Types of data 1.2
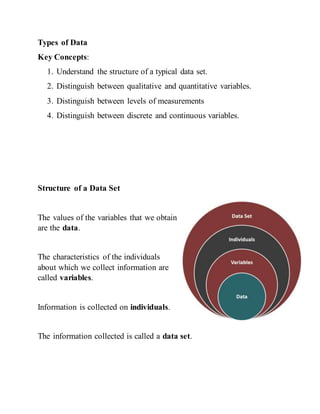
- 1. Types of Data Key Concepts: 1. Understand the structure of a typical data set. 2. Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative variables. 3. Distinguish between levels of measurements 4. Distinguish between discrete and continuous variables. Structure of a Data Set The values of the variables that we obtain are the data. The characteristics of the individuals about which we collect information are called variables. Information is collected on individuals. The information collected is called a data set.
- 2. Example 4 Student Major Exam Score Grade 1 Art 92 A 2 Psychology 75 B 3 Communications 82 B 4 Psychology 72 C 5 Art 85 B
- 3. Parameter: Statistic: A is a number that describes a sample. A is a number that describes a population.
- 4. Example 5: Which of the following is a statistic and which is a parameter? 57% of the teachers at Central High School are female. In a sample of 100 surgery patients who were given a new pain reliever, 78% of them reported significant pain relief.
- 5. Quantitative Data vs Categorical Data Variables can be divided into two types: Quantitative (or numerical) data: consists of numbers representing counts or measurements. The weights of supermodels The ages of respondents Categorical (or qualitative or attribute) data: consists of names or labels (not numbers that represent counts or measurements). The gender (male/female) of professional athletes Shirt numbers on professional athletes uniforms - substitutes for names
- 6. Example 6 Example: Quantitative Data vs Categorical Data Which of the following variables are qualitative and which are Categorical? A person’s age The color of a car The mileage of a car The identification number 1, 2, 3, …….,25 are assigned randomly to the 25 subjects in a clinical trial.
- 7. Working with Quantitative Data: Quantitative data can be further described by distinguishing between discrete and continuous types. Discrete data: result when the data values are quantitative and the number of values is finite, or “countable.” The number of tosses of a coin before getting tails Age of a person at his or her last birthday Continuous (numerical) data: result from infinitely many possible quantitative values, where the collection of values is not countable. Or can take on any value in some interval The lengths of distances from 0 cm to 12 cm Distance a person commutes to work
- 8. Levels of Measurement Another way of classifying data is to use four levels of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. Nominal level of measurement: characterized by data that consist of names, labels, or categories only, and the data cannot be arranged in some order (such as low to high). Survey responses of yes, no, and undecided Ordinal level of measurement: involves data that can be arranged in some order, but differences (obtained by subtraction) between data values either cannot be determined or are meaningless. Course grades A, B, C, D, or F
- 9. Interval level of measurement: involves data that can be arranged in order, and the differences between data values can be found and are meaningful. However, there is no natural zero starting point at which none of the quantity is present. Years 1000, 2000, 1776, and 1492 Ratio level of measurement: data can be arranged in order, differences can be found and are meaningful, and there is a natural zero starting point (where zero indicates that none of the quantity is present). Differences and ratios are both meaningful. Class times of 50 minutes and 100 minutes
- 10. Summary - Levels of Measurement • Nominal - categories only • Ordinal - categories with some order • Interval - differences but no natural zero point • Ratio - differences and a natural zero point