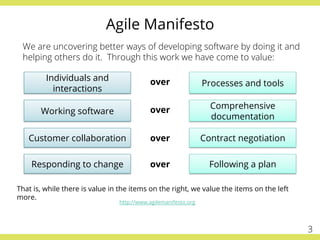
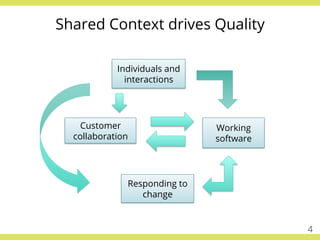
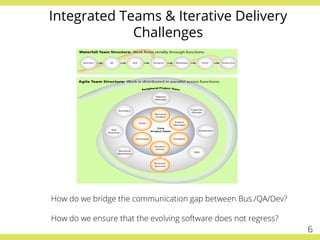
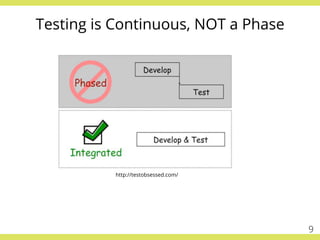
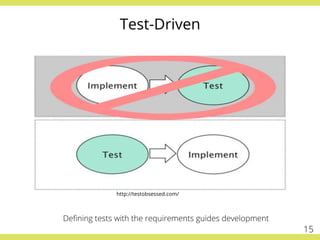
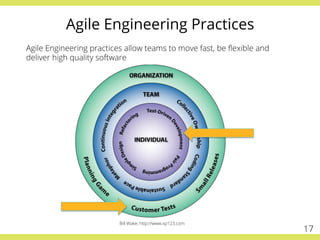
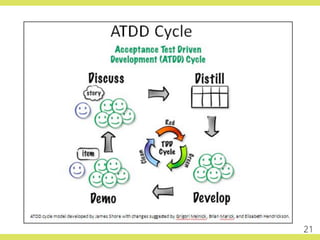
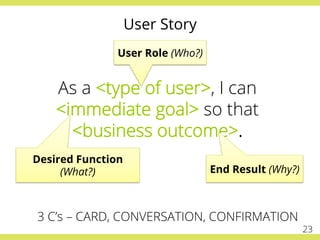
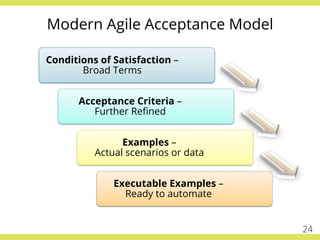
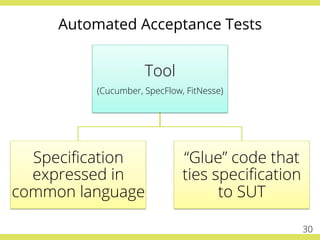
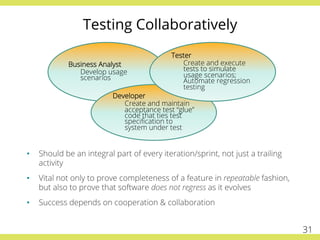
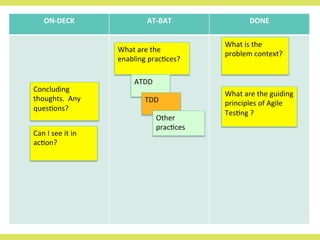
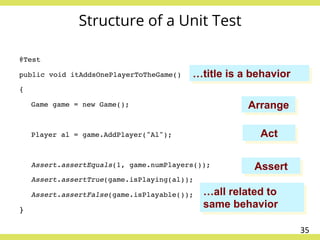
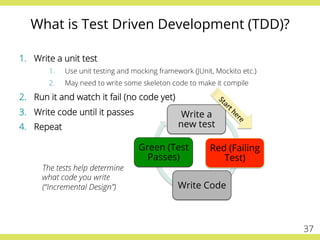
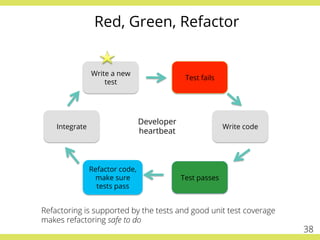
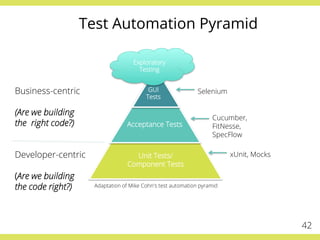
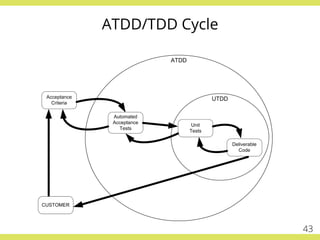
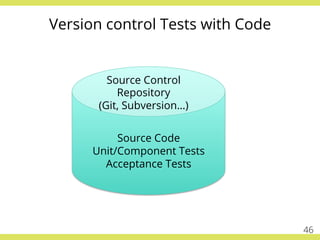
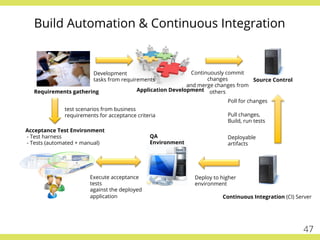
The document discusses effective testing practices in an agile environment, emphasizing principles such as continuous testing, collaboration, and integrating quality assurance throughout the development process. It highlights techniques like Acceptance Test-Driven Development (ATDD) and Test-Driven Development (TDD) that enhance communication and ensure software meets business expectations. The importance of quick feedback and the role of shared understanding in maintaining software quality are also explored.