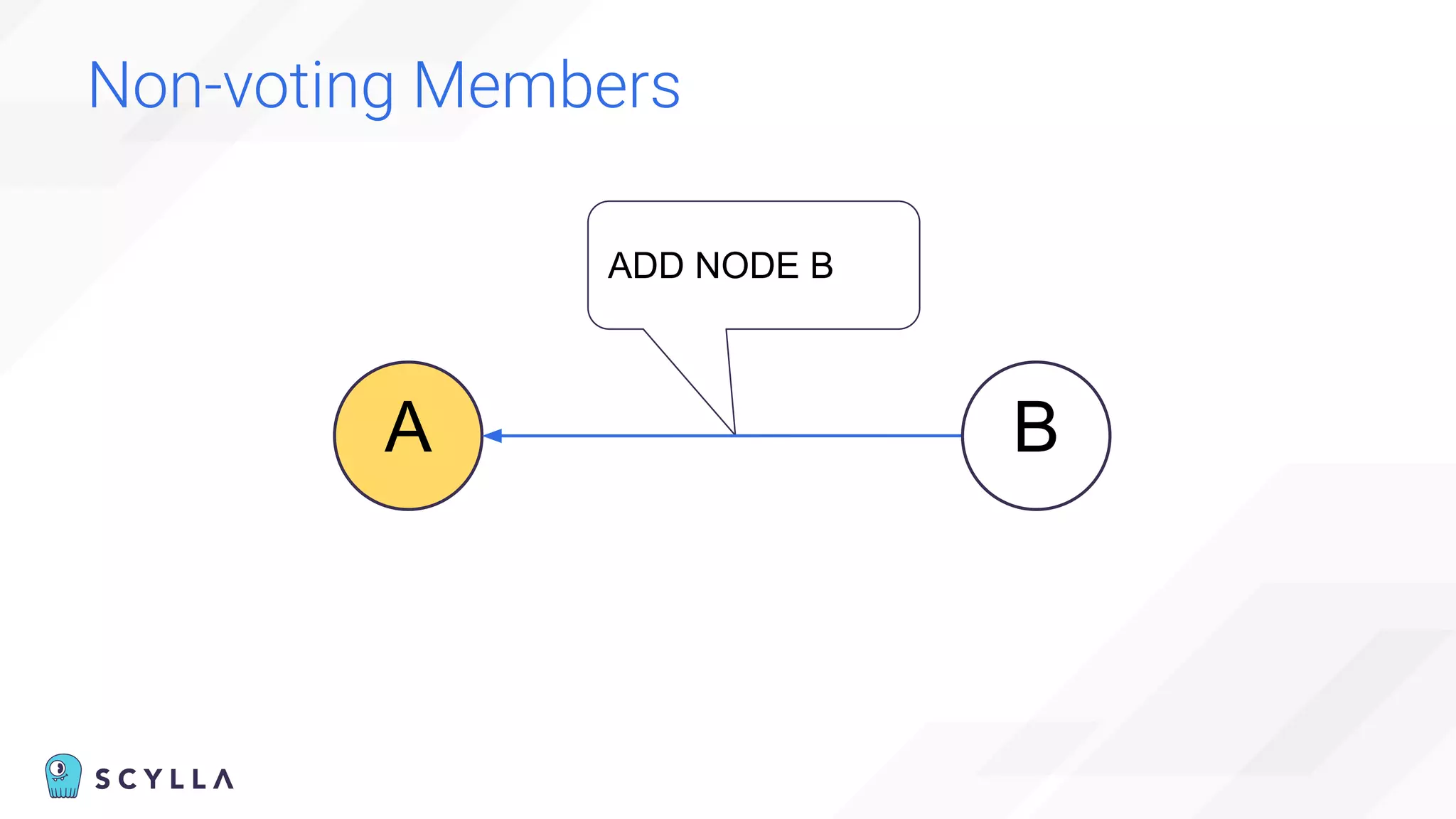
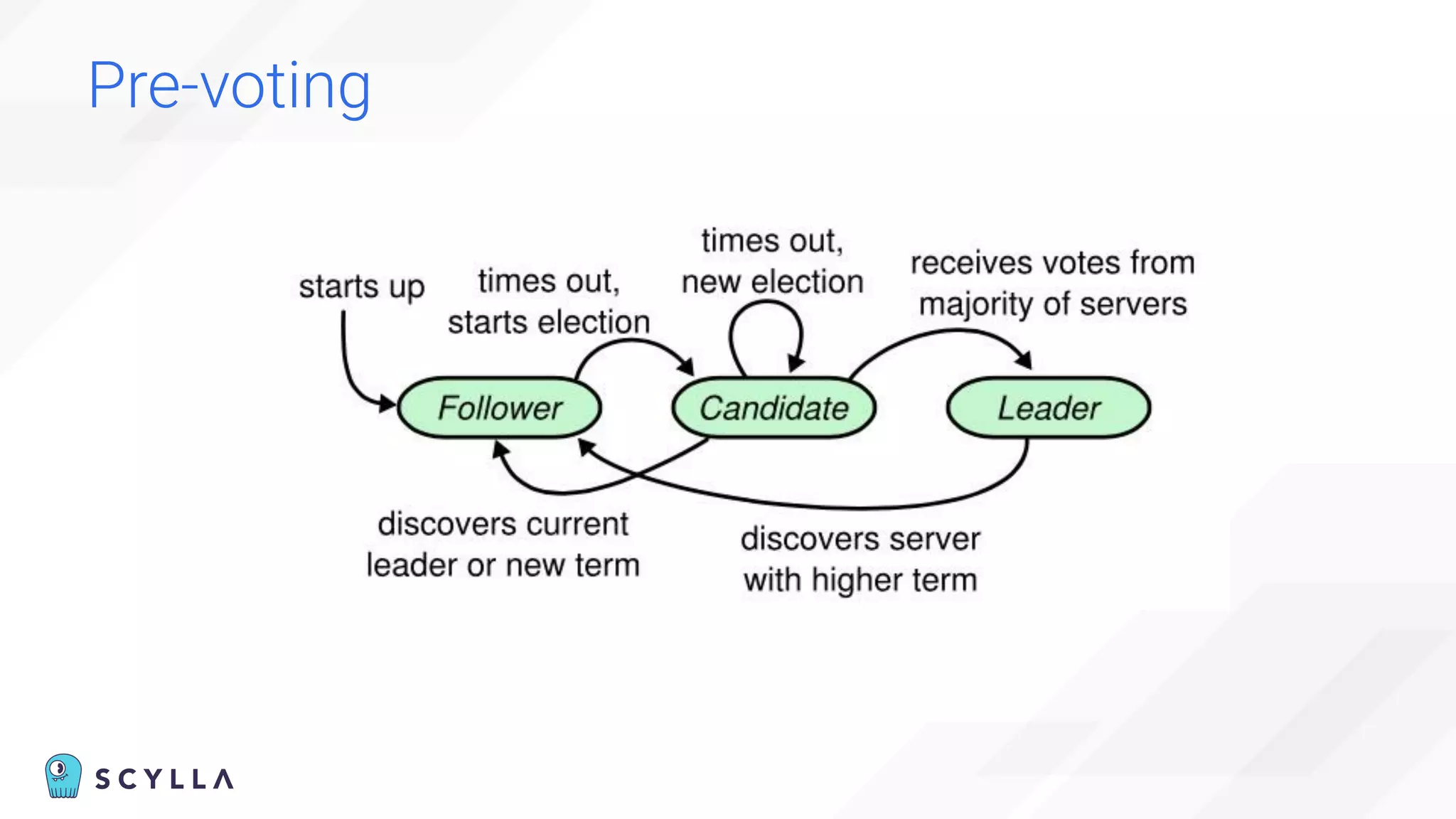
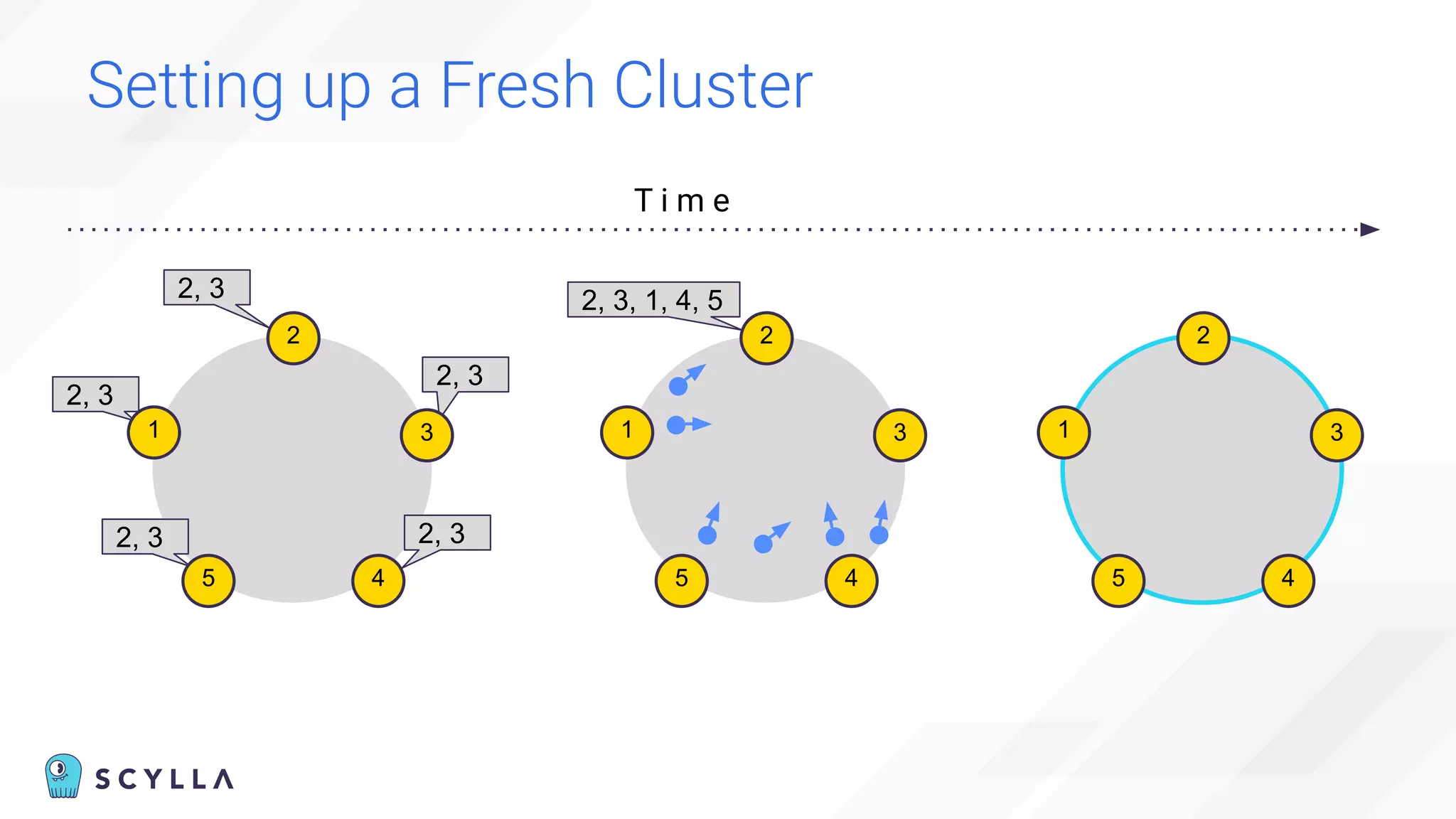
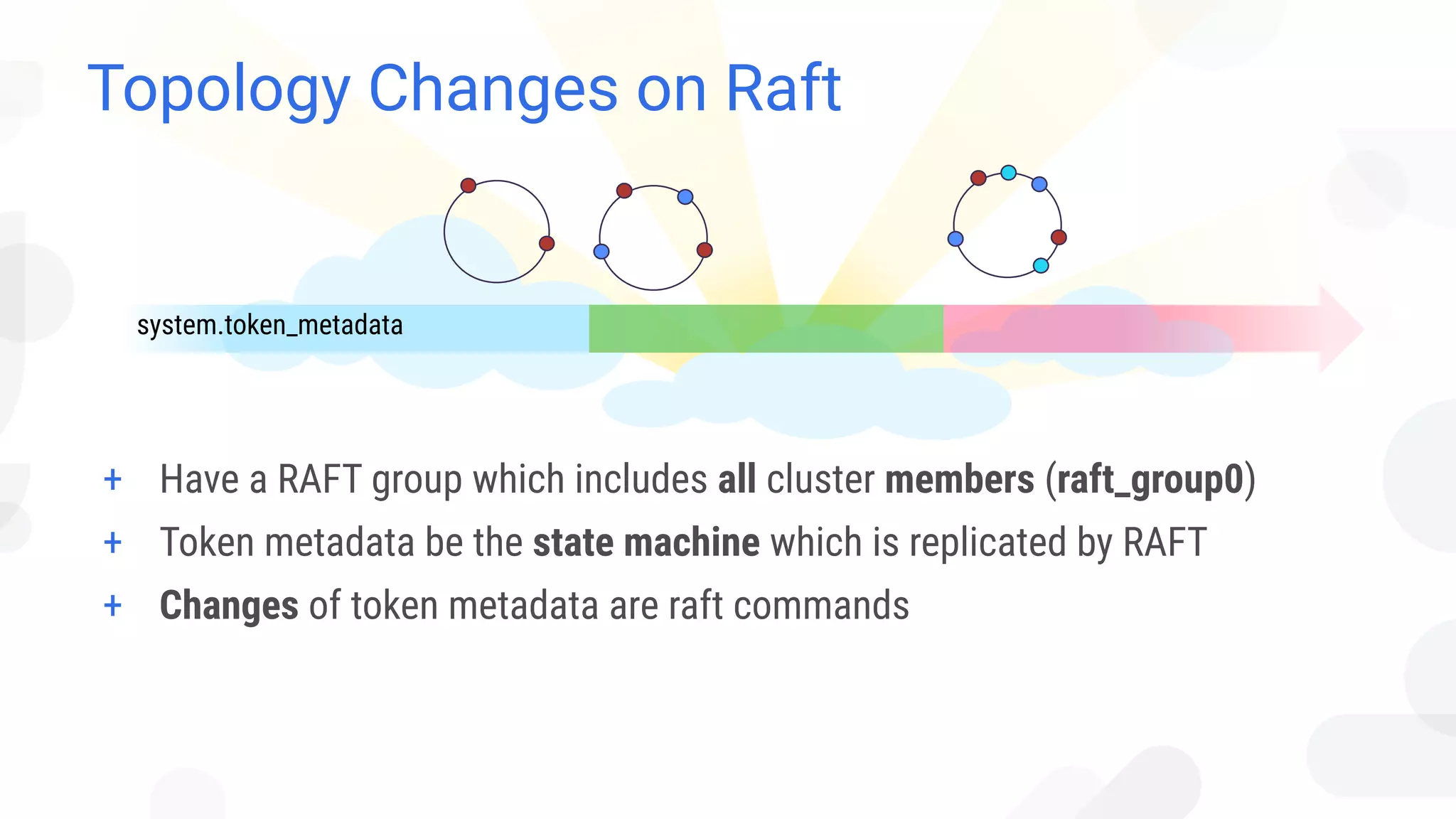
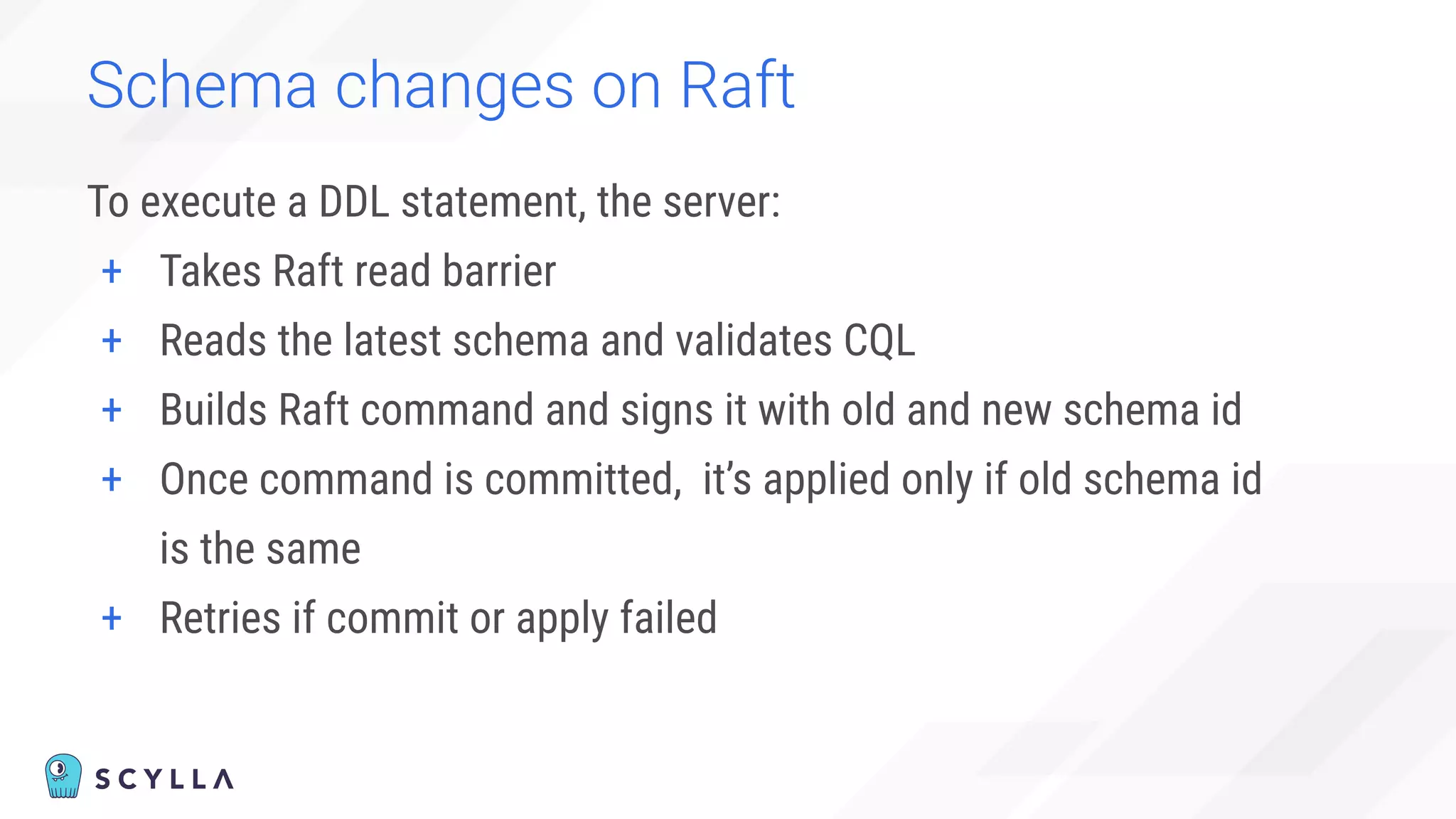
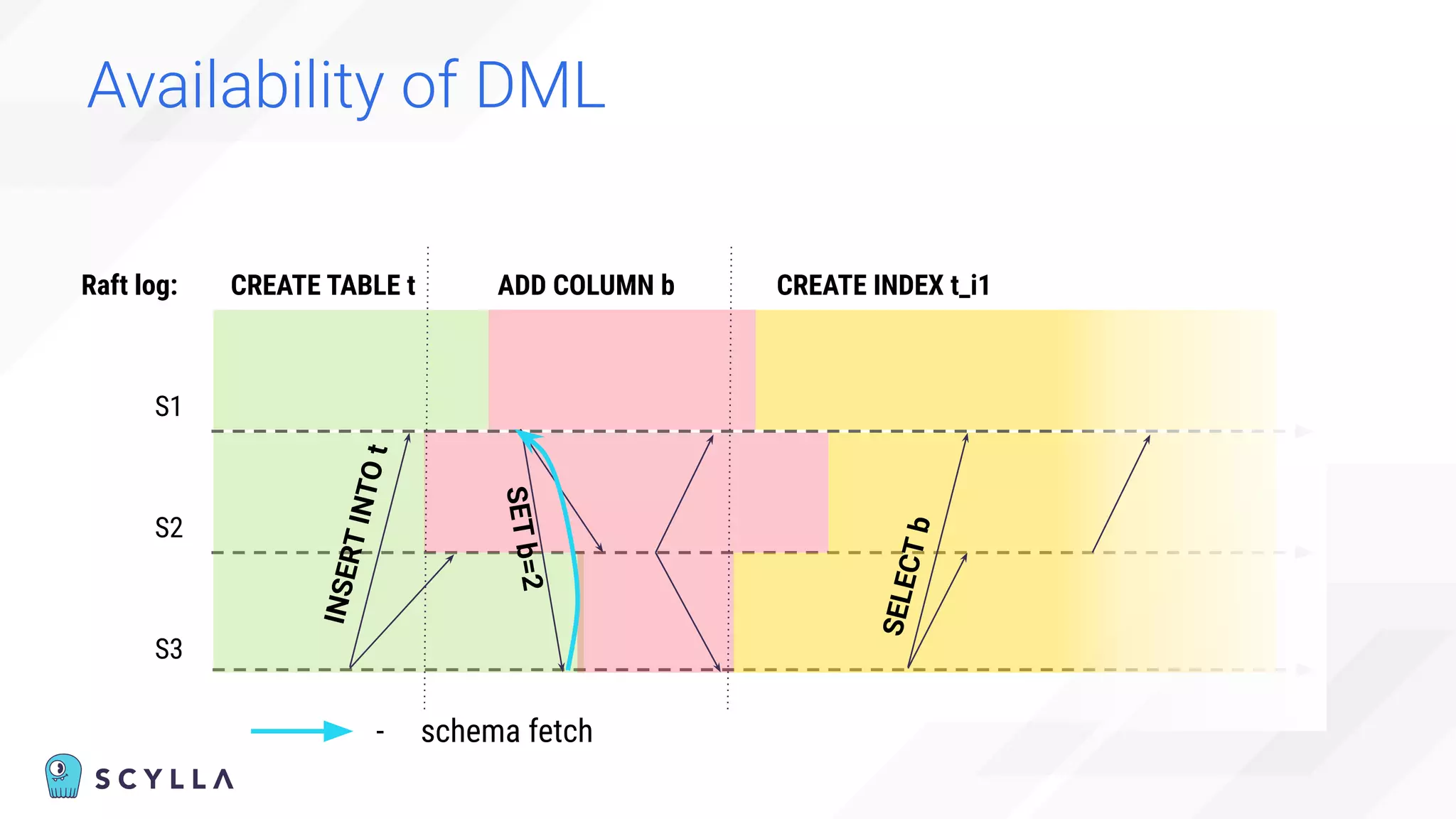
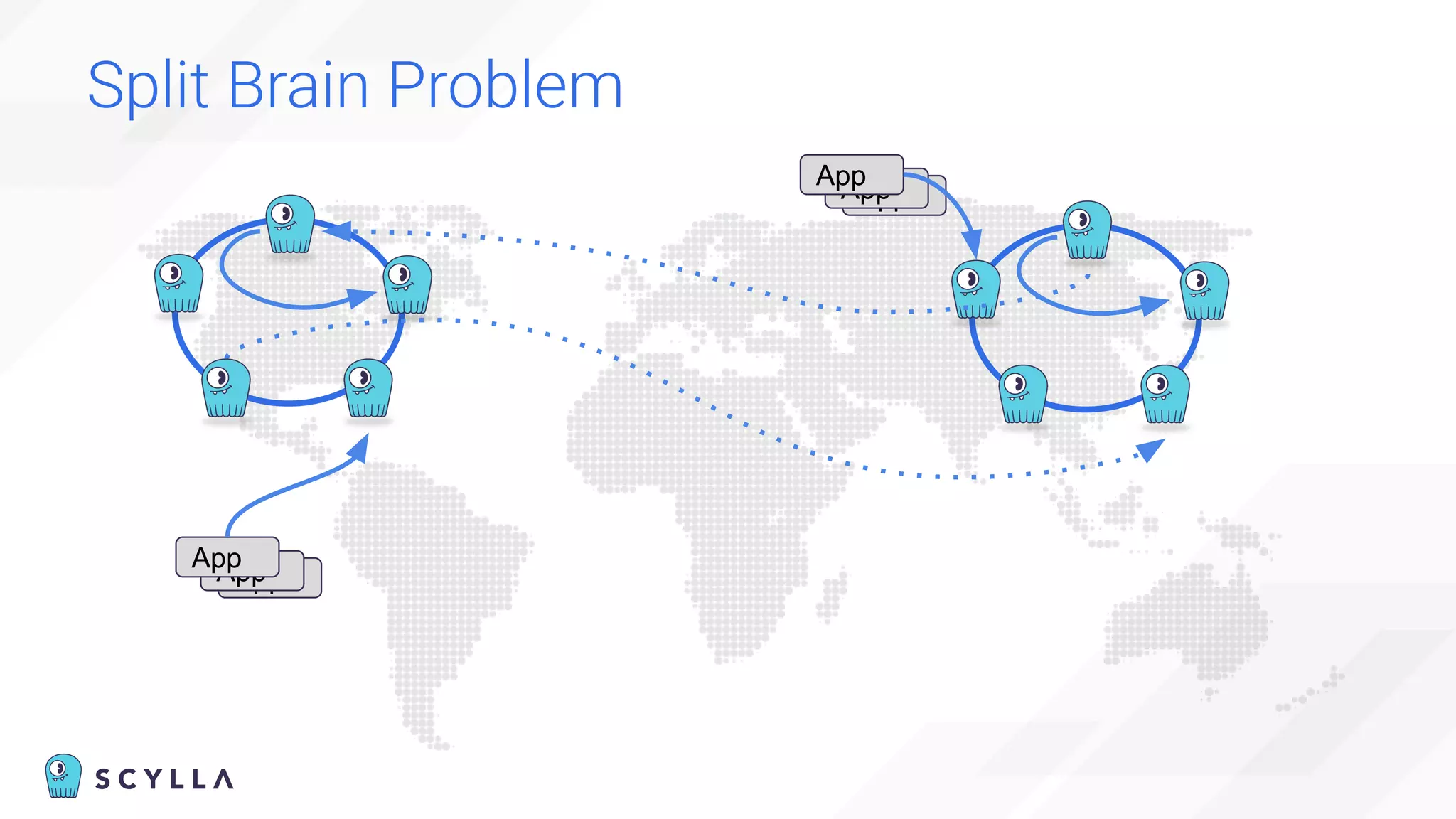
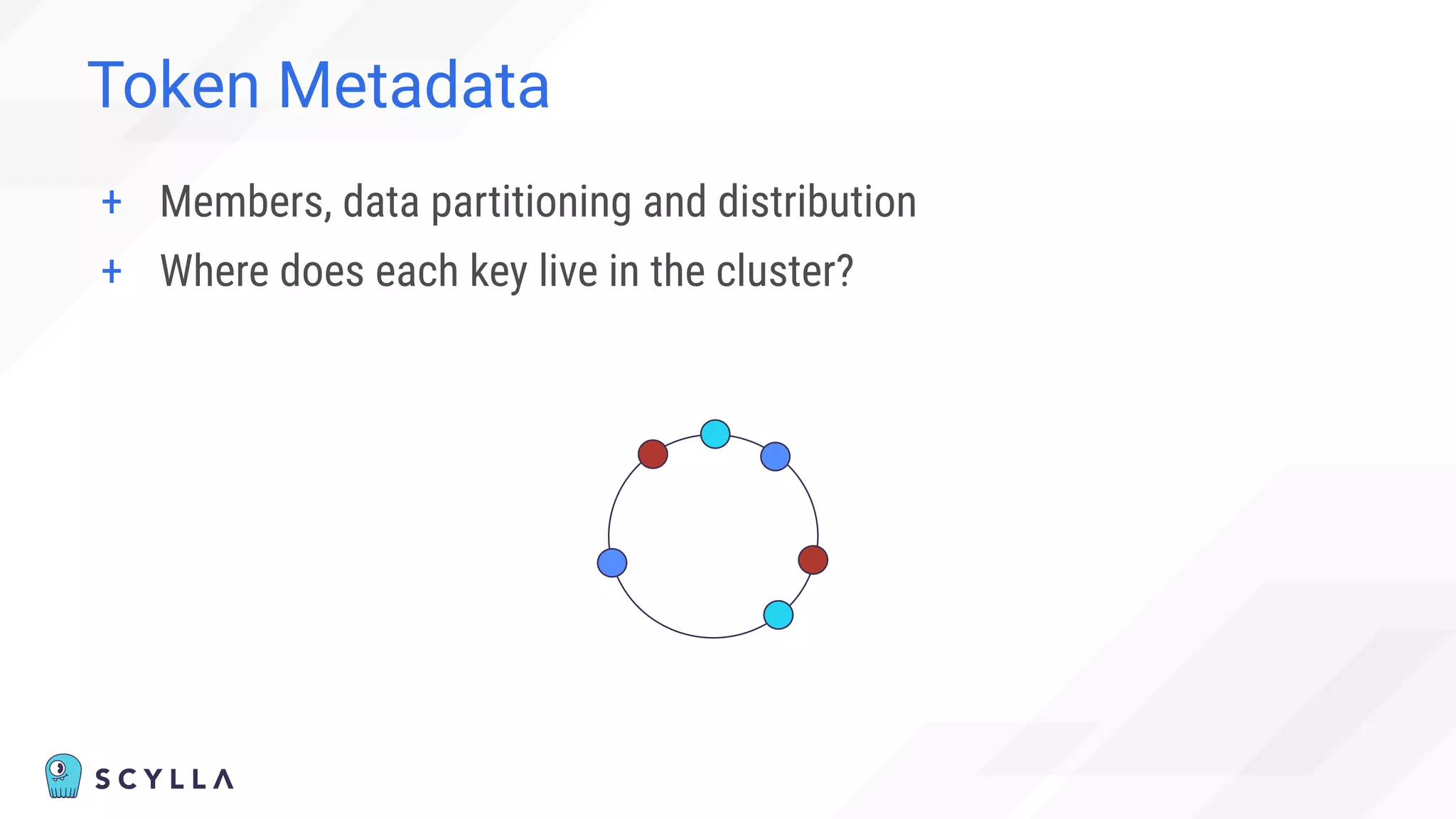
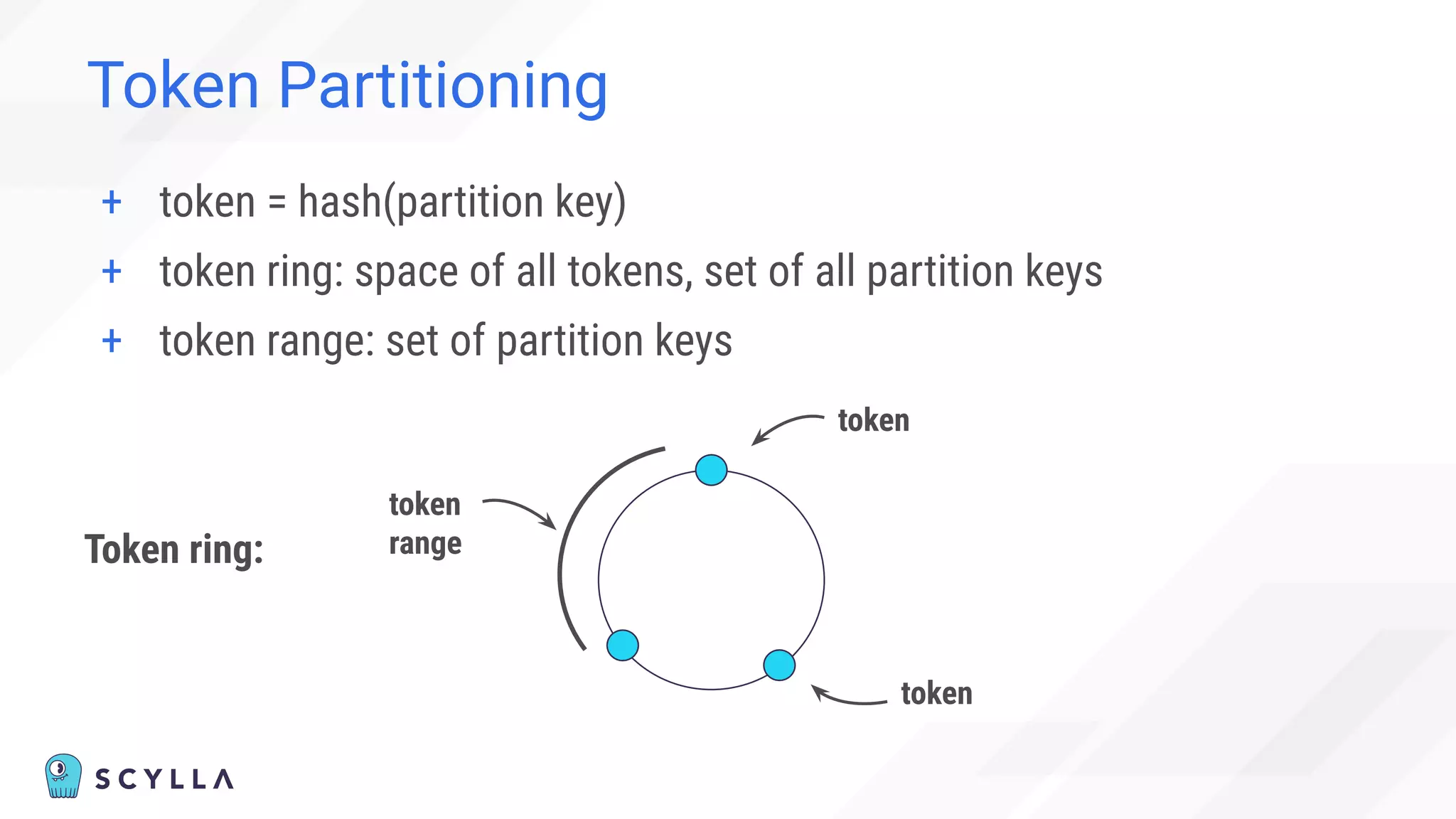
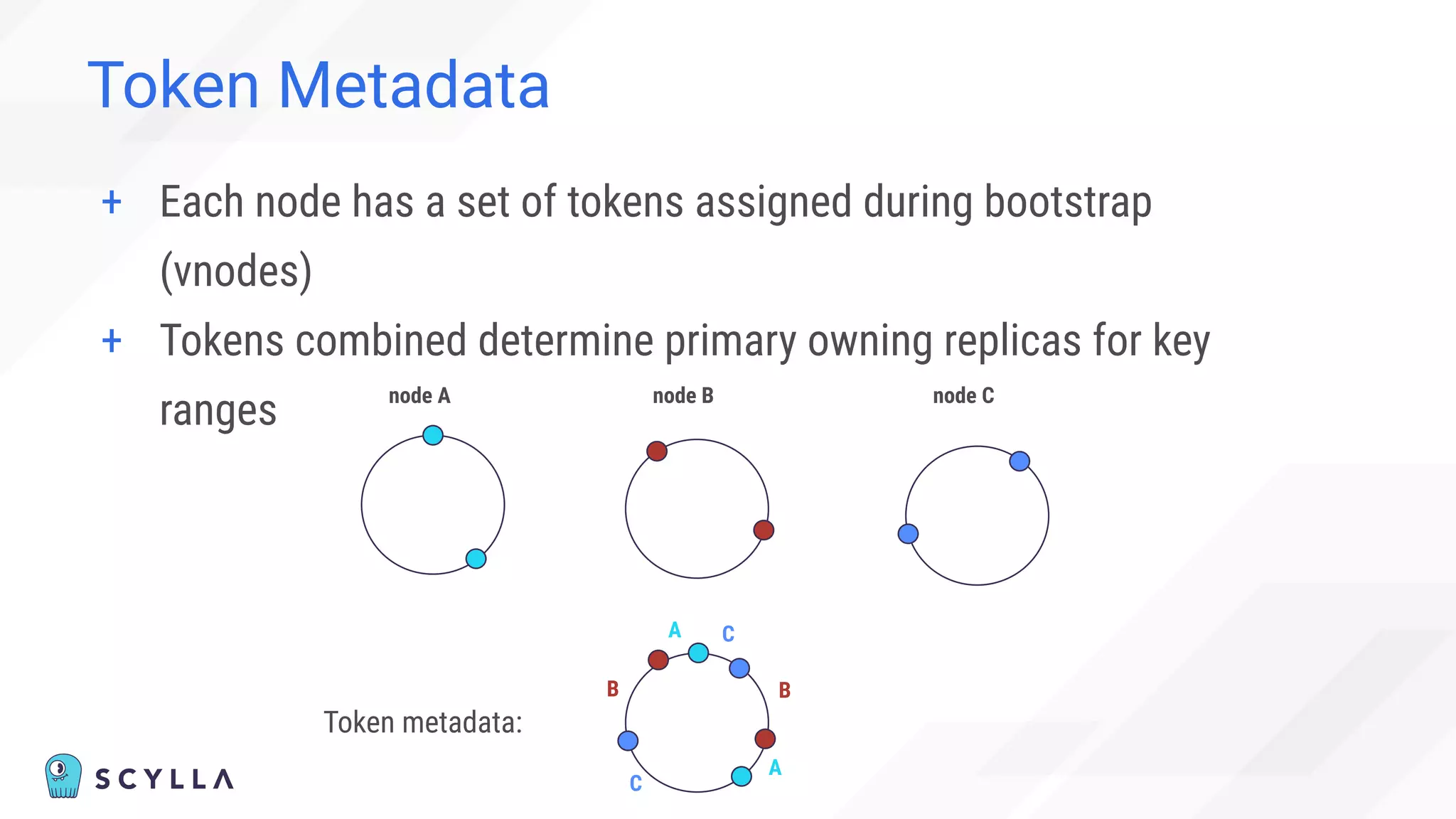
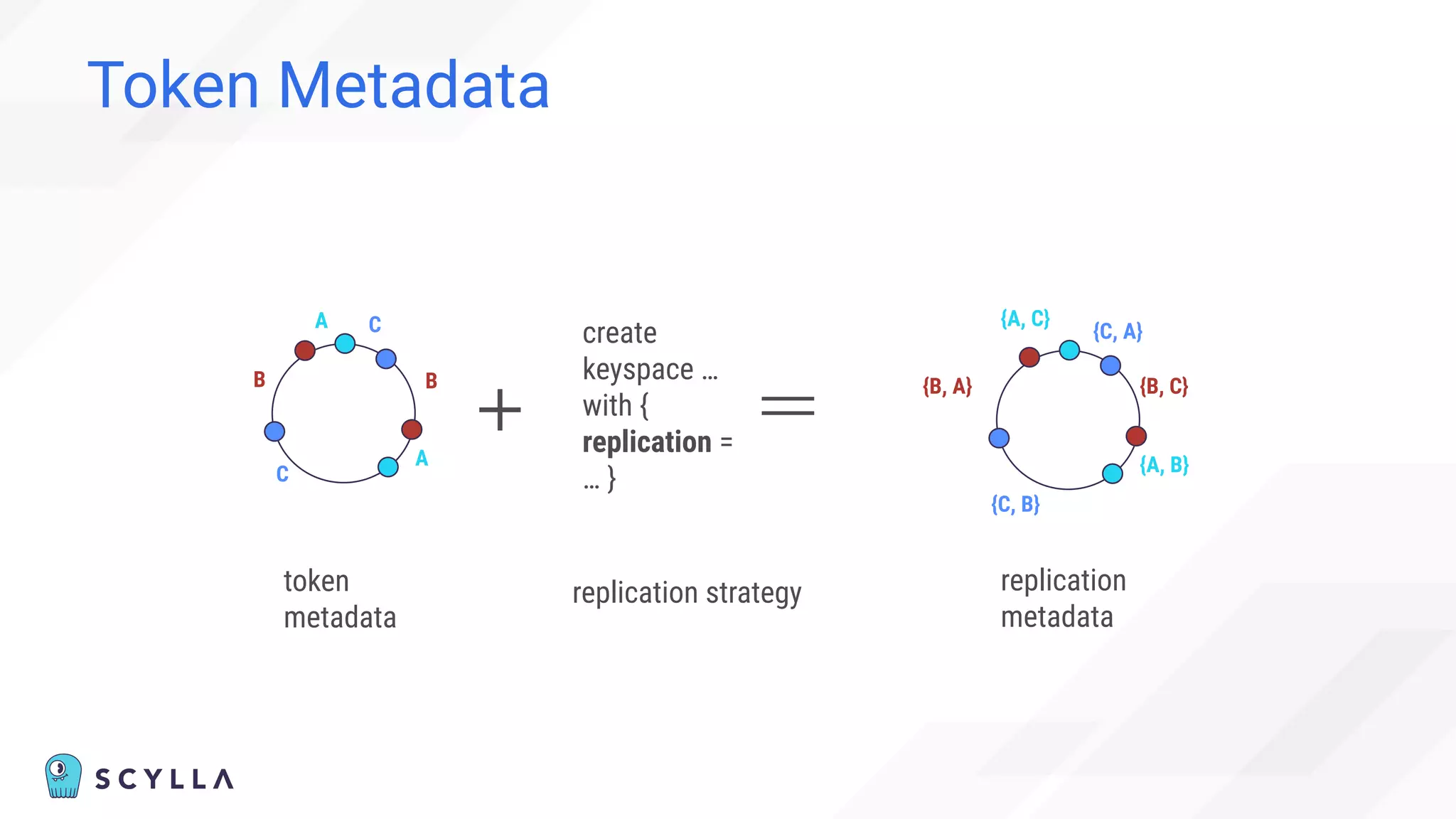
The document discusses architectural considerations and trade-offs in achieving consistency within distributed databases, specifically focusing on ScyllaDB's approach using the Raft protocol for state machine replication. It emphasizes the importance of strong consistency and provides a detailed examination of schema and topology consistency while addressing challenges associated with legacy NoSQL databases. Furthermore, it highlights ScyllaDB's advantages in performance and cost-effectiveness for data-intensive applications.







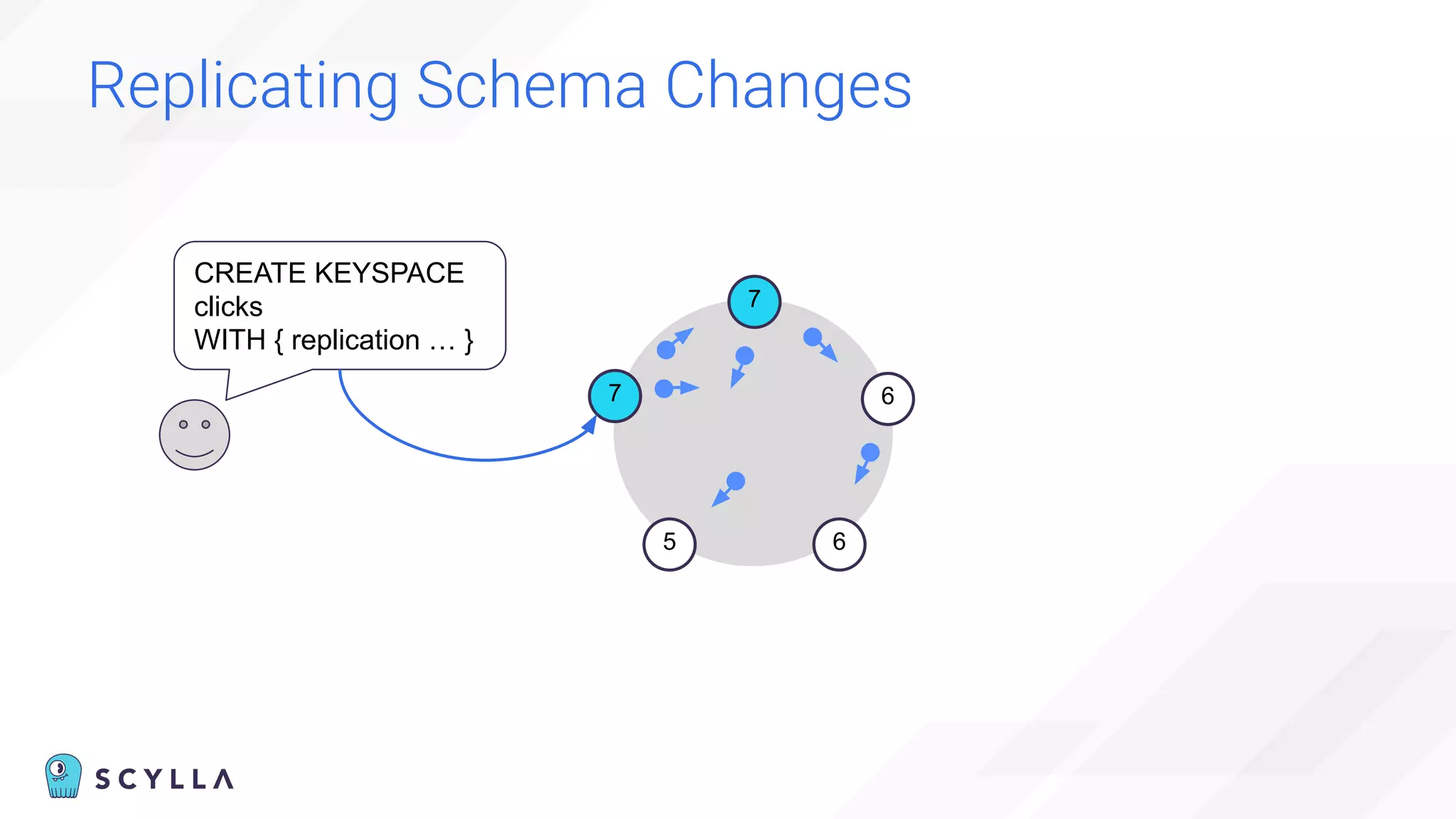
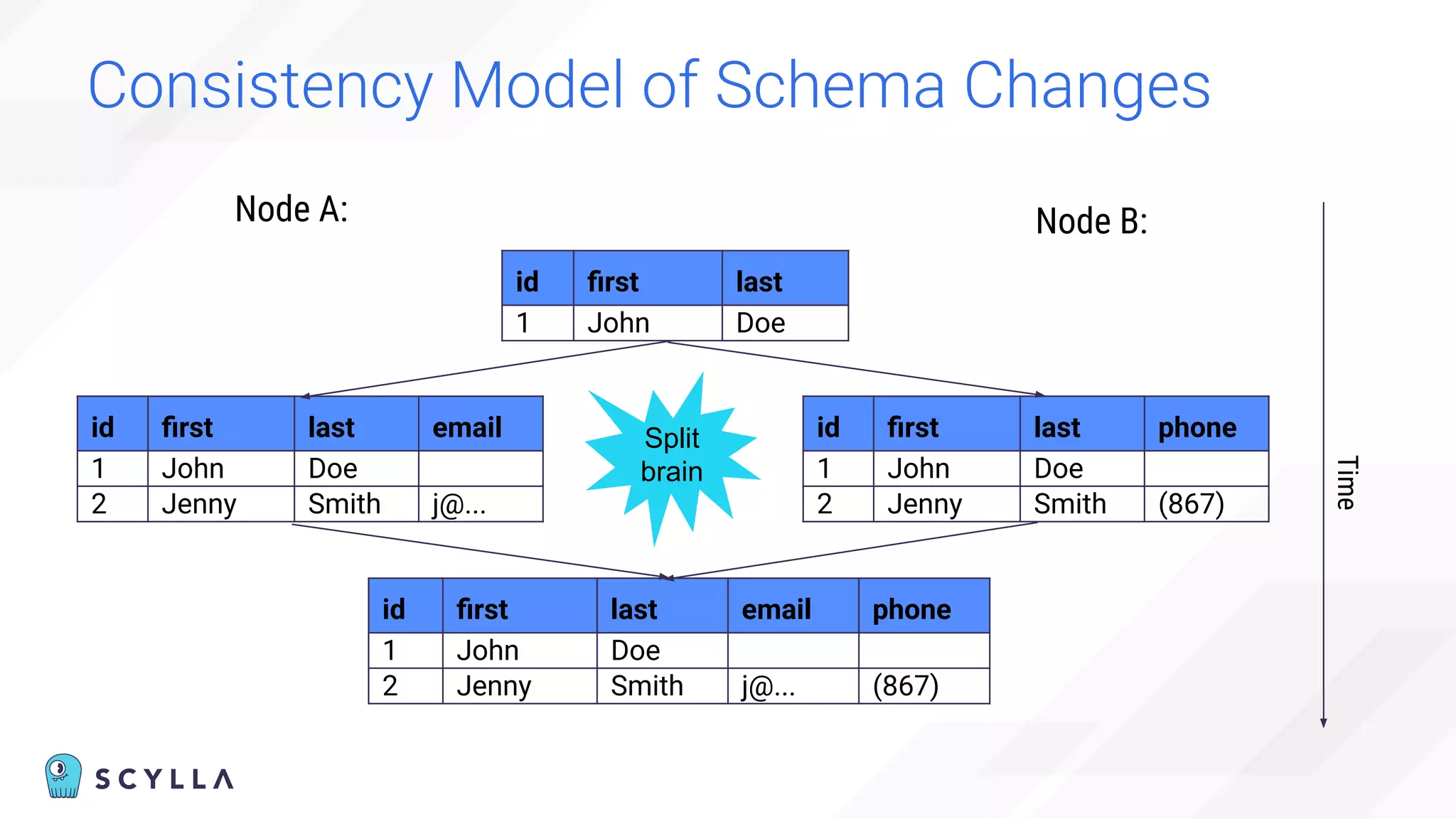
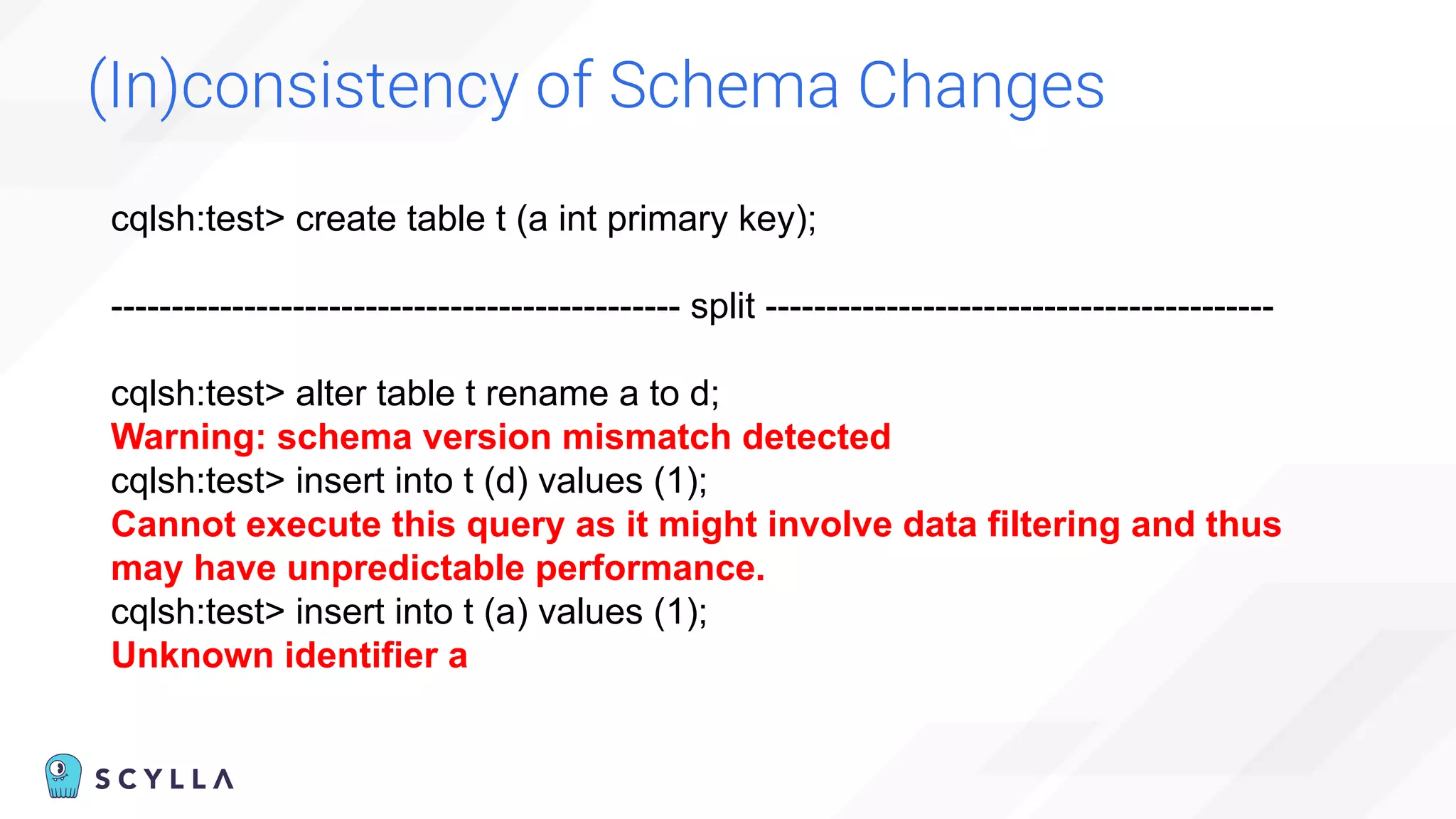

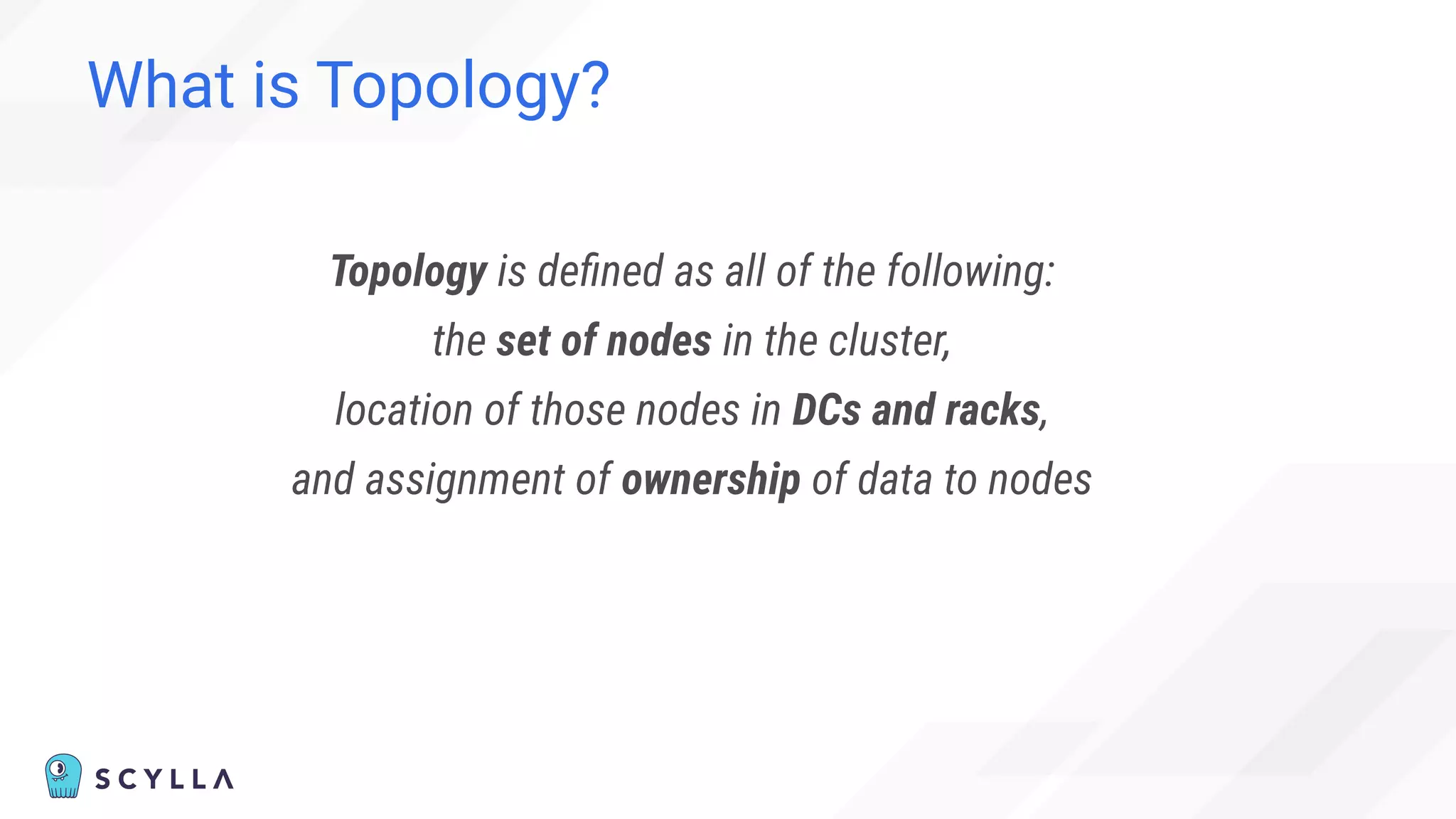
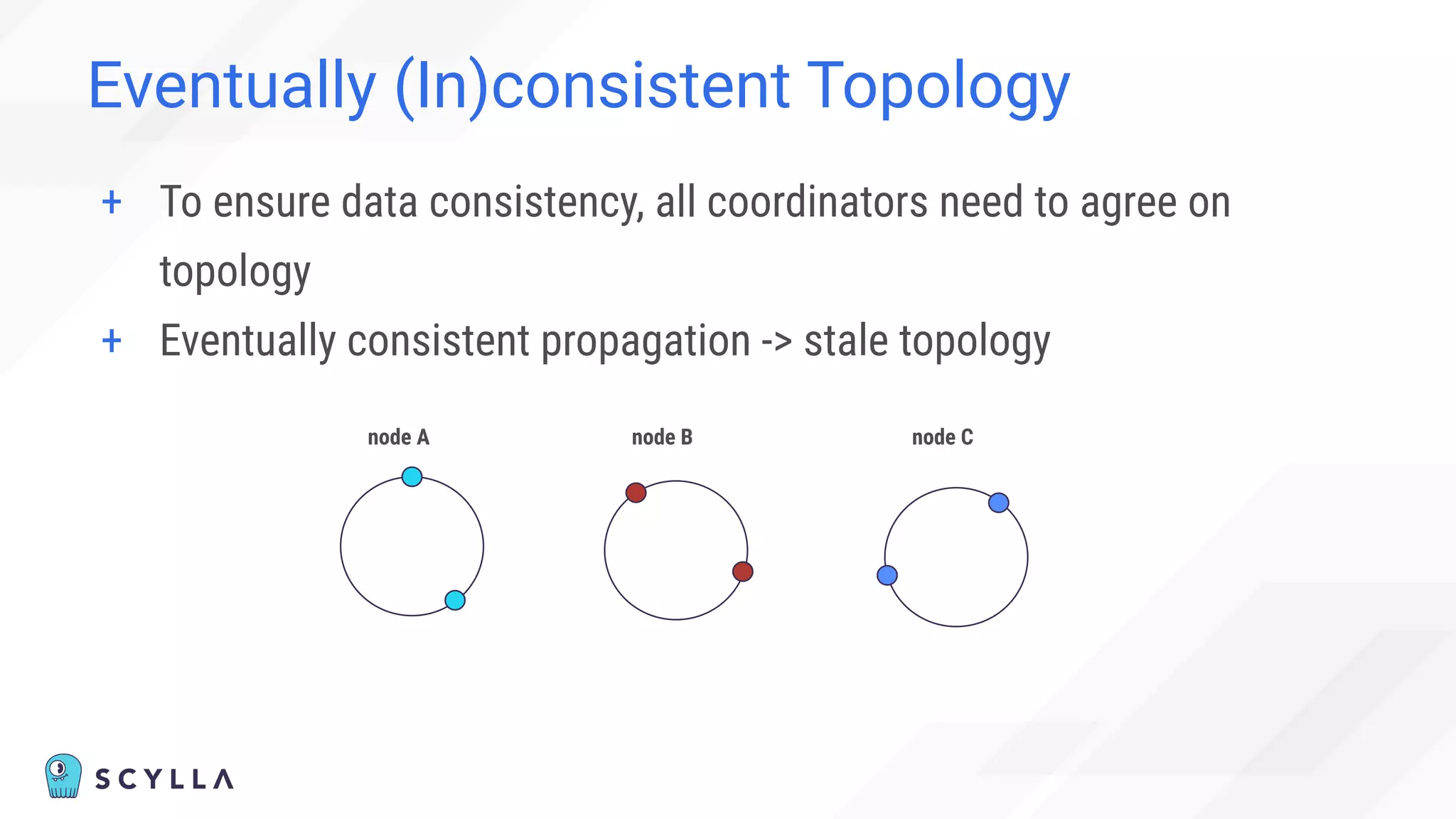
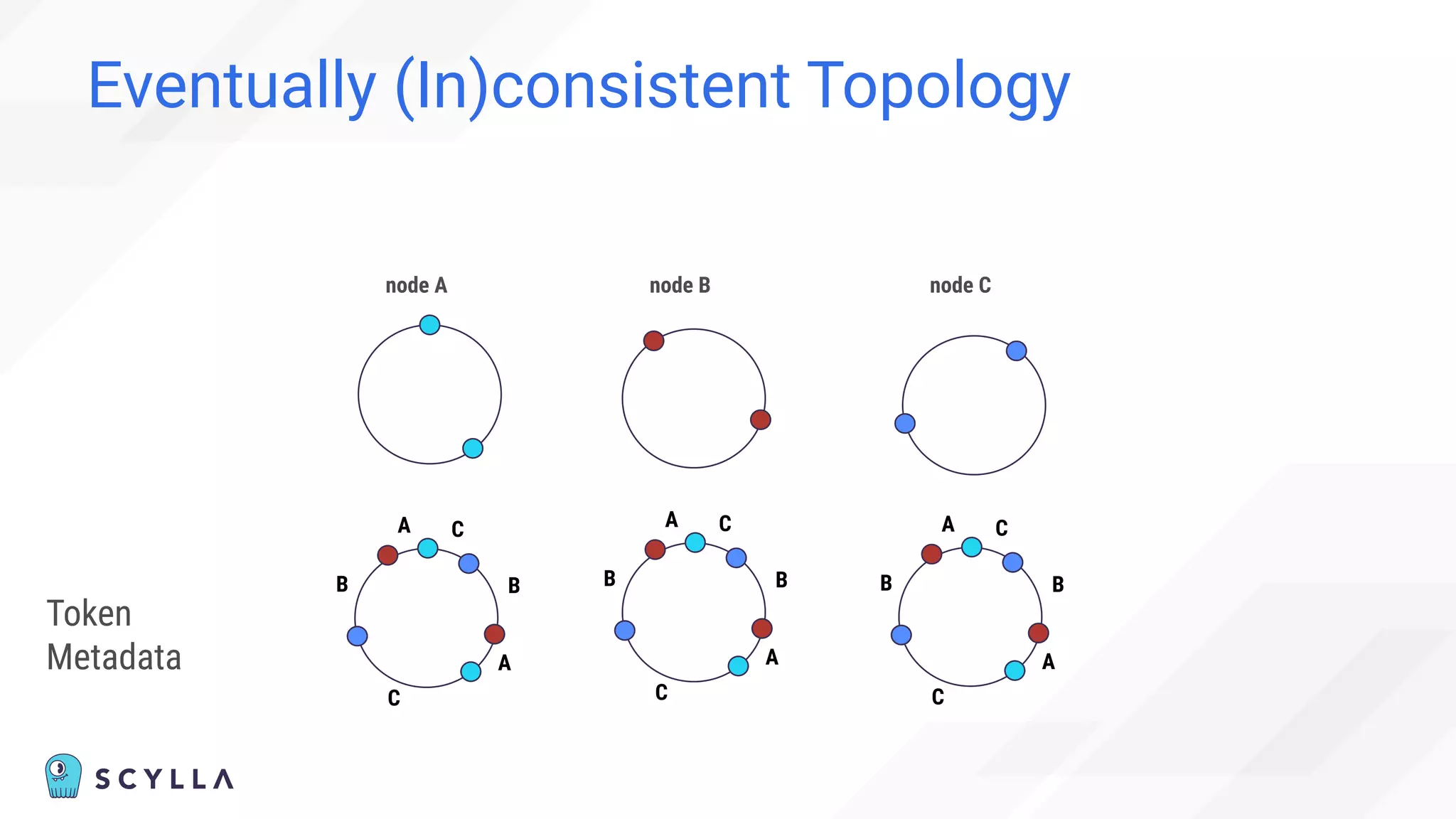
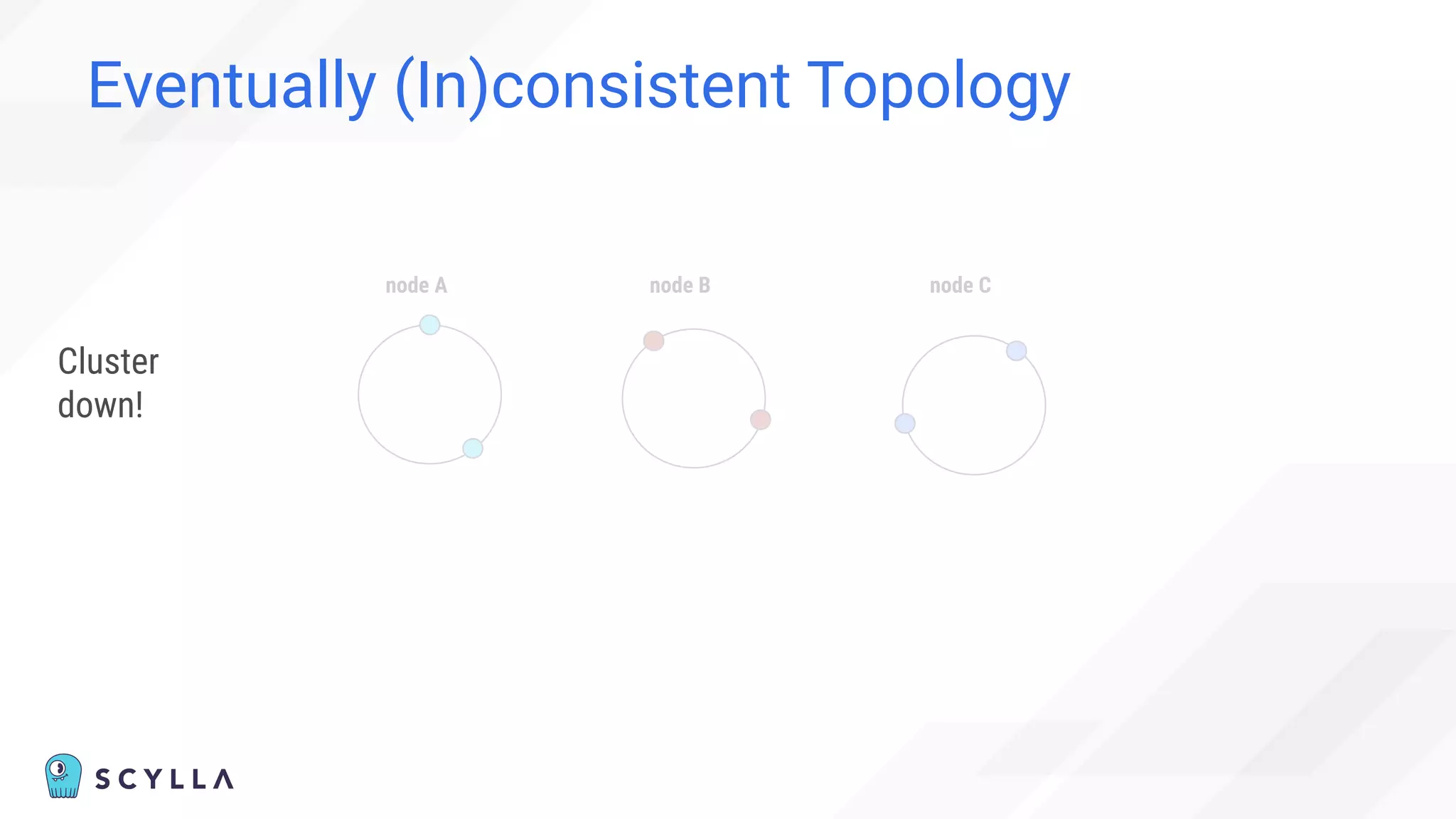
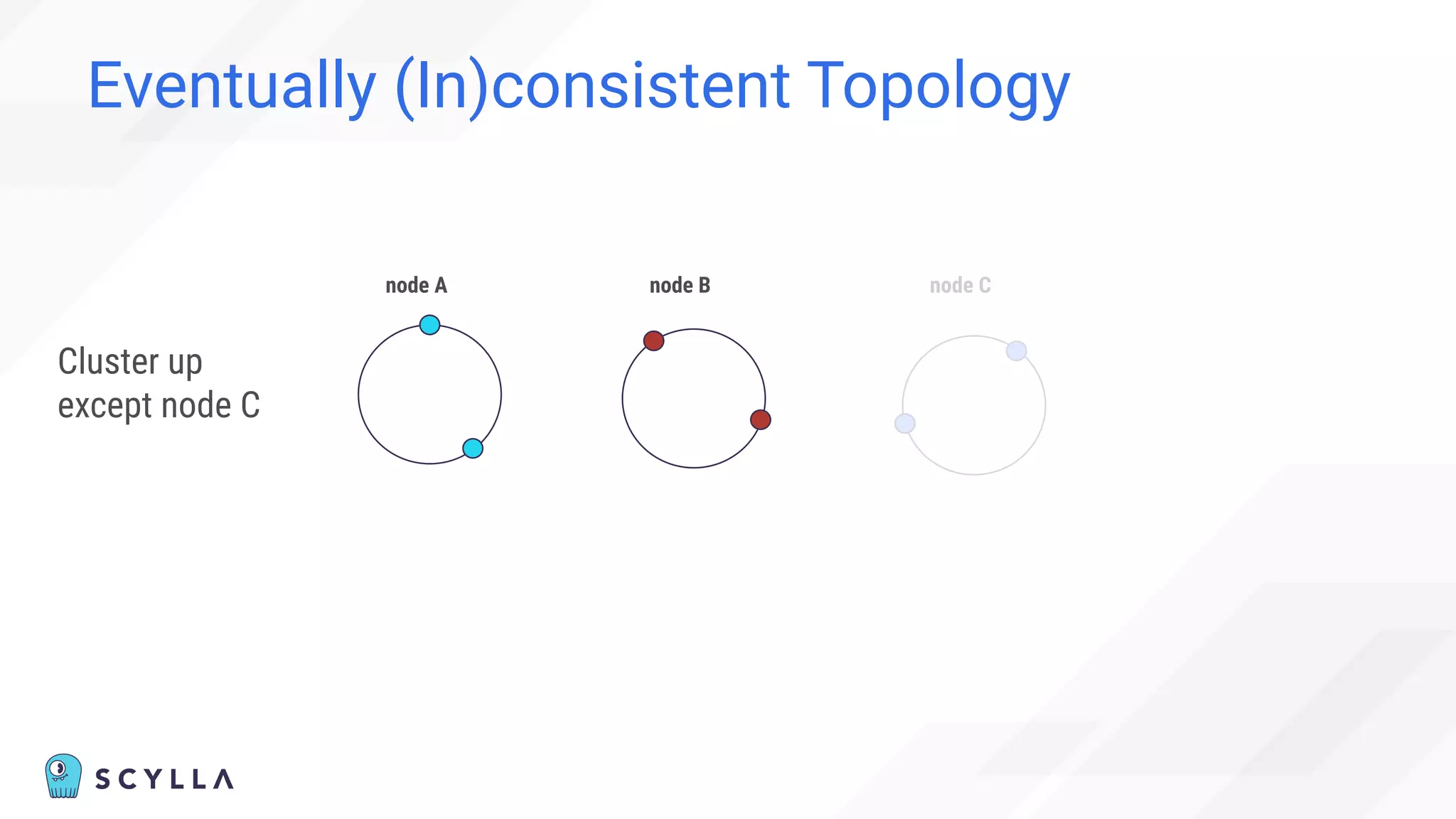
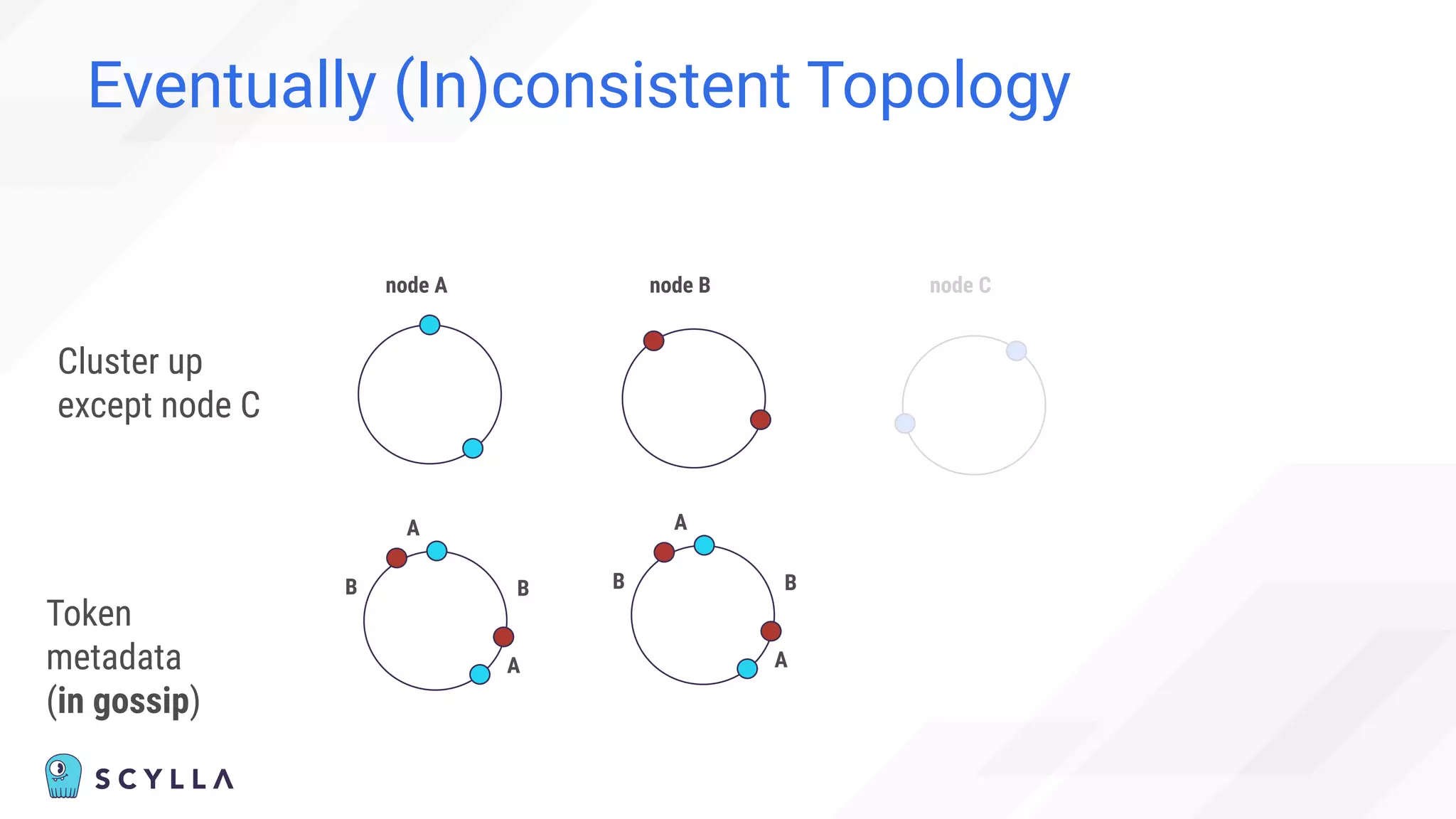
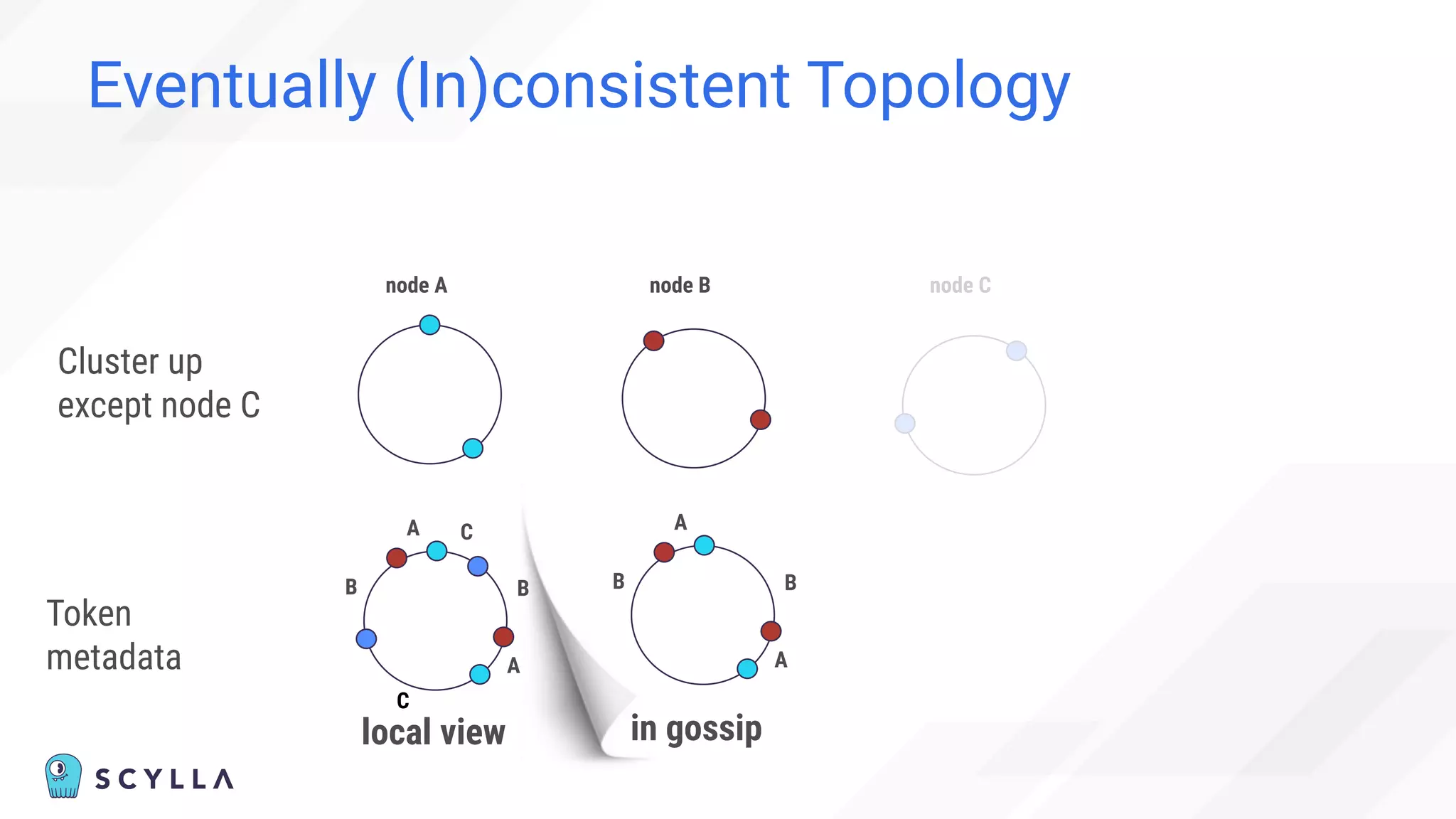
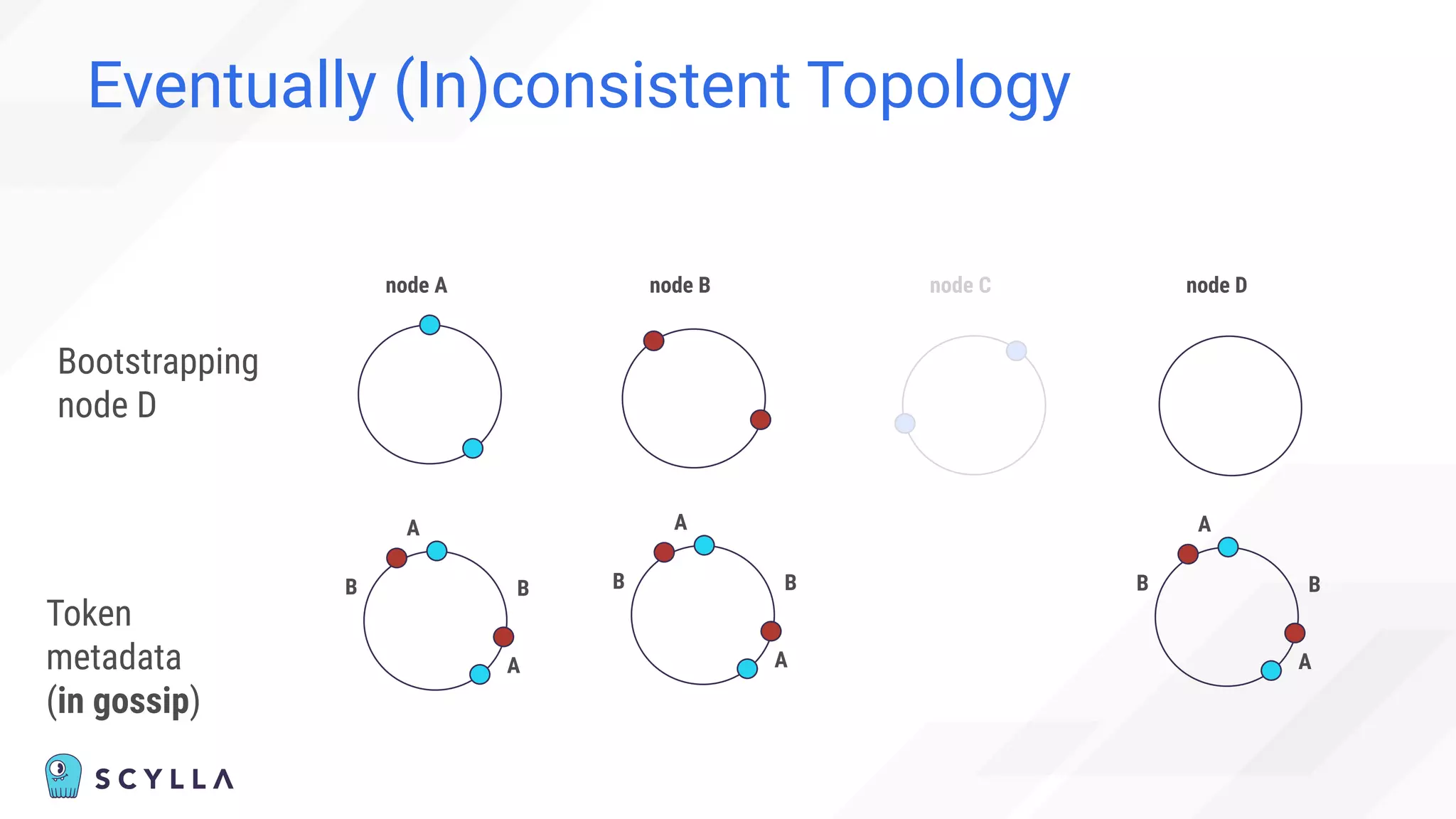
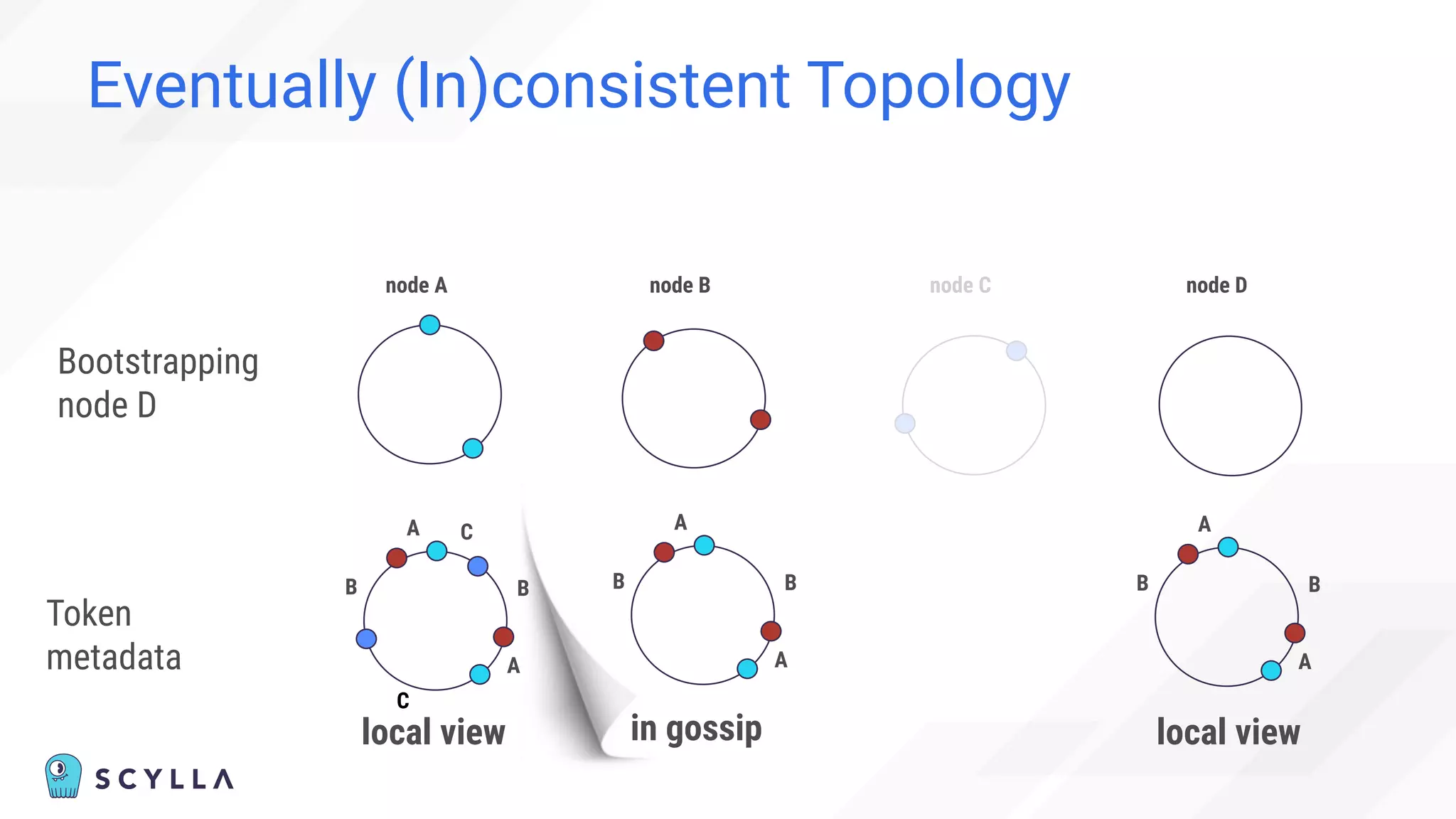
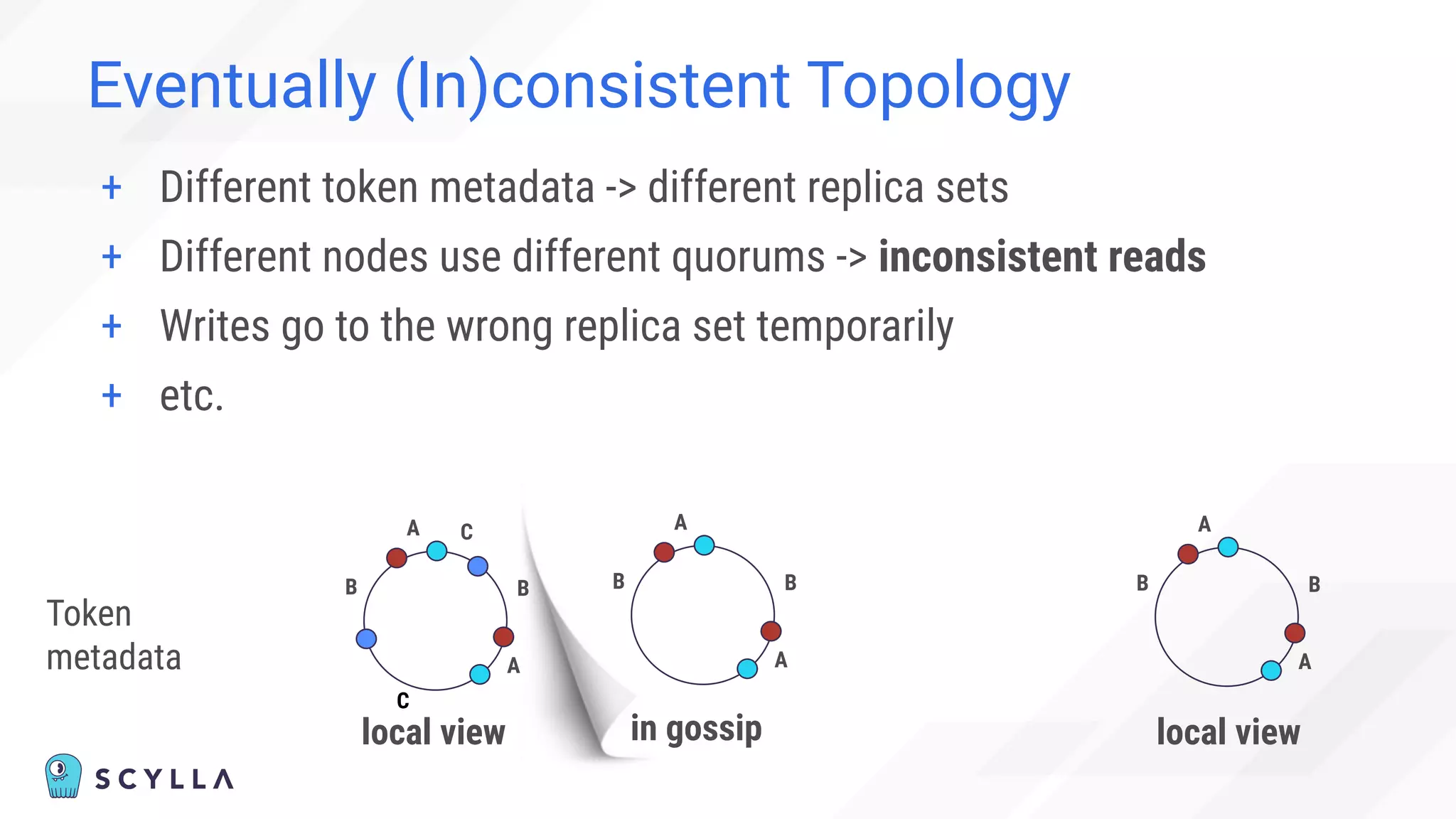
![Eventually (In)consistent Topology
“Cannot” happen:
“Before adding the new node,
check the node’s status in the cluster using nodetool status
command.
You cannot add new nodes to the cluster if any of the nodes are
down.” [1]
[1] https://docs.scylladb.com/operating-scylla/procedures/cluster-management/add-node-to-cluster/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scylladbwebinarjune152022-strongconsistency-220615204757-a0a6b10e/75/Distributed-Database-Consistency-Architectural-Considerations-and-Tradeoffs-37-2048.jpg)