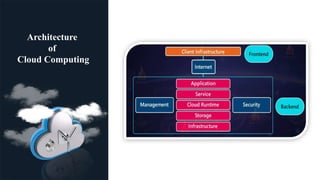
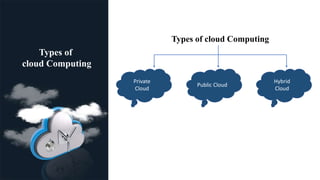
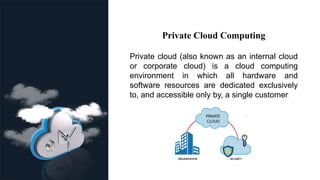
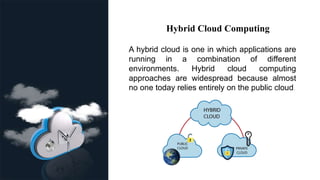
This document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its definition, architecture, types (public, private, and hybrid), and key requirements such as scalability and adaptability. It highlights the benefits of cloud computing, including cost savings, speed, global reach, and increased productivity. The information is intended for an audience familiar with technology and business needs.